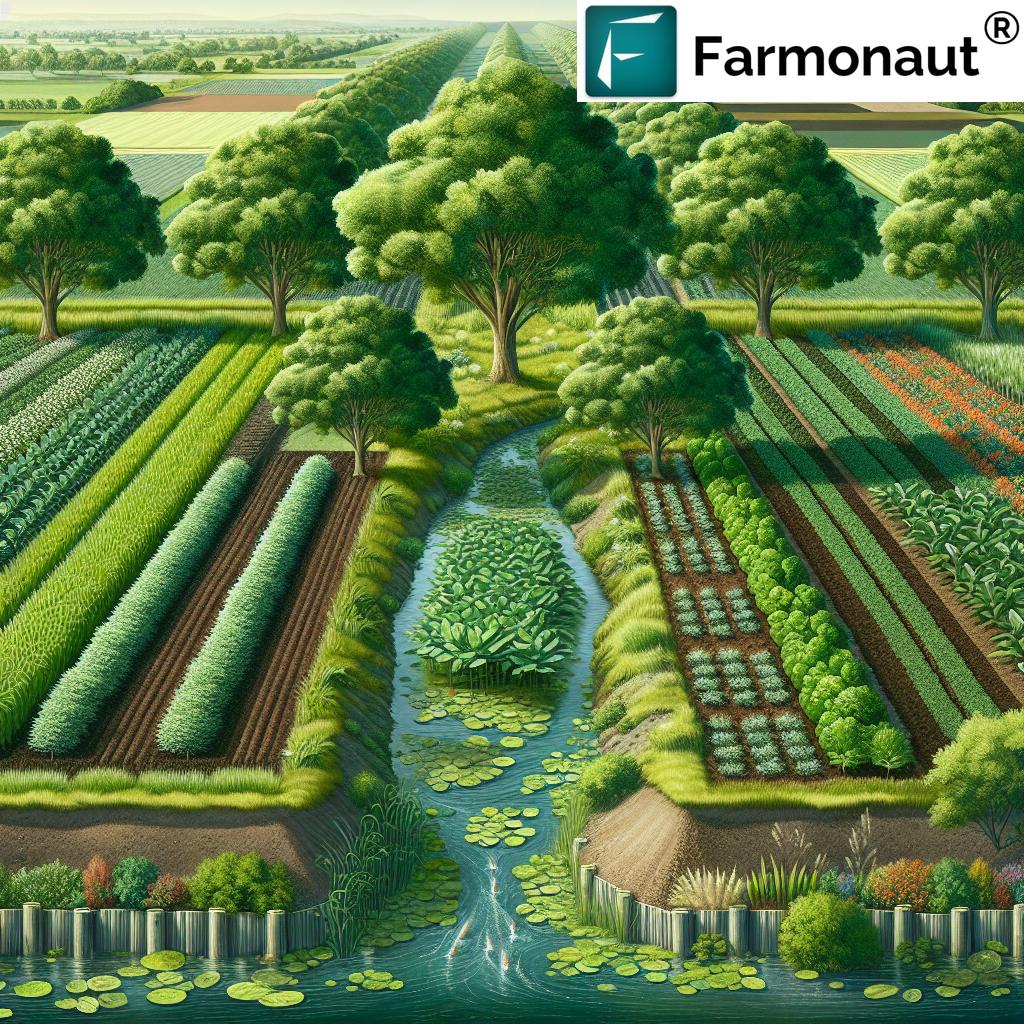
Landscaping: 5 Agroforestry Benefits for Farming
“Agroforestry can increase farm biodiversity by up to 50% compared to conventional monoculture systems.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Evolving Role of Landscaping in Agriculture
- What is Agroforestry?
- Understanding Agroforestry Practices
- Landscaping: 5 Agroforestry Benefits for Farming
- Estimated Impact of Agroforestry on Key Sustainability Metrics
- Implementing Agroforestry: Steps and Technologies
- How Farmonaut Supports Sustainable Agroforestry
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Agroforestry & Landscaping
- Conclusion & Farmonaut Subscriptions
Introduction: The Evolving Role of Landscaping in Agriculture
Landscaping has traditionally been associated with ornamental gardening and the aesthetic enhancement of private spaces. However, in the modern agricultural landscape, landscaping extends well beyond garden borders. It now plays a transformative role in advancing sustainable farming through the integration of agroforestry systems. By intentionally combining trees, shrubs, and vegetation into our farming operations, we can harness both ecological and financial benefits while building climate-resilient, profitable farms.
