Lemon Tree Diseases: 7 Strategies for Healthy Orchards
“Up to 30% of lemon yield can be lost annually due to unmanaged tree diseases.”
Overview: Why Healthy Lemon Orchards Matter
Lemon (Citrus limon) is a cornerstone of global agriculture, providing both significant economic and nutritional benefits to communities worldwide. However, lemon tree diseases remain a primary threat, jeopardizing not only the quality of the fruit but also the long-term productivity and health of entire orchards.
Understanding these diseases, from their earliest symptoms to effective management strategies, is essential for growers committed to maintaining healthy lemon trees and improving orchard output. Whether you are a smallholder farmer or manage large-scale operations, knowing how to prevent lemon tree infection is key to sustaining your harvests.
Farmonaut offers advanced satellite-based crop health and disease monitoring solutions, integrating cutting-edge AI, machine learning, and blockchain-backed traceability into a seamless app and API ecosystem. With Farmonaut, you gain real-time, actionable insights to reduce risk, optimize inputs, and improve yield—all crucial for combating lemon tree fungal diseases, improving lemon tree productivity, and ensuring the longevity of your investment.
Lemon Tree Disease Management Overview
| Disease Name | Estimated Prevalence (%) | Key Symptoms | Likely Cause | Recommended Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus Canker | 15-20 | Raised, corky lesions; water-soaked appearance; defoliation; fruit drop | Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri (bacterial) | Plant resistant varieties, promote airflow, avoid overhead irrigation, prune infected parts |
| Citrus Tristeza Virus (CTV) | 5-10 | Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, dieback, reduced yield | Virus (aphid-vectored) | Use certified virus-free nursery stock, control aphids, avoid infected budwood |
| Phytophthora Root Rot | 10-18 | Wilting, yellowing, root decay, tree decline | Soil-borne Phytophthora fungi | Improve drainage, avoid waterlogging, fungicide as needed |
| Alternaria Brown Spot | 8-15 | Dark brown to black sunken lesions, premature defoliation | Alternaria alternata (fungal) | Prune for airflow, fungicidal sprays (copper/sulfur) |
| Lemon Scab | 4-8 | Raised, corky scabs on fruit, blemished rind | Elsinoë fawcettii (fungal) | Sanitation, fungicide sprays (copper/sulfur), remove infected parts |
| Sooty Mold | 10-18 | Black, sooty coating on leaves and stems | Honeydew from sap-feeding insects | Control insects (mealybugs, whitefly, aphids), neem oil, horticultural sprays |
| Mal Secco | 1-5 | Leaf wilting, twig dieback, internal discoloration | Phoma tracheiphila (fungal) | Remove infected parts, promote airflow, use resistant varieties |
Common Lemon Tree Diseases and Their Management
Lemon trees are susceptible to a variety of diseases, each caused by distinct pathogens ranging from bacteria and viruses to fungi and sap-sucking pests. Early recognition and focused management are essential for maintaining orchards and improving lemon tree productivity.
“Early detection can reduce lemon tree disease spread by over 50% in orchards.”
Citrus Canker: Identifying and Managing a Major Threat
Citrus canker, caused by Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri, is one of the most notorious lemon tree diseases. It is characterized by raised, corky lesions with a water-soaked appearance on leaves, stems, and fruit. These lesions may ooze bacterial fluid, leading to defoliation, premature fruit drop, and decreased fruit quality—all of which can severely impact harvests.
Citrus Canker Management & Prevention
- Prevention first: Plant only disease-resistant lemon varieties and use certified nursery stocks.
- Proper spacing: Ensure adequate distance between trees to promote airflow and reduce humidity, limiting bacterial spread.
- Avoid overhead irrigation: Overhead watering can spread infectious droplets; use drip or root-zone irrigation instead.
