7 Shocking Granular Fertilizer Systems Innovations
“Precision granular fertilizer systems can boost nutrient efficiency by up to 40%, significantly reducing waste and runoff.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Granular Fertilizers
- Types of Granular Fertilizers
- Granular Fertilizer Application Methods
- Benefits of Granular Fertilizers
- Challenges and Considerations in Granular Fertilizer Systems
- 7 Shocking Innovations in Granular Fertilizer Systems
- Comparative Innovations Table
- Sustainable Granular Fertilizer Practices and Environmental Impact
- Farmonaut: Advancing Affordable Precision Fertilizer Solutions
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
- Farmonaut Subscriptions
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape of modern agriculture, granular fertilizers have emerged as a cornerstone technology for optimized plant growth and environmental stewardship. By offering precise nutrient distribution in soil, these solid fertilizer sources enable us as cultivators, agronomists, and innovators to support sustainable fertilizer practices while meeting rising global food demands. This guide explores not only the benefits of granular fertilizers, their application methods, and environmental impact, but focuses especially on shocking technological advancements revolutionizing the fertilizer industry for higher efficiency and sustainability.
We delve into the various types of granular fertilizers, bold new approaches in precision fertilizer application like variable rate systems (VRA), slow-release formulations, and digital innovations. Furthermore, we highlight the importance of sustainable practices and showcase how tools like Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting service help agriculture minimize its ecological footprint. Whether you’re a grower, agri-business, policymaker, or a researcher, you’ll leave here with actionable insights on how to maximize nutrient efficiency while reducing the environmental impact of fertilizers.
Understanding Granular Fertilizers: A Foundation for Efficient Nutrient Management
Granular fertilizers are dry, solid particles or granules that provide essential nutrients—including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)—to the soil in a controlled and efficient manner. Their formulation and physical structure are engineered to deliver precise concentrations of nutrients, with controlled release mechanisms for steady supply and targeted plant nutrition.
As we explore the various types, application methods, and granular fertilizer innovations, it’s crucial to remember their unique role: improving crop yield, reducing waste, and supporting sustainable, data-driven agricultural practices.
Types of Granular Fertilizers: Composition, Mechanisms, and Examples
Granular fertilizers are categorized based on nutrient composition and their nutrient release characteristics. Understanding these categories helps us select the ideal product for targeted plant growth and area requirements, reducing environmental risks.
-
Straight Fertilizers
- Contain one nutrient—like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), or potassium (K).
- Examples:
- Urea (46% N) – rapid nitrogen source.
- Single superphosphate (16% P₂O₅) – provides phosphorus.
- Muriate of potash (60% K₂O) – quick-release potassium.
- Best for supplementing specific soil deficiencies.
-
Compound Fertilizers
- Provide two or more major nutrients in balanced ratios.
- Examples: Diammonium phosphate (DAP), triple superphosphate (TSP).
- Ideal for applying a balanced nutrient profile in a single step.
-
Complex Fertilizers
- Produced via chemical reactions, ensuring nutrients are uniformly distributed within each granule.
- Prevents segregation during handling or application.
- Improves uniformity of nutrient distribution in soil.
- Suitable for crops demanding precise nutrition.
-
Slow Release Fertilizers
- Offer controlled, gradual release of nutrients for a steady nutrient supply.
- Reduce losses from leaching and volatilization.
- Polymer-coated urea and sulfur-coated urea are prime examples.
- Ideal for minimizing environmental impact of fertilizers and promoting sustainability.
Each of these types of granular fertilizers can be selected and blended according to crop, soil, and environmental requirements, contributing to comprehensive and precise nutrient management.
For those aiming to align their nutrient management with eco-friendly standards, Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting service provides vital insights into emissions, helping optimize sustainable fertilizer practices and measure your farm’s total carbon output.
Granular Fertilizer Application Methods: Maximizing Effectiveness and Efficiency
The effectiveness of any granular fertilizer system is deeply influenced by how precisely and efficiently the nutrients are delivered to the intended crops. Advanced granular fertilizer application methods tailor delivery for improved plant uptake with reduced losses, ensuring both agronomic and environmental success.
