Integrated Pest Management: 7 Shocking Secrets Revealed
“IPM can reduce pesticide use by up to 50%, promoting healthier crops and safer environments for farmers and consumers.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Why Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Matters
- Integrated Pest Management: 7 Shocking Secrets Revealed
- Principles of Integrated Pest Management
- Key Components of IPM Pest Control Methods
- Farmonaut & Digital Innovations in Pest Management
- Comparative Table: IPM Strategies & Effectiveness
- Benefits of Integrating IPM Approaches
- Challenges in Implementing IPM Pest Control
- Best Practices for Success in IPM Pest Management Programs
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Sustainable Agriculture Starts With IPM
Introduction: Why Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Matters
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) has become a game changer in modern agriculture. By intelligently merging various pest control methods—from biological to cultural, mechanical, and targeted chemical treatments—we, as proactive growers, can achieve healthier crops, boost yields, and protect the environment. Unlike traditional approaches that often rely too heavily on chemical solutions, IPM follows a systematic strategy that is eco-friendly, efficient, and adaptable.
Across cities, agricultural fields, and even lawns and indoor spaces, pests threaten our crops and yields. Integrated pest management empowers us to monitor, identify, and act decisively—while taking care of our soils, water, biodiversity, and future harvests.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the 7 most shocking secrets of integrated pest management, revealing actionable insights, expert-backed tips, and the science behind sustainable agriculture pest control.
“Over 70% of global farms use at least one IPM strategy to sustainably manage pests and protect biodiversity.”
Integrated Pest Management: 7 Shocking Secrets Revealed
Let’s dive into the top seven secrets that make integrated pest management the most advanced, sustainable, and effective crop pest management strategy in modern agriculture:
-
IPM is Not a Single Method, But a Multi-Tactic Approach
Contrary to popular belief, IPM involves a precise tuning of multiple pest management techniques. By joining monitoring, biological control, cultural practices, mechanical and chemical controls, we address pests holistically—boosting long-term crop health. -
Setting Action Thresholds Saves Costs & Protects Ecosystems
Immediate spraying at the first pest sighting wastes resources and can harm beneficial organisms. IPM’s science-based thresholds help us monitor pest populations to uncover when action is truly justified, making decisions cost-effective and ecologically friendly. -
IPM Reduces Pesticide Use Dramatically Without Sacrificing Yields
Properly executed IPM can reduce pesticide reliance by as much as 50%. By integrating biological, cultural, mechanical, and physical strategies, we manage persistent pests while protecting the environment, pollinators, and water quality. -
Prevention Outranks Cure: Modifying Ecosystems Reduces Pest Infestation
Through crop rotation, habitat manipulation, choosing resistant varieties, and applying pest-free rootstock, we set up crops for defense—often preventing infestations before they strike. -
Accurate Monitoring & Biological Controls Target Only Harmful Organisms
Not all insects or weeds need to be controlled. With IPM, we identify pests, differentiate between harmful and beneficial species, and deploy methods (like releasing natural predators) that keep organism populations balanced. -
High-Tech Tools and Data-Driven Systems Supercharge IPM Efficiency
Satellite-based platforms like Farmonaut give farmers powerful real-time insights into crop health monitoring, pest population mapping, weather patterns, and even carbon footprint, making it easier to plan, prevent, and intervene for optimal outcomes. -
Pest Resistance Management is Best Handled Through Integrated Strategies
Overuse of a single pesticide method invites resistance. By rotating strategies, selecting appropriate targeted controls, and monitoring populations, IPM slows resistance development, protecting future yield potential.
Principles of Integrated Pest Management
The science behind integrated pest management is rooted in four fundamental tiers. Here’s how we integrate them into pest control decisions:
-
Set Action Thresholds:
We determine the “tipping point” at which pest populations or specific environmental conditions indicate a threat: When do we need to intervene to avoid crop damage? Not every sighting justifies action! -
Monitor and Identify Pests:
Using field scouting, traps, and tools such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring, we observe and identify pests (insects, weeds, pathogens, nematodes) accurately. Knowing if an organism is beneficial, neutral, or damaging is critical. -
Prevention:
Cultural adjustments—like rotating crops, using resistant varieties, and planting pest-free rootstock—make our fields less attractive to pests in the first place. -
Select and Apply the Proper Control Methods:
Once preventive methods aren’t enough, we utilize targeted, effective, and least-harmful interventions—choosing first among biological pest control methods, traps, barriers, and highly-targeted pesticide treatments instead of blanket spraying.
