Sustainable Agriculture in Oman: How Blueberry Cultivation in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar is Revolutionizing Mountainous Farming
“Al Jabal Al Akhdhar’s blueberry project introduces Southern Highbush varieties, adapting cold-climate agriculture to arid mountainous regions.”
In the heart of Oman, a remarkable agricultural revolution is taking place. The Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Water Resources has embarked on an innovative journey that promises to transform the landscape of sustainable agriculture in the country. At the forefront of this transformation is the blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar, a pioneering initiative that showcases Oman’s commitment to agricultural diversity and food security in the Middle East.
As we delve into this groundbreaking project, we’ll explore how the Ministry is leveraging the unique climate of Al Jabal Al Akhdhar to introduce cold-climate agriculture in an arid, mountainous region. This initiative not only demonstrates the potential for diversifying Oman’s agricultural sector but also sets a new standard for sustainable farming practices in challenging environments.
The Genesis of Blueberry Cultivation in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar
The blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar is a testament to Oman’s innovative approach to agriculture. Situated in the Wilayat of Al Jabal Al Akhdhar in the Dakhiliyah Governorate, this initiative spans an impressive 1,000 square meters. The project features the planting of 500 blueberry seedlings, carefully selected from four varieties of Southern Highbush blueberries, all imported from the Republic of Georgia.
But why blueberries, and why in this particular location? The answer lies in the unique climatic conditions of Al Jabal Al Akhdhar. This mountainous region naturally provides the cold temperatures essential for blueberry growth, specifically the 200 to 400 hours of temperatures below 7°C that these plants require. By harnessing these natural conditions, the Ministry has created an environment where cold-climate agriculture can thrive in an otherwise arid landscape.
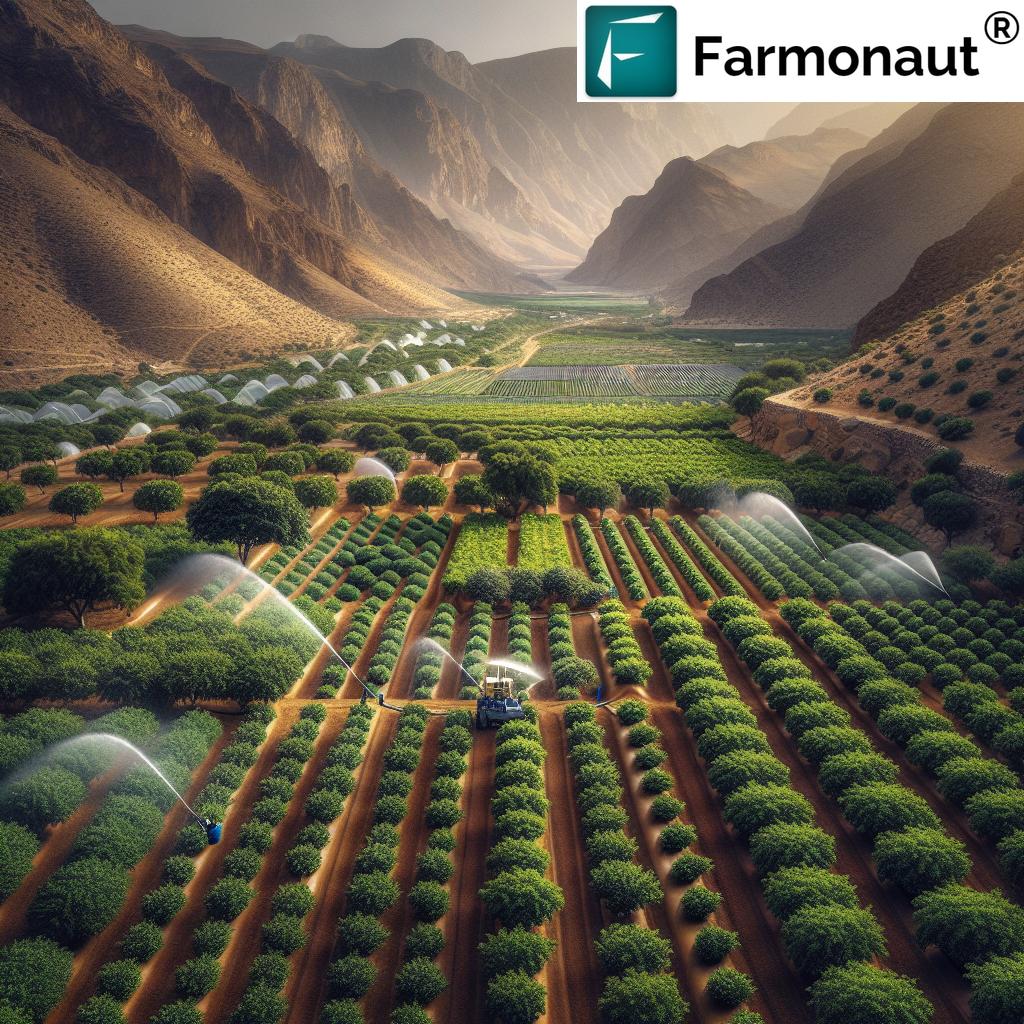

Sustainable Practices at the Core
At the heart of this project lies a deep commitment to sustainability. The Ministry has implemented a range of innovative practices to ensure that the blueberry cultivation is not only productive but also environmentally friendly. Let’s explore some of these key sustainable practices:
- Water-Efficient Irrigation Systems: Recognizing the precious nature of water resources in Oman, the project utilizes modern, water-efficient irrigation systems. These systems minimize water waste while ensuring optimal hydration for the blueberry plants.
- Organic Fertilizers: The use of organic fertilizers for fruit trees is a cornerstone of this project. This approach not only nourishes the plants but also maintains soil health and reduces the environmental impact associated with chemical fertilizers.
