Agriculture Security: 7 Secrets for Unbreakable Farms
“Over 70% of farmers using climate-smart practices report increased resilience to extreme weather events.”
Summary: Agricultural security encompasses the protection of agriculture from threats such as natural disasters, pests, diseases, cyberattacks, and human-induced challenges like agro-terrorism. Ensuring agricultural security is vital for the strength of our food supply chains, economic stability, and national security. This blog demystifies the seven pillars of resilience and offers actionable insights for a sustainable, secure farming future.
What is Agricultural Security?
Agricultural security is the holistic protection of our farming systems, including crops and livestock, against a wide spectrum of risks: natural disasters (such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes), pests, diseases, human-induced challenges like agro-terrorism and increasingly, cyberattacks as we adopt digital agriculture technologies. It encompasses efforts to preserve food supply chain resilience, mitigate economic losses, and uphold national stability, especially as weather patterns and technological vulnerabilities evolve.
In facing these multifaceted challenges, we need resilient strategies that merge tradition with innovation—drawing on climate-smart agriculture, smart farming systems, robust policy, and cutting-edge technologies. Let us now unravel the seven secrets that can make our farms unbreakable.
The 7 Secrets for Unbreakable Farms
1. Climate-Smart Agriculture: Building Natural Resilience
Climate change is fundamentally altering weather patterns, raising temperatures, and increasing the frequency of extreme events like droughts, floods, and hurricanes. These can devastate crops, lead to livestock losses, and cause significant food shortages.
- Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) involves practices that increase productivity, enhance resilience to variable climate, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Practical examples include planting heat-tolerant crop varieties, adopting mulching, and deploying water-saving irrigation methods.
- Benefits: These approaches shield us against unpredictable rainfall and extreme events while promoting long-term sustainability.
By systematically monitoring weather data and adapting our farming techniques season by season, we create robust systems that can withstand shocks and bounce back quickly from adversity. For instance, integrating satellite weather data, like what Farmonaut offers, helps us better plan irrigation and planting, further boosting our adaptive capacity.
2. Embracing Digital Agriculture Technologies for Smarter Decisions
The introduction and adoption of digital agriculture technologies have redefined how we approach agricultural risks, efficiency, and sustainability. Digital transformation leverages a convergence of IoT devices, AI-driven analytics, satellite monitoring, and data platforms for real-time crop, soil, and environmental monitoring.
- Digital agriculture enables us to monitor for signs of crop failures due to droughts, pests, or invasive diseases remotely, using app- or browser-based tools.
- Platforms like Farmonaut combine satellite data and AI advisories to produce actionable crop health insights.
- Benefits: Early warnings for pest outbreaks and disease spread, data-driven irrigation, and instant crop health feedback improve yields and resource efficiency.
The shift to digital solutions also supports broader goals: traceability, transparency, reduced input costs, and enhanced supply chain security. However, as we’ll discuss, increased connectivity also means new vulnerabilities—especially to cyberattacks that could disrupt automated or smart farming systems.
3. Robust Cybersecurity in Agriculture: Defending the Digital Frontier
“Cyberattacks on agriculture rose by 40% in 2023, highlighting the need for robust digital security in food supply chains.”
As agriculture modernizes and becomes digitized, the risk of cyberattacks rises sharply. Cybersecurity in agriculture is no longer optional—it is foundational.
- Threats: Automated irrigation, smart farming systems, and IoT-connected devices managing livestock or crops may be targets for malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Attacks: These can cause massive disruptions by manipulating data, triggering shutdowns, contaminating production, or impacting resource management systems.
- Best practices: Regular system updates, staff cybersecurity training, robust authentication, and isolated cloud data storage are key to protecting operations.
In addition to these technical solutions, using platforms with strong security credentials—such as Farmonaut’s encrypted advisory system and blockchain-based traceability—adds another layer of defense. Blockchain technology presents a robust answer to third-party manipulation and helps ensure all data (from field to supply chain) remains authentic and tamper-proof.
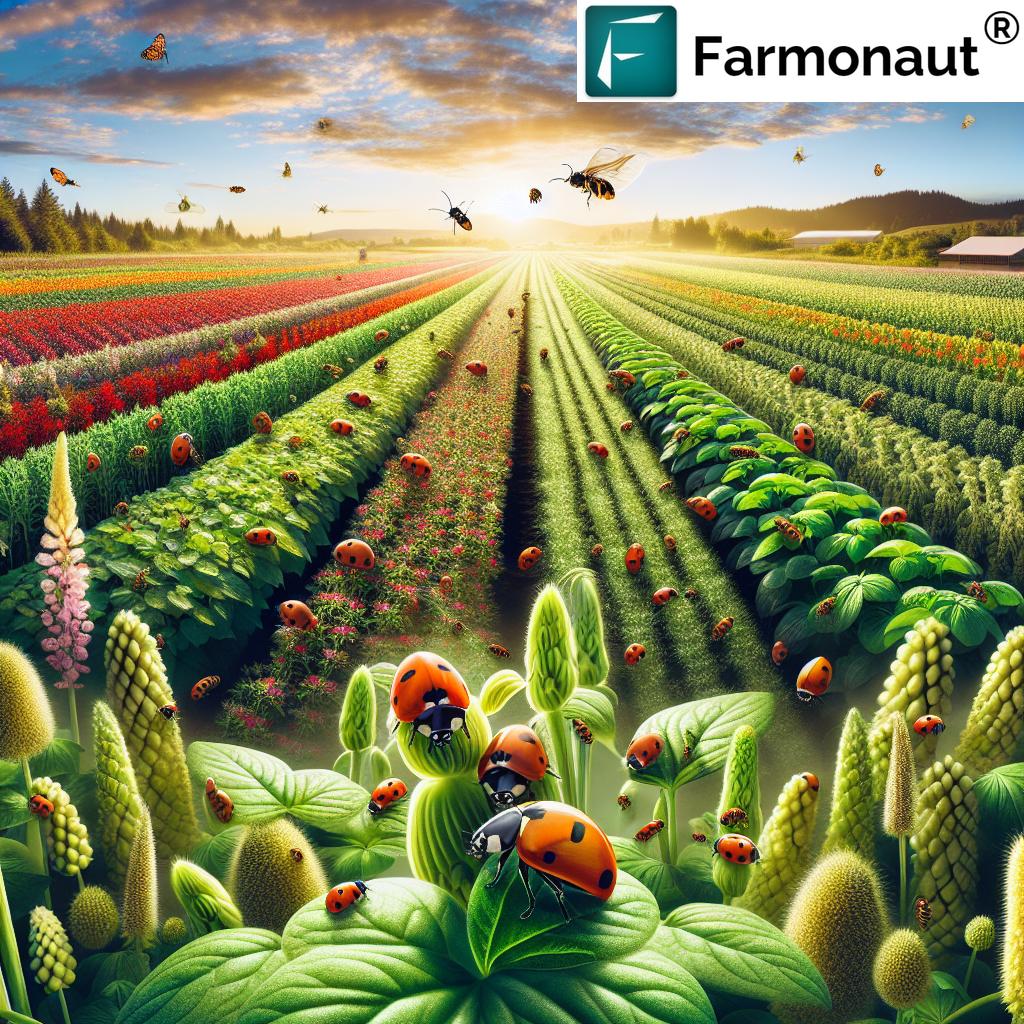
4. Agrobiodiversity and Food Security: Diverse Species for Resilience
Resilience in agriculture stems not just from technology, but also from biological diversity. Agrobiodiversity and food security go hand in hand—diverse crop and livestock species serve as a buffer against disease outbreaks, pest invasions, or climate extremes.
- Why it matters: If one crop type is susceptible to a new pathogen or invasive pest, others may continue to provide income and nutrition, stabilizing production.
- Risks of low diversity: Global food systems dominated by only a handful of species are highly vulnerable to catastrophic failures.
- Practices: Intercropping, crop rotation, seed banking, and growing locally-adapted heritage breeds help preserve agrobiodiversity and bolster national food supply chains.
Technologies that monitor crop diversity and health—such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring—empower us to spot reductions in agrobiodiversity before they impact regional resilience. Promoting such diversity requires not only on-the-ground agricultural practices, but also supporting policy at the governmental and institutional level.
5. Agricultural Disaster Preparedness & Policy: Ready for the Unexpected
Preparedness and policy are the backbone of true agricultural security. Natural and human-induced disasters are inevitable, but their impact can be minimized when emergency readiness is deeply integrated at farm, community, and national levels.
- Governments play a vital role by funding research, developing risk-mitigation policies, and implementing coordinated disaster response systems.
- Timely warning systems—enabled by AI, satellites, and weather analysis platforms—help us prepare for and respond to oncoming threats (see Farmonaut’s integrated real-time weather and crop advisory apps).
-
Effective policy frameworks—like the U.S. National Security Memorandum-16—set strategic priorities for food and agriculture sector security, focusing on:
- Systematic threat assessment
- Highlighting public-private partnerships
- Improved disaster preparedness and recovery
At the operational level, having a contingency plan for every aspect of farming—from seed storage and irrigation backup to safe data handling and staff mobilization—ensures no single disaster can paralyze our food production systems.
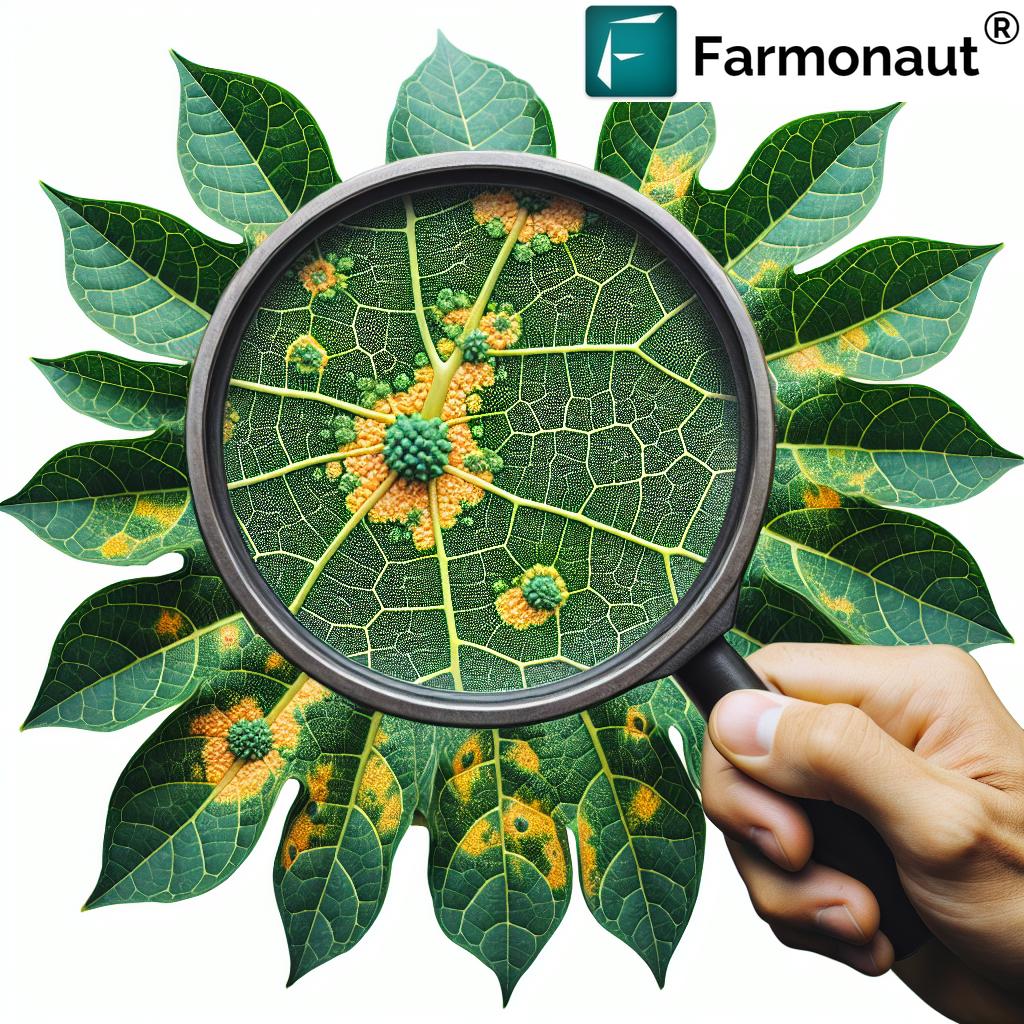
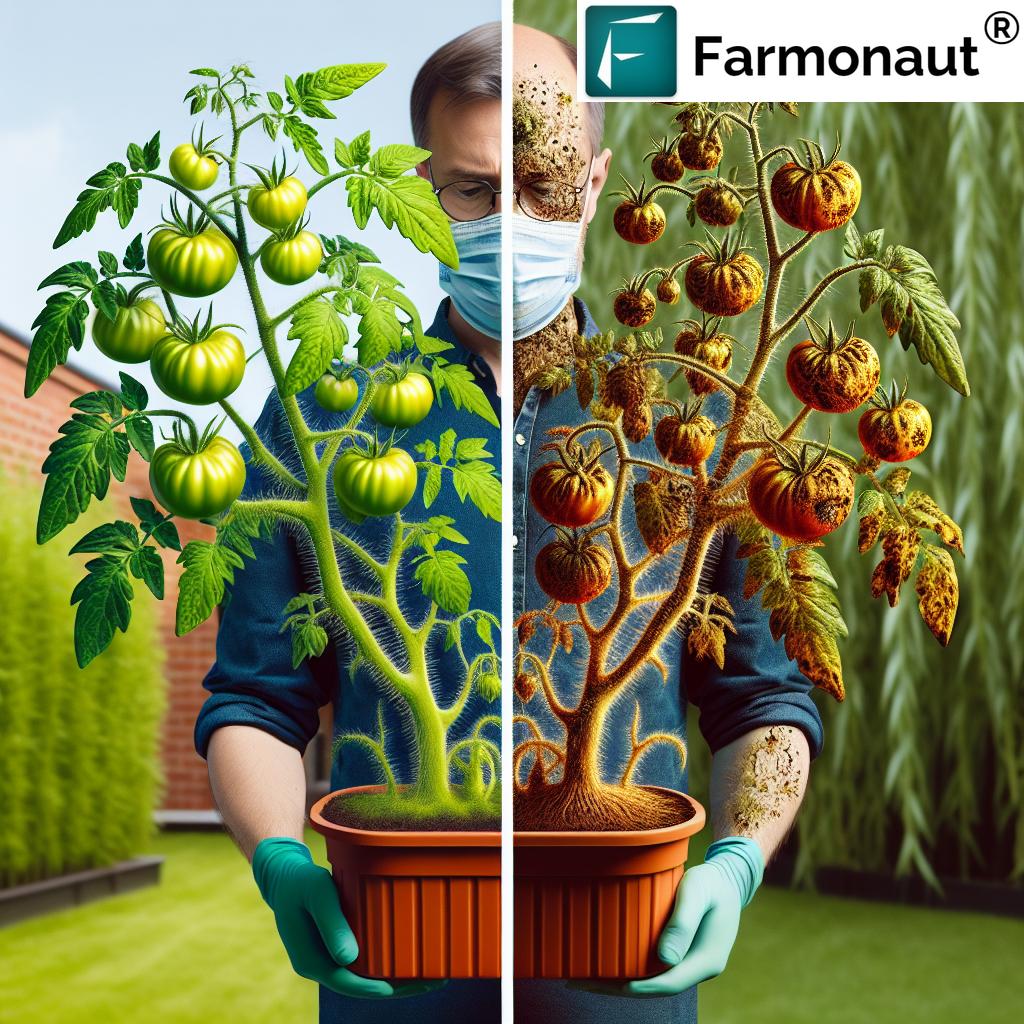
6. Integrated Pest & Disease Management: Smart & Sustainable Approaches
The introduction and spread of invasive pests and diseases, such as the fall armyworm in Africa (impacting maize production), highlight the need for proactive risk management strategies. Unchecked, these biological hazards can lead to crop failures, livestock losses, and destabilize food supply chains.
-
Integrated Pest Management (IPM):
- Combines monitoring, biological controls, and data-driven interventions over blanket chemical use.
- Focuses on early detection, rapid response, and minimal environmental harm.
- Disease surveillance: Using digital tools, remote sensing, and field data collection enables targeted treatment and containment.
- AI & Satellite Insights: Advanced platforms like Farmonaut detect crop stress, analyze changes in NDVI, and flag likely pest or disease hotspots—providing time-sensitive recommendations to minimize losses.
Adopting these resilient farming practices not only prevents crop and livestock diseases but also conserves beneficial species and reduces overreliance on agricultural chemicals, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
7. Food Supply Chain Resilience and Traceability: Strengthening Every Link
Attacks and disruptions—whether physical, biological, or cyber—can reverberate across supply chains, resulting in widespread food shortages, consumer confidence loss, and economic shocks. Food supply chain resilience depends on end-to-end traceability and agile response mechanisms.
- Traceability solutions: By tracking every step—from seed to plate—blockchain-based systems (like Farmonaut’s traceability tools) protect against contamination, fraud, and ensure quick recalls if needed.
- Resource and fleet management: Ensures logistics remain efficient and flexible, even during disasters or market shocks.
- Preparedness for recall & contamination: Digital documentation and integrated alerts allow immediate action, minimizing damage and economic repercussions.
Comparative Table of Agriculture Security Practices
| Security Practice | Main Objective | Environmental Impact | Technology Involved | Implementation Cost | Resilience Boost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate-Smart Agriculture | Adapt to climate change, maintain yields | High | Basic–Advanced | $/Medium | High |
| Digital Agriculture Technologies | Enable real-time monitoring & decisions | Moderate | Advanced | $$ | High |
| Cybersecurity in Agriculture | Defend systems/data from cyber threats | Low | Advanced | $/Medium | High |
| Agrobiodiversity | Reduce vulnerability to shocks/diseases | High | Basic | $ | High |
| Disaster Preparedness & Policy | Systematic risk assessment and readiness | Moderate | Basic–Advanced | Medium | High |
| Integrated Pest/Disease Management | Prevent crop/livestock losses | High | Advanced | $/Medium | High |
| Supply Chain Traceability | Secure chain, ensure recall & transparency | Moderate | Advanced | $$ | High |
Farmonaut Precision Agriculture Solutions for Security & Resilience
Modern agricultural security demands tools that are precise, scalable, and affordable. Farmonaut stands at the forefront by integrating advanced satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory, blockchain traceability, and sustainability solutions. Our platform equips us to:
- Monitor Crop Health in Real-Time: Utilizing satellite imagery and NDVI analytics, Farmonaut tracks vegetation health, stress, and growth cycles for timely interventions.
- Access Personalized AI Advisory (Jeevn AI): Receive expert recommendations on crop management, pest/disease risk, and weather-adaptive farming practices—customized for individual farms.
- Ensure Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Secure the entire supply chain so products reach consumers transparently and safely. This is critical for building consumer trust and protecting against food contamination or fraud.
- Simplify Resource & Fleet Management: Farmonaut’s solutions give us full control over logistics, machinery, and field resources, reducing waste and optimizing operational costs.
- Track Carbon Footprints and Drive Sustainability: Our tools provide live emissions data, allowing agribusinesses to align with environmental compliance and lower their greenhouse impact.
- Flexible, Scalable Access for All Stakeholders: Whether a smallholder farmer, large agribusiness, or policy institution, Farmonaut offers subscription and API access models to fit every need.
- Access powerful satellite and weather data APIs for easy integration with existing agritech platforms and research tools.
- Get started with API developer documentation and accelerate your agricultural innovation.
- Large-scale plantation management has never been easier—coordinate, analyze, and optimize thousands of hectares with a single dashboard.
- Leverage crop, plantation, and forest advisory services for ecosystem-scale management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main threats to agricultural security?
The core threats are natural disasters like droughts, floods, and hurricanes; pests and crop and livestock diseases; technological vulnerabilities to cyberattacks; and human-induced dangers such as agro-terrorism or supply chain contamination.
How does digital agriculture help secure food supply chains?
Digital agriculture technologies provide real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and actionable insights for optimized resource use, pest and disease management, and rapid warning. These support food supply chain resilience and minimize the risk of production losses.
What role does agrobiodiversity play in resilience?
Agrobiodiversity ensures we’re not dependent on a single crop or livestock species. By maintaining a diverse gene pool, our farming systems remain stable even if one species is affected by new diseases or climate impacts.
Why is cybersecurity so important for modern agriculture?
As we depend more on automation, IoT devices, and cloud platforms, our farms face new digital threats. Cybersecurity in agriculture is crucial to protect data, keep automation running, and prevent losses due to malicious manipulation or cyberattacks.
How does Farmonaut improve agricultural security?
Farmonaut offers tools for satellite-based farm management, AI crop and weather advisories, blockchain product traceability, carbon footprint tracking, and fleet/resource management. This comprehensive suite supports resilience, risk reduction, cost savings, and sustainable growth across all farming operations.
Where can I access Farmonaut solutions?
Get started with the web and mobile apps for instant access, or use the robust API for seamless integration.
Conclusion: Towards Unbreakable Agricultural Security
Achieving rock-solid agricultural security in today’s world requires a dynamic, multi-layered approach. By blending climate-smart agriculture, robust digital agriculture technologies, comprehensive cybersecurity strategies, agrobiodiversity protection, data-driven disaster preparedness, and end-to-end traceability, we can shield our farms from an ever-wider array of risks.
The vision is clear: sustainable, resilient, and thriving agricultural systems that continue to feed, empower, and uplift communities—no matter what challenges lie ahead.