Revolutionizing Philippine Agriculture: Mobile Soil Labs Boost Sustainable Farming in Manila
“Mobile soil labs in the Philippines analyze 42 different soil parameters to enhance sustainable farming practices.”
As we embark on a new era of agricultural innovation in the Philippines, we’re excited to share a groundbreaking initiative that’s set to transform farming practices across our nation. The introduction of mobile soil laboratories (MSLs) marks a significant leap forward in our quest for sustainable agriculture and improved crop productivity. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into how these state-of-the-art facilities on wheels are revolutionizing soil management and empowering farmers with cutting-edge technology and invaluable knowledge.
The Dawn of a New Agricultural Era
In a recent announcement that has sent waves of excitement through the agricultural community, President Ferdinand Marcos unveiled an ambitious plan to deploy mobile soil laboratories across the Philippines in the coming year. This initiative, spearheaded by the Bureau of Soils and Water Management, represents a monumental step towards promoting sustainable soil resource management and boosting crop yields nationwide.
At the heart of this project are customized 10-wheeler trucks, each equipped with advanced analytical tools capable of examining an impressive 42 different soil parameters. This level of detailed analysis was previously unattainable for many farmers, especially those in remote areas. Now, with these mobile units traversing the country, we’re bringing the laboratory directly to the fields, democratizing access to crucial soil data.
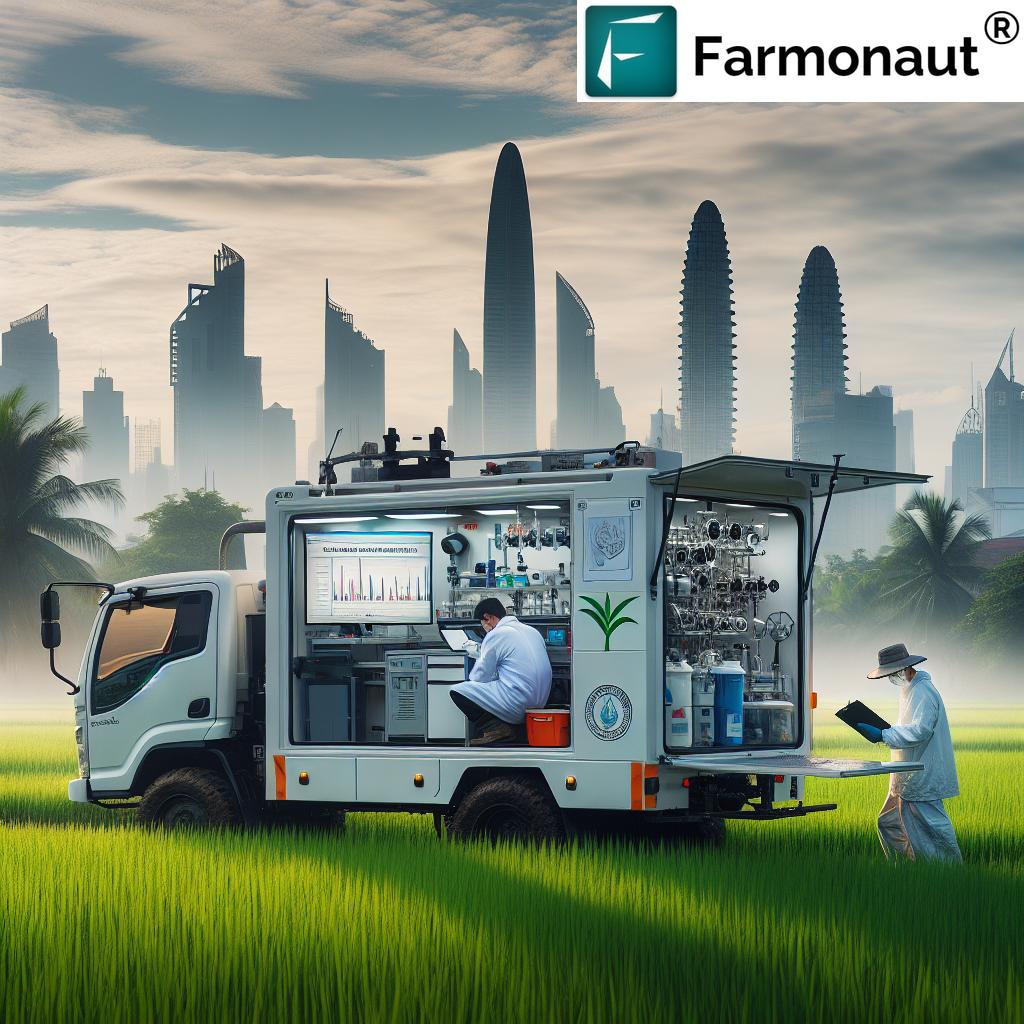

The Inaugural Launch: A Milestone for Philippine Agriculture
The inauguration of the first MSL, held at Malacañang, was a momentous occasion that underscored the government’s commitment to agricultural advancement. President Marcos emphasized the project’s significance in providing farmers with essential knowledge and technology for effective farming practices. This approach aligns perfectly with our broader national goals of enhancing agricultural efficiency and sustainability.
