Black Small Bugs on Plants: 10 Proven Pest Control Methods
Meta Description: Black small bugs on plants are a leading cause of damage. Learn to identify plant pests, understand pest management for crops, spot infestations, and apply proven pest control for healthy plants.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Problem of Black Bugs on Plants
- Trivia
- Identify Plant Pests: Recognizing Black Small Bugs
- Comparison Table of Black Small Plant Pests and Control Methods
- Signs of Pest Infestation in Plants
- Damage Caused by Insects on Plants
- Common Black Bugs on Plants: Top 10 & Detailed Profiles
- Proven Plant Pest Control Methods
- Farmonaut: Precision Pest Monitoring & Management Technology
- Trivia
- Natural Pest Control for Gardens & Crops
- Preventing Pest Infestations in Crops and Ornamental Plants
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion: Achieving Healthy, Pest-Free Growth
Introduction: The Problem of Black Bugs on Plants
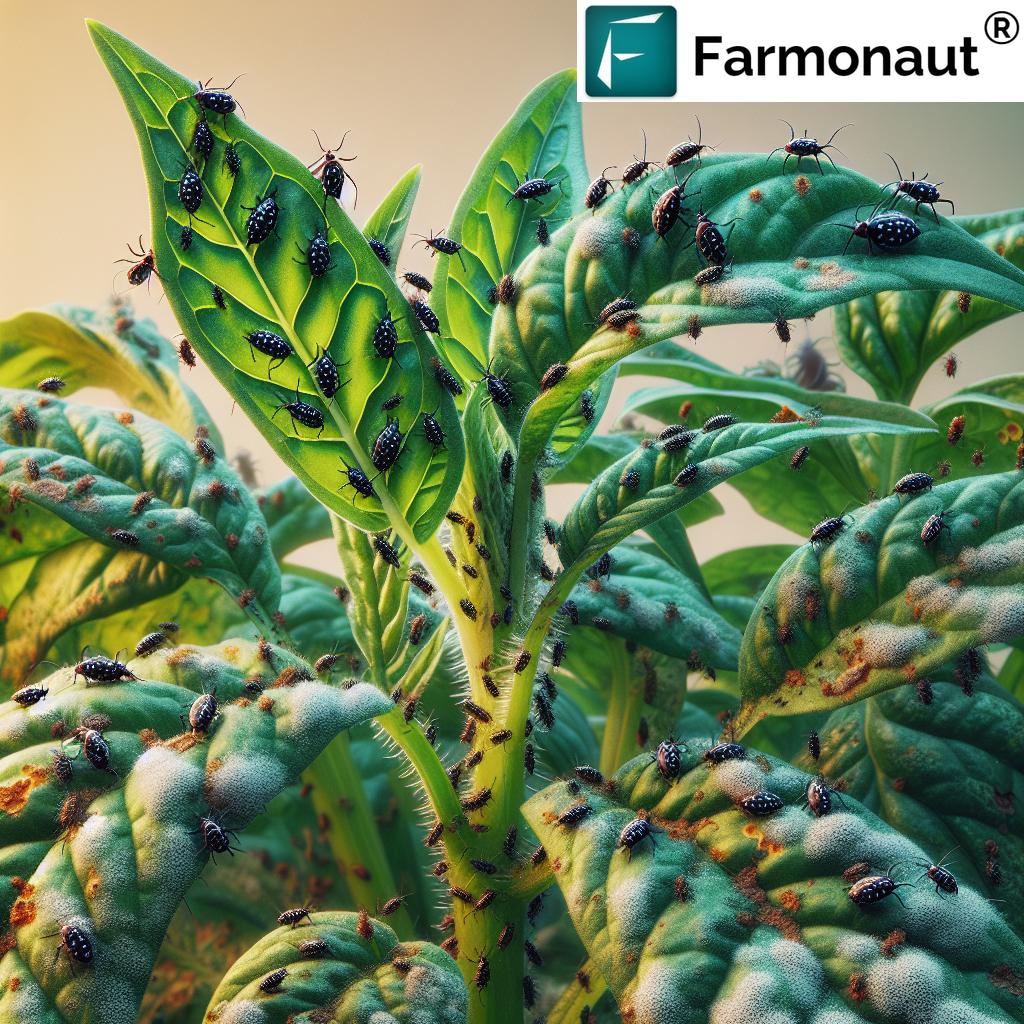
Black small bugs on plants are among the most frustrating and persistent threats faced by farmers, gardeners, and foresters worldwide. Whether you tend lush vegetable beds, broad crop fields, or cherished ornamental plants, small black insects on leaves can quickly escalate from a minor nuisance into a major infestation. These plant pests feed relentlessly on sap, roots, and foliage, leaving behind visible damage and reducing plant health and productivity.
