Table of Contents
- Introduction: Crop Protection Management & Its Importance
- Trivia #1
- What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
- Comparative Table: Traditional vs. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Crop Protection Management: 7 Shocking IPM Secrets!
- 1. Biological Pest Control Methods: The Power of Nature’s Predators
- 2. Cultural Pest Controls: Disrupting the Pest Life Cycle
- 3. Mechanical and Physical Controls: Barriers, Traps, and Smart Interventions
- 4. Chemical Crop Protection: Prudent & Targeted Use
- 5. Non-Pesticidal Crop Protection: Unlocking Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- 6. Technological Innovations: Modern Crop Protection Technologies Redefining IPM
- 7. Environmental and Health Considerations: Minimizing Risks, Maximizing Gains
- Trivia #2
- The Farmonaut Edge: Precision & Sustainability in Crop Protection
- Farmonaut Apps, API & Product Links
- FAQ: Crop Protection Management & IPM
- Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Food Security & Ecological Pest Management
Crop Protection Management: 7 Shocking IPM Secrets!
As we journey into the heart of crop protection management, we quickly realize that the future of sustainable agriculture hinges on our ability to balance high yields, crop quality, and environmental stewardship. Pest outbreaks, diseases, and environmental stresses threaten global food security every season. The answer lies not in heavy-handed chemical use, but in a multidimensional, eco-friendly approach—Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
In this guide, we’ll explore effective strategies, biological pest control methods, and the revolutionary technologies transforming how we safeguard our crops. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or a new stakeholder, understanding these 7 shocking IPM secrets gives us the edge for resilient, productive, and sustainable farming.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
At the core of modern crop protection management is Integrated Pest Management (IPM). This holistic, sustainable agriculture framework combines biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical crop protection tools. The IPM approach meticulously monitors pest populations, sets action thresholds, and applies control methods in an economically and ecologically sound manner. Our focus is not simply to eradicate pests, but to maintain ecological balance, minimize human and environmental risks, and secure long-term yield quality.
- Monitoring: Frequent field scouting helps us detect pests early before they cause economic damage.
- Decision Points: Using pest density data, we establish action thresholds—when (and if) intervention is warranted, instead of spraying blindly.
- Diverse Tactics: IPM integrates natural predators, cultural modifications, mechanical controls, and only when necessary, selective chemicals, ensuring a sustainable agriculture practice at every step.
Let’s compare this modern paradigm to traditional crop protection in the table below.
Comparative Table: Traditional vs. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Approaches
| Aspect | Traditional Pest Control | Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Estimated Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pest Control Methods | Mainly chemical pesticides | Combination of biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical methods | High (traditional); Low (IPM) |
| Cost Efficiency | Variable; high costs over time due to pest resistance | Improved; long-term cost savings, less pesticide needed | Moderate (traditional); Low (IPM) |
| Chemical Usage | Heavy & routine (often >80% of interventions) | Reduced (up to 70% less chemical use), only as needed | High (traditional); Low (IPM) |
| Ecosystem Impact | Frequent harm to beneficial organisms | Supports beneficial organisms; maintains biodiversity | High (traditional); Low (IPM) |
| Long-term Sustainability | Poor; issues with resistance, soil, and water contamination | High; promotes soil health, food security, and ecosystem resilience | Low (IPM) |
By adopting integrated pest management, we reduce pesticide use in agriculture, improve cost efficiency, and help ensure that our crop protection management strategies are both proactive and environmentally responsible.
Crop Protection Management: 7 Shocking IPM Secrets!
1. Biological Pest Control Methods: The Power of Nature’s Predators
Biological pest control methods form the backbone of truly sustainable crop protection management. Instead of relying solely on chemical interventions, we can harness the power of natural predators, parasites, and pathogens to keep pest populations in check. Here’s how:
- Natural Predators: Introducing ladybugs to feed on aphids, or using predatory beetles in greenhouses, provides effective control of common crop pests.
- Parasitoids: Tiny wasps can lay their eggs inside pest larvae, helping reduce infestations.
- Pathogens: Fungi, viruses, and bacteria naturally infect specific insect pests without endangering beneficial organisms or human health.
