How Does Social Media Affect Agriculture? Shocking Truths!
“Over 70% of farmers use social media for real-time agricultural updates and peer knowledge sharing.”
Introduction: The Digital Revolution in Agriculture
Over the past decade, social media in agriculture has rapidly transformed how farmers, agribusinesses, and consumers interact, make decisions, and drive progress. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, TikTok, and YouTube have accelerated the exchange of knowledge, strengthened community bonds, and redefined market access for farmers. These digital changes bring both incredible benefits and notable challenges, impacting industry dynamics, consumer perceptions, and farming practices worldwide—including in emerging hubs like Ghana.
In this comprehensive blog, we’ll explore the shocking truths about the impact of social media on farming: from knowledge sharing and digital engagement to consumer trends and youth inspiration. With the rise of digital farming platforms and direct to consumer farm sales, agriculture is no longer limited to local interactions or traditional markets. Instead, it thrives in vibrant agricultural communities online, supports sustainable growth, and opens up opportunities for all—from smallholders to large agribusinesses.
How Social Media in Agriculture Empowers Knowledge Sharing
Information Dissemination and Agricultural Knowledge Sharing
The heartbeat of agricultural progress is timely, relevant information. Social media platforms empower farmers and agricultural experts to connect, learn, and implement best practices in real-time—regardless of geography or farm size.
- Peer-to-peer learning: On Facebook groups, Twitter chats, and forum threads, farmers constantly exchange ideas about efficient irrigation, pest management, weather patterns, market prices, and the latest agritech solutions.
- Remote support: Digital communities provide support, particularly in remote or underserved areas. For example, in Ghana, more than 57% of farmers routinely access innovative agricultural knowledge via social platforms (see study).
- Collaborative solutions: By sharing pest or weather challenges, farmers are able to collaborate, crowdsource solutions, and apply relevant techniques that can rapidly increase crop yield.
According to research, 89% of Ghanaian farmers recommend or implement information from digital farming platforms—resulting in improved pest management, better yields, and more sustainable agriculture practices (see report).
The Power of Engaged Agricultural Communities Online
Active engagement in agricultural groups, forums, and chats has changed the industry’s culture:
- Farmers engage in live Q&A sessions, join regional WhatsApp groups, or participate in trending Twitter hashtags related to agriculture.
- Facebook groups centered around pest alerts, weather updates, and direct farmer support foster connections that drive rapid learning.
- These communities are especially beneficial in areas lacking classic extension services, acting as digital safety nets for isolated or young farmers.
The result? Faster dissemination of best practices, exposure to modern technology, and robust innovation—transforming agricultural learning into a continuous, borderless process.
Market Access for Farmers: Digital Platforms and Direct-to-Consumer Sales
Expanding Market Access and Boosting Farm Sales
Social media has rewritten the playbook for market access for farmers. Through image-rich posts on Instagram, Facebook Marketplace, and digital classifieds, farmers now bypass intermediaries, showcasing produce directly to consumers and businesses far beyond their local area.
- Direct to consumer farm sales: By tapping into consumer trends through social platforms, farmers have experienced sales growth—USDA analysis found up to a 15% increase in revenue linked to online marketing.
- Digital branding: Videos, reels, and behind-the-scenes photo series allow farms to build an identity, tell authentic stories, and establish loyal consumer communities. Notable farmer-run Facebook pages attract tens of thousands of followers, demonstrating how digital storytelling shapes public perceptions.
- Reduced reliance on intermediaries: Bypassing traditional distributors means more profit margins stay with the farm, supporting reinvestment and long-term sustainability.
Examples of Impactful Social Media Platforms in Agriculture
- Instagram: Used to showcase high-quality crop photos, engage with urban consumers, and track emerging food trends.
- Facebook: Harnessed for both business pages and private groups connecting producers with interested buyers.
- TikTok: Empowers young and experienced farmers alike to share short how-to tutorials, farm tours, and quick product promos, reaching new and younger audiences.