With pests comes the risk of transmitting diseases, weakening growth, and spreading molds that stunt or even kill your plants. The battle to identify plant pests, understand their life cycles, recognize early signs of pest infestation in plants, and deploy the right control methods is ongoing – and crucial for sustainable agriculture and successful gardening.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll equip you with the actionable knowledge needed for effective pest management for crops and gardens. We’ll discuss the ten most significant black bugs on plants, their biology, signs of infestation, and 10 proven natural and integrated methods for pest control.
Pest Control Trivia
“Over 80% of plant damage is caused by small pests like black bugs, making early identification crucial for crop health.”
Identify Plant Pests: Recognizing Black Small Bugs
Anyone striving for healthy plant growth must learn how to identify plant pests efficiently. Black small bugs on plants can be tiny and elusive, especially during the early stages of infestation. However, accurate and timely identification is your first defense against escalating damage.
- Inspect regularly: Look on leaf undersides, stems, base, and at damaged leaves for clusters or tiny crawling insects.
- Look for webbing, residue, or unusual marks: Some bugs produce silk, sticky honeydew, or leave behind sooty mold and bite marks.
- Use a magnifying glass: Many common pests are only a few millimeters long.
- Monitor with sticky traps: Identify winged flying adults like fungus gnats and thrips.
- Learn their behavior: Night activity, sudden jump (flea beetles), or root feeding (wireworms, larvae) gives clues.
By focusing on these points, farmers, gardeners, and foresters can spot the initial signs of pest infestation in plants and act promptly.
Comparison Table of Black Small Plant Pests and Control Methods
| Pest Name | Common Signs of Infestation | Estimated Plant Damage Severity | Recommended Natural Control Methods | Estimated Effectiveness (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Sticky leaves, clustered bugs on stems, yellowing, sooty mold, stunted growth | High | Neem oil, ladybugs, insecticidal soap spray | 70-85% |
| Fungus Gnats | Tiny black flies near soil, larvae in moist dirt, wilting, yellowing | Medium | Dry soil, sticky traps, reduce watering, nematodes | 60-80% |
| Spider Mites | Fine webbing, speckled yellow leaves, weak growth | Medium | Spray water, predatory mites, neem oil | 75-90% |
| Thrips | Silver/brown streaks, distorted flowers, fecal spots | Medium | Sticky traps, predatory insects, blue mulch | 55-75% |
| Flea Beetles | Round holes, sudden leaf wilting, weak plants | High | Crop rotation, row covers, diatomaceous earth | 65-80% |
| Weevils | Notched leaf edges, holes in seeds/grain | Medium | Manual removal, crop rotation, natural predators | 60-75% |
| Wireworms | Root injury, galleries/tunnels in tubers/seeds | High | Crop rotation, beneficial nematodes, trap crops | 65-85% |
| Black Vine Weevil | Notched leaf margins, plant death, root damage | High | Hand collection, nematodes, sticky barriers | 70-85% |
| Striped Flea Beetle | Holes in brassica leaves, disease signs | Medium | Crop rotation, floating row covers, clean debris | 60-75% |
| Mealybugs | White/black clusters, sticky residue, sooty mold | High | Neem oil, ladybugs, insecticidal soap | 70-90% |
Signs of Pest Infestation in Plants
Recognizing the early signs of pest infestation in plants is essential for timely action. Small black bugs on plants often remain hidden until their feeding leads to unmistakable symptoms. Here are tell-tale signals:
- Sticky leaves and honeydew residue: Common with aphids, mealybugs, and some scale insects.