Acting based on these principles ensures that our IPM programs are science-driven, flexible, and optimize both economic and ecological outcomes.
Key Components of IPM Pest Control Methods
A hallmark of integrated pest management is how it combines multiple, complementary methods to reduce pests and improve crop quality. Let’s break down the main components:
Biological Pest Control Methods
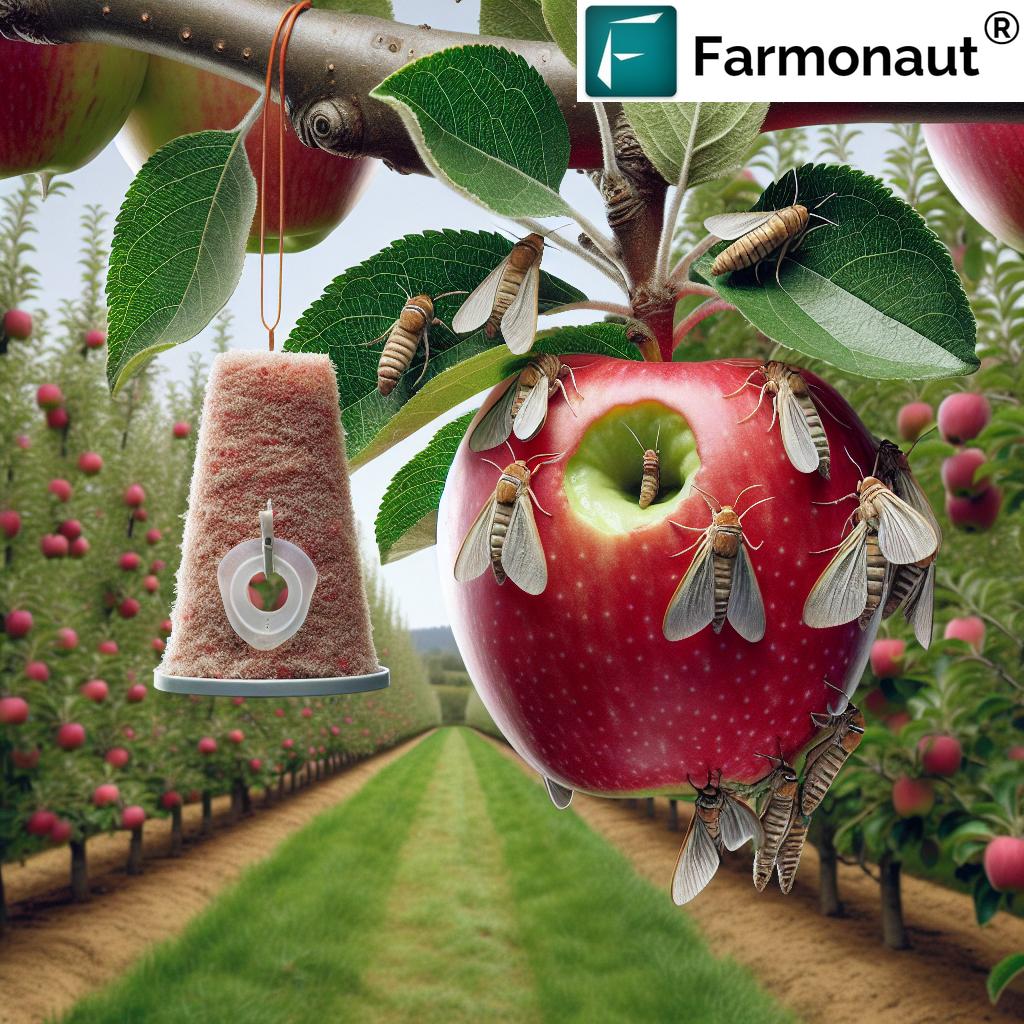
We introduce or encourage natural predators and beneficial organisms—like ladybugs, parasitoid wasps, predators, fungi, and bacteria that suppress pests. This approach is especially effective for targeting crop-specific pests while leaving pollinators and other helpful species untouched.
Cultural Pest Management Practices
Farmers modify their operations to disrupt pest lifecycles—consider crop rotations, changing irrigation patterns to fight disease, adjusting planting dates, and selecting pest-resistant crop varieties. These “background” strategies are our first line of defense in sustainable pest control.
Mechanical & Physical Controls
These are direct, hands-on methods. Think row covers, sticky traps, barriers, tillage to disrupt pest habitats, mulching to discourage weeds, and soil sterilization to reduce pathogens. Modern integrated programs use these methods precisely, often in conjunction with digital field mapping tools.
