What Farming Technology Was Important in Texas? A Historic and Modern Exploration of Agricultural Innovation
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Expert Trivia: Did You Know?
- Early Mechanization and the Cotton Industry in Texas
- Forestry Technology Advancements and Sustainable Practices
- Modern Farming Technology & Precision Agriculture Advancements
- Farmonaut: Enabling Precision and Sustainability in Texas Agriculture
- Technological Innovations Timeline Table
- Texas Agricultural Technology: More Eye-Opening Trivia!
- The Power of Research and Extension Services
- Conclusion: The Future of Agricultural Innovation in Texas
- FAQ: Farming Technology in Texas
Introduction: The Legacy and Transformation of Farming Technology in Texas
When we think about agricultural innovation in Texas, it’s clear that technology has always played a central role in our state’s farming identity. For generations, Texas farmers, ranchers, and forestry professionals have not only embraced but also led the way in technological advancements to make agriculture more productive, efficient, and sustainable. From the early days of mechanical cotton gins to GPS-guided tractors and game-changing precision agriculture advancements, Texas has been at the epicenter of agricultural transformation.
Our journey through the evolution of technology in Texas agriculture reveals more than just machines or software. It showcases our state’s spirit of resilience—adopting tools that increase yields, reduce labor, address water and soil challenges, and provide hope for future generations. Along this path, we’ll uncover the early mechanization of cotton processing, breakthroughs in forestry, and the integration of digital solutions like Farmonaut’s satellite-based technology fueling sustainable agricultural growth for both small and large farm operations.
Let’s explore how agricultural innovation in Texas—from the past to the digital present—is shaping not only the local industry but serving as a model of excellence for crop management across the globe.
Early Mechanization and the Cotton Industry in Texas
The Cotton Gin: Laying the Groundwork for Texas Agricultural Growth
The story of mechanization in farming in Texas begins long before the digital age—with Eli Whitney’s cotton gin, first introduced in 1793. As we know, Texas is synonymous with cotton. But before the cotton gin, separating seeds from fiber was labor-intensive and severely limited production. Whitney’s invention—the cotton gin—efficiently separated seeds from cotton fiber, slashing processing time and labor costs. With this, the foundation for massive expansion of Texas’s cotton fields was laid.
By 1869, Texas produced nearly 350,628 bales of cotton. A decade later, this more than doubled to 805,000 bales (cottongins.org). The direct result of technology increasing production meant that Texas would soon dominate the national cotton market, shaping not only local economies but global textile supply.
Key Innovations:
- The introduction and rapid adoption of the cotton gin increased cotton production exponentially.
- Farmers could grow and process far greater acreage with less manual labor, reducing costs and encouraging investment.
- The groundwork for the mechanization wave in agriculture was laid, allowing rapid scale-up in subsequent decades.
The Rise of Mechanical Cotton Strippers and Harvesters
As our cotton fields expanded, so did the demand for more efficient harvesting methods. By the early 1930s, Texas was once again at the forefront with the development of the first mechanical cotton stripper by the Texas Agricultural Experiment Station in 1931 (en.wikipedia.org). This machine, which would be widely adopted within a decade, mechanized the harvesting process and redefined farm labor:
- Mechanical strippers drastically reduced manpower required for cotton harvesting.
- Harvesting became faster, more precise, and more consistent, minimizing crop loss.
- Less time in the field meant reduced exposure to unpredictable Texas weather, further protecting yields.
By the 1940s, new cotton harvesting machines in Texas were increasing picking efficiency by over 500% compared to manual methods. As the industry grew, so did the fields—Texas farmers could now manage much larger acreages, accelerating both state and national production.
Other Key Early Mechanization Examples
- Animal-drawn plows and planters: Transitioned later to mechanical and motorized versions, improving farming tasks like furrow pulling, planting, and soil aeration.
- Steam-powered and gasoline tractors: Replaced animal power, allowing heavier work and larger scale planting and harvesting—setting the stage for the modern automated tractors used today.
Forestry Technology Advancements and Sustainable Practices in Texas
Logging, Mechanization, and the Environmental Balancing Act
Just as with planting and harvesting, Texas’s timber industry required innovation for growth. Initially reliant on manual labor and animal-powered log hauling, the late 1800s saw the introduction of the skidder—a railway car fitted with a crane and long cables (wikipedia).
The skidder revolutionized efficient logging operations:
- Timber operations could now quickly clear and transport vast numbers of trees, increasing the speed and efficiency of lumber production.
- Rail connections allowed Texas wood products to reach booming urban markets further afield.
Environmental Concerns and Reforestation Initiatives
With rapid logging operations came new environmental concerns. Forest ecosystems were being impacted by intense harvesting, leading to overexploitation that threatened Texas’s long-term ecological balance.
In response, the Texas Forest Service began a landmark reforestation initiative:
- Millions of trees were planted to restore and sustain forest resources.
- Reforestation efforts helped maintain an ecological balance, ensuring the economic viability of the timber sector over the long term.
- New technologies and sustainable forestry practices became standard, paving the way for modern conservation approaches.
Today, Texas’s forest sector is a leader in combining technological advancement with sustainability, balancing production with restoration.
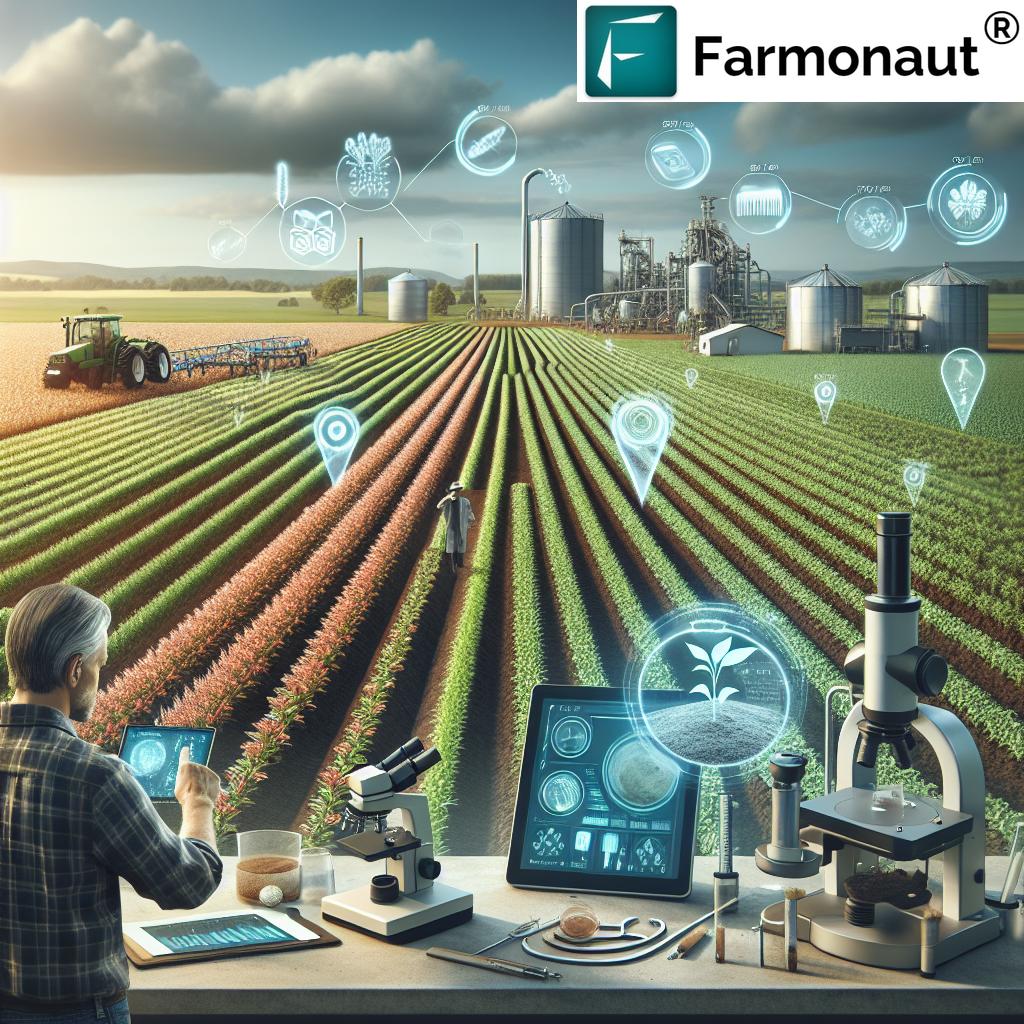
Modern Farming Technology & Precision Agriculture Advancements
The Digital Revolution: Smart Machines, Sensors, and Satellite Technologies
From the late 20th century onward, Texas agriculture has rapidly integrated digital, automated, and data-driven tools. The age of modern farming practices embraces smart systems designed to maximize yields, reduce input costs, and ensure sustainable agriculture in Texas.
Key Modern Advancements:
- Automated Tractors & Harvesters (Equipped with GPS):
- Modern tractors and harvesters utilize GPS-guided control for precise plowing, planting, and reaping. Human intervention is minimal, labor costs are further reduced, and every movement is optimized for efficiency.
- Farmonaut’s Fleet Management technology enables real-time logistics tracking for large farm vehicles, optimizing operational costs.
- Smart Irrigation Systems:
- Sensors monitor soil moisture and weather, delivering water only when and where crops need it.
- Smart irrigation improves resource conservation, enhances crop resilience, and supports long-term sustainability.
