Codling Moth Control: 7 Shocking Hacks That Work!
“Pheromone traps can reduce codling moth populations by up to 80% in sustainable orchard management.”
Introduction
What if we told you there are powerful, sustainable codling moth control techniques that not only save your apple, pear, and walnut orchards from devastation, but also safeguard the environment? As orchard managers, sustainable agriculture advocates, and technology enthusiasts, we know all too well the frustration the codling moth (Cydia pomonella) brings. Each year, millions of tonnes of fruit worldwide go unmarketable due to larval damage. Codling moth larvae burrow deep inside fruit, rendering them unsellable and causing severe economic losses.
Through this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about codling moth management—from its biology to cutting-edge integrated pest management for orchards. We’ll dive into proven cultural and biological control of codling moth, pheromone disruption, and even advanced approaches like the sterile insect technique (SIT).
Our focus: Equipping you with sustainable, actionable strategies and 7 field-tested hacks to keep codling moth populations in check—while maximizing fruit quality, yield, and orchard resilience.
“Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) releases can cut codling moth infestation rates by over 60% in treated orchards.”
Biology and Life Cycle: Why It Matters for Codling Moth Control
Understanding the codling moth life cycle is the first—and most critical—step in any successful control or management program. By monitoring codling moth emergence, egg-laying, larval development, and overwintering, we can time our interventions precisely for maximum effectiveness.
Codling Moth Life Cycle Highlights
-
Generation Count Varies by Region:
In Denmark, codling moths produce a single generation per year, while in Palestine, as many as four or five generations occur annually. In most Europe and North America, there are two generations per year. -
Timing & Temperatures Are Critical:
The lower developmental threshold is 10°C. Males begin flying at 13°C. Mating only happens when nighttime temperatures exceed 16°C. -
Typical Generation Cycle:
– Spring: Overwintered pupae emerge as adults.
– Summer: Adults lay eggs on fruit or leaves.
– Eggs hatch: Larvae burrow into fruit, causing damage.
– Late summer-autumn: Mature larvae exit the fruit, find pupation sites (tree bark, soil, or debris), and overwinter. -
Damage Mechanism:
The larvae tunnel into developing apples, pears, and walnuts, leaving visible entry and exit holes and soiling fruit interiors.