- Yellowing or speckled leaves: Indicates feeding from aphids, spider mites, or thrips which suck sap, disrupting water/nutrient flow.
- Holes in foliage: Flea beetles or weevils munching the leaf tissue, especially on vegetable seedlings.
- Wilting or stunted plant growth: Caused by larvae feeding on roots (wireworms, fungus gnats) or continuous sap loss.
- Notched leaf edges and distorted flowers: Classic of black vine weevil adults, thrips, or severe thrips infestations.
- Fuzzy webs and tiny specks: Indicates spider mite colonies.
- Clusters of bugs at the base or roots: Soil-dwelling pests like gnats and weevil larvae attack unseen parts.
Early and accurate detection is the key to preventing pest infestations in crops and limiting the damage caused by insects on plants.
Damage Caused by Insects on Plants
When left untreated, infestations of small black bugs on plants can result in:
- Leaf distortion and yellowing: From continuous feeding and sap loss.
- Delayed flowering and fruiting: Stunted growth or abnormal flower/fruit development due to stress.
- Sooty mold: Fungi thrive on the honeydew secretion, blocking sunlight and reducing photosynthesis.
- Root rot and stem collapse: Roots weakened by larvae or fungus gnats fail to support plant health.
- Transmission of plant viruses: Aphids, thrips, and mealybugs aid the spread of viral diseases among crops.
- Decreased crop yields: Farms see losses in both quantity and quality of produce.
For commercial farmers and those invested in food security, pest management for crops is directly linked to profitability and sustainability.
Common Black Bugs on Plants: Top 10 & Detailed Profiles
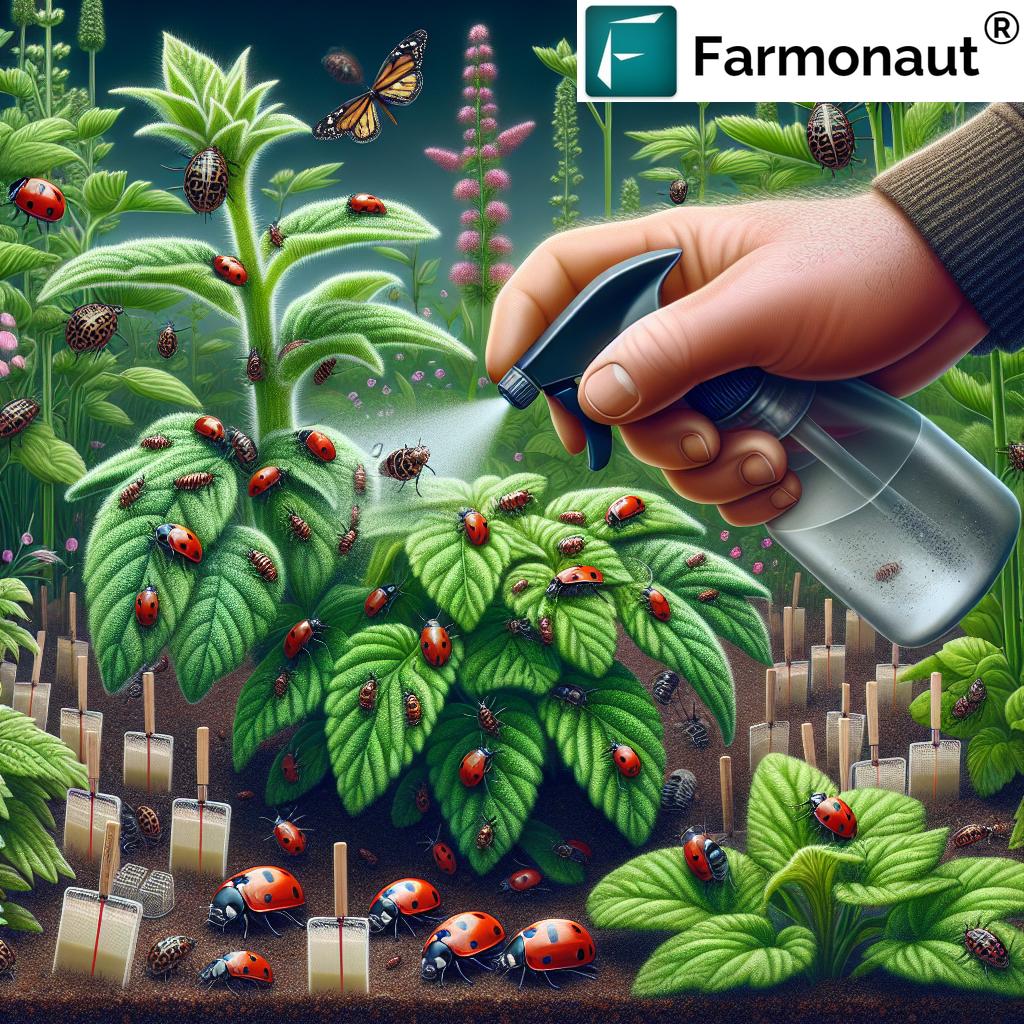
Let’s break down the most important black bugs on plants to aid identification and targeted pest management. Accurate identification helps us get rid of plant bugs using the most suitable approaches.

-
Aphids (Aphis fabae)
Aphids are soft-bodied, often black or green insects found clustered on leaf undersides and stems. They feed by sucking plant sap, causing yellowing, stunted growth, and stunted leaves. Colonies secrete honeydew, fostering sooty mold that limits photosynthesis. Worst of all, aphids are major vectors for plant viruses.
