Farming Process: 9 Steps for Sustainable Yields
Meta Description: Discover the comprehensive farming process with these 9 sustainable steps, harnessing soil health, crop rotation, efficient irrigation, and precision agriculture technology for improved crop yields and food quality.
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% through optimized soil health and efficient irrigation techniques.”
Introduction to Modern Farming
Farming, or agriculture, forms the backbone of human life—it provides food, fiber, medicinal plants, and countless other products that sustain us. Over the centuries, the farming process has evolved from manual labor to incorporate advanced technology and innovative management strategies. Today’s farmers face a dynamic environment, balancing the need for sustainable yields with the demands of a growing population and climate change. This comprehensive guide unpacks the 9 crucial steps in the modern farming process and explores how cutting-edge solutions—like those available on the Farmonaut platform—are empowering farmers worldwide to enhance yields, improve food quality, and foster a more sustainable agricultural future.
“Crop rotation can reduce soil nutrient loss by 30%, supporting sustainable farming and higher food quality.”
Step 1: Planning and Preparation – The Foundation of Sustainable Yields
Every successful farming process begins with rigorous planning and thorough preparation. The choices made at this stage resonate throughout the season, directly influencing yields, soil health, and market success. Here, we examine the critical actions that modern farmers take:
- Assessing Soil Health: Understanding the structure, fertility, and nutrient profile of soil is foundational to crop success. Soil health management tools, such as laboratory analysis and satellite-based sensors, deliver actionable information to drive decisions.
- Climate Conditions: Reviewing historical weather trends and current climate scenarios guides the selection of suitable crops or livestock breeds that can thrive under local conditions.
- Market Dynamics: We must analyze demand, pricing trends, and local or global markets to select the crops or products with the greatest profitability and sustainability potential.
- Crop Selection and Rotation Schedules: Choosing the right crop rotation scheme is recognized as a best practice for maintaining fertility, maximizing yields, and breaking pest and disease cycles.
- Pest and Disease Management Planning: Early identification of potential threats allows for the strategic integration of integrated pest management (IPM) and other holistic defenses.
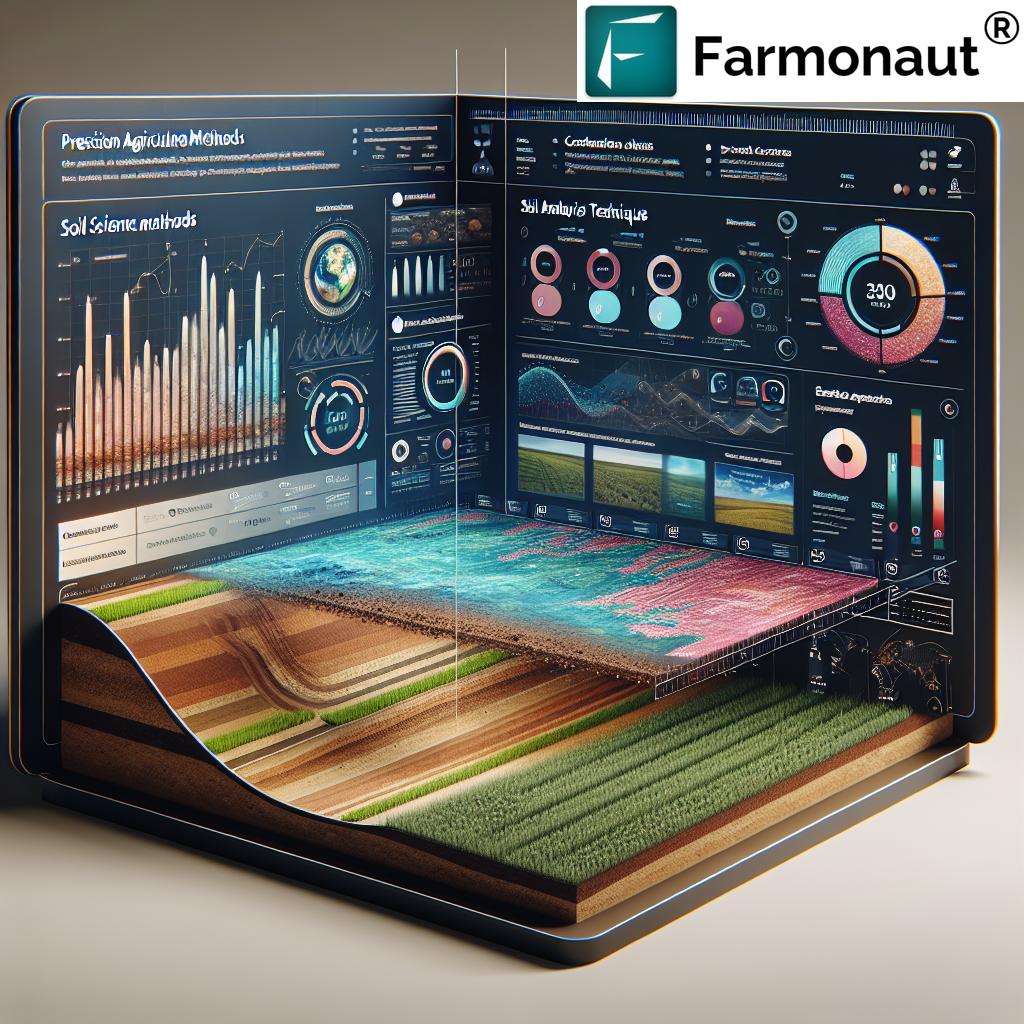