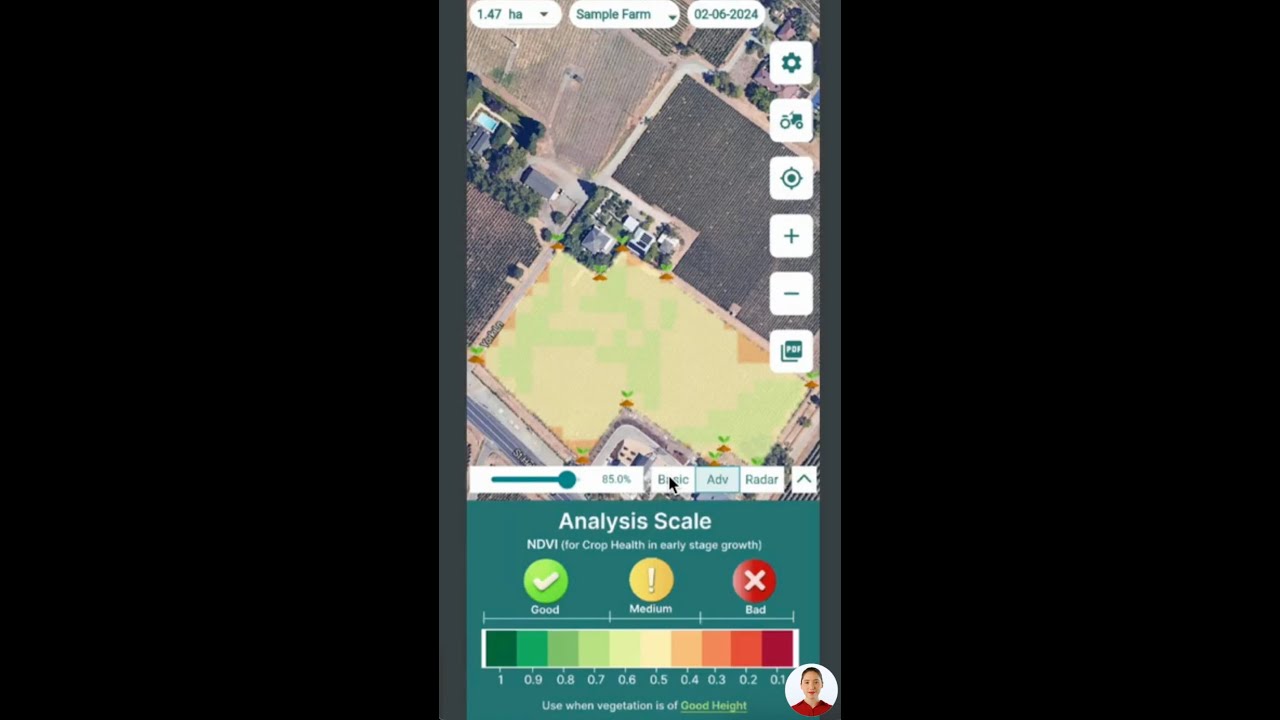
- Monitor orchard health via satellite: Timely identification of high-risk zones through satellite imagery improves decision-making for canker response.
- Prompt removal: Remove and destroy any infected leaves, twigs, and fruit—never compost them.
- Sanitation: Disinfect pruning tools after use.
With Farmonaut’s satellite-based health monitoring tools, growers can get real-time updates on canopy health and disease hotspots—this reduces the risk of missed early infections and supports best practices for healthy lemon orchards.
Citrus Tristeza Virus (CTV): A Devastating Lemon Disease
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral disease threatening lemon and other citrus trees worldwide. Symptoms include:
- Leaf yellowing
- Stunted growth and decline in fruit yield
- Dieback of shoots
- Reduced tree vigor, sometimes leading to death in severe cases
Transmission: CTV is primarily spread by aphid insects and through use of infected budwood for grafting.
How to Prevent Lemon Tree Infection by CTV
- Use certified virus-free nursery stock for planting and grafting.
- Control aphid vectors: Monitor and manage aphid populations with integrated pest management (IPM) strategies.
- Avoid using potentially infected cuttings or budwood.
- Regularly inspect trees for early infection symptoms with technology like Farmonaut’s app for rapid field checks.
There is no cure for CTV: Once widespread, losses can be severe. Preventative sanitation and use of resistant rootstocks are critical.
Phytophthora Root Rot in Lemon Trees: The Hidden Threat Beneath
Phytophthora root rot, caused by diverse species of the Phytophthora fungus, is a persistent soil-borne disease affecting lemon tree roots and the lower trunk. Symptoms such as wilting, yellowing leaves, slow growth, root decay, and ultimate tree decline signal an infected root system.
Management Strategies for Phytophthora Root Rot
- Improve drainage: Avoid overwatering and never allow the soil around trunks to become waterlogged.
- When possible, plant lemon trees in raised beds or on well-draining soils.
- Phytophthora risk mapping: Use satellite analytics for soil moisture monitoring to detect and reduce risk across large orchards.
- Fungicide applications may be made preventatively in high-risk zones, following local recommendations and label instructions.
- Promptly remove and destroy all infected or dead plant parts, including roots.
A focus on prevention, early detection, and better orchard design (enhancing drainage) is the most reliable approach for phytophthora root rot in lemon trees.
Alternaria Brown Spot Treatment & Prevention
Alternaria brown spot (Alternaria alternata) primarily affects leaves and fruits in lemon orchards, causing dark brown or black sunken spots and sometimes leading to premature defoliation and poor fruit quality.
Best Practices for Preventing and Treating Alternaria Brown Spot
- Cultural practices: Prune trees to improve airflow and light penetration, which reduces humidity that favors Alternaria fungus.
- Fungicidal sprays: Use copper- or sulfur-based fungicides early in the growing season, applying preventatively if weather is warm and damp.
- Promptly remove infected plant parts.
- Regularly monitor for brown lesions on young leaves and fruitlets; remove and destroy when spotted.
Alternaria brown spot can spread quickly under suitable conditions, so alternaria brown spot treatment requires diligence, especially during humid periods.
Lemon Scab: Safeguarding Fruit Quality
Lemon scab (Elsinoë fawcettii), a fungal disease, mainly targets fruit of lemon trees, causing raised, corky scabby lesions that diminish market value. Heavy infections may also blemish leaves, sometimes resulting in minor defoliation.
Management Solutions for Lemon Scab
- Implement good orchard sanitation—collect and destroy all visibly affected fruit and fallen leaves.
- Use copper or sulfur fungicidal sprays during the main growing season, especially if scab has been a frequent problem.
- Promote airflow and sunlight penetration via judicious pruning.
By following these steps, growers can reduce infection risk, protect fruit value, and maintain higher standards for commercial lemon harvests.
Sooty Mold on Citrus Leaves: A Symptom, Not a Disease
Sooty mold is the black, powdery fungal growth seen on citrus leaves, stems, and fruit. It is not directly caused by plant pathogens, but rather grows on honeydew—the sticky, sugary liquid excreted by insects like aphids, whitefly, mealybugs, psylids, scale, and leafhoppers.
How to Manage Sooty Mold and Prevent Honeydew Accumulation
- Identify the source: Find and control sap-feeding insect pests causing honeydew production.
- Spray horticultural oils or neem oil on infested trees—covering both upper and lower leaf surfaces removes scales, mealybugs, and whitefly.
- Repeat treatments every 10-14 days as needed.
- For scale insects, use a horticultural spray to smother eggs and larvae.
- If infection is severe, prune the most heavily infested branches.
While sooty mold rarely harms the tree directly, it interferes with photosynthesis, reduces fruit appeal, and often signals a serious pest infestation.
Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring, backed by multispectral satellite imagery, enables detection of pest stress symptoms across orchards—helping address honeydew issues quickly.
Mal Secco (Phoma tracheiphila): The Mediterranean Menace
Mal secco disease, caused by the conidia-producing fungus Phoma tracheiphila, is particularly common in the Mediterranean region. It mainly attacks lemon trees, with symptoms including:
- Leaf wilting and yellowing
- Dieback of shoots and twigs
- Internal wood discoloration, especially on older branches
- Progressive tree decline
Mal Secco Disease Management
- Remove all infected parts promptly—disposal of diseased twigs, branches, and leaves is critical.