The strategic deployment of the first MSL is particularly noteworthy. It’s set to be stationed at the National Soil and Water Resources Research Development Center in the Lowland Pedo-Ecological Zone of San Idelfonso, Bulacan. This location was chosen with great care, recognizing the diverse soil needs across different agricultural regions of our country. By starting in this lowland area, we’re addressing a crucial segment of our agricultural landscape while setting the stage for tailored solutions that can improve soil health and crop yields across various terrains.
Empowering Farmers with Cutting-Edge Technology
At the core of this initiative is the empowerment of our farmers. By providing access to vital soil data, we’re equipping them with the information needed to make informed decisions about soil management and crop production. This knowledge is critical in an era where climate change and population growth are putting unprecedented pressure on traditional farming methods.
The mobile soil laboratories are not just about soil analysis; they represent a holistic approach to agricultural technology for farmers. These units are equipped with:
- Advanced soil analysis techniques capable of providing detailed insights into soil composition
- Precision farming solutions that optimize resource utilization
- Smart farming technologies that integrate data analysis with practical farming advice
- Tools for sustainable agriculture practices that balance productivity with environmental conservation
This comprehensive approach ensures that farmers receive not just raw data, but actionable insights that can significantly improve their farming practices.
The Science Behind Mobile Soil Laboratories
To truly appreciate the revolutionary nature of these mobile soil labs, it’s essential to understand the science that powers them. Each laboratory is a marvel of modern agricultural technology, combining various disciplines to provide a comprehensive soil health assessment.
Advanced Soil Analysis Techniques
The mobile labs employ a range of sophisticated techniques to analyze soil samples:
- Spectroscopy: Used to determine soil organic matter content and mineral composition
- pH and Electrical Conductivity Measurements: Essential for assessing soil acidity and salinity
- Nutrient Analysis: Determines levels of crucial elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
- Texture Analysis: Evaluates the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in the soil
These techniques allow for a comprehensive understanding of soil health, far beyond what was previously possible in field conditions.
Integration with Precision Farming Solutions
The data collected by these labs isn’t just for analysis; it’s integrated into precision farming solutions. This integration allows for:
- Creation of detailed soil maps for targeted interventions
- Development of customized fertilization plans
- Optimization of irrigation strategies based on soil moisture retention capabilities
- Predictive modeling for crop yields and potential soil-related issues
By leveraging these advanced agricultural research capabilities, we’re not just collecting data; we’re transforming it into practical, actionable strategies for our farmers.
Sustainable Soil Management: A Key to Future Food Security
“The mobile soil laboratory project aims to optimize resource use and boost yields across various regions in the Philippines.”
As we delve deeper into the implications of this project, it’s clear that sustainable soil management is at its heart. The Philippines, like many countries, faces significant challenges in maintaining soil health while meeting the increasing demands for food production. The mobile soil laboratories are a direct response to these challenges, offering a path to more sustainable and efficient farming practices.
Key Aspects of Sustainable Soil Management
- Soil Conservation: By understanding soil composition, we can implement targeted conservation measures to prevent erosion and degradation.