- Utilizing Precision Technologies: Systems like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Global Positioning Systems (GPS) enable the precise mapping and analyzing spatial variability across fields. This data-driven approach is core to precision agriculture technology, enhancing every subsequent step by tailoring interventions for optimal growth and resource management.
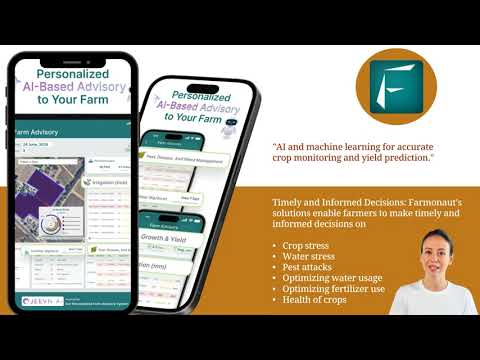
Farmonaut users gain a distinct advantage: our satellite-driven platform offers near real-time mapping and analytics, providing data on vegetation health, soil moisture, and potential stress factors. This allows farmers to make informed decisions, optimize schedules, and reduce resource wastage while supporting sustainable farming practices.
Step 2: Soil Preparation – Building Fertile Foundations
With a plan in hand, attention shifts to the meticulous preparation of the soil. This step is crucial for establishing the right environment for plant growth. Farmers traditionally employ tillage methods, including plowing and harrowing, to break up compacted layers, aerate the earth, and uproot weeds. However, an increased focus on sustainability and soil health has led to innovations:
- No-Till Farming: This method reduces soil disturbance, curtails erosion, and preserves structure. It improves water retention and creates a beneficial habitat for soil organisms.
- Cover Crops: Incorporating cover crops—like clover or vetch—not only reduces erosion but adds organic matter, improves fertility, and boosts soil health management.
- Conservation Agriculture: By rotating crops and minimizing tillage, farmers build sustainable systems with fewer inputs and healthier soil.
- Soil Amendments: Adding compost, manure, or organic matter further enhances structure and nutrient content, supporting robust growth during planting.
Monitoring soil moisture and fertility is simplified with Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring—delivering actionable insights for targeted interventions and improved yields.
Step 3: Planting – Sowing the Seeds for Abundance
Planting is the transformative phase where seeds or seedlings are placed in prepared soil. Here, method and timing are critical—each crop species and variety has specific requirements, and environmental conditions must be optimal for establishment.
- Direct Sowing vs. Transplanting: Some crops are directly sown; others benefit from transplanting seedlings grown in nurseries to improve growth and resilience.
- Precision Planting: Advanced variable rate planting uses precision agriculture technology to adjust seed density and depth—aligning rates to spatial variability in soil fertility. This ensures optimal growth, strengthens root systems, and improves resource use.