-
Fungus Gnats
Fungus gnats are tiny, black, mosquito-like flies that breed in moist soil conditions. Their larvae feed on organic matter and roots, causing root rot, plant wilting, and yellowing leaves. Infestations are first noticed by the presence of adult bugs around pot bases.
-
Spider Mites
Despite their name, spider mites are not true insects but tiny arachnids. They can be black, red, or brown and are usually found on leaf undersides, spinning fine silk webs. Signs include webbing, speckled yellow leaves, and weak growth.
-
Thrips
Thrips are slender, winged, and sometimes black. They feed by sucking plant juices, leaving silver or brown streaks and stippling on leaves. Severe infestation results in deformed flowers and black fecal spots.
-
Flea Beetles
Flea beetles are small, jumping beetles known for chewing tiny round holes in vegetable leaves, especially tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. High numbers mean quick defoliation, stunted growth, and, in bad cases, crop loss.
-
Weevils
Weevils (Curculionidae) are beetles with elongated heads (the ‘beak’). Both larvae and adults cause damage – larvae tunnel in roots and seeds, adults chew leaves and grain in storage.
-
Wireworms (Agriotes lineatus)
The adult black beetle is less damaging, but the wireworm larvae bore through tubers, seeds, roots, and stems. Their feeding leads to galleries in roots, poor plant health, and crop loss.
-
Black Vine Weevil (Otiorhynchus sulcatus)
This matte black beetle feeds at night on leaf edges, causing notching. The real problem is larvae at the base and roots, which can kill ornamental and crop plants during heavy infestation.
-
Striped Flea Beetle (Phyllotreta striolata)
Shiny black with wavy amber stripes, this brassica pest destroys cabbage leaves and transmits plant diseases. The damage caused by these insects on plants can wipe out seedbeds quickly.
-
Mealybugs
Unarmored scale insects, mealybugs thrive in warm and moist habitats. They suck plant juices, excrete honeydew (encouraging sooty mold), and can transmit viruses. Look for cottony clusters (which may appear blackish if moldy) on stems and leaf axils.