This blog explores the science and art of agroforestry—a practice that combines the very best of agriculture and forestry technologies to create integrated, diverse, and productive land-use systems. We’ll discover how integrating these components improves soil health, boosts biodiversity in agriculture, increases carbon sequestration in agriculture, and offers robust economic diversification for farmers.
Focus Keyword: Landscaping: 5 Agroforestry Benefits for Farming
By understanding and implementing these sustainable farming practices, we can move towards healthier ecosystems, greater food security, and improved livelihoods.
What is Agroforestry?
Agroforestry is a sustainable land management system that strategically combines trees, shrubs, crops, and sometimes livestock on the same plot of land. Unlike conventional agriculture, which often relies on monoculture, agroforestry systems are designed to create diverse and resilient ecosystems. This approach improves productivity, enhances environmental sustainability, and increases farm profitability.
- Integrated Approach: At its core, agroforestry involves deliberate, systematic integration of vegetation into farming landscapes.
- Combining Technologies: Utilizes both agricultural and forestry technologies for optimal land management.
- Customizable Design: Can be tailored to suit various climates, soils, and farm sizes, enhancing both ecosystem and economic resilience.
By leveraging agroforestry, we not only boost crop yields but also promote a suite of environmental and economic benefits that make our farms more sustainable and profitable.
Understanding Agroforestry Practices: Integrating Trees for Sustainability
There is no one-size-fits-all system in agroforestry. Rather, we select and customize farming practices based on our climate, land conditions, and farm goals. Here are the key agroforestry techniques proven to drive sustainability and productivity:
1. Silvopasture Management
Silvopasture combines trees with livestock and forage systems—managing all three on the same acreage. By growing trees within animal grazing areas, we provide shade and shelter for livestock, improve forage production, and sequester more carbon than traditional pasture.
- Key Advantages: Reduces animal heat stress, protects against wind, increases forage yields, and enhances carbon sequestration in agriculture.
- Environmental Impact: Improves soil health by stabilizing banks and reducing compaction; manages water quality and erosion.
Learn about forest-specific best practices with our Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory tools for optimizing silvopasture management.
2. Alley Cropping Techniques
Alley cropping (or alley cropping techniques) is the practice where crops are grown in rows between lines of trees (the alleyways). This not only creates annual and long-term income streams, but also provides protection and nutrient cycling benefits.
- Key Advantages: Minimizes wind and water erosion, boosts soil health improvement, and diversifies farm income.
- Environmental Impact: Trees and crops together create microclimates supporting beneficial insects and wildlife.
For advanced monitoring of rows and vegetation health, try Large Scale Farm Management by Farmonaut—enabling satellite insights on crop growth.
3. Forest Farming
Forest farming involves cultivating high-value, shade-loving crops (e.g., mushrooms, medicinal herbs) under a deliberately managed canopy of trees where shade level is finely adjusted. This system maximizes land productivity and offers high-value yields.
- Key Advantages: Generates financial returns up to five times higher than typical monoculture crops.
- Environmental Impact: Preserves biodiversity and stabilizes ecosystems within forested acreages.
4. Riparian Buffer Zones
Riparian buffers are vegetated areas—often made up of trees and shrubs—planted alongside waterways (such as streams, rivers, and lakes). Their primary role is to filter pollutants, stabilize banks, and enhance landscape aesthetics.
- Key Advantages: Reduces nutrient runoff, enhances water quality, and provides valuable wildlife habitat.
- Environmental Impact: Strengthens the resilience of watershed management and supports diverse aquatic and terrestrial life.
5. Windbreaks and Shelterbelts
By planting rows of trees or shrubs as windbreaks, we shield fields and livestock from harsh winds, conserve soil moisture, and maintain favorable microclimates for crops. This agroforestry technique enhances overall productivity, curbs wind erosion, and protects biodiversity.
“Integrating trees in farms can boost soil organic carbon by 20-30% within a decade.”
Landscaping: 5 Agroforestry Benefits for Farming
Implementing agroforestry systems in our farms is more than a trend—it’s a sustainable shift that directly improves our health, profitability, and environmental impact. Here are the top five agroforestry benefits for farming:
1. Enhanced Biodiversity in Agriculture
Biodiversity forms the foundation of healthy agricultural systems. By integrating trees into farming, we create diverse habitats for numerous plant, animal, and insect species. These trees and shrubs support pollinators, birds, natural pest predators, and beneficial microorganisms. The complex ecosystem established in agroforestry systems delivers ecological balance, reduces crop pests, and preserves essential pollination services.