- Crop Rotation Benefits: Strategically rotating crops prevents disease and pest buildup, balances nutrient depletion, and enhances sustainability.
Farmonaut offers crop management tools that help schedule planting and select varieties based on real-time geographic data, thus improving crop yields while reducing wasted resources.
Step 4: Irrigation – Efficient Water Supply for Maximum Growth
Irrigation ensures crops receive the water needed for healthy growth, regardless of rainfall reliability. The choice of irrigation methods significantly impacts both yields and environmental sustainability:
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to the root zone with minimal loss, supporting efficient irrigation techniques and reducing water wastage.
- Sprinkler Systems: Distributes water evenly across a field, simulating natural rainfall but can be less efficient in windy or arid conditions.
- Surface Methods: Traditional furrow and flood irrigation are low-tech but often inefficient and lead to soil erosion, salinization, and water loss.
- Smart Irrigation Scheduling: Utilizing soil moisture sensors, weather data, and AI-driven models (available via Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI) to adjust frequency and amount based on actual need, driving efficiency and sustainability.
With Farmonaut’s AI and satellite-enabled systems, real-time soil moisture mapping assists in diagnosing optimal irrigation timing, ensuring plants receive the precise amount of water needed—leading to higher quality and yields.
Step 5: Fertilization – Powering Crop Growth Responsibly
Fertilization is the science of supplying essential nutrients that stimulate vigorous plant growth and bolster yields. Balanced nutrition and environmentally conscious selection of fertilizers are vital for both food quality and sustainability.
- Organic Fertilizers for Crops: Using manure, compost, and green manure provides slow-release nutrients, boosts organic matter, and promotes soil biodiversity.
- Chemical Fertilizers: Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium-based chemical fertilizers deliver rapid nutrient boosts and are widely used, but excessive use risks pollution and soil degradation.
- Precision Application: Adopting variable rate technology—made possible with tools like Farmonaut’s satellite imagery and AI-based advisories—aligns fertilizer use with actual crop need, reducing wastage and runoff.
- Balanced Nutrition: Regular soil analysis and monitoring ensure that no single nutrient is over- or under-supplied, helping prevent both deficiency and toxicity, and maintaining high food quality.
We empower farmers with data-driven recommendations for both organic fertilizers for crops and judicious chemical fertilization—helping achieve not just abundant yields, but resilient and healthy soil systems.
Step 6: Pest and Disease Management – Safeguarding Crop Health
Pests and diseases pose persistent threats to agricultural productivity worldwide. Modern integrated pest management (IPM) harmonizes multiple tactics to defend crops while protecting the broader environment:
- Biological Controls: Encouraging predatory insects, nematodes, or microorganisms that naturally suppress pests and disease.
- Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, proper spacing, and field hygiene disrupt disease cycles and deter pest infestation.
- Physical Interventions: Manual removal, traps, and barriers help prevent outbreaks without chemicals.
- Chemical Control: When required, chemical pesticides are used strategically and minimally to avoid resistance and negative environmental impacts.
- Early Warning and Monitoring: Real-time pest and disease scouting, enabled by satellite monitoring on Farmonaut, directs timely intervention for optimal plant health.
Our Jeevn AI advisory system delivers tailored risk alerts, helping farmers deploy IPM strategies confidently, achieve better quality produce, and avoid blanket chemical applications.
Enhance your crop insurance and loan processes with Farmonaut’s reliable remote farm verification.
Step 7: Harvesting – Reaping the Rewards with Modern Methods
Harvesting marks the culmination of the farming process. Timing is critical: too early or late can compromise yield and food quality. Modern crop harvesting methods and machinery are revolutionizing this stage:
- Timing: Monitoring crop maturity indices—whether by visual cues, laboratory tests, or satellite imagery—ensures harvesting at the peak of quality.
- Mechanization: Combine harvesters, reapers, and threshers streamline the process, enabling farmers to cover large fields swiftly and minimize post-harvest losses.
- Labor Savings: Automation reduces labor dependence, freeing up time for other essential steps and improving operational efficiency.
- Yield Mapping: New technologies log yield data during harvest, informing future planning and management decisions.
Our satellite monitoring and advanced yield prediction tools help determine the ideal harvest window, boosting economic returns while upholding quality.