Examples from around the globe have showcased that, with these methods, pesticide reliance is slashed dramatically—beneficial insects thrive, and biodiversity is maintained.
2. Cultural Pest Controls: Disrupting the Pest Life Cycle for Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Cultural pest management is all about proactive planning to disrupt pest establishment and life cycles. These crop protection strategies are not only eco-friendly but are often cost-effective too.
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops prevents the buildup of pests and diseases specific to certain plant species.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops between main cash crops reduces weed pressure and even supports beneficial insects.
- Proper Planting Times: Adjusting sowing dates minimizes crop exposure to peak pest periods.
Implementing these sustainable agriculture practices allows us to manage pest pressures organically and promote long-term soil health and resilience.
3. Mechanical and Physical Controls: Barriers, Traps, and Smart Interventions
We also safeguard our crops with mechanical and physical crop protection controls. These direct actions limit pest access and impact without resorting to broad-spectrum chemical crop protection.
- Physical Barriers: Nets, row covers, and greenhouse screens exclude pest organisms and protect vulnerable seedlings and fruit.
- Traps: Sticky, pheromone, or light traps are used to monitor and capture pests, reducing their numbers proactively.
- Soil Solarization: Utilizing clear plastic covers to use solar heat for eliminating soil-borne pests, nematodes, and diseases pre-planting.
When we integrate these proactive measures with IPM, pest outbreaks become rare, and non-target organisms remain unharmed.
4. Chemical Crop Protection: Prudent & Targeted Use Only When Needed
Chemical pesticides remain a tool in our arsenal, but modern crop protection management teaches us to use them only when all other methods are insufficient. IPM ensures:
- Selective Application: Only specific, targeted pesticides are chosen after careful monitoring and action threshold determination.
- Reduced Quantity: Using modern spray oils and improved application technologies shrinks the environmental footprint compared to broad, routine sprays of the past.
- Resistance Management: By rotating chemicals and reducing use, we limit the chance of pests developing resistance.
These approaches help us minimize risks to humans, non-target organisms, and the broader environment, aligning with true sustainable agriculture practices.
5. Non-Pesticidal Crop Protection: Unlocking the Potential for Organic & Eco-Friendly Pest Control
Non-pesticidal management is a major pillar of ecological pest management. This philosophy promotes both organic farming and reduces our dependence on chemical crop protection entirely. Key techniques include:
- Natural Insecticides: Substances like neem oil, pyrethrum, and other botanicals act as potent, biodegradable pest solutions.
- Trap Crops: Planting decoy crops that purposely attract pests away from high-value plants (pesticide alternatives for crops).
- Field Sanitation: Regular removal of pest habitats—such as crop residues—lowers ongoing pest establishment.