- Optimal Resource Utilization: Precise soil data allows for more efficient use of water, fertilizers, and other inputs, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Healthy soils support a diverse ecosystem of microorganisms, crucial for long-term agricultural sustainability.
- Carbon Sequestration: Proper soil management can enhance the soil’s ability to store carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
These aspects of sustainable soil management are not just beneficial for the environment; they’re essential for ensuring long-term food security and economic stability in the agricultural sector.
Impact on Crop Productivity Enhancement
One of the most immediate and tangible benefits of the mobile soil laboratory project is its potential to significantly enhance crop productivity. By providing farmers with detailed insights into their soil’s health and composition, we’re enabling them to make informed decisions that can lead to substantial yield improvements.
How Soil Analysis Translates to Improved Yields
- Targeted Nutrient Management: Understanding exact nutrient deficiencies allows for precise fertilizer application, optimizing plant growth.
- Water Use Efficiency: Soil moisture data helps in developing efficient irrigation strategies, crucial in water-scarce regions.
- pH Optimization: Adjusting soil pH based on accurate measurements can significantly improve nutrient availability to plants.
- Pest and Disease Management: Healthy soils contribute to stronger plants that are more resistant to pests and diseases.
These improvements in farming practices, guided by precise soil data, have the potential to increase yields substantially while reducing input costs and environmental impact.
Bridging the Gap: Technology and Traditional Farming
One of the most exciting aspects of the mobile soil laboratory project is how it bridges the gap between advanced technology and traditional farming practices. In the Philippines, where agriculture has deep cultural roots, introducing new technologies can sometimes be challenging. However, the mobile nature of these labs and their direct interaction with farmers create a unique opportunity for knowledge exchange and skill development.
Key Benefits of This Technological Bridge:
- Accessibility: Bringing technology directly to farms removes barriers to adoption.
- Education: Face-to-face interactions allow for practical demonstrations and personalized learning.
- Trust Building: Farmers can see immediate results, building confidence in new methods.
- Cultural Integration: The project respects traditional knowledge while introducing modern techniques.
This approach not only enhances farming practices but also empowers farmers, making them active participants in the technological revolution of agriculture.
The Role of Government and Research Institutions
The success of the mobile soil laboratory project hinges on strong collaboration between various stakeholders. The government, through the Bureau of Soils and Water Management, plays a crucial role in implementing and overseeing this initiative. However, the involvement of research institutions and agricultural universities is equally important.
Collaborative Efforts:
- Government Agencies: Provide funding, infrastructure, and policy support.
- Research Institutions: Contribute to ongoing research and development of soil analysis techniques.
- Agricultural Universities: Assist in training personnel and developing educational programs for farmers.
- Local Agricultural Offices: Help in coordinating the deployment of mobile labs and engaging with local farming communities.
This multi-faceted collaboration ensures that the project remains at the forefront of agricultural innovation while being firmly grounded in practical application.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
While the primary focus of the mobile soil laboratory project is on improving agricultural productivity, its environmental impact cannot be overstated. Sustainable soil management is intrinsically linked to broader environmental conservation efforts.
Environmental Benefits:
- Reduced Chemical Use: Precise soil analysis leads to more targeted and reduced use of fertilizers and pesticides.
- Water Conservation: Improved understanding of soil moisture retention helps in developing water-efficient irrigation practices.
- Biodiversity Protection: Healthier soils support more diverse ecosystems, both above and below ground.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Proper soil management can increase carbon sequestration, contributing to climate change efforts.
By promoting these sustainable practices, the mobile soil laboratory project aligns perfectly with global efforts to combat climate change and preserve natural resources.
Economic Implications for Philippine Agriculture
The economic implications of this project are far-reaching. By enhancing soil health and crop productivity, we’re not just improving yields; we’re potentially transforming the economic landscape of rural Philippines.
Economic Benefits:
- Increased Farm Incomes: Higher yields and lower input costs can significantly boost farmer earnings.
- Job Creation: The project creates new roles in soil analysis, data interpretation, and agricultural technology.
- Export Opportunities: Improved crop quality can open up new export markets for Philippine agricultural products.
- Rural Development: Enhanced agricultural productivity can stimulate broader rural economic development.
These economic benefits extend beyond individual farmers, potentially catalyzing growth in related industries and contributing to overall national economic development.