- YouTube: Facilitates in-depth technical demonstrations, product launches, and ongoing educational series—firmly placing agricultural knowledge sharing in the spotlight.
Research published in the Western Growers Magazine highlights stories like “Keeping it Real: Through the Lens of a Farm Girl”, where authentic photo diaries won nearly 30,000 Facebook fans, proving that engagement and transparency build trust and loyalty (see article).
The Direct-to-Consumer Revolution: More than a Trend
Consumers are increasingly willing to buy directly from producers. This trend not only improves sales but also makes the supply chain more transparent. According to industry data, farms using direct-to-consumer channels have reported up to a 25% increase in profits—demonstrating the huge benefits when market dynamics are transformed through digital platforms.
“Direct-to-consumer sales via social platforms have increased farm profits by up to 25% in recent years.”
Interested in digital solutions for traceability and transparency? Discover Farmonaut’s Blockchain-based Product Traceability—ensuring every step from farm to fork is secure, transparent, and trusted by consumers and brand partners.
Social Media’s Influence on Consumer Behavior, Demand, and Transparency
How Digital Engagement Shapes Consumer Perceptions and Behaviors
As consumers gain access to farmer stories, sustainability initiatives, and behind-the-scenes operations via social media, their buying behavior and demand patterns shift rapidly. Transparency becomes an expectation—leading to better trust and more loyal relationships between farms and their audiences.
- Sustainable agriculture practices: Farmers who highlight responsible land management, resource conservation, and low-carbon methods are able to tap into green-conscious market segments.
- Traceable supply chains: With growing interest in ethical produce, tools like blockchain (see: Farmonaut Traceability) give consumers a window into each product’s journey—fostering trust and winning new markets.
- Influencer marketing and viral trends: Social platforms amplify food and farming fads, such as eco-farming challenges, local food movements, or unique crop varieties—impacting both demand patterns and pricing.
A recent article noted that, increasingly, agricultural experts and digital-savvy farms are shaping global demand simply by how they communicate their values and results.
Transparency, Trust, and the Era of Digital Agriculture
- Visibility means accountability: Consumers expect transparency and are quick to challenge inconsistencies or misconceptions, making honesty and authenticity central to agricultural branding online.
- Building trust: Regular updates, live-streamed operations, and clear labeling of sustainable actions help producers establish long-term, loyal customer bases.
- Online reviews and feedback: Social platforms double as real-time feedback loops—helping farmers quickly adjust offerings or communicate directly with enthusiastic and critical fans alike.
Platforms like Instagram and Facebook have become the new “open farm gates,” providing a direct line to consumer sentiment and making it easier to react swiftly to market trends.
Want to actively monitor and reduce your farm’s environmental impact? Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting service offers real-time emissions tracking for improved sustainability and market compliance.
Youth Engagement in Farming: The Next Generation of Ag Influencers
How Social Media Inspires Tomorrow’s Agricultural Leaders
Digital platforms are shattering stereotypes about agriculture and attracting a new, ambitious, and tech-savvy generation to farming. Youth engagement in farming is now a global trend as social media shares the excitement of modern techniques, high-tech equipment, and entrepreneurial stories.
- Inspiring careers: YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok showcase the diversity of ag careers, from drone pilots and satellite agronomists to eco-entrepreneurs and sustainability advocates.
- Supporting career growth: Studies show digital communication tools help young farmers develop business plans, connect with mentors, and transition into full-time farm management (see: NCBI report).
- Global conversations: Joining online agricultural communities connects young farmers with international experts and up-to-date resources, preparing them for climate-resilient and sustainable farming models.
Whether by sharing a harvest vlog or participating in regional ag-challenges online, young producers are not only inheriting farms—they’re building the digital “face” of agriculture for the future.
Challenges: Misinformation, Digital Divide, and Accessibility
Overcoming Misinformation and Misconceptions in Agriculture
For all its positives, the spread of viral misinformation on social platforms remains a critical challenge for modern agriculture. Farmers must navigate:
- False claims: Rapidly circulating misconceptions about GMOs, pesticides, animal welfare, and food safety can harm public perceptions and demand for certain products.
- Dealing with sensational news: When controversy or crisis arises, farmers must engage in proactive clarification—offering educational live streams, Q&A videos, and behind-the-scenes tours.
- Expert counter-narratives: It’s crucial to empower reputable voices, highlight certified sustainable practices, and provide real-world case studies to build community trust.
Navigating the Digital Divide
While smartphone adoption is climbing in countries like Ghana and elsewhere, access to stable internet and affordable data continues to limit some farmers’ participation in the digital revolution. Digital literacy training and equitable infrastructure rollouts remain essential for closing this gap.
- Inequality in rural areas: Many remote farm regions still lag in broadband access or digital skills training.
- High data costs: Even where smartphones are prevalent, expensive data packages reduce engagement levels.
- Farmonaut’s response: By leveraging low-infrastructure, satellite-based apps and offering intuitive user interfaces, Farmonaut aims to bridge these accessibility gaps (try it here).
Comparative Impact Table: Pre and Post Social Media Era
The following table summarizes how social media has influenced key areas of agriculture, comparing estimated values before and after its wide adoption:
| Area of Impact | Pre-Social Media (Estimated Values) | Post-Social Media (Estimated Values) |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Farming Best Practices | 40% of farmers accessed up-to-date information via traditional extension services; average lag: 2-4 weeks | 70%+ farmers engaged in real-time knowledge sharing, 30% increase in adoption of new techniques |