Proven Plant Pest Control Methods
Effective management of black bugs on plants always involves a multi-pronged strategy—targeting the pest’s entire lifecycle, minimizing collateral plant damage, and favoring non-toxic core solutions. Here are the 10 proven methods farmers, gardeners, and foresters rely on:
-
Cultural Controls
- Crop Rotation: Prevents pests like wireworms, weevils, and flea beetles from building up in one crop. Useful for pest management for crops over large areas.
- Proper Watering: Avoid overwatering (moist soil conditions attract fungus gnats and promote root rot).
- Sanitation: Remove weeds, dead plants, or debris—these harbor eggs, larvae, and adults for the next season.
-
Biological Control Methods
- Natural Predators: Release or attract ladybugs (aphids), predatory mites (spider mites), nematodes (soil pests), and green lacewings (mealybugs).
- Encouraging Birds and Beneficial Insects: Birds, predatory beetles, and hoverflies control a variety of insects across their life stages.
-
Physical Barriers
- Sticky Traps: Place yellow or blue sticky cards at plant base or among foliage to catch winged adults (gnats, thrips, whitefly).
- Floating Row Covers: Lightweight meshes stop flea beetles and weevils from accessing young crops.
-
Manual Removal & Monitoring
- Pick off visible bugs (beetles, weevils) and larvae.
- Regularly inspect (by hand or with magnification) the undersides of leaves and stems.
-
Insecticidal Soaps
- Sprays based on gentle soaps or dish soap and water solution disrupt cell membranes of soft-bodied insects like aphids and mealybugs.
- Apply early morning or late afternoon, and always test on a small part of the plant for sensitivity first.
-
Neem Oil and Plant-Based Sprays
- Neem Oil: Used widely for natural pest control for gardens, effective against aphids, thrips, mites, and mealybugs. It smothers eggs and disrupts feeding/egg laying.
- Other plant-based sprays (garlic, pepper, essential oils) can repel certain bugs without harming plants.
-
Diatomaceous Earth & Soil Amendments
- Sprinkle food-grade diatomaceous earth at plant base to cut and dehydrate crawling insects (flea beetles, thrips larvae).
- Introduce compost and mulch judiciously to foster beneficial organisms while keeping harmful larvae/pupae in check.
-
Beneficial Nematodes
- These microscopic worms invade larvae in the soil—especially for fungus gnats, wireworms, and root-feeding weevils.
-
Crop and Resource Management Tools
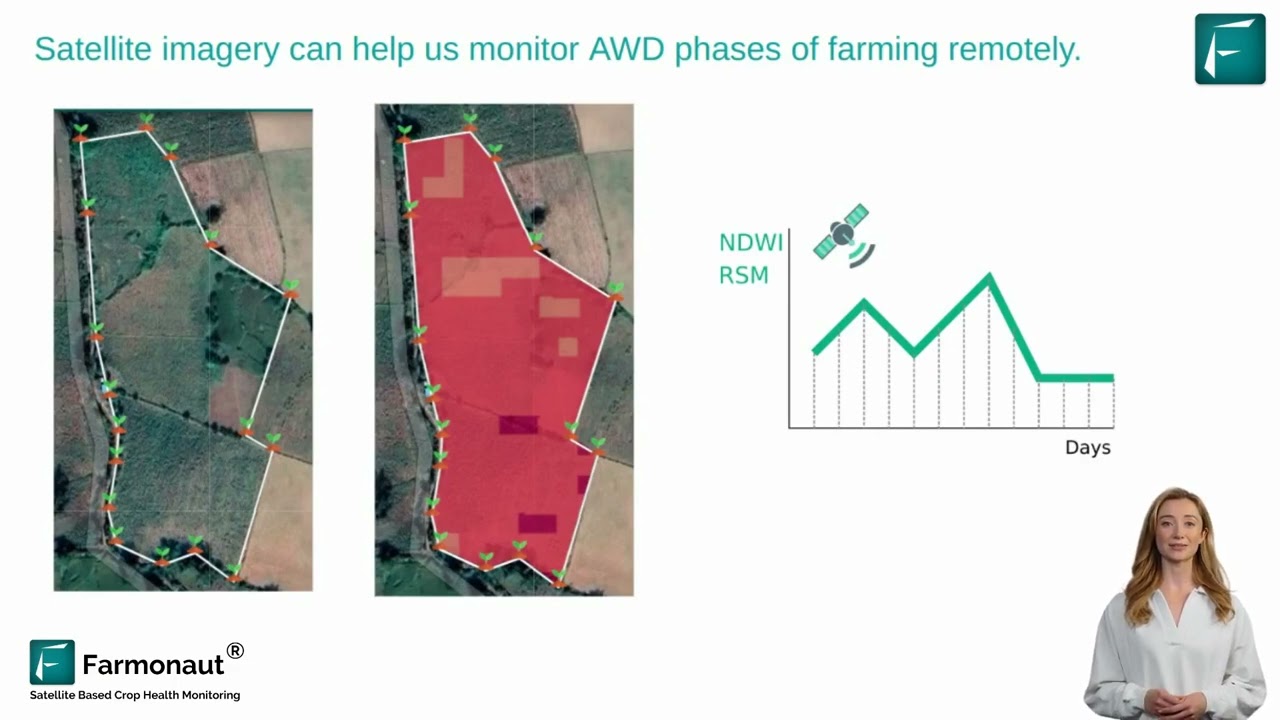
- Automated irrigation, sensor networks, and satellite crop monitoring help maintain plant health and spot stress due to pest activity early.
- We recommend using large scale farm management apps for optimal resource allocation and monitoring change over time.
-
Selective Chemical Intervention
- When infestations are out of control, use targeted, low-impact insecticides (soap, pyrethroids) and always adhere to guidelines for organic agriculture or consumer safety.
- Rotate active ingredients to reduce resistance development.
Integrated pest management—blending these approaches—is the best way to protect crop and ornamental plant health while promoting sustainability.
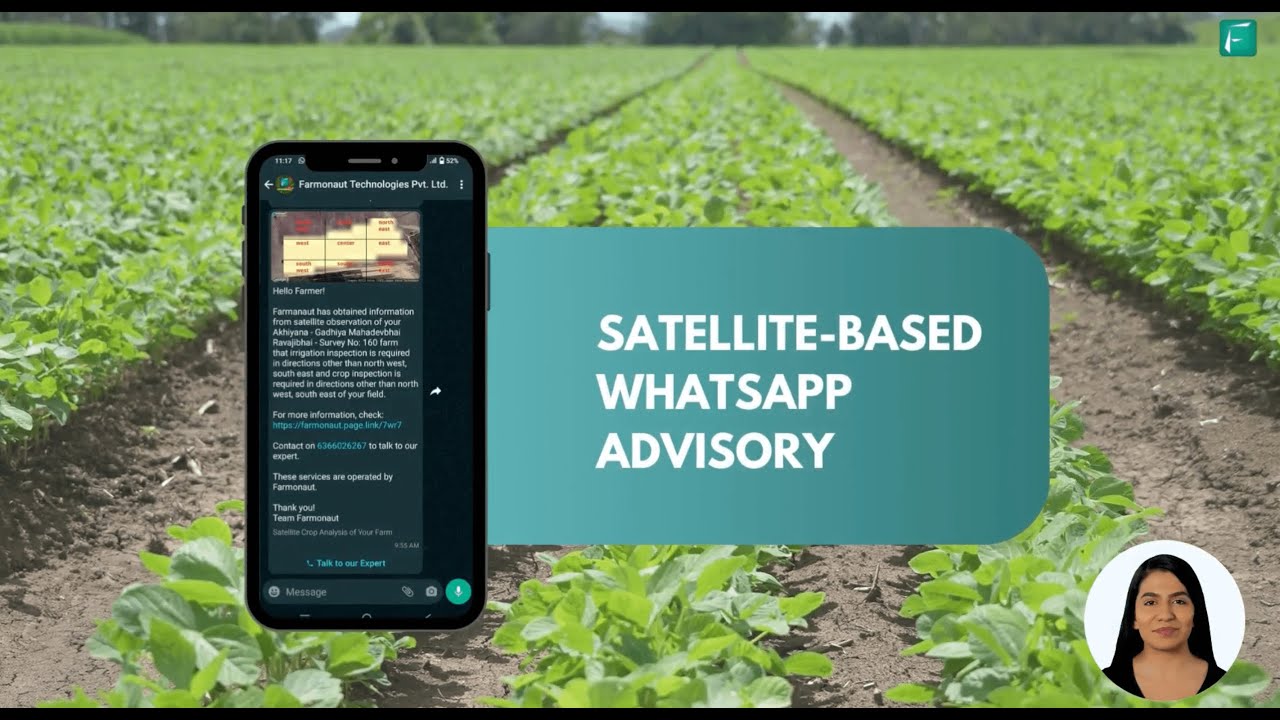
Farmonaut: Precision Pest Monitoring & Management Technology
For farmers, agribusinesses, and organizations looking for scalable, high-tech solutions to preventing pest infestations in crops, Farmonaut offers advanced, satellite-powered tools that turn accurate data into actionable insights:
-
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring:
Farmonaut’s platform combines multispectral satellite imagery with AI, offering real-time views of plant health, stress patterns, and potential pest outbreaks. By visualizing vegetation health, users can identify where pests might be hiding and catch early warning signals before major damage sets in. -
Jeevn AI Crop Advisory:
The Jeevn AI system integrates weather forecasts, satellite, and crop data to deliver personalized, field-specific recommendations—including optimal pest management for crops and irrigation advice. -
BlockChain-Based Product Traceability:
For industries concerned about supply chain integrity and biological risks, Farmonaut’s traceability solutions ensure full transparency. -
API for Developers & Businesses:
Farmonaut provides a versatile API (API access here |
Developer Docs) so partners can build their own crop health, yield monitoring, or pest scouting apps. -
Fleet and Resource Management:
For large operations, Farmonaut’s fleet management tools help optimize machinery deployment and resource tracking to reduce costs (especially relevant for crop spraying and monitoring schedules). -
Carbon Footprinting Reports:
Minimizing pesticide use and farm emissions is crucial today. Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting platform tracks emissions and helps organizations move toward more sustainable, healthy plant growth. -
Crop Loan & Insurance Satellite Verification:
To manage financial risk associated with pest/disease outbreaks, Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance tools enable accurate, satellite-based verification of losses—empowering both lenders and farmers with credible documentation.
Try Farmonaut’s powerful crop, forest, and plantation advisory on Android, iOS, or Web for smarter pest prevention and complete crop health control: Get started now.
Pest Control Trivia
“Natural pest control methods can reduce black bug infestations by up to 60% without harming plant growth.”
Natural Pest Control for Gardens & Crops
Natural pest control for gardens and large-scale crops focuses on non-toxic, eco-friendly tactics to suppress black bugs on plants effectively. Let’s highlight some practical, sustainable approaches:
1. Companion Planting
- Use deterrent plants (garlic, marigold, basil) beside high-value crops to repel harmful insects naturally.
- Trap crops lure pests away from key crops (e.g., nasturtiums for aphids).
2. Homemade Sprays
- Mix water, dish soap, and oil for insecticidal sprays. Add neem oil for broader efficacy (avoid overuse to preserve beneficials).
- Chili, garlic, and essential oil solutions can also deter certain chewing and sucking bugs.
3. Natural Predators & Insect Habitat
- Encourage ladybugs, praying mantises, lacewings, parasitic wasps for aphids, mealybugs, and caterpillars.
- Provide flowering plants and undisturbed edges to attract beneficial insects.
4. Soil Health and Compost
- Healthy, living soil with diverse microbes outcompetes and breaks down pest eggs and larvae, reducing outbreaks before they start.
5. Pruning & Removal
- Promptly remove and destroy infested leaves, stems, or flowers to contain the issue.
- Keep garden tools clean to prevent spreading pests from plant to plant.
6. Mulching & Row Covers
- Mulch maintains even soil moisture—reducing fungal gnat outbreaks and supporting root health.