Targeted Chemical Controls
Chemical intervention is used only when monitoring data and action thresholds justify it. We select least-toxic, highly targeted pesticides—for example, using pheromones for mating disruption or spot treatments to target only the harmful organism, reducing collateral damage and slowing pesticide resistance development.
Monitoring and Identifying Pests
Frequent, data-driven observations tell us what organisms are present, how populations are changing, and when they may pose a risk. By choosing Farmonaut’s real-time satellite-based crop health monitoring, we can efficiently map pest outbreaks and quickly respond before damage threatens yields.
Looking to maximize yields and implement sustainable agriculture pest control on your farm?
Leverage Farmonaut’s blockchain-based product traceability for supply chain trust and transparency. Learn more about traceability for your crops.
Need to reduce your carbon footprint and monitor eco-friendly practices? Explore Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool for end-to-end tracking: See how to measure your impact.
Farmonaut & Digital Innovations in Pest Management
Implementing integrated pest management can feel overwhelming without the right tools. That’s where Farmonaut steps in—offering data-driven, easy-to-use solutions mapped to the latest scientific IPM pest control principles.
- Satellite-based Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut uses multispectral satellite imagery to monitor field health, soil moisture, and crop vigor—flagging potential stress areas related to pest infestations and diseases for timely action.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Our AI-driven platform provides actionable advice, from tailored crop management tips to integrating IPM strategies, helping reduce resource wastage and boost yields.
- Blockchain Traceability: Secure, transparent supply chains protect brand credibility for food and textile companies, while providing consumers with confidence in sustainably produced goods.
- Resource & Fleet Management: For large farms or agribusinesses, our tools streamline machinery usage, cut operational costs, and help optimize logistics—all from a single dashboard. Discover smarter fleet management
- API Access for Developers: Tap directly into Farmonaut’s data ecosystem to power weather and pest monitoring in your own applications.
Explore the Farmonaut API | API Developer Docs
Investing in large-scale farm management? Our scalable platform serves everyone—from individual farmers to agribusinesses and government agencies.
Comparative Table: IPM Strategies & Effectiveness
| IPM Strategy | Description | Estimated Pesticide Reduction (%) | Environmental Benefit | Estimated Crop Yield Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Rotation | Changing crops each season to break pest and disease cycles. | ~30% | Improves soil health, reduces build-up of pest populations, conserves biodiversity. | 10–20% |
| Biological Controls | Introducing natural enemies like predators or pathogens to manage pests. | 30–50% | Targets pests without disrupting beneficial organisms, pollinators, or the food chain. | 10–15% |
| Habitat Manipulation | Altering the ecosystem (weeding, mulching, irrigation, border crops) to deter pests. | 15–20% | Fosters beneficial insects and reduces pest reproduction rates. | 5–10% |
| Monitoring & Thresholds | Routine inspection and data-led action only when pest levels exceed set limits. | Up to 40% | Prevents unnecessary chemical use, targets only harmful organisms. | 10–25% |
| Mechanical Control | Traps, barriers, tillage, and other physical disruptions of pest habitats or migration. | 10–20% | Minimizes environmental residue and collateral ecosystem effects. | 5–15% |
Benefits of Integrating IPM Approaches
The primary goal of IPM isn’t just to control pests—it’s to enhance the entire agricultural ecosystem while protecting yield, reducing costs, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Reduced Crop Loss & Improved Crop Quality: Data shows integrated IPM can slash losses due to insects, pathogens, and weeds while boosting overall produce quality.
- Environmental Protection: By minimizing reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides, IPM protects our water, soils, pollinators, and non-target organisms. This supports biodiversity and ecosystem services far beyond our fields.
- Economic Savings: Using the right control at the right time cuts expenses—saving money on unnecessary chemicals, lowering application costs, and improving resource efficiency.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Practices such as carbon footprinting and resource optimization, especially through platforms like Farmonaut, keep our farms productive for generations to come.
- Slowed Pesticide Resistance Development: By keeping chemical use low and rotating modes of action, resistance development in pest populations is delayed, preserving the effectiveness of existing solutions.
- Positive Social & Policy Impacts: Healthier crops, reduced chemical exposure, and improved rural livelihoods support sustainable agriculture pest control on a regional and global scale.