These techniques are integral to organic and regenerative farming systems, allowing increased biodiversity and long-term soil health without compromising yield or quality.
6. Technological Innovations: Modern Crop Protection Technologies Redefining IPM
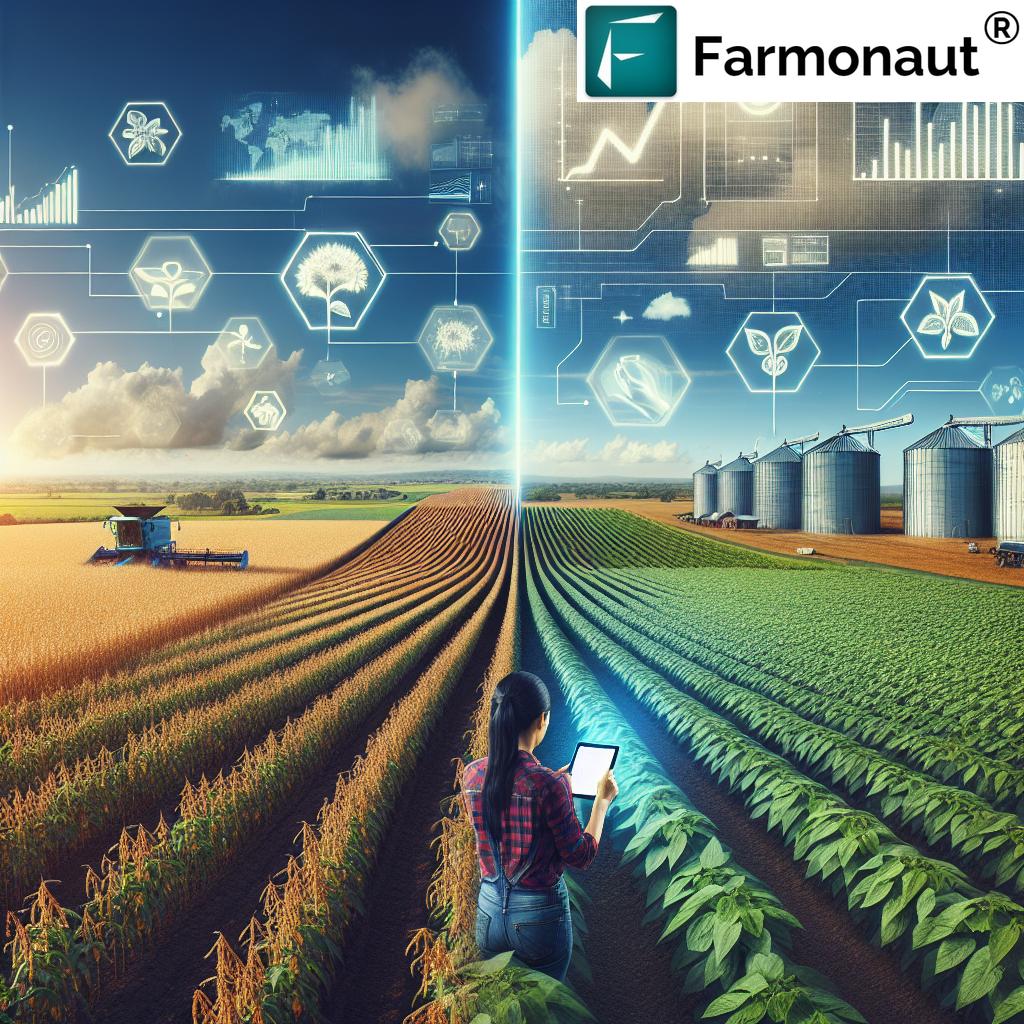
Technology is reshaping every aspect of crop protection management. The rise of precision agriculture—powered by AI, machine learning, and satellite data—enables us to apply pest control methods exactly when and where needed, reducing both costs and environmental harm.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral satellite imagery identifies stress, pest, or disease outbreaks early. Farmonaut’s platform provides instant diagnostics and actionable insights for targeted interventions—minimizing resource wastage and input costs.
- AI Advisory Systems: With tools like Jeevn AI, farmers receive real-time, personalized recommendations based on weather, crop stage, and current field data. This empowers precise decision-making for effective pest management.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Optimizing logistics cuts costs and environmental impact. For streamlined operations, see Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tools for agribusinesses.
- Blockchain Traceability: Enhances food safety and transparency at every stage of the supply chain. Read more about secure food systems with Farmonaut Product Traceability.
- Real-Time Emissions Tracking: Monitoring the carbon footprint of each activity allows us to select the most sustainable pest control measures for a healthy environment.
These advancements collectively support environmentally friendly pest control and help us reduce pesticide use in agriculture—delivering on the true promise of sustainable farming.
7. Environmental and Health Considerations: Minimizing Risks, Maximizing Gains
The environmental impact of agricultural inputs remains a pressing global concern. IPM and modern crop protection management commit to:
- Reducing Pesticide Drift: Ensuring that chemicals do not spread to non-target crops, water bodies, or nearby rural communities—preserving biodiversity and human safety.
- Maintaining Soil Integrity: Avoiding chemical overuse protects valuable beneficial organisms, improves soil structure, and enhances nutrient cycling.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Holistically integrating biological, cultural, non-chemical, and precision controls supports pollinators, native species, and resilient farm ecosystems.
By following an integrated pest management pathway, we not only repel immediate threats to crop yield and food security but foster an enduring ecological balance for generations ahead.
The Farmonaut Edge: Precision & Sustainability in Crop Protection Management
Farmonaut stands at the intersection of modern crop protection technologies and traditional farming wisdom. Our mission is to make precision agriculture—including AI-powered crop monitoring, pest management, and resource tracking—affordable and accessible for every stakeholder in agriculture.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Our platform offers real-time insights on vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and pest/disease stress. Farmers gain early warnings and actionable data to safeguard crops efficiently.
