Precision Agriculture: Top 7 Technologies for Farm Management
“Over 70% of modern farms use GPS-guided equipment for precise planting and harvesting, boosting efficiency and accuracy.”
Introduction: The Evolution of Precision Agriculture
In today’s rapidly changing agricultural landscape, precision agriculture stands as a transformative approach—redefining how we manage fields and maximize crop yield. With growing pressure on global food systems and a need for sustainable farming practices, leveraging technology has become more than a luxury; it’s a necessity. Precision agriculture, sometimes referred to as precision farming technology, is a data-driven methodology that integrates advanced tools like GPS, remote sensing, and IoT devices into everyday farming operations.
Our mission is to harness these advanced technologies for improved farm management, better resource allocation, and reduced environmental impact—all while enhancing productivity and farm profitability. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the top 7 technologies for precision agriculture, their applications, and how modern platforms like Farmonaut are making these capabilities more accessible and affordable for farmers worldwide.
Top 7 Precision Agriculture Technologies for Farm Management
Let us begin by delving into the seven key precision agriculture technologies that are optimizing farm processes, enabling informed decisions, and paving the way toward sustainable farming and higher productivity.
1. GPS – Global Positioning System for Precise Field Operations
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is the backbone of location-based farm management. By enabling precise geolocation of farm equipment, boundaries, and processes, GPS empowers us to map, plant, fertilize, and harvest with unmatched accuracy. GPS makes it possible to:
- Automate tractor guidance across fields for straight rows and consistent spacing
- Ensure uniform input application during fertilization and planting
- Facilitate yield mapping and crop health assessment, especially when paired with data-driven analytics
- Reduce input waste by guiding equipment only over intended zones, which is crucial for sustainable farming practices
Did you know? GPS-guided equipment can reduce overlaps during field tasks by up to 10%, saving both time and resources.
Learn more about GPS in precision agriculture
2. GIS – Geographic Information System Mapping for Optimized Applications
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a digital framework for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data vital to precision agriculture. By integrating information about soil types, elevation, irrigation systems, and crop health, GIS empowers us to:
- Build detailed field maps showing variability in soil properties, moisture content, and nutrient levels
- Monitor historical crop performance and forecast future yields
- Allocate resources like water and fertilizer to areas most in need, based on objective metrics
- Spot problem areas (e.g., low productivity or pest hotspots) for targeted intervention
GIS, when combined with remote sensing in agriculture and satellite data, is at the core of data-driven farm management and supports seamless integration of other precision farming technologies.
Discover how GIS revolutionizes agricultural mapping
3. Remote Sensing in Agriculture: Satellites & Drones for Real-Time Monitoring
Remote sensing in agriculture leverages satellites, drones, and aerial imagery to collect vital data on crop health, soil moisture, and field conditions—often in real-time. This capability allows us to:
- Get comprehensive field overviews, even in hard-to-reach or vast areas
- Detect stress, pest infestations, or nutrient deficiencies early through multispectral imagery
- Pinpoint exact areas that require intervention, ensuring precise and targeted management
- Monitor changing environmental conditions that affect yield
For example, Farmonaut’s platform uses multispectral satellites for large-scale crop health monitoring (NDVI) and soil moisture mapping, empowering timely and efficient interventions for improved yield and reduced resource waste.
Read more about remote sensing applications in precision agriculture
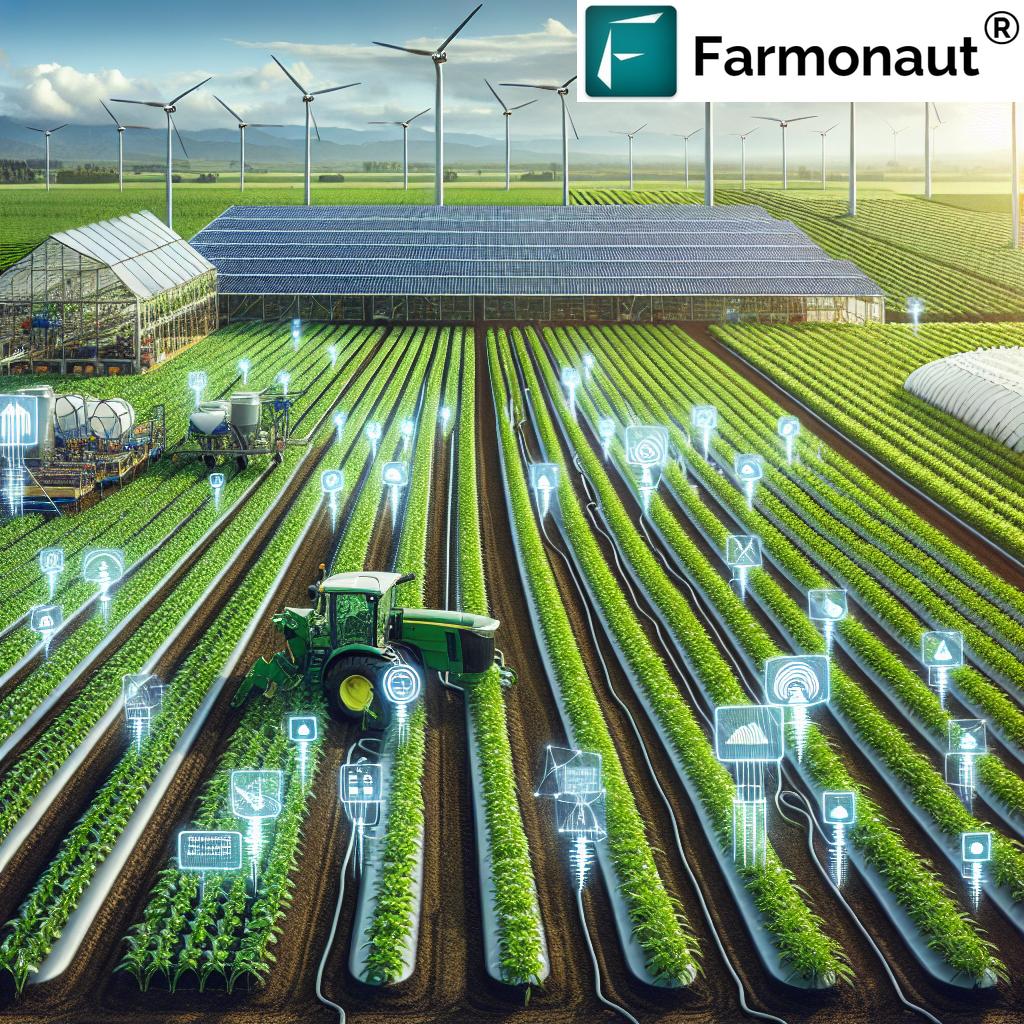
4. IoT Devices & Soil Moisture Sensors for Continuous Data Collection
The Internet of Things (IoT) has opened new dimensions in precision agriculture. IoT devices—ranging from soil moisture sensors and weather stations to nutrient analyzers—gather invaluable data across the field. With continuous measurement, we can:
- Monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other field conditions 24/7
- Enable precision irrigation systems that only apply water when and where required, conserving water and energy
- Trigger real-time alerts for critical events like drought stress or sudden weather changes
- Inform tailored decisions for fertilizer and pesticide application
The result: higher efficiency, minimized input use, and improved resilience to climate variability. In Farmonaut’s ecosystem, IoT sensors work synergistically with satellite data to enable informed interventions tailored to actual field variability.
Dive deeper into IoT devices in agriculture
5. Automated Machinery & Autonomous Operations
Automated machinery—encompassing driverless tractors, autonomous harvesters, and agricultural drones—are redefining farming operations. These machines leverage GPS, IoT, and data analytics to:
- Plant, fertilize, spray, and harvest with minimal human intervention
- Enhance accuracy and productivity, reducing operational variability and human errors
- Allow farmers to scale up their farming businesses efficiently, even with labor shortages
- Lower labor costs, streamline fleet management, and optimize use of resources for specific field tasks
These advances are particularly instrumental in large-scale farm management, where efficiency is pivotal for economies of scale.
Explore how automation is shaping the future of farming
“Remote sensing technologies can monitor up to 100 acres of crops in a single satellite image, revolutionizing farm management.”
6. Variable Rate Technology (VRT) for Input Optimization
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) transforms the traditional “one-size-fits-all” approach by facilitating inputs—seeds, fertilizer, pesticides—at variable rates across a field. Relying on GPS, soil and crop sensors, and historical mapping, VRT enables us to:
- Apply the right amount of input at the right location, tailored to actual field conditions
- Reduce input waste, operational costs, and environmental impact
- Boost yield and productivity for each specific field zone
- Perform real-time adjustments during planting, fertilization, and spraying tasks, ensuring optimal output
Research shows that consistent use of VRT can significantly lower both chemical usage and labor costs, all while driving measurable yield improvements.
Find out how VRT revolutionizes input application
7. Data Analytics Platforms & AI for Farm Decision-Making
Agricultural data analytics platforms and AI tools synthesize massive volumes of farm data from satellites, sensors, weather stations, and equipment. With smart algorithmic analysis, we are able to:
- Generate actionable insights for every plot and season, improving overall farm management
- Predict yield, pest infestations, and disease outbreaks with high accuracy
- Enable predictive and prescriptive analytics for input management and risk reduction
- Integrate blockchain for supply chain traceability and transparency, improving security and stakeholder trust
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI system and blockchain-powered traceability are leading examples of how integrated analytics are enhancing decision-making, monitoring, and market transparency throughout the agricultural value chain.
Comparative Table: Precision Technologies at a Glance
To help you quickly understand the relative advantages of each advanced tool, here is a comparative table summarizing their main functions, benefits, and estimated quantifiable impacts:
| Technology Name | Main Function | Key Benefits | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Resource Saving (%) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-Guided Tractors | Precise navigation and field mapping | Reduces overlaps; ensures accurate input application | 5–10% | 8–12% | Automated planting and fertilizing |
| Remote Sensing (Satellites & Drones) | Real-time crop and field monitoring | Timely detection of stress and pests | 8–15% | 10–15% | Field health mapping and targeted intervention |
| Drones | Aerial surveying and variable input spraying | Fast data collection and input delivery | 5–10% | 5–8% | Spot spraying, vegetation mapping |
| Soil Moisture Sensors | Continuous soil condition monitoring | Optimizes irrigation and fertilizer use | 4–6% | 10–15% | Precision irrigation systems |
| Variable Rate Technology (VRT) | Application of inputs at variable rates | Reduces waste; increases efficiency | 10–16% | 12–18% | Site-specific seeding and fertilization |
| Satellite Imagery | Large-scale field surveillance | Enhances monitoring and planning | 8–12% | 5–10% | Regional crop management |
| Data Analytics Platforms | Farm data integration and AI-driven insights | Informs strategic planning; improves decisions | 10–20% | 10–18% | Predictive analytics, traceability, resource allocation |
Applications of Precision Agriculture: Making Every Acre Count
Precision agriculture isn’t just about technology—it’s about integrating advanced systems into real-world farm management practices to achieve measurable outcomes. Let’s review how these technologies enable smarter, more sustainable farming through core applications:
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) for Tailored Inputs
With VRT, we can apply seeds, fertilizer, and pesticides at variable rates, matched to the specific needs of each field zone. This is powered by GIS mapping, soil sensors, and on-the-go analytics:
- Site-specific management: Apply only what’s needed per area, optimizing input costs and reducing waste
- Environmental benefits: Lower chemical runoff and minimize environmental impact
- Increased productivity: Address underperforming sections and maximize overall yield
Why VRT is a game-changer for resource management
Crop Yield Mapping for Informed Decisions
Yield mapping integrates GPS and harvesting sensors to measure crop yields spatially across fields. This data highlights:
- Productivity variability: Spot both high and low-yield zones
- Decision guidance: Allocate resources efficiently and prioritize interventions
- Long-term planning: Adjust strategies for specific crops, zones, or years—optimizing for profitability
How yield maps improve decision making
Precision Irrigation Systems for Water Efficiency
By pairing soil moisture sensors and weather data with precision irrigation systems, we ensure:
- Water delivered only where and when needed, minimizing evaporation and deep percolation losses
- Significant resource savings and improved crop health
- Automation based on real-time data from sensors and remote sensing imagery
Read more about actionable precision irrigation
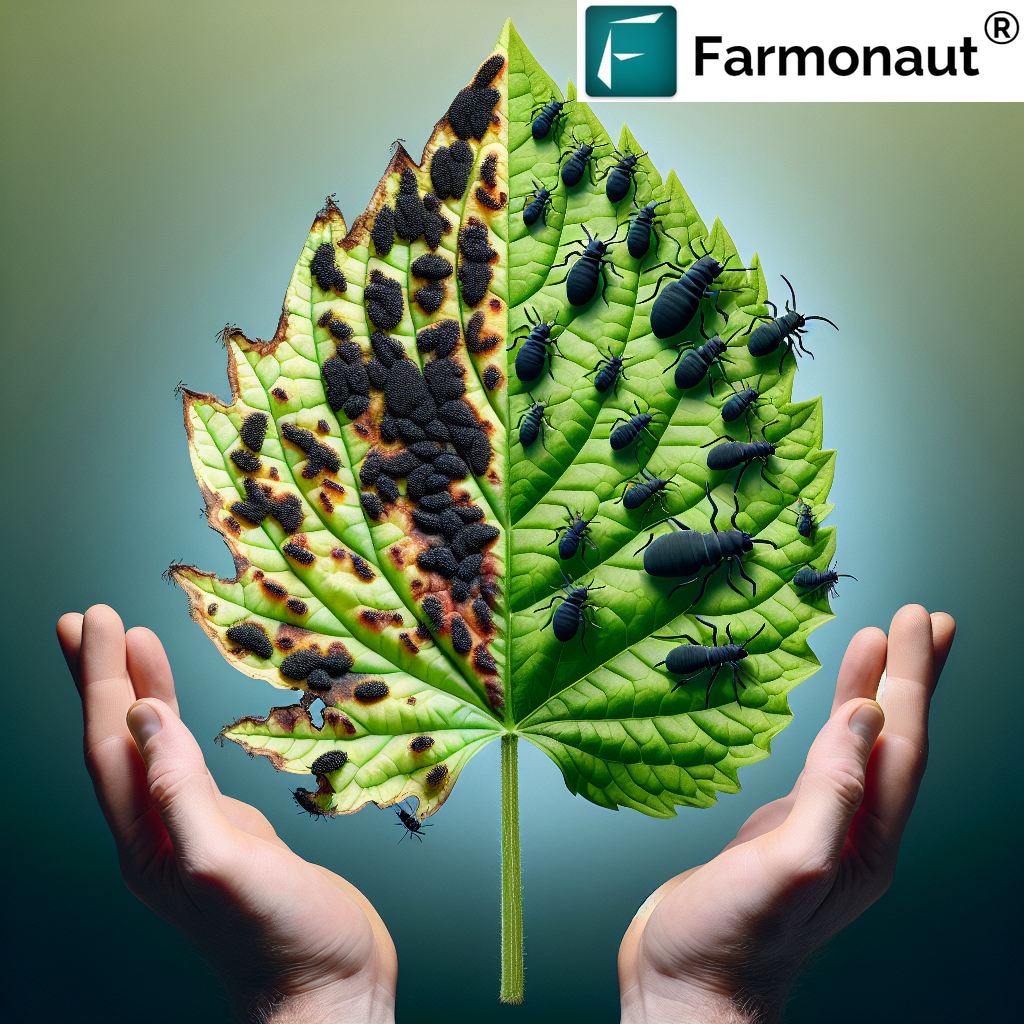
Pest and Disease Management with Targeted Interventions
Remote sensing, combined with predictive analytics, enables rapid detection of pest infestations and disease outbreaks. This helps us:
- Intervene early and only in affected areas thanks to targeted mapping
- Reduce overall chemical usage—lowering costs and promoting environmental sustainability
- Protect crop health and prevent large-scale losses through timely action
Environmental benefits of targeted pest management
Real-Time Crop Health Monitoring and Advisory
With satellite imagery, IoT, and AI-driven analytics (like Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI), we achieve:
- Proactive monitoring of vegetation health (NDVI) and soil moisture
- Automated alerts and expert advice, instantly accessible through mobile/web apps
- Informed recommendations that optimize every step—from planting to harvesting
Fleet and Resource Management for Operational Efficiency
Managing logistics and resources (equipment, vehicles, operators) is streamlined with Farmonaut’s fleet management tools. These systems:
- Track equipment in real time for better utilization and scheduling
- Improve safety and reduce operational costs
- Facilitate coordination for expansive or multi-location farm operations
Blockchain-Based Traceability for Farm Products
With consumer demand for transparency, blockchain-based traceability systems provide:
- End-to-end tracking of products from farm to table
- Enhanced trust and reduced fraud across agri supply chains
- Secure, tamper-proof records for compliance and marketing
Carbon Footprinting and Environmental Sustainability
Precision agriculture isn’t just about yield—it’s about sustainability. Platforms like Farmonaut’s carbon footprint tracker allow us to:
- Monitor and reduce greenhouse gas emissions in real-time
- Adopt sustainable farming practices to protect long-term soil and environmental health
- Comply with regulatory standards and enhance brand reputation
Farmonaut: Making Precision Agriculture Accessible and Affordable
Modern farmers and agribusinesses face challenges in accessing affordable, scalable precision farming technology for real-time farm management. Farmonaut addresses these pain points by providing a comprehensive, cost-effective platform that democratizes data-driven farm management.
Farmonaut’s Core Technologies
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Real-time NDVI analysis and soil moisture mapping help optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Offers AI-driven, personalized crop and weather advisory for increased productivity and proactive risk reduction.
- Blockchain Traceability: Verifies every stage in the farm-to-fork journey, building consumer trust through secure supply chain solutions.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Streamlines fleet operations and equipment use for optimal efficiency.
- Carbon Footprinting: Calculates and helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions for sustainable agriculture.