- Higher Diversity Index: Research shows agroforestry can raise farm biodiversity by up to 50%—supporting a resilient, adaptable, and productive farm environment.
- Sustainable Habitat Creation: Every riparian buffer and windbreak planted forms new corridors for wildlife and enriches the local ecosystem.
2. Soil Health Improvement and Productivity
Healthy soil is paramount for any sustainable farm. Agroforestry systems replenish and rejuvenate soil health through:
- Organic Matter Addition: Annual leaf litter and roots from trees boost soil organic carbon by 20–30% within a decade.
- Better Soil Structure: Roots hold soil together, minimize compaction, increase aeration, and prevent runoff.
- Efficient Nutrient Cycling & Water Retention: Trees draw nutrients from deeper soil layers and redistribute them to crops, while also maintaining moisture—crucial for drought resilience.
For actionable soil and crop insights backed by satellite technology, use Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution—it helps quantify soil carbon and track improvements over time.
3. Carbon Sequestration for Climate Change Mitigation
Carbon sequestration is one of the critical environmental benefits of integrating trees and shrubs into our farms. As trees grow, they sequester atmospheric carbon, locking it within their trunks, roots, and surrounding soil—making agroforestry a powerful tool in climate action.
- Impressive Carbon Storage: Silvopasture systems can store up to 2.5 tons of carbon per hectare, per year, far more than monoculture fields.
- Long-Term Climate Impact: Widespread agroforestry can significantly reduce farm greenhouse gas emissions and build resilience against climate extremes.
- Tracking Carbon Reductions: New technologies, such as those provided by Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting platform, allow real-time monitoring and management of farm carbon emissions and sequestration.
4. Economic Diversification for Farmers
Relying on one crop or market can leave farms vulnerable to shocks. Agroforestry helps us diversify our income streams:
- Multiple Revenue Sources: Harvesting timber, fruits, nuts, medicinal plants, and fodder alongside annual crops provides both immediate and recurring economic returns.
- Risk Mitigation: Economic diversity improves our farm’s resilience to commodity price drops, pests, or unpredictable weather.
For supply chain transparency and verifying your sustainable claims, leverage Farmonaut’s Traceability Solution.
Farmers can also explore satellite-based crop loan and insurance validation using Farmonaut’s Crop Loan & Insurance tools for easier, fraud-free access to financing.
5. Improved Water Quality & Ecosystem Services via Riparian Buffers
By establishing riparian buffer zones along streams and water ways, we provide multiple ecosystem services:
- Pollutant Filtering: Trees and grasses in vegetated strips trap sediments, absorb farm runoff, and keep nutrients from entering water bodies.
- Bank Stabilization: The roots of shrubs and trees stabilize stream banks, reduce erosion, and slow flood runoff.
- Wildlife Habitat & Landscape Aesthetics: These buffers serve as critical habitat for aquatic and terrestrial wildlife while beautifying our farm landscape.
Estimated Impact of Agroforestry on Key Sustainability Metrics
| Benefit | Description | Estimated Improvement | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Health | Enhances organic matter, nutrient cycling, and structure | 10–20% increase in soil organic matter | Reduces erosion, improves fertility |
| Biodiversity | Provides diverse habitats for plants & wildlife | Up to 30% greater biodiversity index | Supports ecosystem stability, pollinators |
| Carbon Sequestration | Captures & stores atmospheric carbon in trees and soils | 1–3 tons carbon/ha/year sequestered | Mitigates climate change, improves air quality |
| Water Conservation | Reduces runoff, improves water infiltration, stabilizes banks | 10–25% reduction in surface runoff | Protects water quality, prevents flooding |
| Crop Diversity | Diversifies income and improves system resilience | Adds 2–4 new crop/product types per farm | Reduces risk, enhances food security |
Implementing Agroforestry: Steps and Modern Technologies
Transitioning to an agroforestry system is a strategic, yet rewarding step towards sustainable farming. Here’s how we can get started and optimize operations:
- Site Assessment: Analyze our fields—consider waterways, slopes, soil type, and current land use.