| Number of Market Connections | Local/regional buyers only; 7 average connections per farmer/year | Global/urban reach; 20+ connections per farmer/year, 40% increase |
| Consumer Engagement Rate | Limited to farm gates/farmers’ markets; 3% engagement on average | Social platforms, live Q&A, reviews; 10%+ engagement, 200%+ increase |
| Average Time to Access New Information | 2 weeks (print/news, in-person seminars) | Instant (90% reduction) via social feeds, alerts, group chats |
| Direct-to-Consumer Sales | 5% of total farm sales | 20%+ of total sales (and rising)—25%+ profit margin improvement |
| Access to Peer Support & Communities | Limited to local circle/family, slow response times | Vibrant 24/7 peer support; global exchange of ideas and project collaboration |
Farmonaut’s Role in Empowering Digital Farming Communities
Integrating Advanced Technologies for Sustainable Agriculture
Beyond the social sphere, the adoption of precision and digital agriculture tools amplifies every benefit outlined above. Farmonaut is at the forefront, delivering accessible, satellite-powered decision support for farmers worldwide.
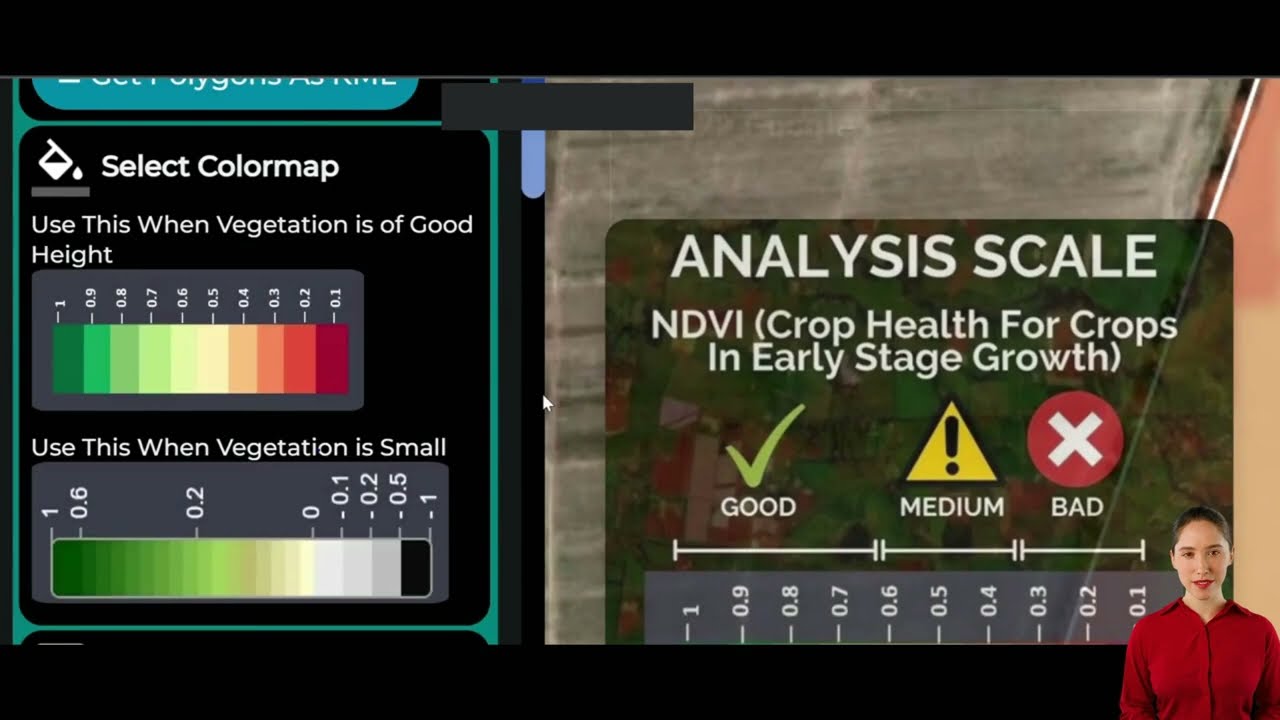
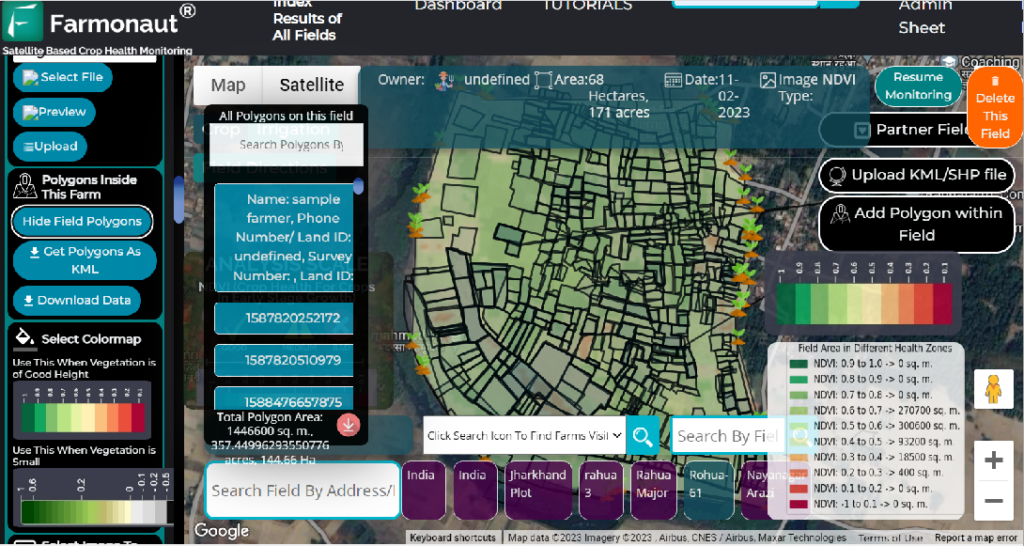
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut’s Android, iOS, and web apps deliver real-time insights on vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and irrigation needs, enabling precision resource use, improved crop yields, and lower environmental impact.
- AI-Based Advisory (Jeevn): Personalized, expert-driven recommendations based on weather patterns, imminent threats, and crop-specific techniques—helping farms implement best practices at scale.