- Innovative Soil Management: One of the most fascinating aspects of this project is the use of pine wood as a growing medium. This innovative soil management technique improves the quality of the growing environment, demonstrating how creative solutions can overcome traditional agricultural challenges.
These sustainable farming practices in arid regions not only contribute to the success of the blueberry cultivation but also serve as a model for future agricultural projects in similar environments.
Economic and Environmental Impact
The blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar is more than just an agricultural experiment; it’s a strategic initiative with significant economic and environmental implications:
- Economic Value: Each blueberry plant is expected to yield between 3 to 5 kilograms of fruit annually. With 500 plants, this translates to a substantial harvest that can contribute to local markets and potentially even exports.
- Diversification of Agriculture: By introducing blueberries, Oman is diversifying its agricultural portfolio, reducing reliance on traditional crops and enhancing food security.
- Eco-Tourism Opportunities: The blueberry-picking season, which runs from May to late June, offers unique eco-tourism opportunities. Visitors can engage in fruit picking while learning about sustainable agricultural practices, adding a new dimension to Oman’s tourism industry.
- Environmental Conservation: The sustainable practices employed in this project contribute to soil conservation, water efficiency, and overall environmental health in the region.
For those interested in leveraging technology for sustainable agriculture, Farmonaut offers advanced satellite-based farm management solutions. Check out their  for cutting-edge agricultural insights.
for cutting-edge agricultural insights.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Sustainable Blueberry Cultivation
To fully appreciate the revolutionary nature of the blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar, let’s compare it with traditional mountain farming practices:
| Aspect | Traditional Mountain Farming | Sustainable Blueberry Cultivation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage (estimated L/hectare/year) | 10,000 – 15,000 | 5,000 – 7,000 |
| Soil Management Techniques | Conventional tilling, limited soil amendments | Pine wood medium, organic matter incorporation |
| Fertilizer Type | Primarily chemical fertilizers | Organic fertilizers |
| Crop Yield (estimated kg/hectare) | Varies by crop, generally lower | 15,000 – 25,000 (for blueberries) |
| Environmental Impact | Higher soil erosion, potential chemical runoff | Reduced erosion, minimal environmental impact |
| Tourism Potential | Limited | High (fruit-picking experiences, agro-tourism) |
| Economic Viability | Moderate, subject to traditional market fluctuations | High, premium product with growing market demand |
This comparison clearly illustrates the advantages of the sustainable blueberry cultivation project, showcasing its superior water efficiency, environmental stewardship, and economic potential.