- Floating row covers keep fleas, beetles, and some flies away from seedlings without pesticides.
7. Smart Water Management
- Water at the base and avoid evening/midday splashes to reduce fungal growth and harmful moisture for gnats/mites.
8. Crop Diversity and Rotation
- Mixing plant species breaks pest lifecycles, especially helpful in organic farms and permaculture settings.
9. Integrated Warning Systems
- Satellite or sensor monitoring (like Farmonaut) alerts growers to pest stress zones for targeted intervention, rather than blanket spraying.
10. Organic Biopesticides
- Neem, pyrethrin (from chrysanthemums), or biological products target pest vulnerabilities with minimal environmental harm.
Preventing Pest Infestations in Crops and Ornamental Plants
Prevention is always preferable to cure. To protect plant health and long-term yields, consistently apply these strategies:
- Regularly inspect plants, using sticky traps and direct observation on leaf undersides, stems, and soil surface.
- Maintain healthy plant nutrition—over- or under-fertilization can make plants more attractive or susceptible to pests.
- Practice proper spacing to increase airflow, reduce humidity, and discourage fungus gnats, spider mites, and molds.
- Rotate crops, even in small home gardens, to interrupt pest life cycles and reduce soil-borne larvae populations.
- Sanitize tools and materials, especially if you’re moving between plots or handling sick plants.
- Use predictive technology—for example, Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring offers early warning signs for stress and potential infestations (learn more).
- Dispose of trimmings and infected material far from main plots to avoid reintroduction during the next growing cycle.
Frequently Asked Questions About Black Small Bugs on Plants
1. What are the most dangerous black bugs on plants?
Aphids, mealybugs, spider mites, and flea beetles are particularly harmful due to their rapid reproduction, sap-sucking damage, and potential to transmit viral diseases in crops and ornamental plants.
2. How can I quickly identify plant pests?
Look for clusters of tiny bugs, sticky or shiny residue on leaves, stippling or holes in foliage, and the presence of webbing on leaf undersides. Sticky traps and hand magnification also help.
3. Are chemical pesticides the only way to control infestations?
No. Natural pest control methods—like cultural practices, biological predators, neem oil, and physical barriers—can resolve most infestations when applied early and diligently.
4. Is it possible to use technology for pest prevention?
Absolutely. Satellite crop health monitoring platforms like Farmonaut enable farmers, agribusinesses, and even home gardeners to detect early stress zones—correlating with potential pest hotspots—and inform timely, targeted interventions.
5. How can I ensure infestations don’t return?
Practice integrated prevention strategies: regular monitoring, rotation, soil health, sanitation, use of monitoring technology, and prompt removal of infected materials.
6. What if I need plant-specific pest control advisories for my region?
Try Farmonaut’s Android, iOS apps, or web platform for regionally tailored, satellite-driven advisories on pest detection, precise crop health data, and resource-efficient management.
Conclusion: Achieving Healthy, Pest-Free Growth
Black small bugs on plants represent a universal challenge, threatening yields, garden beauty, and food security alike. However, the arsenal for plant pest control has never been more sophisticated or accessible. From accurate visual identification to proven natural pest control for gardens and AI-powered, satellite crop monitoring from Farmonaut, growers worldwide now have the tools to tackle bugs and preventing pest infestations in crops or gardens.
By understanding damage caused by insects on plants, remaining vigilant for the signs of pest infestation in plants, and implementing both traditional and high-tech solutions, you can get rid of plant bugs while protecting crop health, biodiversity, and yields for the seasons ahead.
For truly scalable, affordable, and precision-based monitoring, empower yourself with Farmonaut’s real-time crop management, AI-guided advisory, and advanced reporting tools—all designed to make healthy plant growth and integrated pest management part of every grower’s future.
Images: Black Small Bugs on Plants: 10 Proven Pest Control Methods – Common black bugs on plant leaves, crop root damage by pest larvae, early pest infestation signs, and natural pest control practices for gardens. All images open Farmonaut’s App download page for precision crop pest management.