Key Granular Fertilizer Application Methods
-
Broadcast Application
- Granules are evenly spread across the soil surface—suitable for large fields but can result in uneven nutrient distribution in soil, especially under windy or variable moisture conditions.
- Often followed by incorporation to blend nutrients into the soil.
-
Band Application
- Fertilizers are placed in narrow bands near seeds or roots, promoting localized, targeted uptake.
- Reduces nutrient fixation and improves efficiency.
-
Incorporation
- Granules are mixed into the soil—either prior to planting or during field preparation.
- Minimizes volatilization of nitrogen and prevents nutrient loss by deep placement.
-
Side-Dressing
- Additional fertilizer is applied alongside growing plants during the season.
- Responds to real-time crop nutrient needs.
Choosing the optimal method from these granular fertilizer application methods depends on:
- Crop type and root structure
- Soil characteristics (texture, moisture, pH, etc.)
- Existing nutrient levels and crop stage
- Weather and irrigation practices
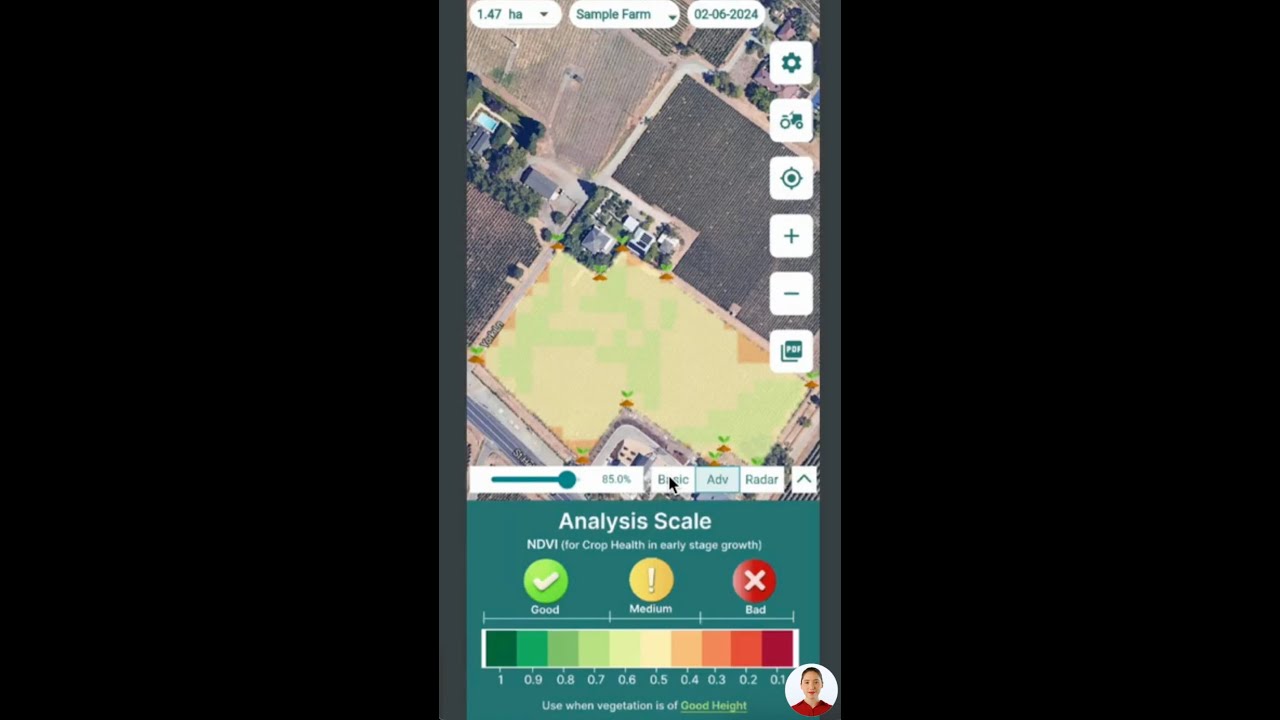
Innovative platforms like Farmonaut use real-time satellite data, field-level soil moisture, and vegetation metrics to provide actionable advice for precision fertilizer application. This lets us minimize wastage, improve uptake, and ensure every granule delivers maximum plant-available nutrients.