Why This Matters: By aligning our monitoring, trapping, and treatment schedules with the codling moth’s biology, we improve control outcomes and safeguard yields.
Monitoring & Trapping: First Step in Codling Moth Management
The first actionable step in any apple orchard pest control or pest management program is accurate monitoring. By using pheromone traps for codling moth and smart tools, we determine the scale and timing of interventions and minimize unnecessary chemical applications.
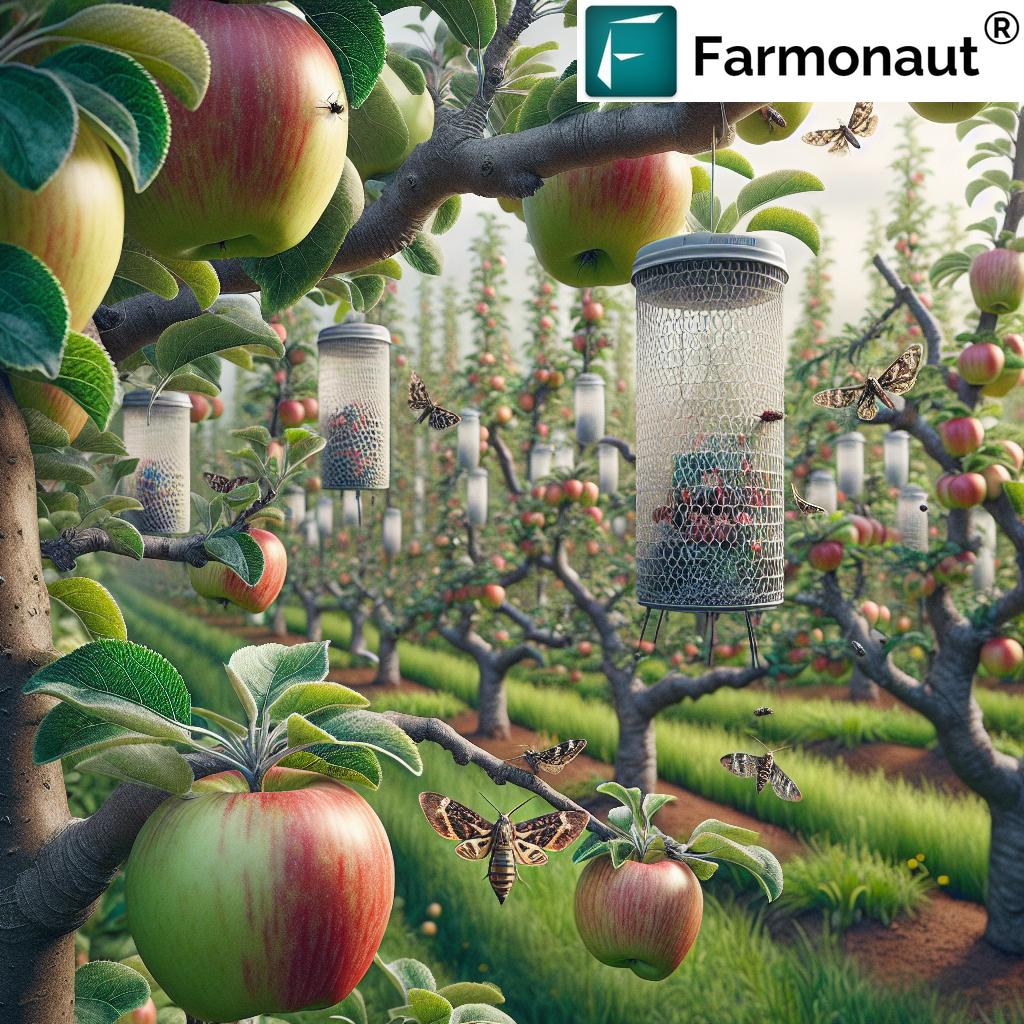
Pheromone Traps for Codling Moth: How They Work
- Synthetic Sex Attractant: Traps contain species-specific synthetic pheromones to attract male moths.
- Trap Placement: Set up from mid-March in California’s Central Valley, or by late March in more coastal regions. Place traps as high as possible in tree canopies for maximum catch rates.
- Trap Counts Guide Action: Capturing 5+ moths per trap per week signals the need for intervention.
- Regular Checks: Check traps weekly and record counts to monitor adult flight activity and population peaks.
By integrating smart technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring, we can complement trap data with real-time orchard health, soil moisture, and even pest stress detection for a holistic management approach. (See Large Scale Farm Management solutions for optimizing orchard monitoring.)
Other Monitoring Aids
- Degree-Day Models: Track accumulated heat units above 10°C to refine predictions of egg hatch, larval emergence, and best application timing. Multiple free degree-day calculators are available online.
- Visual Inspections: Regularly inspect developing fruit, leaves, and bark for eggs, larvae, and early fruit injury.
When we combine trap data with weather analytics and satellite imagery (like those from Farmonaut), we win back valuable time and resources for efficient codling moth management.
Cultural Practices: Sustainable Strategies for Orchard Success
Cultural controls are the foundation of sustainable pest management. They target codling moth populations at different stages and work synergistically with other methods to reduce reliance on chemicals and protect orchard biodiversity.
Key Cultural Practices for Codling Moth Control
- Sanitation: Regularly remove and destroy fallen fruit and plant debris. This eliminates breeding and overwintering sites, preventing a population explosion in the next year.
- Pruning & Thinning: Prune trees to open up the canopy for better spray penetration and sunlight, which can suppress codling moth activity. Thin fruit clusters to reduce the risk of multiple eggs laid per fruit and improve air circulation.