- AI-Based Advisory: The Jeevn AI System provides tailored recommendations, weather forecasts, and proactive strategies—helping users make smarter, more sustainable crop protection decisions.
- Blockchain Traceability: Transparency is ensured from farm to consumer. Track produce origins and safety with our traceability solution.
- Resource and Fleet Management: For large farms and agribusiness, optimize logistics using Farmonaut’s fleet tools, ensuring cost savings and efficient machinery use.
- Crop Loan and Insurance Verification: Secure crop financing and insurance faster with verified satellite data—discover more at Farmonaut Crop Loan & Insurance.
- Large Scale Farm Management: The Agro Admin App streamlines operations for government agencies and agribusinesses, supporting region-wide crop protection and resource allocation.
- Multi-Platform Access: Use the Farmonaut app via Android, iOS, or web for 24/7 data-driven crop management.
Ready to enable seamless integration of Farmonaut technology into your own agri-products, dashboards, or research? Access our versatile API and explore detailed developer documentation.
FAQ: Crop Protection Management & Integrated Pest Management
Q1: What is the primary goal of crop protection management?
A: Crop protection management aims to safeguard crops from pests, diseases, and environmental stresses using integrated, sustainable, and eco-friendly methods. This ensures yield, quality, and food security while maintaining environmental balance.
Q2: How does integrated pest management (IPM) differ from conventional pest control?
A: IPM combines multiple, proactive methods—biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical—driven by monitoring and threshold-based interventions. Conventional control often relies solely on chemical pesticides, leading to higher environmental and health risks.
Q3: Which non-chemical pest control methods are most effective?
A: Biological controls (like natural predators), cultural practices (such as crop rotation), and mechanical interventions (nets, traps) are highly effective and support sustainable agriculture.
Q4: What is the role of technology in modern crop protection?
A: Technologies like AI, satellite imagery, machine learning, and blockchain make pest monitoring, crop health management, and supply chain traceability smarter and more efficient. Farmonaut’s solutions help reduce costs, inputs, and environmental impact with real-time data.
Q5: Can IPM increase crop yields?
A: Yes. Integrated pest management can boost yields by up to 40% (according to available research), while minimizing environmental harm—thanks to optimized pest control and resource use.
Q6: What Farmonaut app features support crop protection management?
A: Farmonaut delivers satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-powered pest management advisories, resource and fleet tools, and blockchain traceability. These bolster our ability to anticipate, manage, and minimize pest threats efficiently.
Q7: How can I start using Farmonaut for sustainable crop protection?
A: Simply download the Farmonaut app, register your farm, and begin monitoring your fields for pest or disease risks in real-time, supported by satellite intelligence and expert AI recommendations.
Farmonaut Apps, API & Product Links
- Access the Farmonaut App Web Version:
Click Here - Android Farmonaut App:
Get it on Google Play - iOS Farmonaut App:
Download on App Store - Farmonaut Satellite & Weather API:
API Portal
| Developer Documentation - Farmonaut Product Traceability:
Transparency in Supply Chains - Farmonaut Fleet Management Solutions:
Optimize Agri-Logistics - Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting:
Track and Lower Emissions - Farmonaut Crop Loan & Insurance Verification:
Satellite-Verified Financial Security - Agro-Admin App for Large Scale Farm Management:
Region-Level Monitoring
Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Food Security & Ecological Pest Management
Crop protection management is not just an agricultural necessity—it’s a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture practices, global food security, and environmental health. We now understand that a holistic approach, rooted in integrated pest management, is our best tool for effective, long-lasting control of pests, diseases, and other threats. By combining biological, cultural, mechanical, and targeted chemical controls with the immense power of modern crop protection technologies, we can:
- Safeguard our crops and livelihoods
- Promote ecological balance and biodiversity
- Minimize environmental and human health risks
- Ensure the highest standards for food quality and yield
With the support of platforms like Farmonaut, precision farming and ecological pest management are now within reach for all. Let’s drive the future of agriculture—one that respects nature, sustains productivity, and embraces innovation at every step.