Challenges in Implementing IPM Pest Control
While IPM offers immense rewards, there are practical hurdles that growers must be prepared to address:
-
Pesticide Resistance Management:
Overreliance on a single intervention—like repeated chemical applications—can spark resistance development, reducing the effectiveness of controls over time. -
Knowledge and Training Gaps:
Effective IPM requires a deep understanding of pest biology, population thresholds, and management techniques. Regular training and farmer education are essential. -
Economic Constraints:
Upfront investment in monitoring equipment, technology, and expert support can be a barrier, particularly for smallholder farmers. However, real-time tools like Farmonaut are closing the gap, making high-tech IPM affordable and accessible. -
Implementation Complexity:
Deciding which combination of cultural, biological, mechanical, or chemical approaches to use, and when, can challenge even experienced growers. Decision support tools and data-driven advisory platforms can help streamline choices. -
Monitoring & Data Interpretation:
Collecting and correctly interpreting data on pest populations and crop health is crucial. Fortunately, satellite data and AI-based advisories are making this step achievable at any farm scale.
It’s clear—while the path isn’t always simple, integrating various practices and using technology can help overcome common IPM implementation challenges.
Ready to Upgrade Your Pest Management with Farmonaut?
Experience affordable, scalable solutions for crop monitoring, pest alerts, and sustainability insights. Check our subscription options below!
Best Practices for Success in IPM Pest Management Programs
- Regular Scouting: Visually inspect fields and use monitoring data to quickly identify emerging issues—before they cross thresholds.
- Combine Multiple Control Tactics: Don’t rely on a single control method. Diversity in tactics supports both resistance management and long-term sustainability.
- Keep Accurate Records: Document pest occurrences, interventions, and results. This supports both decision making and regulatory compliance.
- Stay Informed: Follow research, leverage AI-based advisories, and join local or online IPM training programs to stay ahead of pest trends.
- Adapt to Local Conditions: Tailor strategies to your specific crops, region, and ecosystem for the most effective results.
- Invest in Eco-Friendly Digital Tools: Use innovative apps and analytics platforms to supercharge your IPM pest control—making your farm smarter, more resilient, and more sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is integrated pest management (IPM)?
Integrated pest management is a holistic approach to pest control that combines biological, cultural, mechanical, and targeted chemical methods to sustainably manage pest populations and protect crops, reducing negative effects on the environment and human health.
How does IPM reduce pesticide use?
IPM combines precise monitoring, accurate pest identification, action thresholds, and alternative controls (like biological and mechanical) before using chemicals. This targeted philosophy can cut pesticide use by up to 50%.
What are examples of biological pest control methods?
Examples include introducing ladybirds to eat aphids, releasing beneficial nematodes against soil-borne pests, encouraging parasitoid wasps, and using microbial pesticides (such as Bacillus thuringiensis) to target insects.
How can technology help with IPM?
Technologies like Farmonaut provide satellite-based crop monitoring, AI-driven advice, and real-time data analysis—guiding us to detect infestations early, take preventive measures, and intervene efficiently.
Can IPM be used for small farms?
Absolutely! IPM principles scale from backyards to large agribusinesses. Affordable platforms like Farmonaut are specifically designed to empower small and medium-sized farms with precision data.
Does IPM work for all types of pests?
Yes. Integrated pest management can target insects, weeds, disease pathogens, nematodes, and even vertebrate pests by combining customized approaches for each crop and region.
Where can I get started with IPM digital solutions?
Start by exploring Farmonaut’s Web and Mobile Apps. Monitor your fields, receive AI-driven advisories, and implement eco-friendly IPM practices with ease—no expensive hardware required!
Conclusion: Sustainable Agriculture Starts With IPM
The era of “spray and pray” is over. As we face mounting pressure to produce more food with fewer resources—and lessen our environmental impact—integrated pest management leads the way toward resilient, eco-friendly farming. IPM unites scientific knowledge, advanced technology, and hands-on experience, guiding us to healthier crops, better yields, and a safer planet.
Platforms like Farmonaut make monitoring, decision-making, and action simpler and scalable for every grower—large or small. By harnessing actionable data and integrating tried-and-true IPM pest control methods, we proudly cultivate a legacy of sustainable agriculture for generations to come.
Summary: Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive strategy that prevents pest damage and enhances crop yields by integrating biological, cultural, mechanical, and targeted chemical methods. IPM relies on monitoring and data-driven decisions, using pesticides only when necessary, and prioritizing ecosystem balance. Farmonaut, as a pioneering agricultural technology provider, delivers affordable, satellite-based solutions tailored for precision agriculture—empowering farmers globally to adopt IPM best practices, improve productivity, and make farming both sustainable and profitable.

















very informative articles or reviews at this time.
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.