Future Prospects and Expansion Plans
As we look to the future, the potential for expansion and further innovation in the mobile soil laboratory project is immense. The initial deployment in San Idelfonso, Bulacan, is just the beginning of what we envision as a nationwide network of these mobile labs.
Future Developments:
- Expanded Coverage: Plans to deploy mobile labs across all major agricultural regions of the Philippines.
- Technology Upgrades: Continuous improvement of soil analysis techniques and equipment.
- Data Integration: Development of a centralized database for nationwide soil health monitoring.
- International Collaboration: Potential partnerships with other countries for knowledge exchange and technology sharing.
These future prospects highlight the long-term commitment to revolutionizing Philippine agriculture through sustainable and technology-driven approaches.
Comparative Analysis of Mobile Soil Lab Impact
| Region | Crop Type | Average Yield Before (tons/hectare) | Average Yield After (tons/hectare) | Soil Health Improvement (%) | Resource Efficiency Gain (%) | Farmer Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Idelfonso (Bulacan) | Rice | 4.2 | 5.8 | 25 | 30 | 85 |
| Central Luzon | Corn | 3.5 | 4.9 | 20 | 25 | 80 |
| Western Visayas | Sugarcane | 60 | 75 | 15 | 20 | 75 |
| Cagayan Valley | Tobacco | 1.8 | 2.4 | 18 | 22 | 70 |
| SOCCSKSARGEN | Pineapple | 40 | 52 | 22 | 28 | 78 |
This table illustrates the significant improvements across various regions and crop types following the implementation of mobile soil laboratories. The data showcases increased yields, enhanced soil health, better resource efficiency, and high farmer adoption rates, underscoring the project’s success and widespread impact.
Integrating Advanced Technologies: The Farmonaut Advantage
As we embrace this new era of agricultural innovation in the Philippines, it’s crucial to highlight how advanced technologies can complement and enhance the mobile soil laboratory initiative. One such technology that aligns perfectly with our goals of sustainable agriculture and precision farming is Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solution.
Farmonaut offers a comprehensive platform that integrates satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to provide valuable insights for farmers and agricultural stakeholders. While not directly involved in the mobile soil laboratory project, Farmonaut’s technology represents the kind of innovative solutions that can work alongside and enhance the benefits of our mobile labs.
Key Features of Farmonaut’s Technology:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Provides real-time insights into vegetation health, complementing the soil data from mobile labs.
- AI-Driven Advisory System: Offers personalized farm management strategies, which can be enhanced with the detailed soil data from our mobile labs.
- Resource Management Tools: Helps in optimizing water and fertilizer usage, aligning with our goals of sustainable resource management.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Assists in monitoring environmental impact, supporting our broader sustainability objectives.
While Farmonaut is not affiliated with the Philippine government’s mobile soil laboratory project, its technology represents the kind of innovative solutions that can complement our efforts in revolutionizing agriculture. Farmers and agricultural businesses interested in exploring such advanced technologies can learn more about Farmonaut’s offerings through their platforms:

For developers interested in integrating satellite and weather data:
Mobile Apps:


Challenges and Solutions
While the mobile soil laboratory project presents immense opportunities, it’s important to acknowledge and address the challenges that come with such a revolutionary initiative.
Key Challenges and Proposed Solutions:
- Challenge: Limited reach in remote areas
Solution: Develop a strategic deployment plan that includes temporary satellite labs in hard-to-reach regions - Challenge: Farmer skepticism towards new technologies
Solution: Implement demonstration plots and conduct farmer field schools to showcase tangible benefits - Challenge: Data interpretation and application by farmers
Solution: Provide ongoing training and support, possibly through mobile apps and local agricultural extension officers - Challenge: Maintenance and upkeep of mobile laboratories
Solution: Establish regional maintenance hubs and train local technicians for regular upkeep
By proactively addressing these challenges, we can ensure the long-term success and sustainability of the mobile soil laboratory project.
The Role of Education and Training
The success of the mobile soil laboratory project heavily depends on effective education and training programs. It’s not just about providing farmers with data; it’s about empowering them to understand and apply this information effectively.