- Blockchain Traceability: Secure, tamper-proof records for each product’s journey, reinforcing transparency and building consumer trust in sustainability claims.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Digital tracking and optimization ensure that vehicles, machinery, and staff are used efficiently, reducing costs and maximizing uptime. Learn more: Farmonaut Fleet Management
- Carbon Footprinting: Track and minimize agricultural emissions with ease for compliance and market advantage—see Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting
- APIs for Integration: For developers, businesses, and research organizations seeking to bring satellite and weather data into their own systems, Farmonaut provides robust, scalable API access (API, Developer Docs).
Farmonaut’s value lies in making precision digital agriculture affordable. There’s no need for expensive hardware or complex installations—just satellite data, mobile tools, expert AI guidance, and clear dashboards accessible to every farmer, agribusiness, or institutional user.
Need large-scale operation oversight? Farmonaut’s Agro Admin App is designed for large scale farm management, connecting numerous fields, staff, and resources for regional or national projects.
Complementary Digital Tools & Resources
Social media in agriculture only reaches its full transformative potential when combined with affordability, accessibility, and advanced digital infrastructure. Farmonaut continues to set the standard:
- Crop Loan and Insurance Verification: Satellite-based farm validation increases accuracy for lenders and insurance providers. See Crop Loan and Insurance for details on reducing fraud and enabling broader access to financing.
- Crop Plantation and Forest Advisory: For plantation managers, NGOs, and rural development authorities—gain actionable, AI-powered insights at every step. Try the Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory free.
Frequently Asked Questions
How exactly does social media help disseminate agricultural knowledge?
Social media enables real-time sharing of best practices, market prices, weather alerts, and innovative farming techniques. Farmers can both teach and learn instantly from peers, experts, or institutions—driving continuous improvement in crop yield, pest management, and resource use.
What are direct to consumer farm sales and why are they important?
Direct to consumer farm sales refer to selling produce directly from the farm to buyers via social platforms, without middlemen. This improves farm profits, strengthens consumer relationships, and offers producers full control over their branding and pricing.
How can farmers manage misinformation online?
By proactively sharing educational content, live video tours, and fact-based resources, farmers can address misconceptions and build trust. Joining verified agricultural communities online and amplifying expert voices helps correct common myths.
How do Farmonaut’s tools support sustainable agriculture practices?
Farmonaut offers satellite-based monitoring for real-time crop and soil health, AI-powered advisory for optimized resource management, and robust carbon footprinting for sustainability compliance. These solutions help identify problems early, maximize yields, and minimize environmental impact.
What’s the role of youth engagement in modern agriculture?
Youth engagement is vital for the industry’s future. Social media brings young people into the sector—offering inspiration, mentorship, and digital skills training—helping them envision agriculture as a high-tech and rewarding career.
How does Farmonaut ensure accessibility for remote or smallholder farmers?
Farmonaut’s platform is available on mobile (Android, iOS) and web, requires minimal bandwidth, and uses easy-to-understand dashboards—democratizing precision agriculture for farms of all sizes and locations.
Conclusion: The Future of Social Media and Agriculture
The impact of social media on farming is profound and ongoing. Today, farmers in both developed and emerging economies like Ghana can instantly access a world of agricultural knowledge, market their produce in new ways, and build direct relationships with conscious consumers—transforming centuries-old industry dynamics. At the same time, social media empowers young leaders, promotes sustainable agriculture practices, and pushes for greater accountability, transparency, and innovation in all corners of the agriculture ecosystem.
As new digital farming platforms and precision tools like Farmonaut lower barriers, the union of social connectivity and data-driven decision making is ushering in a smarter, greener, and more inclusive agricultural era. With continuous investment in digital literacy, equitable internet access, and trusted technology partners, farming communities worldwide stand to reap even greater rewards.
Ready to experience the benefits of precision and digital agriculture? Join the Farmonaut platform today and unlock affordable, scalable solutions to empower your agricultural journey—no matter where or what you farm.
For more, check the Farmonaut API and Developer Docs to integrate advanced satellite insights directly into your systems.
Transform your farm’s future. Stay informed. Stay connected. Grow with Farmonaut.