Transforming Ethiopia’s Agriculture: Sustainable Agro-Industrial Parks Boost Food Security and Economic Growth
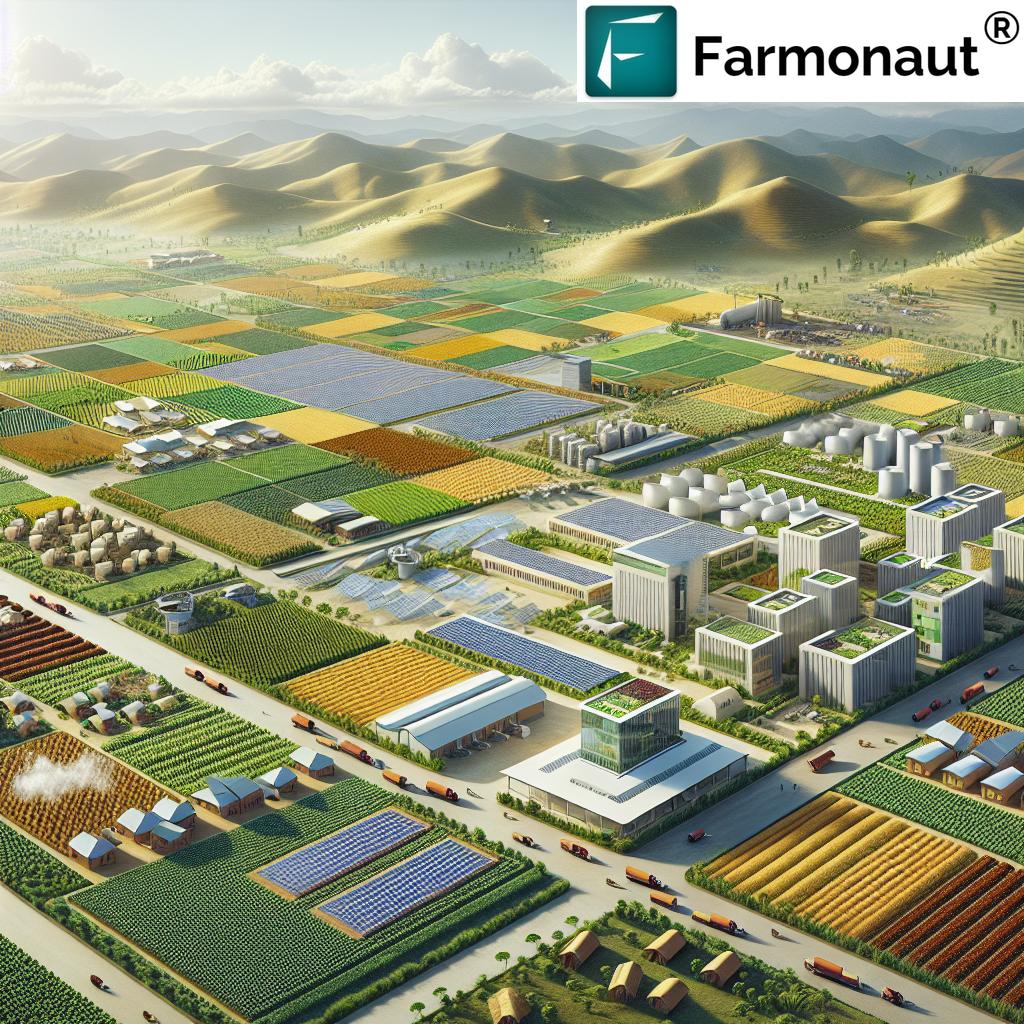
“Ethiopia’s agro-industrial parks aim to reduce post-harvest losses by up to 25%, significantly improving food security.”
In the heart of East Africa, a remarkable agricultural transformation is taking place. Ethiopia, a nation once synonymous with food insecurity, is now pioneering innovative strategies to boost sustainable growth and ensure food security for its burgeoning population. We’re witnessing a shift towards a demand-driven agricultural system that’s not only feeding the nation but also fueling economic growth. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into Ethiopia’s agricultural revolution, focusing on the game-changing integrated agro-industrial parks and rural transformation centers that are reshaping the country’s agricultural landscape.
The Vision: A Demand-Driven Agricultural System
At the core of Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation is the transition from a supply-driven to a demand-driven agricultural system. This paradigm shift is crucial for aligning production with market needs, enhancing efficiency, and boosting productivity. The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) has thrown its weight behind this initiative, recognizing its potential to revolutionize Ethiopia’s agricultural sector.
Dejene Tezera, Director of the Division of Agribusiness and Infrastructure Development at UNIDO, emphasizes the organization’s commitment to supporting Ethiopia’s efforts. The goal is clear: sustainably increase agricultural production to meet rising food demand, provide industrial raw materials, and enhance foreign currency earnings.
The Pillars of Transformation: Integrated Agro-Industrial Parks
Central to Ethiopia’s agricultural strategy are the integrated agro-industrial parks (AIIPs). These innovative hubs are designed to bridge the gap between farmers and industries, creating a symbiotic relationship that benefits both sectors. Let’s break down the key components and benefits of these parks:
- Infrastructure Development: The AIIPs incorporate essential infrastructure such as water, power, and storage facilities. This comprehensive approach ensures that all necessary resources are available in one location, streamlining the agricultural value chain.
- Rural Transformation Centers: These centers act as satellites to the main parks, providing farmers with critical access to inputs, technical support, and aggregation and processing facilities. By bringing these services closer to farmers, the centers play a pivotal role in enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Value Addition: The parks enable farmers to enhance the value of their products before supplying them to industries. This value addition increases market competitiveness and ensures better returns for farmers.
- Market Linkages: By connecting smallholder farmers directly with industrial sectors, the AIIPs create a stable market for agricultural produce, reducing uncertainties and encouraging increased production.
The Ethiopian government has demonstrated its commitment to this initiative by investing a staggering 620 million USD into developing agro-park infrastructure. This significant investment underscores the government’s dedication to industrialization and rural development.
Empowering Smallholder Farmers: The Backbone of Ethiopia’s Agriculture
Smallholder farmers are the lifeblood of Ethiopia’s agricultural sector. Recognizing their crucial role, the transformation strategy places a strong emphasis on supporting these farmers to improve productivity and connect with industrial sectors. Here’s how the initiative is empowering smallholder farmers:
- Extension Services: Farmers receive essential extension services, providing them with the knowledge and skills needed to enhance their agricultural practices.
- Access to Inputs: The strategy ensures that farmers have access to quality agricultural inputs, including seeds, fertilizers, and pest control products.
- Technical Support: Through the Rural Transformation Centers, farmers receive ongoing technical support to address challenges and implement best practices.
- Market Access: By linking farmers directly with industries, the initiative creates a stable market for their produce, reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring fair prices.
The impact of these efforts is already visible. Currently, approximately 170,000 farmers are engaged in supplying raw materials to industries, resulting in an impressive export generation of around 50 million USD last year.
The Role of Technology in Ethiopia’s Agricultural Transformation
As Ethiopia embraces agricultural transformation, technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing productivity and sustainability. Innovative solutions like those offered by Farmonaut are revolutionizing farm management practices across the country.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring system provides Ethiopian farmers with real-time insights into vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This data-driven approach enables farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, ultimately optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.
The integration of such technologies aligns perfectly with Ethiopia’s goals of increasing agricultural productivity and sustainability. By leveraging satellite imagery and AI-driven insights, Ethiopian farmers can participate in precision agriculture practices that were once out of reach for smallholder farmers.
Boosting Agribusiness Investment Opportunities
The transformation of Ethiopia’s agricultural sector is creating a wealth of agribusiness investment opportunities. The shift towards a demand-driven system, coupled with the development of integrated agro-industrial parks, has made Ethiopia an attractive destination for both domestic and foreign investors. Here’s why:
- Ready Infrastructure: The government’s significant investment in agro-park infrastructure provides a solid foundation for businesses to operate efficiently.
- Access to Raw Materials: The direct link between farmers and industries ensures a steady supply of quality raw materials for agro-processing.
- Export Potential: With improved productivity and processing capabilities, Ethiopia is poised to increase its agricultural exports, offering investors access to international markets.
- Supportive Policies: The Ethiopian government has implemented policies to create a conducive environment for agribusiness growth, including incentives for investors in the agricultural sector.
Investors looking to capitalize on these opportunities can leverage technology solutions like Farmonaut’s API to integrate cutting-edge agricultural data into their operations. The Farmonaut API provides access to satellite and weather data, enabling agribusinesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their operations.
“Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation strategy targets increasing irrigated land from 3% to 10%, boosting crop yields nationwide.”
Enhancing Food Security Through Sustainable Practices
Food security is at the heart of Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation. The initiatives being implemented are designed not just to increase production, but to do so sustainably. Here’s how Ethiopia is addressing food security challenges:
- Reducing Food Waste: UNIDO is working with Ethiopia to address the issue of food waste, which accounts for roughly 30% of food produced globally. By improving storage and processing facilities, Ethiopia aims to significantly reduce post-harvest losses.
- Expanding Irrigation: The strategy includes ambitious plans to expand irrigation capabilities, reducing reliance on rain-fed agriculture and increasing crop yields.
- Improving Agro-Processing: By enhancing agro-processing capabilities, Ethiopia is not only reducing food waste but also creating value-added products for both domestic consumption and export.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: The adoption of sustainable farming practices, supported by technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring, helps conserve resources while improving productivity.
For farmers and agribusinesses looking to implement these sustainable practices, Farmonaut offers mobile applications that provide easy access to critical farm management tools.
The Impact on Rural Development and Economic Growth
The agricultural transformation strategy is having a profound impact on rural development and overall economic growth in Ethiopia. Here’s how:
- Job Creation: The development of agro-industrial parks and the expansion of agro-processing capabilities are creating new job opportunities in rural areas.
- Income Generation: Improved productivity and market access are increasing incomes for smallholder farmers, contributing to poverty reduction.
- Rural Infrastructure: The establishment of Rural Transformation Centers is bringing essential infrastructure and services to rural areas, improving quality of life.
- Foreign Currency Earnings: Increased agricultural exports are boosting Ethiopia’s foreign currency earnings, strengthening the country’s economic position.
Ethiopia’s Model: A Blueprint for African Agricultural Transformation
The success of Ethiopia’s integrated agro-parks and agricultural transformation strategy is gaining attention across Africa. It serves as a potential model for other nations looking to boost their agricultural sectors and achieve food security. Here’s why Ethiopia’s approach could be a blueprint for the continent:
- Holistic Approach: By addressing all aspects of the agricultural value chain, from production to processing and marketing, Ethiopia’s model offers a comprehensive solution to agricultural challenges.
- Scalability: The modular nature of the agro-industrial parks makes the model scalable and adaptable to different contexts and countries.
- Focus on Smallholders: The strategy’s emphasis on supporting smallholder farmers aligns with the agricultural realities of many African countries.
- Technology Integration: The incorporation of technologies like satellite monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems demonstrates how African agriculture can leapfrog into the digital age.
For countries looking to implement similar strategies, tools like Farmonaut’s API Developer Docs can provide valuable insights into integrating advanced agricultural technologies into national strategies.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation strategy has shown promising results, it’s not without challenges. Some of the key hurdles include:
- Infrastructure Development: Continuing to develop the necessary infrastructure, especially in remote areas, remains a significant challenge.
- Climate Change: Ethiopia, like many African countries, is vulnerable to climate change impacts, which could affect agricultural productivity.
- Capacity Building: Ensuring that farmers and agribusinesses have the skills and knowledge to leverage new technologies and practices is an ongoing process.
- Market Access: While the strategy improves market linkages, expanding access to international markets remains a priority for sustainable growth.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for Ethiopia’s agricultural sector is positive. With continued investment, technological adoption, and support from organizations like UNIDO, Ethiopia is well-positioned to become a model of agricultural transformation in Africa.

Ethiopia’s Agricultural Transformation – Key Initiatives and Impacts
| Initiative | Description | Estimated Investment (USD) | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Agro-Industrial Parks | Centralized hubs for agricultural processing and value addition | 620 million | Increase in agro-processing capacity by 50%, boost in agricultural exports |
| Rural Transformation Centers | Satellite facilities providing inputs and services to farmers | 100 million | Support for 170,000+ smallholder farmers, improved market access |
| Irrigation Expansion | Increase in irrigated land from 3% to 10% | 200 million | 30% increase in crop yields, reduced vulnerability to climate variability |
| Agro-Processing Capabilities | Enhancement of food processing and packaging facilities | 150 million | 25% reduction in post-harvest losses, increased value-added exports |
| Smallholder Farmer Support Programs | Extension services, input provision, and technical support | 80 million | 20% increase in smallholder productivity, improved rural livelihoods |
Leveraging Technology for Agricultural Advancement
As Ethiopia continues its agricultural transformation journey, the role of technology in enhancing productivity and sustainability cannot be overstated. Solutions like Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI-driven advisory systems are becoming increasingly crucial in this landscape.
Farmonaut’s technology enables Ethiopian farmers and agribusinesses to:
- Monitor crop health in real-time using satellite imagery
- Receive personalized farm management advice through AI algorithms
- Track and reduce carbon footprints, aligning with sustainability goals
- Improve resource management and reduce waste
By integrating such advanced technologies, Ethiopia is not only addressing current agricultural challenges but also preparing for future ones. The adoption of these tools supports the country’s vision of creating a modern, efficient, and sustainable agricultural sector.
The Road Ahead: Sustaining Growth and Expanding Impact
As Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation strategy continues to unfold, the focus is on sustaining the initial successes and expanding their impact. Key areas of focus for the future include:
- Scaling Up: Expanding the network of agro-industrial parks and rural transformation centers to cover more regions.
- Technology Adoption: Encouraging wider adoption of precision agriculture technologies among smallholder farmers.
- Value Chain Development: Strengthening entire agricultural value chains to maximize efficiency and profitability.
- Export Market Expansion: Developing strategies to penetrate new international markets for Ethiopian agricultural products.
- Sustainability: Ensuring that growth in the agricultural sector is environmentally sustainable and climate-resilient.
The journey of transforming Ethiopia’s agriculture is ongoing, but the foundation laid by current initiatives provides a strong basis for continued growth and development.
Conclusion: A New Era for Ethiopian Agriculture
Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation strategy, centered around sustainable agro-industrial parks and innovative technologies, marks the beginning of a new era for the country’s agricultural sector. By focusing on a demand-driven system, empowering smallholder farmers, and leveraging cutting-edge technologies, Ethiopia is not only addressing food security challenges but also creating significant economic opportunities.
The success of this model offers valuable lessons for other African nations facing similar agricultural challenges. As Ethiopia continues to refine and expand its approach, the country is poised to become a leading example of how sustainable, technology-driven agriculture can drive economic growth and improve livelihoods across the continent.
For those looking to be part of this agricultural revolution, whether as farmers, agribusinesses, or investors, tools like Farmonaut offer a gateway to the future of farming. By embracing these innovations, stakeholders can contribute to and benefit from Ethiopia’s transformative journey towards agricultural excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What are integrated agro-industrial parks?
Integrated agro-industrial parks are centralized hubs that bring together agricultural production, processing, and marketing facilities. They aim to add value to agricultural products, reduce post-harvest losses, and create stronger market linkages for farmers. - How is Ethiopia supporting smallholder farmers in this transformation?
Ethiopia is supporting smallholder farmers through extension services, access to quality inputs, technical support, and improved market access through Rural Transformation Centers and connections to agro-industrial parks. - What role does technology play in Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation?
Technology plays a crucial role, with solutions like satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, and precision agriculture techniques being adopted to improve productivity and sustainability. - How is the transformation strategy addressing food security?
The strategy addresses food security by increasing agricultural productivity, reducing post-harvest losses, expanding irrigation, and improving agro-processing capabilities to ensure a stable food supply. - What are the main challenges facing Ethiopia’s agricultural transformation?
Key challenges include infrastructure development, climate change impacts, capacity building for farmers and agribusinesses, and expanding access to international markets.