Step 8: Post-Harvest Handling and Storage – Preserving Value
Once crops are collected, careful handling and storage are needed to maintain quality, minimize spoilage, and comply with market standards. Efficient post-harvest handling and storage drives profitability:
- Cleaning & Sorting: Removal of debris and defects ensures only premium products reach markets.
- Packaging: Proper packaging—using breathable, protective materials—reduces mechanical damage and spoilage.
- Controlled Environments: Storage facilities with regulated temperature, humidity, and light conditions delay spoilage and extend shelf life.
- Processing: Processing activities, such as drying, milling, or preparing value-added products, can significantly enhance food quality and increase margins.
- Rapid Transportation: Moving perishable goods swiftly to markets or processing centers is vital to keep crops fresh.
Farmonaut’s traceability solutions, powered by blockchain technology, guarantee transparent and reliable records from farm to table—assuring traceable quality for consumers and businesses.
Step 9: Marketing and Distribution – Connecting Farms to Consumers
The journey from farm to market involves strategic marketing, efficient logistics, and agile distribution systems:
- Market Awareness: Understanding consumer preferences and market trends helps farmers target their products efficiently—whether through local sales or global exports.
- Branding: Developing a recognizable brand or certification (for organic or sustainable products) can command premium prices and boost loyalty.
- Distribution Networks: Partnering with wholesalers, retailers, or leveraging digital platforms ensures timely delivery and reduced losses.
- Value-Addition: Processing raw crops into niche or value-added products (e.g., jams, juices, organic powders) multiplies profitability.
With Farmonaut’s fleet management solutions, agribusinesses can optimize shipping routes, monitor vehicles in real-time, and ensure traceable, efficient supply chains.
Comparative Table: Traditional Steps vs. Modern Sustainable Farming Practices
| Farming Step | Innovative Practice/Technology | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Sustainability Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning & Preparation | Precision crop selection with GIS/GPS analysis | 10-15% | Optimized resource allocation, reduced input waste |
| Soil Preparation | No-till/minimum tillage, cover cropping, satellite soil data | 8-12% | Improved soil health, erosion control |
| Planting | Variable rate seeding, rotation algorithms | 7-10% | Enhanced stand establishment, biodiversity |
| Irrigation | Drip systems, AI moisture scheduling, satellite monitoring | 12-18% | Reduced water use, minimized runoff |
| Fertilization | Variable-rate application, organic amendments, AI-advisory | 10-13% | Lower pollution, improved nutrient efficiency |
| Pest & Disease Management | IPM, satellite pest/disease alerts | 6-12% | Reduced chemical use, improved ecosystem health |
| Harvesting | Modern harvesting machinery, yield mapping, drones | 9-15% | Efficient labor use, lower losses |
| Post-Harvest Handling | IoT climate control, blockchain traceability systems | 7-10% | Extended shelf life, safer food |
| Marketing & Distribution | Digital supply chain platforms, fleet tracking | 6-8% | Reduced spoilage, enhanced transparency |
Sustainable Farming Practices: Building a Resilient Future
At the heart of sustainable farming practices is a commitment to stewardship—meeting today’s food needs without compromising soil, water, or ecosystem health for future generations. Key strategies proven to improve long-term yields and sustainability include:
- Crop Rotation Benefits: Breaking cycles of pest and disease, managing soil fertility, and enhancing resilience to climate stressors.
- Integrated Pest Management: Using a combination of biological, cultural, and limited chemical interventions to minimize negative environmental impacts.
- Efficient Irrigation Techniques: Maximizing every drop of water through drip, mulching, and smart scheduling.
- Organic Fertilizers for Crops: Building soil organic matter and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs.
- Agroforestry: Intercropping trees with annuals to stabilize soils, provide shade, and diversify products for markets.
Adopting these practices—supported by precision agriculture technology and real-time monitoring—leads to improved food quality, resilient ecosystems, and enduring prosperity for farmers.
Technology & Innovation: The Farmonaut Edge in Sustainable Agriculture
The future of agriculture lies in actionable insights, real-time data, and technology-driven decision support. That’s where we at Farmonaut come in. Our solutions are carefully designed to address the real-world challenges farmers face in the era of digital and sustainable farming.