- Removal of Unmanaged Trees: Eliminate wild, abandoned, or volunteer host trees (apples, pears, walnuts) in and around your orchard. Such trees can harbor high codling moth populations and disrupt management efforts.
- Trunk Banding: Install cardboard or burlap bands around trunks in late summer. These attract larvae seeking to pupate beneath tree bark. Remove and destroy bands before next spring to kill overwintering pupae.
When systematically implemented, these cultural techniques make your orchard less attractive and suitable for codling moth reproduction and survival.
And by augmenting these practices with comprehensive resource management tools, such as Farmonaut’s Fleet Management platform, orchard owners can streamline their teams’ workflow for effective orchard maintenance and pest control rounds.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
- No chemical residues
- Enhances orchard sustainability
- Low input cost
- Reduces pest pressure year over year
Biological Control of Codling Moth: Harnessing Nature
Embracing biological control of codling moth supports a healthy, resilient orchard ecosystem. While natural enemies alone may not eradicate pest populations, they’re invaluable as part of a larger integrated pest management for orchards program.
Main Natural Enemies and Their Roles
- Parasitoid Wasps: Trichogramma platneri targets codling moth eggs, while Mastrus ridens attacks larvae in pupal cocoons. Although widely used, these wasps offer best results when combined with other strategies.
- Predators: Birds (especially woodpeckers) and arthropods such as ants and spiders actively predate on larvae and pupae. They contribute to background suppression but do not prevent outbreaks.
Biopesticides for Codling Moth Larvae
- Codling Moth Granulosis Virus (CpGV): A biological insecticide that works by infecting codling moth larvae, causing mortality. It’s applied as a spray multiple times across the season due to short residual activity. Best results are achieved when timing aligns with egg hatch periods.
Biological interventions are inherently sustainable: they protect beneficial species, pose negligible risk to the environment, and fit perfectly alongside carbon footprint tracking solutions such as those offered by Farmonaut to help orchards quantify their ecological impact.
Chemical Interventions for Codling Moth: Smart & Safe
Despite global emphasis on reducing synthetic pesticide usage, chemical interventions for codling moth remain necessary in many regions where pest pressures are intense. However, new best practices, careful product selection, and strategic timing maximize effectiveness while minimizing risks.
Types of Chemical Controls
- Insecticides: Modern insecticides should target newly hatched larvae, before they bore into fruit. Popular classes include IGRs (insect growth regulators), spinosyns, and selective ovicides. To delay resistance, rotate modes of action each generation.
- Horticultural Oils: Ovicides like horticultural oil suffocate eggs but have a very short residual period. Apply during peak egg laying, with weather considerations.
- Biological Chemical Interventions: As introduced above, granulosis virus products are efficient, highly specific larva-killers, but require multiple, carefully timed applications every season.
Critical Points:
- Base all application timing on trap counts, degree-days, and fruit inspections.
- Be aware of the risks of resistance development, especially to organophosphates.
- Preserve beneficial insect populations by applying at dusk and targeting only high-pressure zones.
Farmonaut supports optimized chemical planning and residue risk reduction through blockchain-based product traceability—allowing apple, pear, and walnut growers to assure consumers of safe practices from orchard to table.
Mating Disruption for Codling Moth: Stop Reproduction in Its Tracks
Arguably the most revolutionary shift in codling moth control this century is the adoption of mating disruption for codling moth—an entirely non-toxic, species-specific, and eco-friendly technology.
How Does Mating Disruption for Codling Moth Work?
- Pheromone Dispensers: Hand-applied devices or aerosol puffers release synthetic sex pheromones, saturating orchards and preventing males from finding females, thus blocking mating and fertility.
- Tactical Application: Apply dispensers before the first generation flight or predicted emergence in the year, especially in large, contiguous orchard blocks. This maximizes the disruption effect and reduces edge migration.