- Species Selection: Choose trees, shrubs, and crops that are complementary and well-adapted to local climate and soil.
- System Design: Plan spatial arrangement—such as alley width, buffer location, and livestock movement—in line with integrated management principles.
- Management Practices: Regularly maintain vegetation, monitor pest activity, manage organic matter, and adapt practices as necessary.
- Technology Integration: Leverage advanced monitoring and decision-support tools like those from Farmonaut for real-time crop, vegetation, and environmental data.
For developers and researchers, integrate Farmonaut’s API and Developer Docs into your agri-tech applications for seamless, satellite-based farm data access.
How Farmonaut Supports Sustainable Agroforestry
As precision agriculture rapidly becomes essential for sustainable farming, Farmonaut stands at the forefront with solutions specifically tailored for agroforestry systems:
- Satellite-Based Crop & Tree Health Monitoring: With Farmonaut’s platform, we can monitor vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and key performance indicators for both crops and trees—helping us adjust practices in real time and sequester more carbon.
- AI-Driven Jeevn Farm Advisory: Get personalized, location-specific guidance on shade management, irrigation, and nutrient utilization—boosting farm productivity and health.
- Blockchain Traceability: Use traceability tools for transparent, verifiable records of sustainable farming operations and environmental impact.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Specialized for larger-scale forest farms, Farmonaut’s Fleet Management platform helps efficiently track and allocate vehicles, machinery, and labor.
- Carbon Footprinting & Reporting: With real-time carbon footprint tracking, we can prove the climate benefits of our agroforestry systems and optimize our environmental stewardship.
Access Farmonaut from any device and empower your farm with data-driven, sustainable, and scalable technologies—no extra hardware needed.
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Affordable Precision for Every Farm
Achieve data-driven agroforestry management at an affordable rate. Explore flexible subscription plans designed for individual farms, cooperatives, and agribusinesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Agroforestry and Landscaping
Q1: How do trees improve soil health in agroforestry?
Trees increase soil organic matter through leaf litter and root turnover, enhancing nutrient cycling. Their roots stabilize soil, boost water retention, and reduce erosion, resulting in improved health, fertility, and productivity.
Q2: What are the key differences between conventional agriculture and agroforestry systems?
Conventional agriculture tends to focus on a single crop with minimal biodiversity, leading to increased erosion and reduced soil health over time. Agroforestry systems integrate diverse trees, shrubs, crops, and livestock, offering more resilience, better pest control, and improved ecosystem services.
Q3: How do riparian buffers help water quality?
Riparian buffer zones are vegetated areas along waterways that trap sediments, absorb excess nutrients, and filter other pollutants before they enter streams. This process preserves water quality, protects aquatic habitats, and curbs erosion.
Q4: What technologies support large-scale monitoring of agroforestry?
Modern farms use satellite imagery, AI-based advisory, and digital mapping—like Farmonaut’s solutions—to track crop and tree health, monitor soil moisture, and optimize fleet and resource deployment across wide acreage. This reduces input costs and increases production efficiency.
Q5: Can agroforestry practices qualify for carbon credits or sustainability certifications?
Yes. By sequestering carbon and enhancing ecosystem health, well-managed agroforestry systems often qualify for carbon credit programs and eco-labels. Farmonaut helps you track and report your environmental improvements to meet sustainability standards.
Q6: Is Farmonaut a marketplace or farm input supplier?
No. Farmonaut is an agricultural technology platform delivering precision data, digital advisory, and sustainability tools via satellite, AI, and cloud solutions. It is not a farm equipment or input marketplace, nor a regulatory body.
Conclusion: Building Resilience with Agroforestry and Farmonaut
Landscaping in farming is now a forward-looking practice—one that shapes the future of sustainable agriculture. By integrating trees, shrubs, crops, and in some systems, livestock, we unlock higher biodiversity, improved soil health, greater carbon sequestration, enhanced water management, and vital economic diversification for farmers.
The technologies we use, as exemplified by Farmonaut, empower us to monitor, measure, and optimize every aspect of these agroforestry systems. Whether you are looking to boost yields, access new income sources, or ensure your farm is climate-resilient, embrace agroforestry. Through smart landscaping, let’s build a more sustainable, productive, and healthy agricultural future for all.
Ready to make sustainable land management your competitive edge? Access Farmonaut’s Web, Android, or iOS apps for real-time insights or integrate advanced data into your systems via our API.