- Biotechnology and GMOs:
- Biotechnology in agriculture is now standard in Texas fields. Crops engineered for pest- and drought-resistance reduce the need for synthetic chemicals, lower input costs, and bring more reliable crops to market.
- Cotton and corn GMOs are especially prevalent in our state, driving both profitability and resource efficiency.
- Satellite Monitoring and Precision Agriculture:
- Multi-spectral satellite imagery delivers comprehensive crop health reports, soil moisture assessment, and land-use analytics—empowering farmers at all scales to make data-driven decisions.
- Farmonaut’s satellite-based platform brings advanced monitoring and AI-driven advisories right to the farm gate, elevating the standard for precision agriculture in Texas.
- AI & Machine Learning in Agriculture:
- AI platforms predict yields, recommend resource allocation, and automate early pest and disease detection—so that farmers can proactively address threats and optimize every season.
- Blockchain Traceability:
- Farmonaut’s traceability solutions enable secure, transparent food and fiber chain monitoring from Texas fields to tables, boosting consumer trust and market competitiveness.
As these technologies become mainstream, Texas continues to set the bar for precision agriculture advancements, smart irrigation systems, and overall sustainable agriculture nationwide.
Looking for satellite-powered API solutions? Our platform offers robust APIs for satellite, crop, and weather data. Integrate Farmonaut with your own apps or agribusiness systems:
For large-scale operations: Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management App revolutionizes how organizations manage plantations, fleets, and resources with up-to-date satellite insights.
Farmonaut: Enabling Precision and Sustainability in Texas Agriculture
In the modern era, platforms like Farmonaut are democratizing access to precision ag. By leveraging satellite data, AI advisories, and blockchain, we empower individual Texas farmers, agribusinesses, and government agencies:
- Crop Health Monitoring:
- NDVI and multi-spectral imagery for real-time crop insight, enabling proactive management of irrigation, fertilizer, and pest control.
- AI-Driven Advisory (Jeevn AI):
- Weather and farm analytics are delivered directly to farmers’ phones for smarter, more efficient decision-making.
- Fleet & Resource Management:
- Digitally track all vehicles and farming equipment, reducing fuel consumption and maximizing utilization across thousands of Texas acres.
- Carbon Footprinting:
- Want to measure and reduce your farm’s environmental impact?
Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting Tools for real-time sustainability tracking.
- Want to measure and reduce your farm’s environmental impact?
- Blockchain Traceability:
- Transparent tracking from field to consumer, enhancing trust and enabling premium market access.
- Crop Loans & Insurance:
- Verified field analytics make it easier for Texas farmers to access crop loans and insurance faster and with less hassle.
With services like Crop Plantation, Forestry & Advisory,
our approach supports everything from timber to row crops—making advanced technology available for every segment of Texas agriculture.
Zero hardware investment, flexible subscriptions, and mobile/web access mean that farms of every size—from Central Texas prairie cotton fields to East Texas pine forest—can benefit from cutting-edge technology, data-driven insight, and sustainable practices.
Technological Innovations Timeline Table
| Year Introduced | Technology Name | Description/Function | Impact on Texas Farming | Current Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1793 | Cotton Gin | Efficiently separates cotton seeds from fiber | Catalyzed expansion, increased cotton production by 100%+ in a decade | Obsolete; laid mechanization foundation |
| Late 1800s | Steam/Gasoline Tractors | Replaced animals for fieldwork, plowing, and planting | 30–50% increase in fieldwork efficiency, enabled larger farms | Obsolete; replaced by modern tractors |
| 1931 | Mechanical Cotton Stripper | Automated cotton picking, reduced manual labor | 500% increase in harvesting efficiency in 1940s | Still in use (modern versions) |
| Early 1900s | Skidder (Railway Car with Crane) | Enabled large-scale, efficient timber extraction | Dramatic increase in timber output; raised environmental concerns | Rare; replaced by eco-friendly tech |
| 1940s–1960s | Automated Harvesters | Mechanical machines for various crop harvesting | Significant reduction in labor costs across crops | Ubiquitous |
| 1970s–1980s | Sprinkler & Drip Irrigation Systems | Soil moisture monitored, targeted water delivery | 20–40% reduction in water use, improved crop resilience | Still expanding rapidly |
| 1990s | Biotechnology (GMOs) | Genetic modification for pest/drought resistance | 30+% yield increases, reduced chemical pesticide demand | Standard for staple crops |
| 1999–2008 | GPS-Equipped Tractors | Automated exact plowing, seed, and harvest paths | 10–15% input savings, improved labor and operational efficiency | Industry standard |
| 2010s | Satellite Crop Monitoring | NDVI, soil, and crop health automated from above | Real-time insights, data-driven management, loss reduction | Rapidly expanding (see Farmonaut) |
| 2015–Present | AI Advisory Systems | Data analysis, predictive analytics, automated recommendations | Smarter, proactive farm management; resource optimization | Now foundational |
| 2020s | Blockchain Traceability | Data-secure farm-to-table product tracking | Boosts export value, enhances consumer trust and transparency | Rapidly growing (see Farmonaut) |
The Power of Research and Extension Services: Driving Texas Innovation
Texas Experiment Stations & Knowledge Transfer
As we reflect on the rapid adoption of farming technology in Texas, it’s clear that research institutions have been instrumental. The Texas Agricultural Experiment Station (now Texas A&M AgriLife Research), founded in 1887, has developed and tested nearly every game-changing agricultural advancement in the state.
- In 1931, this station rolled out the first mechanical cotton stripper, changing the harvesting landscape across Texas and the wider cotton belt.
- Continuous research and development from these institutions—machine testing, crop trials, and advisory program rollouts—have ensured that Texas remains a technology leader in agriculture.
Extension Services—including Texas A&M Engineering Extension—amplified the impact of this innovation by:
- Giving farmers hands-on training and technical support to implement new technology effectively.
- Educating rural communities about the benefits of modern agricultural practices and environmental conservation.
- Ensuring that even small-scale operations could access information and tools that once benefitted only the largest farms.
The ongoing collaboration between research institutions and farmers continues to:
- Open the door to AI-powered advisory and big data tools.
- Promote the rapid adoption of biotech crops, advanced machines, and blockchain for traceable supply chains.
- Establish Texas as an example state for sustainable, technology-driven agriculture—where the balance between profit and environment is constantly optimized.
Conclusion: The Future of Agricultural Innovation in Texas
The evolution of farming technology in Texas is a testament to what happens when resilience, research, and purposeful investment in innovation meet. As a state with a proud agricultural legacy, we have always placed value on working smarter, not just harder. From the early days of the cotton gin and mechanical strippers to today’s satellite-powered, AI-driven, and sustainable solutions, Texas continues to lead the way.
Key Takeaways:
- Every new technology—from the mechanical cotton picker to blockchain traceability—has enabled us to produce more, waste less, and nurture our land for future generations.
- Balancing intensive agriculture with sustainability has become a core goal, as seen in both our evolving forestry practices and row crop management.
- Platforms like Farmonaut make it affordable and accessible for everyone—from an individual cotton grower in Lubbock to a large forestry operation in East Texas—to access precision agriculture advancements, manage resources efficiently, and protect our environment.
As technological advancements continue—driven by our universities, agtech platforms, and pioneering farmers—Texas agriculture will remain a powerhouse of both productivity and innovation, prepared to meet whatever challenges the next century brings.
Ready to experience the future of farm management?
Download Farmonaut for Android or iOS or access the Web app today!
FAQ: Farming Technology in Texas
1. What are the most important farming technologies that originated or were first adopted in Texas?
Texas has been instrumental in the adoption and development of several farming technologies, including the cotton gin, mechanical cotton stripper, GPS-guided tractors, and modern precision agriculture platforms. The state’s early leadership in mechanization paved the way for today’s reliance on digital monitoring, AI-advisory, and sustainable water and resource management systems.
2. How has precision agriculture improved sustainable farming in Texas?
Precision agriculture uses data, satellite imagery, and AI to optimize fertilizer, irrigation, and pest control interventions. In Texas, it has improved yields while reducing input waste, preserving water, lowering environmental impacts, and boosting profitability for farms of all scales.
3. What is the role of biotechnology and GMOs in Texas agriculture?
Biotechnology in agriculture has enabled Texas farmers to grow crops that withstand local pests, diseases, and periods of drought. As a result, less chemical spraying is needed, yields are more consistent, and the agricultural industry has become more resource efficient.
4. Which sectors of Texas agriculture use satellite and AI-based technology?
Satellite and AI solutions are now used across row crops (like cotton and corn), fruit and nut orchards, vegetable farmers, and even in the forestry sector for reforestation monitoring, tree counting, and land use analysis. Farmonaut’s platform exemplifies these advanced technologies in action.
5. Why is blockchain traceability important for Texas agriculture?
With blockchain traceability, every step in the supply chain— from planting and harvesting to sale—can be tracked and audited. This boosts consumer and buyer trust, helps Texas products stand out in domestic and export markets, and protects farmers and brands from fraud or supply chain uncertainty.
6. How does Farmonaut support sustainability and innovation in Texas agriculture?
Farmonaut delivers real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisories, blockchain traceability, and carbon footprint tracking via web, iOS, and Android—requiring no large equipment investment. Its focus is on affordable precision agriculture for every stakeholder, from smallholders to large agribusinesses and government bodies.
Explore innovative, sustainable agricultural and forestry management with Farmonaut. Take advantage of cutting-edge technology to grow yields, protect natural resources, and keep Texas a leader in farm innovation for the generations to come.