Soybean Cultivation Technology: 7 Yield-Boosting Innovations
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Revolutionizing Soybean Cultivation
- Traditional Soybean Cultivation Practices
- Advancements in Soybean Planting Techniques
- Precision Agriculture in Soybean Farming
- Automation and Robotics in Crop Management
- Biotechnology in Soybeans: Engineering the Future
- Sustainable Soybean Production & Integrated Pest Management
- Climate-Resilient Soybean Varieties & Technologies
- Innovation Impact Comparison Table
- Farmonaut: Empowering Modern Soybean Farming
- The Future: Shaping Global Soybean Cultivation
- FAQ: Soybean Cultivation Technology
“Precision agriculture can increase soybean yields by up to 20% using advanced soil and crop monitoring technologies.”
Introduction: Revolutionizing Soybean Cultivation
Soybean cultivation has witnessed a remarkable transformation over recent decades. Previously anchored in traditional methods, this essential crop’s farming landscape now unites age-old wisdom with cutting-edge technologies. In response to mounting global food security concerns, environmental pressures, and the call for enhanced productivity, our industry has embraced innovative practices and tools that are shaping how we approach sustainable soybean production.
In this comprehensive overview, we’ll explore the dramatic evolution of soybean farming—highlighting the most significant yield-boosting innovations, from improved planting techniques to biotechnology and precision agriculture. We’ll also delve deeply into the integration of digital technologies such as satellite imagery, automation, and data-driven management—empowering us to manage crops, soil, water, and resources like never before. Let’s embark on an in-depth journey through the top seven innovations that are defining the future of soybean cultivation.
Traditional Soybean Cultivation Practices: Foundations and Limitations
For generations, soybean farming practices were characterized by manual labor, natural pest control, and conventional tillage to prepare the seedbed, control weeds, and retain soil moisture. These foundational methods, although time-tested and valuable, aren’t without their downsides. Excessive tillage can disrupt soil structure, promote erosion, and lead to organic matter degradation, often posing significant challenges for long-term productivity and sustainability.
Key Traditional Methods
- Tillage: Used primarily to prepare the seedbed, incorporate crop residues, control weeds, and manage soil moisture. However, repeated tillage may lead to the breakdown of vital soil aggregates, ultimately increasing the risk of erosion and nutrient loss.
- Manual Planting: Seeds are sown by hand or with simple tools, making it labor-intensive, dependent on local labor availability, and often susceptible to inconsistent planting depth and population.
- Natural Pest Control: Reliance on beneficial insects, crop rotations, and companion planting to manage pests without heavy reliance on chemicals.
- No-Till Farming (Emerging): A major shift towards no-till and reduced-till methods is underway, allowing seeds to be planted directly into undisturbed soil. This not only helps in conserving soil structure and moisture but also significantly reduces erosion—especially beneficial in regions like the Midwestern United States, where soil conservation is paramount.
These traditional practices have paved the way for modern advancements, forming the critical baseline upon which innovative soybean cultivation practices continue to build.
Advancements in Soybean Planting Techniques: Enhancing Precision and Yields
One of the most significant shifts in soybean cultivation practices has stemmed from our growing understanding of optimal planting densities, row configurations, and sowing timings. Scientific research consistently shows that achieving the ideal population and spacing is crucial for maximizing photosynthesis, light capture, and overall crop vigor.
Optimal Planting Specifications
- Ideal Population: Approximately 450,000 plants per hectare delivers the best results under varied agronomic conditions.
- Row Spacing: Evidence suggests that 45 cm spacing is ideal for northern zones (such as the upper Midwest, US), while 30 cm spacings suit central and southern regions, due to temperature and sunlight variations.
- Adjusting for Delays: Adjusting planting densities upward and narrowing rows can help compensate for delayed sowing, ensuring a robust canopy and increased yield potential despite shorter growing windows.
Refining these soybean planting techniques dramatically reduces gaps in the field, optimizing resource use, and supporting higher plant populations without crowding stress. This evolution in planting method, together with technologies that enable uniform seed placement and depth control, lays the groundwork for enhanced productivity and resource efficiency.
Precision Agriculture in Soybean Farming: Integrating Technology for Smarter Decisions
The advent of precision agriculture marks one of the great agricultural revolutions of our era. Instead of applying uniform treatments across an entire field, we now leverage advanced sensing and data analysis tools—integrating digital systems for unparalleled oversight and actionable decision-making.
Let’s explore the pivotal components of precision agriculture in soybean farming:
Key Technologies Empowering Precision Agriculture
- Satellite Imagery: Advanced multispectral images allow us to monitor crop health, detect stressed zones, measure soil moisture, and even forecast potential issues before they affect yield.
- Drone Technology: Drones offer high-resolution, rapid scouting of specific zones, capturing imagery and even applying targeted crop inputs—greatly enhancing the precision of our field interventions.
- Data Monitoring & AI Analysis: With platforms like Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring (NDVI, soil moisture, chlorophyll), we’re able to make timely irrigation decisions, optimize fertilizer usage, and ensure early detection of pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies.
- Variable Rate Application: Our ability to apply fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation variably, based on real-time field data rather than averages, is transforming both our efficiency and sustainability.
The integration of these practices leads to reduced input waste, higher yields, and less environmental impact—key drivers for sustainable soybean production.
For large and multi-location farms, Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management tools enable comprehensive monitoring and management of vast soybean fields through satellite insights and centralized dashboards. This streamlines resource allocation, optimizes field operations, and boosts overall farm efficiency.
“Adopting sustainable soybean cultivation methods has reduced water usage by nearly 30% in innovative farms worldwide.”
Automation in Crop Management: Robotics and the Modern Soybean Field
Automation is reshaping what’s possible in our soybean fields. Tasks that traditionally required substantial manual effort, such as pod counting or maturity assessment, can now be efficiently managed through robust robotic systems. These advances support modern soybean farming methods that are more data-driven, timely, and scalable.
Notable Impacts of Automation in Soybean Production
- Pod Counting Robots: Using machine vision and AI, these machines traverse fields, counting pods—one of the strongest predictors of final yields. This enables precise yield forecasting and proactive harvest planning.
- Automated Machinery: From seeders with AI depth control to autonomous harvesters and robotic weeders, automation in crop management boosts efficiency and reduces labor costs.
- Data Collection & Reporting: By integrating sensors and connectivity, we’re able to continuously monitor machine performance, field variability, and crop health, improving visibility and enabling swift interventions when issues are detected.
The rise of automation in crop management is a cornerstone of yield-enhancing soybean cultivation practices, particularly as labor supply fluctuates and operational costs rise.
Biotechnology in Soybeans: Engineering Higher Resilience and Nutrition
Our journey towards greater productivity and environmental stewardship is powerfully accelerated by biotechnology in soybeans. These scientific breakthroughs allow us to breed, select, or engineer varieties with superior traits—delivering benefits that would take generations to develop through traditional breeding alone.
Game-Changers in Soybean Biotechnology
- Drought Resistance: Take, for example, enhanced HB4 soybeans. Engineered to withstand prolonged dry conditions, these varieties are critical in arid regions, enabling us to maintain yields while using less water—bolstering both food security and resource sustainability.
- Improved Disease and Pest Resistance: Genomic tools and marker-assisted selection help us develop soybeans that naturally resist common fungal pathogens and insects, further reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and supporting integrated pest management for soybeans.
- Enhanced Nutritional Profiles: Through biotech interventions, we are advancing the nutritional profile of soybeans—fortifying certain amino acids, vitamins, and healthy oils for improved human and livestock nutrition.
Genome editing and genetic engineering remain essential in developing climate-resilient soybean varieties—responding to localized conditions, evolving pest threats, and rising consumer expectations.
For those seeking improved financial confidence, Farmonaut’s Crop Loan & Insurance solution relies on satellite-based crop verification. It enables streamlined insurance claims, risk assessment, and loan approvals, leveraging accurate farm data for the benefit of soybean growers and lending institutions alike.
Sustainable Soybean Production and Integrated Pest Management for Soybeans
Sustainability is the heartbeat of our industry’s future. By integrating efficient water management and integrated pest management for soybeans (IPM), we strive for environmentally conscious, productive, and resilient cropping systems.
Core Elements of Sustainable Soybean Production
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM applies a holistic approach—combining crop rotation, biological controls, resistant varieties, and judicious use of pesticides. By monitoring pest populations and thresholds through technologies like satellite and drone scouting, we greatly reduce unnecessary pesticide applications, safeguarding the environment and beneficial organisms.
- Efficient Irrigation Techniques: Methods such as drip irrigation or sprinkler systems result in significant water savings and yield improvements. Research shows, for example, that drip fertigation can boost water use efficiency by over 26% and crop yields by 12% compared to traditional flood methods.
- Conservation Tillage & Cover Crops: Reducing tillage and embracing no-till/conservation tillage retains soil structure, minimizes erosion, and enhances soil organic matter. This approach also enhances resilience to extreme rain events while storing critical soil moisture for dry spells.
- Resource Monitoring & Optimization: Using platforms like Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting, we’re able to track and reduce our environmental impact through precise, real-time information on farm emissions—helping us adopt more sustainable soybean farming practices and comply with evolving environmental regulations.
Climate-Resilient Soybean Varieties and Technologies: Securing Our Future
As climate unpredictability intensifies, developing climate-resilient soybean varieties is both a challenge and a necessity. Our strategy centers on regional adaptability, ensuring reliable yields in the face of extreme weather, disease epidemics, and shifting growing seasons.
Innovations Supporting Climate-Resilient Soybean Cultivation
- Advanced Breeding and Selection: Leveraging genomics, we’re accelerating the adaptation of soybeans to drought, heat, floods, and soil salinity—ensuring robust performance under stress.
- Biodegradable Films and Soil Covers: These technologies are vital in areas with short growing seasons, conserving soil warmth and moisture to promote germination and early growth, particularly in northern and continental climates.
- Big Data & Adaptive Modeling: By monitoring crop and climatic parameters in real-time, we can model trends and proactively manage emerging risks, ensuring resiliency and sustainability for future generations.
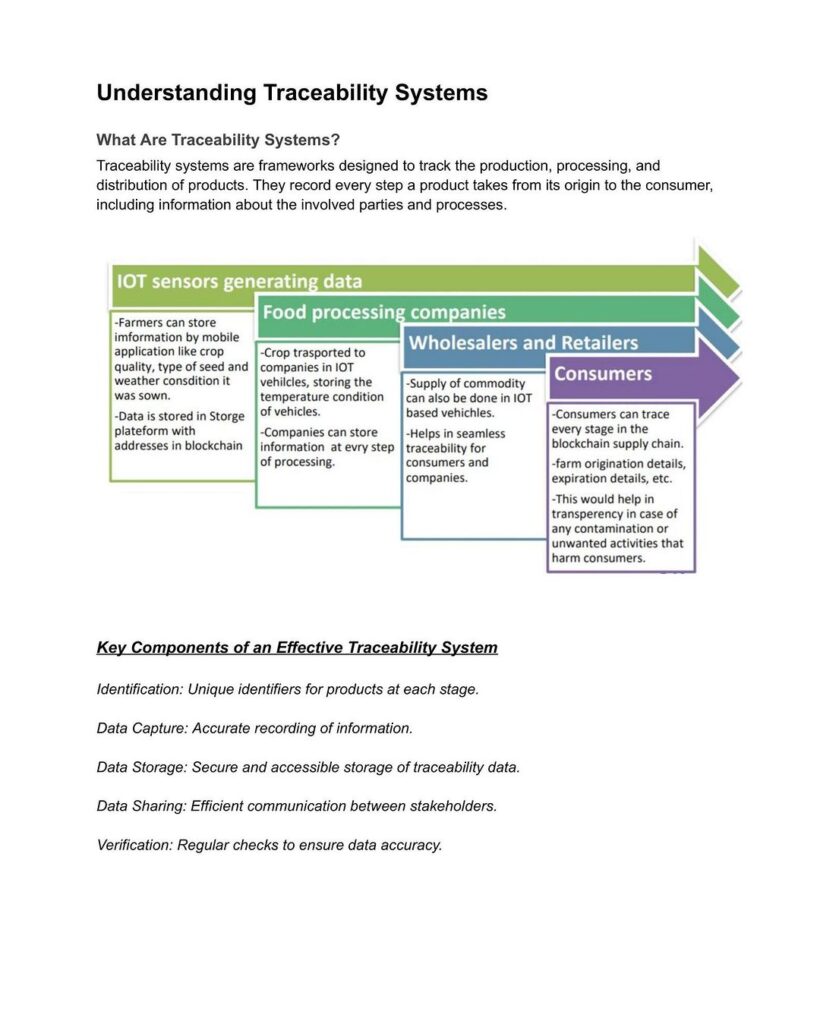
Transparency is a growing demand in food supply chains. With Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Product Traceability, every stage of your soybean’s journey—from field to consumer—can be securely tracked. This ensures authenticity, builds consumer trust, and helps you comply with both export and retailer requirements.
Innovation Impact Comparison Table: 7 Yield-Boosting Technologies Shaping Soybean Cultivation
| Innovation Name | Technology Description | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Sustainability Benefit | Cost Implication | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Till & Conservation Tillage | Seeds are planted directly into undisturbed soil; soil structure conserved | 10–15% | Yes (reduces erosion & improves soil health) | Low | 60 |
| Optimized Planting Techniques | Precision row spacing (30–45 cm), plant population adjustments, uniform sowing | 8–12% | Yes (resource optimization) | Low–Medium | 55 |
| Precision Agriculture | Satellite/drone imagery, variable rate inputs, digital crop health monitoring | 15–20% | Yes (reduced resource waste) | Medium | 35 |
| Automation & Robotics | AI-driven robots for pod counting, automated machinery, machine vision | 5–10% | Yes (optimizes labor & input use) | High | 15 |
| Biotechnology (GM & Genome Editing) | Development of drought-, disease-, and pest-resistant soybean varieties | 12–18% | Yes (input reduction, food security) | Medium–High | 28 |
| Sustainable Water & IPM | Drip/sprinkler irrigation, integrated pest management, chemical reduction | 10–14% | Yes (less water & pesticide) | Medium | 50 |
| Climate-Resilient Varieties | Breeding & biotech for stress (drought/flood/heat) adaptation, biodegradable films | 6–15% | Yes (crop stability) | Medium | 12 |
Farmonaut: Empowering Modern Soybean Farming Practices
To stay at the forefront of modern soybean farming methods, we must harness advanced digital platforms that deliver actionable insights across every stage of cultivation. Farmonaut embodies this vision by providing affordable precision agriculture for farms of all sizes, worldwide.
Key Features and Benefits of Farmonaut
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral satellite imagery reveals crop vigor (NDVI), soil moisture, and other vital signs—enabling us to diagnose and address problems early while efficiently managing water, fertilizers, and pest risks.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: This artificial intelligence tool delivers tailored recommendations and weather forecasts directly to farmers, improving in-field decisions and boosting productivity.
- Blockchain Product Traceability: Assures downstream consumers about product origins, supporting transparency and compliance for soybean producers.
- Resource Management and Fleet Tracking: For larger operations, tools like Fleet Management optimize machinery usage, cut costs, and manage logistics seamlessly.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track, analyze, and reduce on-farm greenhouse gas emissions in real time for more sustainable operations and reporting. Find out more at Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting.
- Scalable App and API: Whether managing a single plot or national-scale programs, Farmonaut’s solutions are available through Android, iOS, web app, and a robust API for system integrations. View API docs here.
Farmonaut’s subscription-based model ensures flexibility for smallholders, cooperatives, and agribusinesses alike. Whether you’re looking to maximize soybean yields, cut costs, or improve sustainability, Farmonaut has you covered with reliable, data-backed agricultural intelligence.
Ready to experience the future of precision agriculture in soybean farming? Download the Farmonaut app below and start optimizing your fields today!
The Future: Shaping Global Soybean Cultivation
As we look to the future, it is clear that the path to enhancing soybean yields and safeguarding our environment lies in even deeper technology integration and sustainability. New frontiers in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data will enable smarter decisions—allowing us to fine-tune every hectare in real time based on weather, soil, and crop-specific algorithms.
Vision for the Next Decade
- Digital Twins & Predictive Analytics: Creating virtual representations of entire farms powered by continuous data streams. This will enable not just real-time interventions but also predictive maintenance of fields, machinery, and supply chains.
- Next-Generation Biotech: Enhancing genetic diversity for nutrition, climate resilience, and biotic stress resistance, ensuring soybean remains a pillar of our food systems.
- Automated, Connected Systems: Autonomous machinery, intelligent irrigation, and interconnected pest management will further strengthen sustainable soybean production.
- Greater Transparency & Compliance: Blockchain and satellite-tracked data will drive traceability, sustainability certifications, and fair market access for producers across the globe.
The synergy between innovative technologies and time-honored knowledge ensures soybean cultivation will remain adaptive, resilient, and capable of meeting the demands of a growing global population.
FAQ: Soybean Cultivation Technology
1. What are the top yield-boosting innovations in soybean cultivation?
The key innovations include no-till/conservation tillage, optimized planting techniques (population and row spacing), precision agriculture (satellite/drone tech), automation and robotics, biotechnology (drought and pest resistance), sustainable water usage, and the breeding of climate-resilient varieties.
2. How does precision agriculture benefit soybean farmers?
Precision agriculture uses real-time data from satellites and sensors to optimize resource allocation, schedule irrigation, detect crop issues early, and reduce input waste, ultimately improving yield and environmental outcomes.
3. Why is integrated pest management important in soybean farming?
Integrated pest management (IPM) combines crop monitoring, biological, cultural, and chemical methods to control pests responsibly, reducing over-reliance on chemicals, protecting beneficial organisms, and improving field health.
4. How can Farmonaut help in modern soybean farming?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory, blockchain traceability, resource management, and sustainability tracking. These tools support data-driven soybean cultivation practices for both large and small farms.
5. Is adopting biotechnology in soybeans safe and sustainable?
Yes, modern biotech developments undergo strict safety assessments. Drought and pest-resistant soybeans reduce resource needs, improve resilience, and can lessen the environmental impact of traditional farming.
Conclusion
Soybean cultivation stands at an extraordinary crossroads of tradition and technology. Each innovation—from precision agriculture and biotechnology to climate-adaptive methods—has contributed to building a more productive, resilient, and sustainable future for soybean farming. As a global community of growers, researchers, and technologists, it’s upon us to continue integrating these yield-enhancing practices—fostering food security and environmental health across key soybean-producing regions.
We encourage all forward-thinking farmers, agribusinesses, and stakeholders to step into a future defined by smart data, advanced biotechnology, and environmentally responsible methods. Embrace the evolution—grow more, harm less, and let’s shape the next era of sustainable soybean success together.