- Encourage good airflow in the canopy through regular pruning.
- As the disease is disseminated by wind and rain, regular inspections after storms are advised.
- Where available, plant disease-resistant varieties.
Maintaining orchard health by monitoring symptoms, removing infected tissues, and reducing moisture and humidity remain the foundation of mal secco management.
“Early detection can reduce lemon tree disease spread by over 50% in orchards.”
Discover Farmonaut’s Advanced Resource Management Tools
-
Carbon Footprinting:
Want to reduce the environmental impact of your lemon cultivation? Farmonaut’s carbon footprint tracking helps orchards measure and minimize emissions, promoting sustainability and compliance for modern agriculture. -
Blockchain Traceability Solutions:
Strengthen your lemon supply chain with Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability for full product origin verification—a vital tool for exporters and food brands demanding transparency. -
Satellite-Based Crop Loan & Insurance Verification:
Enhance your access to financing and safeguard lemon orchards with Farmonaut’s satellite-verified crop insurance solutions, reducing fraud and streamlining loan approvals. -
Farmonaut API:
Seamlessly integrate lemon tree disease monitoring, weather data, and crop health analytics into your own agricultural systems with Farmonaut’s robust API. For developers, visit the
API developer documentation here.
7 Key Strategies for Managing Lemon Tree Diseases
Effective management of lemon tree diseases involves an integrated approach. Below, we outline the 7 crucial strategies that empower growers to tackle common and emerging threats, yielding healthier, more productive orchards while preserving citrus fruit quality.
-
1. Strict Sanitation (Remove and Destroy Infected Parts Regularly)
- Inspect trees and orchard floor for leaves, twigs, or fruit with lesions or other disease symptoms.
- Promptly remove all infected material and destroy away from lemon trees—never compost these items.
- This significantly reduces disease spread, especially for fungal and bacterial citrus diseases.
-
2. Implement Smart Cultural Practices
- Proper tree spacing helps maintain airflow and reduces humidity around foliage, hindering disease establishment.
- Prune regularly to improve light penetration and canopy health.
- Avoid overhead irrigation—instead, use drip or root irrigation to reduce water contact with foliage and stems.
-
3. Use Certified, Disease-Free Planting Material
- Only plant virus- and disease-free nursery stocks and avoid the use of unknown or potentially infected budwood for grafting.
- This minimizes the introduction of persistent citrus viruses, such as CTV, into orchards.
-
4. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Monitor and control sap-feeding insects—such as aphids, whitefly, and mealybugs.
- Apply neem oil or horticultural sprays to control pest populations, halting honeydew and sooty mold development.
-
5. Targeted Chemical Controls (Fungicides & Bactericides)
- Apply copper/sulfur-based fungicides as preventatives for susceptible lemon tree fungal diseases such as brown spot, lemon scab, or alternaria.
- Only use chemical controls as needed, following local regulations and avoiding overuse.
-
6. Early Detection: Technology-Driven Monitoring
- Leverage Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring for real-time detection of disease hotspots and canopy stress.
- Act immediately on visible lemon tree disease symptoms—this may involve field inspections triggered by remote alerts.
-
7. Resistant Varieties and Crop Rotation
- Where available, plant disease-resistant lemon varieties—especially important for citrus canker, tristeza virus, and mal secco regions.
- Rotating citrus with unrelated crops where feasible can break pest and disease cycles in the soil.
How Technology Is Empowering Lemon Growers
Modern lemon growers face increasing challenges, from unpredictable weather and new disease variants to more stringent global market requirements on fruit quality and traceability. Advanced farm management solutions like those delivered by Farmonaut empower orchard owners to rise above conventional farming limitations and scale up their disease detection, monitoring, and prevention protocols.
Farmonaut’s Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
- Real-time crop health analytics: Monitor NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), soil moisture, and canopy health from anywhere with Farmonaut’s web and mobile apps.