“Oman’s sustainable agriculture initiative uses pine wood as a growing medium, revolutionizing soil management in challenging environments.”
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
While the Al Jabal Al Akhdhar project demonstrates innovative agricultural practices, technology plays a crucial role in modern sustainable farming. Farmonaut, a leading agricultural technology company, offers solutions that complement such initiatives:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: Farmonaut’s technology allows for real-time monitoring of crop health, crucial for optimizing blueberry cultivation.
- AI-Driven Insights: The Jeevn AI advisory system provides personalized recommendations, which could be invaluable for managing blueberry crops in mountainous regions.
- Water Management: Farmonaut’s tools can help farmers implement water-efficient irrigation systems, aligning with the sustainable practices in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar.
Explore Farmonaut’s technology through their mobile apps:
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar shows great promise, it’s not without its challenges:
- Climate Adaptation: Despite the region’s natural cold periods, ensuring consistent temperature conditions for blueberry growth throughout the year may be challenging.
- Water Management: Although water-efficient systems are in place, maintaining optimal water levels in an arid region requires constant vigilance and innovation.
- Market Development: Creating a robust market for locally grown blueberries within Oman and potentially for export will be crucial for the project’s long-term success.
However, the future prospects for this initiative are bright. The success of the blueberry project could pave the way for:
- Introduction of other cold-climate fruits and vegetables in Oman’s mountainous regions
- Expansion of sustainable farming practices across other agricultural projects in the country
- Enhancement of Oman’s food security through diversified local production
- Development of a niche agro-tourism sector centered around sustainable farming experiences
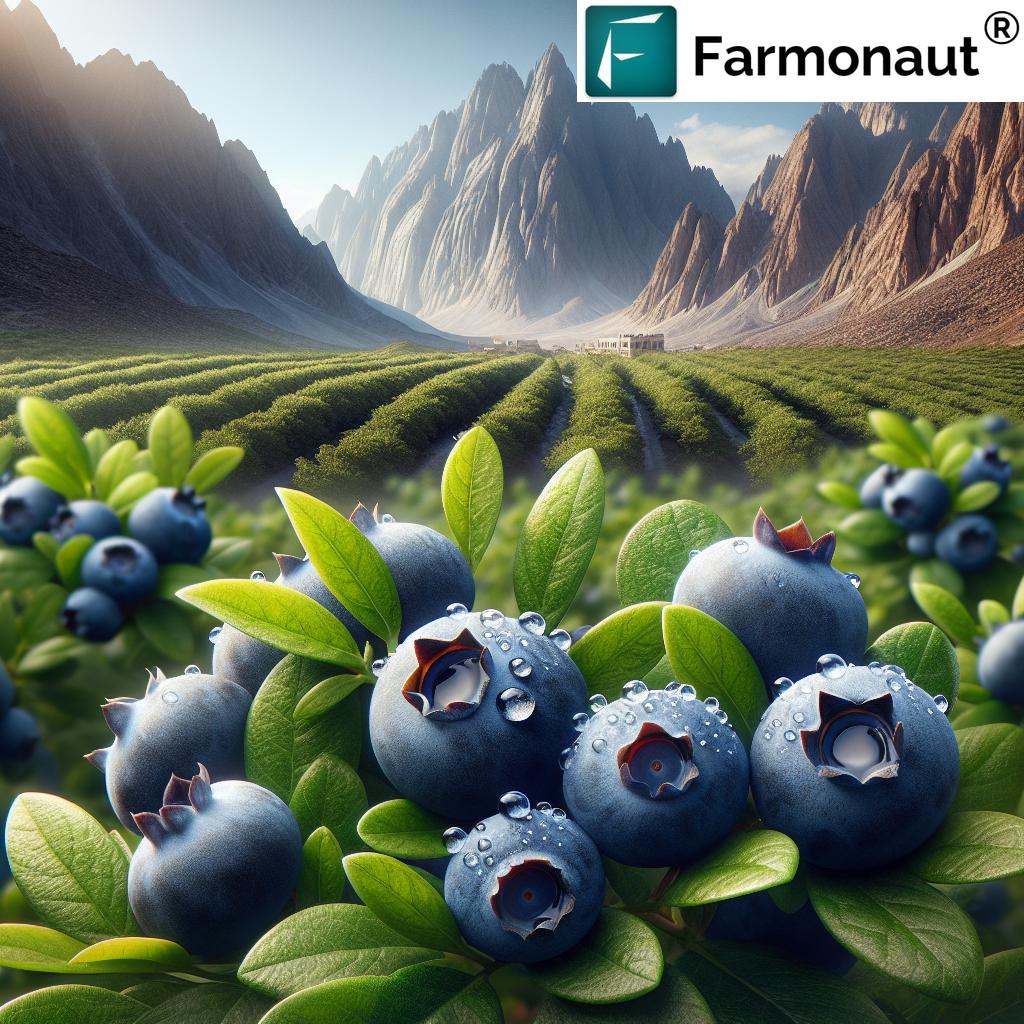

The Broader Impact on Oman’s Agricultural Landscape
The blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar is more than just an isolated agricultural experiment; it represents a significant shift in Oman’s approach to farming and food security. This initiative aligns with several key national objectives:
- Diversification of the Economy: By introducing high-value crops like blueberries, Oman is taking steps to diversify its economy beyond oil and gas, creating new revenue streams in the agricultural sector.
- Enhancing Food Security: The successful adaptation of blueberries to Oman’s climate demonstrates the potential for growing a wider variety of crops domestically, reducing reliance on imports and strengthening national food security.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: The emphasis on water-efficient irrigation and organic fertilizers sets a precedent for sustainable farming practices across Oman, contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
- Developing Rural Areas: Projects like this can stimulate economic activity in rural mountainous regions, creating jobs and improving livelihoods in these areas.
- Fostering Innovation in Agriculture: The use of innovative techniques such as pine wood as a growing medium encourages further research and development in agricultural technologies suitable for Oman’s unique climate.
For those interested in leveraging technology for sustainable agriculture, Farmonaut’s API offers powerful tools for developers. Explore the Farmonaut API and API Developer Docs for integration possibilities.
The Role of Education and Training
A crucial aspect of the blueberry cultivation project is its focus on education and training. The Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Water Resources is not just implementing new farming techniques; it’s also investing in the future of Oman’s agricultural sector by:
- Training Local Farmers: Providing hands-on training to local farmers in the specialized techniques required for blueberry cultivation.
- Knowledge Transfer: Facilitating the exchange of knowledge between international experts and local agricultural professionals.
- Promoting Agricultural Education: Using the project as a living laboratory for agricultural students to learn about sustainable farming practices and crop diversification.
- Public Awareness: Educating the general public about the importance of sustainable agriculture and its role in Oman’s future.
This educational component ensures that the benefits of the project extend far beyond the immediate harvest, building a foundation for long-term agricultural innovation in Oman.
Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity
The blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar isn’t just about producing fruit; it’s also contributing to environmental conservation and biodiversity in the region:
- Soil Conservation: The use of organic fertilizers and innovative soil management techniques helps preserve and enhance soil quality in the mountainous region.
- Water Conservation: Water-efficient irrigation systems not only benefit the blueberry crops but also contribute to overall water conservation in this arid area.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Introducing a new crop species like blueberries can attract different pollinators and beneficial insects, potentially increasing local biodiversity.
- Erosion Control: The establishment of permanent crop cover through blueberry plantations can help reduce soil erosion on mountain slopes.
These environmental benefits showcase how sustainable agriculture can play a vital role in ecological conservation, especially in sensitive mountainous ecosystems.
The Future of Sustainable Agriculture in Oman
As we look to the future, the blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar serves as a beacon for sustainable agriculture in Oman. Its success could pave the way for:
- Expansion of Cold-Climate Crops: The potential introduction of other cold-climate fruits and vegetables in Oman’s mountainous regions, further diversifying agricultural production.
- Advanced Agricultural Technologies: Increased adoption of precision agriculture techniques, possibly integrating technologies like those offered by Farmonaut for satellite-based crop monitoring and management.
- Research and Development: Continued investment in agricultural research to develop crop varieties and farming techniques specifically adapted to Oman’s unique climate conditions.
- International Collaborations: Potential partnerships with other countries and international organizations to exchange knowledge and best practices in sustainable mountain agriculture.
- Policy Development: The formulation of new agricultural policies that prioritize sustainability, water conservation, and crop diversification across Oman.
Earn With Farmonaut: Join our Affiliate Program
Earn 20% recurring commission with Farmonaut’s affiliate program by sharing your promo code and helping farmers save 10%. Onboard 10 Elite farmers monthly to earn a minimum of $148,000 annually—start now and grow your income!
Conclusion
The blueberry cultivation project in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar stands as a testament to Oman’s commitment to sustainable agriculture and food security. By leveraging the unique climate of the mountainous region and implementing innovative farming practices, the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Water Resources has not only introduced a new crop to Oman but has also set a new standard for sustainable farming in arid and mountainous environments.
This initiative demonstrates how creative solutions and a commitment to sustainability can overcome traditional agricultural challenges. From water-efficient irrigation systems to the use of organic fertilizers and innovative soil management techniques, every aspect of this project has been designed with sustainability in mind.
As Oman continues to diversify its economy and strengthen its agricultural sector, projects like the blueberry cultivation in Al Jabal Al Akhdhar will play a crucial role. They not only contribute to food security and economic growth but also promote environmental conservation and offer new opportunities in agro-tourism.
The success of this project opens up exciting possibilities for the future of agriculture in Oman. It paves the way for the introduction of other cold-climate crops, encourages the adoption of advanced agricultural technologies, and sets a precedent for sustainable farming practices that can be applied across the country.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that sustainable agriculture will be a key driver of Oman’s development. By combining traditional knowledge with modern innovations and a commitment to sustainability, Oman is not just growing blueberries – it’s cultivating a sustainable and prosperous future for its people and its land.
FAQ Section
Q1: Why was Al Jabal Al Akhdhar chosen for blueberry cultivation?
A1: Al Jabal Al Akhdhar was chosen due to its unique climate, which naturally provides the cold temperatures essential for blueberry growth. The region experiences 200 to 400 hours of temperatures below 7°C, ideal for Southern Highbush blueberry varieties.
Q2: What sustainable practices are being used in this project?
A2: The project employs water-efficient irrigation systems, uses organic fertilizers, and incorporates innovative soil management techniques, including the use of pine wood as a growing medium.
Q3: How does this project contribute to Oman’s food security?
A3: By successfully cultivating blueberries, Oman is diversifying its agricultural portfolio, reducing reliance on imports, and demonstrating the potential for growing a wider variety of crops domestically.
Q4: What is the expected yield of the blueberry plants?
A4: Each blueberry plant is expected to yield between 3 to 5 kilograms of fruit annually.
Q5: How does this project impact tourism in Oman?
A5: The project offers eco-tourism opportunities, particularly during the blueberry-picking season from May to late June, allowing visitors to engage in fruit picking and learn about sustainable agricultural practices.
Q6: What role does technology play in this sustainable agriculture project?
A6: While the project itself focuses on innovative agricultural practices, companies like Farmonaut offer complementary technologies such as satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven insights that can further enhance sustainable farming practices.
Q7: How does this project contribute to environmental conservation?
A7: The project contributes to soil conservation, water efficiency, and overall environmental health through its sustainable practices. It also helps in erosion control and potentially enhances local biodiversity.
Q8: What are the future prospects for this initiative?
A8: The success of this project could lead to the introduction of other cold-climate crops in Oman’s mountainous regions, expansion of sustainable farming practices, and the development of a niche agro-tourism sector.