Our Core Technologies and Services:
-
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring:
Offers detailed, multispectral maps of crop health, stress indices, soil moisture, and spatial variability—enabling precise and efficient interventions. -
Jeevn AI Advisory:
Personalized, AI-driven advisory delivers actionable crop management tips, weather forecasts, and risk alerts for pests and diseases. This tool analyzes conditions on your field in real time for maximum impact. -
Blockchain Product Traceability:
Ensure end-to-end traceability for your crops and other agricultural products, meeting strict market and consumer standards for transparency and reducing supply chain fraud. -
Fleet & Resource Management:
Monitor vehicle and machinery activity in real time with Farmonaut’s fleet management platform, lowering logistics costs and increasing overall efficiency. -
Carbon Footprint Tracking:
Quantify and monitor your farm’s carbon emissions with our dedicated dashboard for environmental compliance and maximizing sustainability. -
API Integration:
Businesses and developers can integrate our satellite and weather data with their own platforms via our API and access extensive documentation at API Developer Docs. -
Crop Loan & Insurance Assistance:
Support is available for satellite-based verification of farm areas—streamlining access to credit and insurance. Learn more about fast-tracking your crop loan approval with Farmonaut.
With our cross-platform accessibility—Android, iOS, and web-based interfaces—plus affordable, flexible pricing, we ensure precision agriculture and sustainable farm management are within reach for all farmers and agribusinesses.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Join thousands of users who trust Farmonaut to manage their entire farming process with ease and confidence. Whether you’re managing a small plot or a large commercial property, our flexible subscription models fit every need.
Sign up now and start using Farmonaut for free on web, Android, or iOS!
FAQ: Sustainable Farming Process Explained
Q1. What is the main objective of crop rotation?
Crop rotation’s main role is to maintain soil fertility, disrupt pest and disease cycles, and improve crop yields and quality. By alternating plant families, farmers reduce the risk of built-up pathogens and balance nutrient usage in the soil.
Q2. Why is soil health management crucial for sustainable agriculture?
Healthy soil underpins resilient crop growth by supporting nutrient cycling, water retention, and disease resistance. Soil health management ensures long-term productivity and sustains ecosystem services essential for future generations.
Q3. How does precision agriculture technology improve yields?
Precision agriculture technology uses GIS, GPS, and remote sensing to monitor and respond to field-level variability. This enables farmers to apply inputs where and when needed most, reducing waste and maximizing yields.
Q4. What are the key environmental benefits of integrated pest management?
Integrated pest management (IPM) minimizes reliance on chemical pesticides, mitigates pesticide resistance, preserves beneficial organisms, and protects water and wildlife—promoting a healthier, more sustainable environment.
Q5. How can Farmonaut help me make better farming decisions?
Farmonaut provides real-time crop health monitoring, weather forecasts, pest and disease alerts, and customized AI-driven advisories for every step of the farming process. This empowers you to make informed, timely, and sustainable decisions that enhance productivity and reduce costs.
Q6. What are the advantages of using organic fertilizers for crops?
Organic fertilizers for crops improve soil structure, boost microbial activity, and provide a steady nutrient release. They contribute to soil health and reduce the risk of pollution associated with chemical fertilizers.
Q7. Where can I find technical support and documentation for integrating Farmonaut’s API?
You can learn more and access all developer resources at the Farmonaut API Developer Docs page.
Conclusion: Transforming Agriculture for Sustainable Yields
The farming process stands as a testament to human innovation and adaptability. Each step—from planning and soil preparation to advanced harvesting and sustainable marketing—plays a crucial role in improving yields, enhancing food quality, and protecting our planet. By embracing sustainable farming practices, efficient irrigation techniques, integrated pest management, and precision agriculture technology, today’s farmers can cultivate abundance in a way that sustains both people and nature.
Farmonaut is proud to empower this revolution. With our next-generation, satellite-powered platform, we are committed to making high-tech farm management accessible, affordable, and results-driven for farmers, agribusinesses, and food producers worldwide. Join us to experience the future of agriculture—where every decision is smarter, more sustainable, and more profitable.