- Early detection and alerts: Receive notifications when stress or possible disease symptoms are detected across your lemon orchards—enabling faster action, targeted inspections, and precision chemical use.
- Resource management tools: Optimize your farm fleet and resources using Farmonaut’s logistics dashboard, reducing operational costs and maximizing orchard safety.
AI-Based, Data-Driven Advisories
Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI delivers weather forecasts, disease risk predictions, and personalized orchard management insights—why rely solely on intuition when you have satellite and artificial intelligence at hand?
Blockchain Traceability for Citrus Exports
Whether exporting fresh lemons or processed citrus products, Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability ensures transparent, tamper-evident tracking of fruit origin and handling, boosting market trust and reducing transaction disputes.
Carbon Footprinting for Sustainable Orchards
As sustainability becomes central to international trade standards, Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tools enable lemon growers to monitor and reduce their environmental impact—helping secure certifications and access new markets.
Farmonaut App & Subscription Options
Farmonaut is committed to democratizing precision agriculture for lemon and citrus growers globally. Our affordable, scalable platform is available via Android, iOS, web browser, and API—enabling lime, lemon, and citrus farmers of all sizes to monitor, manage, and improve orchard health with ease.
Browse our flexible subscription plans below, designed for both smallholder and large orchard operations:
Frequently Asked Questions about Lemon Tree Diseases & Management
What are the most common lemon tree diseases growers should watch for?
The most prevalent diseases in global lemon orchards include citrus canker, citrus tristeza virus (CTV), phytophthora root rot, alternaria brown spot, lemon scab, sooty mold, and mal secco. Each presents distinct symptoms and management requirements—early recognition is crucial to minimize damage and improve productivity.
What are the early lemon tree disease symptoms?
Look for yellowing or wilting leaves, brown or black lesions (spots) on leaves and fruit, raised corky tissue, water-soaked areas, black sooty coatings, stunted shoots, or rapid leaf drop. Precise symptom identification enables targeted responses and disease containment.
How can I prevent lemon tree fungal diseases most effectively?
Emphasize regular orchard sanitation, proper spacing, disease-free planting material, careful irrigation, and use of preventive fungicidal sprays. Employ satellite and AI-driven monitoring tools (like Farmonaut) for faster detection and risk management.
How does sooty mold affect citrus leaves and fruit?
Sooty mold grows on honeydew secreted by sap-feeding insects. While mostly cosmetic, severe infestations reduce photosynthesis, stunt growth, and lower fruit market value. Address by controlling the underlying pest population.
Can I use Farmonaut’s technology for small home lemon groves?
Yes, Farmonaut’s platform is designed for both individual growers and large agribusinesses. The mobile app and web dashboard provide tailored insights no matter the scale—helping maximize fruit quality, productivity, and reduce losses.
What’s the best way to prevent virus (CTV) spread in new lemon plantations?
Always plant certified, virus-free nursery stock, avoid using budwood from untested sources, and incorporate regular pest monitoring (especially aphids) as part of orchard IPM protocols.
Is there a way to track and reduce my orchard’s carbon footprint?
Absolutely. Use Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool to monitor, analyze, and minimize emissions—promoting both environmental stewardship and compliance with evolving market standards.
Conclusion: Best Practices for Healthy Lemon Orchards
Lemon trees form a vital part of the world’s citrus agricultural landscape, valued for their fruit, nutrition, and economic benefits. But their susceptibility to a diverse range of bacterial, viral, and fungal diseases demands proactive management. Understanding key pathogens, identifying symptoms early, and applying integrated strategies for sanitation, pest control, preventive chemistry, and orchard hygiene are the foundation for healthier, more productive lemon orchards.
By leveraging modern solutions—such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven advisories, blockchain traceability, resource management, and carbon footprinting—growers worldwide can reduce risk, improve lemon tree productivity, and ensure sustainable, transparent, and resilient citrus production.
For anyone serious about citrus health, adopting a combination of traditional best practices and technology-powered insights is the next step towards hassle-free, high-yield harvests every season. Start today: download the Farmonaut app or explore our advanced farm management solutions.