- Area-Wide Programs: The most dramatic reductions (up to 95% less fruit injury) are achieved by coordinating across multiple adjacent orchards or entire production regions.
By integrating disruption products and pheromone traps for codling moth, we catch only those moths unaffected by the saturated pheromone environment and respond quickly if control slips.
For orchard blocks using mating disruption, tools like Farmonaut’s satellite API and developer documentation help automate orchard monitoring, intervention scheduling, and data integration with digital records.
Sterile Insect Technology (SIT): A Modern, Eco-Friendly Approach
If you’re asking how to get rid of codling moths with zero chemical impact and without harming natural enemies, Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) is the answer. This technique has transformed orchard pest control in various parts of the world.
How SIT Works: The Process
- Mass Rearing and Sterilization: Large quantities of male codling moths are reared and sterilized (via radiation under strictly controlled conditions) in special facilities.
- Field Release: Sterile males are released into orchard populations. When they mate with wild females, no viable eggs are produced. This can rapidly suppress population growth.
- Results: Case studies from Tasmania, New Zealand, and North America have shown SIT can drive down codling moth populations by over 60% when properly implemented (especially as part of an integrated area-wide program).
Why SIT Is Environmentally Preferred
- No chemical residues or non-target effects
- Safe for pollinators and beneficial insects
- Ideal for sensitive production zones and organic transitions
- Sustainably reduces reliance on insecticides
While SIT requires upfront logistics and is most viable in highly managed production areas, it complements all the sustainable pest management strategies discussed in this guide.
Comparison Table of Sustainable Codling Moth Control Methods
| Control Method | How It Works | Estimated Effectiveness (% Reduction in Moth Population) | Environmental Impact | Cost (USD/acre) | Application Frequency (per season) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pheromone Traps | Attract & monitor adult male moths using synthetic pheromones | 60-80% | Low | $20-35 | 1-2 |
| Cultural Practices | Sanitation, pruning, tree removal, trunk banding reduce breeding and survival sites | 40-60% | Low | $10-40 | 2-3 |
| Biological Controls | Release of parasitoids, application of granulosis virus | 30-65% | Low | $40-90 | 3-6 |
| Chemical Interventions | Selective insecticides/ovicides target larvae and eggs during hatch | 65-85% | Medium-High | $60-120 | 3-5 |
| Mating Disruption | Pheromone dispensers confuse males, blocking mating | 75-95% | Low | $70-180 | 1 |
| Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) | Mass release of sterilized males to reduce fertility | 60-90% | Very Low | $110-250 | 2-4 |
Note: Actual costs and effectiveness for each method may vary between regions, product types, and orchard sizes. Combining methods typically delivers the highest success rates and helps delay resistance development.
Integrated Pest Management for Orchards: The Ultimate Strategy
No single method can assure complete, lasting codling moth control. The answer is a holistic, adaptive Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for orchards that blends monitoring, cultural, biological, chemical, mating disruption, and SIT techniques within a tailored, environmentally sound program.
How to Build an Effective IPM Program for Codling Moth
- Regular Monitoring: Deploy pheromone traps and analyze degree-day accumulations to anticipate pest activity.
- Sanitation & Cultural Practices: Implement strict orchard cleanups, pruning, and host tree removal every season.
- Enhance Biological Control: Foster beneficial insect populations and utilize biopesticides when appropriate.
- Judicious Chemical Use: Use only when trap thresholds indicate, targeting peak egg hatch with minimal broad-spectrum insecticides.
- Mating Disruption/SIT: Adopt advanced, area-wide strategies to minimize reproduction and keep populations below damaging levels.
- Record Keeping & Technology: Use management platforms like Farmonaut for digital record-keeping, real-time orchard health tracking, and precision application scheduling.
Benefits of Orchard IPM
- Reduces chemical reliance and resistance risk
- Supports biodiversity and pollinator health
- Enhances fruit quality and crop yield
- Protects water, soil, and air quality
- Can be audited and traced for compliance or certification using digital records and blockchain traceability (see Farmonaut Traceability solutions)
Farmonaut: Tech Solutions, Sustainability, and More
To successfully implement integrated pest management for orchards, modern growers rely more and more on technology. Farmonaut stands out as a pioneer, making advanced farm management not only effective but also affordable and environmentally responsible.
What Does Farmonaut Offer?
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Get real-time views on orchard stress, soil moisture, and pest hotspots to streamline scouting and interventions.
- AI-Driven Jeevn Advisory: Receive customized, science-based, and weather-adapted crop management advice via mobile app—timing pest controls for peak effectiveness.
- Blockchain Traceability: Demonstrate product quality and sustainable practices to buyers with verifiable blockchain product traceability.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Optimize spray applications, team movements, and orchard logistics with Farmonaut’s fleet tools.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Quantify and report your orchard’s greenhouse emissions profile—essential for eco-conscious branding or compliance (learn more here).
Subscription-based Model: Accessible on web, iOS, and Android devices, Farmonaut makes data-driven, sustainable farming affordable for all orchard sizes—streamlining codling moth control and improving overall yields. The platform is also open for API integration for developers, research organizations, and agritech companies.
Want to future-proof your orchard?
- Satellite-based insurance and loan verification—guarantee your coverage and financing with trustworthy, fraud-resistant verification of orchard health and practices.
- Monitor your emissions and rapidly implement the most climate-positive pest management methods for green certifications.
- Manage even the largest orchard with Agro-Admin—scale your codling moth control (and all other orchard management) with one dashboard, from anywhere!
FAQs: All About Codling Moth Control
What is the most effective codling moth control method?
No method works alone. The best approach is integrated pest management: regular monitoring, strict sanitation, pheromone traps, biological controls, carefully timed selective insecticides, and—if possible—mating disruption or sterile insect technology (SIT).
When should I start monitoring for codling moth?
Set up pheromone traps for codling moth by mid- to late March, tracking degree-days (above 10°C) and recording trap catches immediately.
Can I use only organic methods to control codling moth?
Organic programs combine cultural, mechanical, biological (like granulosis virus), and mating disruption methods. Results can be excellent in low to moderate pressure areas, but severe infestations may require spot-targeted interventions.
How do I prevent codling moth resistance to insecticides?
- Rotate products with different modes of action
- Apply only when pest thresholds are reached
- Incorporate non-chemical controls like pheromone disruption, biologicals, and sanitation to reduce pesticide need
Will SIT or mating disruption harm bees and other beneficials?
No—both methods are highly selective for codling moths only and pose no risk to beneficial insect populations.
How can I check if my orchard is at high risk?
- High trap counts (>5-10 moths/trap/week)
- Nearby unmanaged or infested orchard blocks
- Warm spring and summer temperatures (accelerated moth generations)
- Poor orchard sanitation and debris management
Does Farmonaut supply insecticides or biocontrol agents?
No. Farmonaut provides advanced farm management technologies only—real-time crop monitoring, AI-based advisory, traceability, carbon tracking, and fleet/resource management to optimize all your planning and application decisions.
Can I integrate Farmonaut with existing orchard software?
Yes—via Farmonaut’s secure API and open developer documentation.
Conclusion
Codling moth management is a complex, ever-evolving challenge for orchardists worldwide. The keys to consistent, sustainable, and profitable control are knowledge, vigilance, strategic diversification of interventions, and adopting new technologies.
By combining monitoring, cultural practices, biological controls, chemical options, pheromone disruption, and SIT—and using digital and satellite solutions like Farmonaut—we can protect our apples, pears, and walnuts, while upholding the highest standards of crop quality, yield, profitability, and environmental stewardship.
Are you ready to revolutionize your orchard’s codling moth control program?
Together, let’s set a new standard for sustainable codling moth management—protecting our orchards, our environment, and our future harvests.