Benefits of Granular Fertilizers: Why Choose Granules for Sustainable Agriculture?
Adopting granular fertilizers brings numerous crucial advantages in the field—particularly regarding ease of use, robust storage, and environmental savings:
- Ease of Handling and Storage: Granules are robust and non-hygroscopic, making them simple to transport, store, and apply. No need for special tanks or mixers.
- Uniform Nutrient Distribution: Engineered granules provide even distribution across large fields, minimizing hotspots or deficient zones.
- Reduced Risk of Overdosing: Application devices can deliver a precisely measured rate of nutrients. This helps prevent over-fertilization that could otherwise damage young crops and contaminate waterways.
- Slow-Release Options: Advanced slow release fertilizers and coatings reduce rapid leaching or volatilization losses, delivering a steady supply of nutrients matched to plant requirements.
- Adaptability to Precision Methods: Compatible with the latest variable rate fertilizer application technologies, ensuring sustainability and cost-effectiveness at scale.
These key benefits of granular fertilizers are essential for profitable, responsible, and scalable food production globally.
“Innovative sustainable practices in granular fertilizers can cut environmental impact by nearly 30% compared to traditional methods.”
Challenges and Considerations in Granular Fertilizer Systems
Despite their many benefits, the use of granular fertilizers is not without challenges:
- Delayed Nutrient Availability: Many solid formulations need time (and moisture) to dissolve, which can delay nutrient release and affect early crop vigor.
- Limited Mobility: Unlike liquid fertilizers, most nutrients in granule form (N, P, K) are less mobile, risking poor root uptake unless properly incorporated or adequate irrigation is present.
- Environmental Impact: If over-applied or left on the surface, granules can leach into groundwater, run off into waterways (eutrophication), or be lost to volatilization—emphasizing the need for precision application and tailored rates.
- Segregation: Some older blended products risk segregation of nutrients during handling, leading to inconsistent field application.
Addressing these challenges calls for a combination of
technological advancements,
strategic application methods, and a strong commitment to sustainable fertilizer practices.
Did you know? For minimizing risks and ensuring compliance, Farmonaut’s Crop Loan and Insurance Verification tool uses satellite-based evidence, helping both agribusinesses and individual farmers access loans securely when adopting modern fertilizer methods.
7 Shocking Granular Fertilizer Systems Innovations Revolutionizing Nutrient Use
The future of fertilizer systems is here! Discover the seven most disruptive innovations dramatically improving nutrient efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring more sustainable crop production.
1. Variable Rate Granular Fertilizer Application (VRA)
VRA systems utilize geospatial, satellite, and sensor data to control the rate of fertilizer applied across different parts of a field in real-time. This innovation directly responds to in-field variability—such as soil fertility, moisture, and crop vigor—by adjusting nutrient rates exactly where needed. Data suggests systems can achieve
errors as low as ±6% and respond within seconds.
- Benefits: Reduced waste, maximized yield, and minimal risk of leaching or over-application.
-
Farmonaut Large-Scale Farm Management unlocks actionable insights from real-time satellite data, informing smarter, more precise VRA decisions across plantations and large fields.
2. Coated Slow-Release Fertilizers
Slow-release fertilizers encase nutrient-rich cores (like urea) with advanced polymer coatings, controlling when and how nutrients become available. This prevents nutrient surges, synchronizes supply with plant needs, and drastically reduces losses via runoff or volatilization.
- Examples: Polymer-coated urea, sulfur-coated urea.
- Benefits: Steady growth, higher nutrient use efficiency, reduced groundwater contamination.
3. Multi-Nutrient and Customized Granule Engineering
Advanced engineering now allows us to produce complex granules with site-specific formulations—combining macro (NPK) and micronutrients tailored to local soil test data. These ensure that each plant receives a balanced, tailored nutrient package for optimal growth.
- Benefits: No nutrient segregation, uniform coverage, field-wide balance in crop nutrition.