Farmonaut’s business model includes flexible subscriptions for farmers, cooperatives, agribusinesses, and government agencies. Users access actionable insights via the web and mobile apps, or can integrate features with their own software via Farmonaut’s API (API docs).
Target Audience:
- Individual Farmers: Affordable precision farm monitoring, crop health alerts, and resource management tools
- Agribusinesses: Large-scale field and plantation monitoring, operational analytics, and improved fleet efficiency
- Governments/NGOs: Sector-wide crop monitoring, policy support, and program implementation
- Financial Institutions: Satellite-based crop verification to streamline loans and insurance processes (see more)
- Corporate Clients: Secure, blockchain-fortified traceability solutions for food, textile, and export supply chains
Benefits of Precision Agriculture for Modern Farming
When we adopt precision farming technology, the impact is far-reaching. Here’s how these tools and approaches fundamentally transform today’s agriculture:
- Increased Productivity: Optimal use of inputs and targeted interventions mean higher yields and better-quality crops.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced wastage and precise resource allocation translate to direct operational savings.
- Environmental Sustainability: By minimizing chemical and water use, we reduce runoff, conserve resources, and improve farm ecology.
- Enhanced Farm Management: Integrated, data-driven systems take the guesswork out of decision-making—goodbye to gut-based uncertainty!
- Improved Traceability & Security: Blockchain-powered platforms bolster supply chain transparency, food safety, and consumer trust.
- Greater Resilience: Precision tools enable adaptation to climate volatility and pest threats much faster than traditional approaches.
Check the economic and environmental gains of precision agriculture
Read about quantified sustainability impact here
Challenges in Adopting Precision Farming Technology
While the promise of precision agriculture is immense, there are several hurdles on the road to widespread implementation:
- High Initial Investment: Setting up advanced systems, sensors, and automated machinery may be financially taxing for small and medium farmers.
- Data Management & Security: Handling vast amounts of farm data requires secure infrastructure and robust protocols to ensure data privacy and integrity.
- Technological Barriers: Farmer training, technical know-how, and digital literacy are all critical to effectively using these tools.
- Connectivity Issues: Inadequate internet coverage in rural and remote areas can disrupt the functioning of IoT devices and delay real-time analytics.
More about barriers and solutions in precision farming adoption
Future Outlook: Where is Precision Agriculture Headed?
The future of precision agriculture is brighter than ever. Our industry is moving toward:
- Affordable, user-friendly tools tailored for both smallholders and large-scale operators
- Increased AI integration for predictive analytics and prescriptive decision support
- Greater automation with advanced robotics and autonomous machinery
- Enhanced sustainability tracking (e.g., carbon footprinting) to comply with climate regulations and boost brand value
- Expanded API access and platform interoperability, as offered by Farmonaut’s developer API (docs)
- Easier access to loans and insurance by leveraging satellite-based crop verification
As technology evolves, data management becomes more seamless, and platforms become even more accessible across devices and geographies, precision farming will continue to drive global food security and sustainable farm management for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Precision Agriculture
What is precision agriculture?
Precision agriculture is a data-driven methodology that uses GPS, remote sensing, IoT, and data analytics to optimize field-level management, boost productivity, reduce waste, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Which are the top technologies used in precision farming?
The leading technologies are GPS, GIS, remote sensing, IoT devices and soil moisture sensors, automated/autonomous machinery, variable rate technology, and data analytics platforms.
How do IoT sensors improve farm management?
IoT sensors monitor soil moisture, weather, temperature, and more—enabling real-time, tailored interventions that save water, reduce input waste, and increase yields.
Are precision farming tools suitable for small farmers?
Yes, platforms like Farmonaut offer scalable, subscription-based services that make advanced precision agriculture accessible and affordable for farms of all sizes.
How does blockchain traceability benefit agriculture?
Blockchain fortifies supply chain transparency, ensuring product authenticity and minimizing fraud—critical for regulatory compliance, export, and consumer trust.
What challenges exist in adopting precision agriculture?
Challenges include initial setup costs, technological training, reliable internet connectivity, and the need for secure data management systems.
Where can I learn more about Farmonaut’s API and developer tools?
Visit the Farmonaut API portal and dedicated documentation.
Get Started with Farmonaut: Precision Agriculture in Your Palm
With the world’s top precision agriculture platform, you can monitor fields, track crop health, and make data-driven decisions in minutes—anytime, anywhere.
Looking to unleash the full power of precision agriculture with scalable farm management tools? Deploy Farmonaut and integrate data-driven technology into your sustainable farming practices—turning every data point into a step toward higher yield, lower cost, and a healthier planet.