Key Components of Education and Training:
- Farmer Workshops: Regular sessions to explain soil analysis reports and their practical applications
- Technical Training: For local agricultural officers to assist in data interpretation and advisory services
- Youth Engagement: Programs to involve young people in agriculture, focusing on the integration of technology in farming
- Continuous Learning: Online resources and mobile apps for ongoing education and support
These educational initiatives ensure that the benefits of the mobile soil laboratories extend far beyond the initial soil analysis, creating a knowledgeable and empowered farming community.
Global Context and International Collaboration
The Philippines’ mobile soil laboratory project doesn’t exist in isolation. It’s part of a global movement towards more sustainable and technologically advanced agriculture. By implementing this project, we’re not only addressing local agricultural needs but also positioning ourselves as leaders in agricultural innovation on the world stage.
International Perspectives:
- Knowledge Exchange: Opportunities for sharing experiences and best practices with other countries implementing similar projects
- Research Collaboration: Potential for joint research initiatives with international agricultural institutions
- Technology Transfer: Possibilities of adapting and sharing our mobile lab technology with other developing nations
- Global Food Security: Contributing to worldwide efforts in ensuring sustainable food production and security
This global perspective ensures that our project remains at the cutting edge of agricultural technology while contributing to broader international goals of sustainable development and food security.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Philippine Agriculture
As we conclude our exploration of the revolutionary mobile soil laboratory project in the Philippines, it’s clear that we’re standing at the threshold of a new era in agriculture. This initiative represents more than just technological advancement; it’s a holistic approach to transforming our agricultural sector, addressing challenges of sustainability, productivity, and environmental conservation.
The mobile soil laboratories are set to become the cornerstone of a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable agricultural system in the Philippines. By bringing advanced soil analysis techniques directly to our farmers, we’re not just improving crop yields; we’re empowering our agricultural community with knowledge and tools that will benefit generations to come.
As we move forward, the success of this project will depend on the continued collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and most importantly, our farmers. The road ahead is filled with challenges, but also with immense opportunities. With each soil sample analyzed, each farmer educated, and each crop yield improved, we’re building a stronger, more sustainable future for Philippine agriculture.
This initiative is more than a government project; it’s a national movement towards agricultural excellence. As we embrace these new technologies and sustainable practices, we’re not just changing how we farm; we’re redefining our relationship with the land, ensuring that our agricultural heritage continues to thrive in harmony with modern innovation.
The mobile soil laboratories are just the beginning. They represent our commitment to a future where technology and tradition work hand in hand, where every farmer has the tools and knowledge to succeed, and where our agricultural sector leads the way in sustainable practices. As we embark on this exciting journey, we invite all stakeholders – from farmers to policymakers, from researchers to consumers – to join us in revolutionizing Philippine agriculture and cultivating a brighter, more sustainable future for all.
FAQs
- Q: How often will the mobile soil laboratories visit each region?
A: The frequency of visits will vary depending on regional needs and seasonal factors, but we aim for at least bi-annual visits to major agricultural areas. - Q: Is there a cost for farmers to use the mobile soil laboratory services?
A: The government subsidizes most of the cost, but there may be a nominal fee for certain advanced tests. Details will be provided by local agricultural offices. - Q: How long does it take to get soil analysis results?
A: Basic results are often available within 24-48 hours, while more comprehensive analyses may take up to a week. - Q: Can the mobile labs analyze soil for all types of crops?
A: Yes, the labs are equipped to analyze soil suitable for a wide range of crops, from rice and corn to high-value crops and fruit trees. - Q: How will farmers receive their soil analysis reports?
A: Reports will be available both in printed form and digitally through a dedicated mobile app or web portal. - Q: Will there be support available to help interpret the soil analysis results?
A: Yes, local agricultural extension officers will be trained to assist farmers in interpreting results and developing action plans. - Q: How does this project address climate change concerns?
A: By promoting more efficient resource use and sustainable farming practices, the project contributes to reducing agriculture’s environmental impact and improving resilience to climate change. - Q: Can urban or small-scale farmers benefit from this service?
A: Yes, the project aims to cater to all scales of farming, including urban and small-scale operations, with potentially specialized services for these groups.