4. Tabletized and Precision-Insertion Granules
This method uses compact tablets or larger granules—sometimes with help from robotics or planters—inserted directly near the seed or root zone during planting. Delivers nutrients with laser accuracy in bands or clusters, boosting early availability and uptake.
- Benefits: Immediate root access, less environmental contact, ideal in challenging soils.
5. Smart Sensors and IoT-Driven Fertilizer Spreaders
We are now integrating smart sensors, IoT modules, and GPS into fertilizer spreaders for:
- Real-time monitoring of application rates
- Dynamic, data-driven control based on live crop/soil conditions
- Ensuring uniform nutrient distribution in soil
Benefits: Minimized over-application, audit trails for compliance, resource conservation.
6. Satellite-Guided Mapping and Fertilizer Recommendations
High-resolution satellite imagery is now used to map field variability in moisture, health (NDVI), and nutrient needs. Platforms like Farmonaut use this for advanced nutrient recommendation engines—enabling managers to allocate fertilizer precisely where, when, and how it is most needed. Learn more on our platform!
7. Blockchain-Based Nutrient Traceability Systems
With sophisticated traceability platforms, it’s now possible to track every bag—and even each field-level application—using blockchain technology. This prevents adulteration, ensures transparent nutrient sourcing, and builds trust across supply chains from manufacturer to field.
- Farmonaut Traceability Product provides such blockchain-enabled traceability for agri-supply chains, promoting transparency and proof of sustainable fertilizer practices.
Comparative Innovations Table: The Impact, Efficiency, and Scope of 7 Fertilizer Breakthroughs
| Innovation Name | Description | Technology/Method Used | Estimated Nutrient Efficiency Improvement (%) | Estimated Reduction in Environmental Impact (%) | Application Area / Suitable Crops |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Rate Granular Fertilizer Application (VRA) | Adjusts rate and placement dynamically using sensor data and maps | GPS, satellite, sensor control (VRA spreaders) | 30–40% | 25–35% | All field crops (maize, wheat, rice, soybeans) |
| Coated Slow-Release Fertilizers | Encapsulated nutrients for gradual, timed release | Polymer/sulfur-coated granules | 20–30% | 15–25% | Cereals, vegetables, fruit trees, turf |
| Multi-Nutrient Complex Granules | Blends macro and micro-nutrients in each granule | Chemical engineering/Formulating | 10–15% | 8–12% | Custom: horticulture, commercial crops |
| Tabletized Precision-Insertion Granules | Large tablets or bands placed deep near roots | Tablet engineering/Precision planters | 16–22% | 20–28% | Orchards, plantation crops, row crops |
| Smart Sensor & IoT-Driven Spreaders | Controlled via live feedback for perfect distribution | Sensor arrays, IoT, automation | 15–24% | 12–20% | All field crops, high-value veggies |
| Satellite-Guided Mapping & Recommendations | Remote mapping to customize rates spatially | Satellite imaging, AI-based analysis | 28–36% | 20–30% | Broadacre farms, precision plots |
| Blockchain-Based Nutrient Traceability | Tracks every fertilizer bag/application for transparency | Blockchain, QR/barcode tracking | 9–15% | 10–18% | Multi-sector: grains, fruit, export crops |
Sustainable Granular Fertilizer Practices and the Environmental Impact of Fertilizers
As environmental pressures mount—regulation, climate change, and consumer demand for eco-friendly production—sustainable fertilizer practices are not just an option but a necessity. Modern granular fertilizer systems support this shift through:
1. 4R Nutrient Stewardship
- Right fertilizer
- Right rate
- Right time
- Right place
This framework is at the core of precision agriculture and all leading environmental impact of fertilizers standards.
2. Advanced Slow-Release Formulations
- Reduce nitrate and phosphate leaching into waterways, preventing algal blooms and aquatic damage.
- Cut greenhouse gas emissions from fertilizer volatilization.
3. Soil Testing & AI Recommendations
- Regular soil testing enables targeting only what crops actually need—no more, no less. This technology is being democratized by platforms like Farmonaut, which automates recommendations with AI.
4. Digital Traceability and Blockchain
- Farmonaut Traceability Service ensures supply chain transparency—vital for brands adhering to eco-certification and consumer sustainability requirements.
5. Carbon Footprint Tracking
- By monitoring and reporting the greenhouse gas emissions associated with fertilizer applications, robust platforms like Farmonaut enable compliance and proactive emissions reduction.
Organizations managing large estates or corporate supply chains can utilize Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management and integrated
API’s (see API details,
API Developer Docs)
to automate recommendations, field mapping, and input traceability.
Farmonaut: Advancing Affordable Precision Fertilizer Solutions for All
We at Farmonaut are dedicated to bringing precision fertilizer application and the latest granular systems innovations to every corner of the globe—regardless of farm size, resources, or location. Our technology suite leverages:
- Multispectral satellite imagery for crop health, soil moisture levels, and nutrient deficiency mapping
- AI-powered personalized advisory (Jeevn AI) for real-time, field-specific fertilizer recommendations
- Blockchain-based traceability solutions for proof of origin, application, and sustainability
- Mobile, web/app, and API access to insights—making precision ag and sustainable fertilizer practices accessible to all
- Tools for fleet/resource management and carbon footprinting for broader ecological impact
With accessible subscription models and scalable services, we empower everyone—from individual farmers to agribusiness, NGOs, government institutions, and corporate clients—to build a sustainable, profitable, and traceable agricultural future.
Experience next-gen precision fertilizer tools — Try Farmonaut’s platform today!
Advanced plantation, forest, and crop advisory solutions are available for those focusing on high-value perennial uplands and forestry using satellite and digital fertilizer recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a granular fertilizer and how is it different from liquid fertilizers?
Granular fertilizers are solid particles or granules containing essential nutrients for crops. Compared to liquid fertilizers, granular forms offer greater storage stability, controlled release, and more precise nutrient distribution in soil. Proper application prevents leaching and over-fertilization.
What are the main benefits of granular fertilizer systems?
Key benefits include ease of use and storage, reduced application errors, even distribution, and options for slow-release formulations. Advanced systems also improve nutrient efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of fertilizers.
How do variable rate fertilizer application systems improve efficiency?
Variable rate application (VRA) systems use satellite sensors and AI analysis to tailor fertilizer rates across a field based on real data (soil, moisture, crop health). This approach ensures that only the necessary nutrients are applied, amplifying yield and minimizing waste.
What is the environmental impact of fertilizers and how can it be minimized?
If over-applied or poorly managed, fertilizers can leach or run off, causing water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The environmental impact can be minimized with slow-release granules, sustainable fertilizer practices (like 4R stewardship), and precision digital tools for application.
How can Farmonaut help me implement sustainable fertilizer practices?
Farmonaut provides satellite-based monitoring, personalized recommendations, carbon footprinting, and traceability services—helping you optimize fertilizer use, track sustainability metrics and comply with regulations affordably.
Can these innovations be scaled for both smallholder farmers and commercial agribusinesses?
Absolutely. Farmonaut’s platform is designed for scalability—from individual plots to large commercial operations—with flexible subscriptions, app-based guidance, and API integrations.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Built on Granular Fertilizer Innovation
Granular fertilizers remain an indispensable pillar of modern, sustainable agriculture, offering robust support for balanced nutrient availability, superior precision application possibilities, and a suite of innovative new systems. By embracing variable rate application, coated slow-release formulations, digital mapping, and traceable supply chains, we as an agricultural community can dramatically increase efficiency while slashing the environmental impact of fertilizers.
The transition to data-driven, sustainable fertilizer management is not only possible but affordable, thanks to platforms like Farmonaut that unlock precision agriculture and resource efficiency at any scale. We invite you to join us in building a more resilient, productive, and environmentally conscious farming future—one granule at a time.
Farmonaut Subscriptions: Powering Your Next Fertilizer Revolution
Whether you’re looking to adopt VRA, reduce your carbon footprint, or create a transparent fertilizer traceability system, Farmonaut offers subscription packages for individual farmers, agribusinesses, and government agencies.
Get started now: