Localized Farming: Unbelievable Agroforestry Benefits!
Table of Contents
- 1. Historical Context and the Evolution of Agroforestry
- 2. Key Practices in Localized Farming Systems
- 3. Environmental Benefits of Agroforestry
- 4. Economic and Social Benefits of Agroforestry
- 5. Comparative Table: Agroforestry vs. Conventional Farming
- 6. Farmonaut: Satellite-Powered Precision Agroforestry
- 7. Challenges and Considerations in Agroforestry Implementation
- 8. Farmonaut’s Tools for Sustainable Farming and Agroforestry
- 9. FAQ: Localized Farming & Agroforestry Benefits
- 10. Conclusion: Toward a Resilient Agroforestry Future
“Agroforestry can boost crop yields by up to 56% compared to conventional farming methods.”
Localized farming (also known as agroforestry) stands at the crossroads of tradition and innovation, offering an unbelievable array of benefits for farmers, the environment, and our planet’s future. By integrating trees and crops alongside livestock within the same area, we nurture resilient landscapes, safeguard resources, and unlock a revolution in sustainable land management. Today, with precision tools like those from Farmonaut, we can amplify these benefits through data-driven insights, empowering communities to harness agroforestry’s full potential.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept, evolution, key practices, and transformative advantages of agroforestry. You’ll discover detailed insights, compelling comparisons, actionable advice, and the latest technologies to integrate sustainability and productivity on your farm.
1. Historical Context and the Evolution of Agroforestry
Agroforestry may sound modern, but its roots are ancient and widespread. For centuries, indigenous communities across continents, including Native Americans in the eastern United States, have practiced managing land as a harmonious patchwork of woodlands, orchards, and forest gardens. These time-tested methods combine plant species, animal activities, and diverse cropping systems to build productive, resilient, and sustainable environments.
The term “agroforestry” was introduced in 1973 by Canadian forester John Bene, but the practice itself has been an integral part of human agriculture for millennia. Today, we honor these collective traditions even as we enhance them with research, technology, and new sustainable farming practices. By studying the historical context and evolution of agroforestry systems, we ensure that our modern approaches both respect tradition and foster innovative soil conservation techniques, biodiversity in agriculture, and climate change mitigation through agroforestry.
Ancient Practices, Modern Insights
- Forest gardens and woodlands: Early communities cultivated multi-species forests, combining edible plants, timber trees, and medicinal crops in productive mosaics.
- Orchards, intercropping, and silvopasture: Growing fruit and nut trees alongside crops and pasture, while incorporating livestock, maximized land utility and provided diversified food sources.
- Resilient landscapes: By incorporating forests into farming, communities developed a natural resilience to drought, pests, and climate fluctuations—traits especially crucial today.
Why Localized Farming is Gaining Ground
Our modern food systems face unprecedented challenges: degraded soil, biodiversity loss, water scarcity, climate instability, and rural economic pressures. Localized farming—rooted in agroforestry principles—responds by blending sustainability with productivity. As scientists, policymakers, and farm families reawaken to these systems, we witness an agroforestry renaissance that is changing the face of global agriculture.
2. Key Practices in Localized Farming Systems
Let’s explore the core practices that make up modern agroforestry systems—strategies that integrate trees with crops, livestock, and diverse plant species to deliver profound environmental and economic benefits.
Agroforestry Systems: Blending Trees, Crops, and Livestock
- Alley Cropping: We plant rows of trees and crops in alternating patterns, allowing mutual support and protection. This boosts biodiversity, improves soil and water infiltration, and enhances crop yield.
- Forest Farming Methods: Under the canopy of intentionally managed forests, we cultivate high-value specialty crops—such as medicinal plants, edible mushrooms, and understory plants. This maintains healthy forest structure while providing diversified income.
- Silvopasture Farming: By integrating trees, pasture, and livestock on the same land, we benefit from increased shade (lowering animal stress), improved forage quality, and cycle nutrients efficiently—key for sustainable animal production and soil conservation techniques.
- Riparian Forest Buffers: Establishing strips of trees and shrubs along watercourses helps control runoff, filter pollutants, stabilize riverbanks, and support aquatic ecosystem health.
- Windbreaks: We plant tree rows as wind barriers. Windbreaks reduce wind erosion, improve microclimates for crops, and prevent soil degradation.
- Integrated Crop-Livestock-Forestry Systems (ICLFS): These systems maximize land productivity by combining crops, animal husbandry, and forest management—often through intercropping, crop rotation, and planned spatial/temporal arrangements.
Integrating Trees with Crops: Productive Diversity
The integration of trees with crops and livestock isn’t just about adding trees to a farm. It’s about redefining how we manage our landscapes for maximum productivity, resilience, and biodiversity. When we practice agroforestry, we:
- Improve soil health and structure with perennial root systems
- Increase on-farm resources by producing timber, fruits, nuts, and medicinal plants
- Create microclimates that support crop and animal health
- Contribute to climate change mitigation through carbon sequestration
- Provide natural habitats that promote beneficial species diversity
A Closer Look at Silvopasture Farming
Silvopasture is one of the most sustainable practices where trees, pasture, and livestock interact for mutual benefit. On hilly or flood-prone land, silvopasture’s deep-rooted trees stabilize soil, withstand drought, and enhance water infiltration. The shade from trees shields animals and pasture from extreme weather, while leaf litter boosts soil fertility, enabling higher-quality forage growth.
Forest Farming Methods: Hidden Value in Every Canopy
Forest farming allows us to cultivate edible mushrooms, medicinal herbs, and valuable plants beneath an intentionally managed timber or fruit tree canopy. This not only creates an additional yield but also maintains forest biodiversity and supports ecosystem services vital for sustainable agriculture.
Integrated Crop-Livestock-Forestry (ICLFS): Optimized Land Use
ICLFS combines crops, animal husbandry, and forest management in a single area. By strategically rotating and integrating activities—such as timing crop planting with animal grazing and timber harvest—we maximize land productivity and ensure that soil nutrients are conserved and recycled for sustainable production.
Tree Species Selection: A Foundation for Success
Choosing the right tree species is crucial for the success of agroforestry systems. We prioritize species that:
- Enhance soil structure and boost nitrogen levels (e.g., leguminous trees)
- Provide valuable products: timber, fruits, nuts, fodder, or medicinal substances
- Adapt well to local conditions and complement crops and livestock needs
“Integrating trees in farms increases soil organic carbon by 21% on average, enhancing long-term soil fertility.”
3. Environmental Benefits of Agroforestry
The environmental advantages of agroforestry are vast—touching every facet of soil conservation, biodiversity, climate resilience, and water management. When we choose to practice agroforestry, we make a profound impact on the land and the communities it sustains.
Soil Conservation Techniques for Sustainable Farming
- Reduced erosion: Tree roots anchor the soil, their leaves mitigate rain impact, and root mass breaks compacted layers to improve structure.
- Enhanced organic matter: Leaf litter and root decay continuously add carbon and nutrients, rebuilding topsoil naturally.
- Improved infiltration: Agroforestry increases water infiltration, reduces surface runoff, and supports resilient crop growth in variable climates.
Biodiversity in Agriculture: A Built-In Pest Control and Pollinator Network
- Agroforestry landscapes offer complex habitats for birds, pollinators, and beneficial insects.
- Greater species diversity supports resilient food webs and reduces pest and disease outbreaks naturally.
- We protect endangered species and genetic resources, crucial for adapting agriculture to a changing climate.
Climate Change Mitigation Through Agroforestry
- Carbon sequestration: Trees draw down and store carbon from the atmosphere, locking it in trunk, root, and soil biomass.
- Buffering climate extremes: Tree canopies reduce heat, wind, and flooding impacts, making farm systems more climate-resilient.
Agroforestry is a natural hedge against climate change, a fact recognized by international bodies and supported by precision monitoring tools like Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting. With satellite-powered carbon tracking, we ensure our activities contribute positively to planetary health.
Water Conservation and Landscape Hydrology
- Trees slow down water flow and increase infiltration, reducing flash floods and maintaining groundwater.
- They protect surface waters with riparian buffers, minimizing agricultural runoff and preserving aquatic ecosystems.
- Shaded pastures require less irrigation, saving valuable resources.
4. Economic and Social Benefits of Agroforestry
Beyond the ecological value, agroforestry systems are engines for diversified income, community resilience, and cultural preservation.
- Diversified Income for Farmers: Agroforestry integrates timber, crops, nuts, fruits, edible mushrooms, and animal products, providing multiple revenue streams and reducing market risks. This flexibility protects farm families from market shocks.
- Job Creation: Tree planting, sustainable harvesting, and processing of diverse agricultural and forest products create rural employment, strengthening economies and reducing poverty.
- Cultural Preservation: Traditional agroforestry practices ground us in ancestral wisdom, maintain landscapes essential to cultural identity, and offer intergenerational learning opportunities.
- Community Cohesion: Shared land management strengthens social fabric and passes traditional ecological knowledge to new generations.
With modern advancements, we can now use blockchain-based traceability to add value and transparency to agroforestry products. Explore blockchain solutions for farm-to-fork product authenticity with Farmonaut Traceability.
5. Comparative Benefits Table: Agroforestry vs. Conventional Farming
| Aspect/Indicator | Agroforestry (Estimated Value) |
Conventional Farming (Estimated Value) |
Environmental Impact Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Fertility Improvement | +20% to 30% increase | 0% to 5% increase | Higher organic carbon from trees enriches soil |
| Biodiversity (species count per hectare) | 70–150 | 15–30 | More species foster resilience, reduce pests |
| Water Retention Capacity | 15–30% boost | 0–5% improvement | Tree roots improve infiltration/reduce runoff |
| Crop Yield Stability (% annual variation) | ≤15% | 20–35% | Agroforestry buffers climatic extremes |
| Carbon Sequestration (t/ha/yr) | 3–12 | 0.2–0.5 | Agroforestry sequesters far more carbon |
| Pest Reduction (% decrease, biological control) | 20–60% | 5–10% | Natural enemies thrive in diverse agroforestry systems |
6. Farmonaut: Satellite-Powered Precision Agroforestry
As we embrace the future of agroforestry, harnessing the power of precision agriculture is essential for optimum results. Farmonaut leads the charge with its satellite-based farm management platform—empowering farmers with:
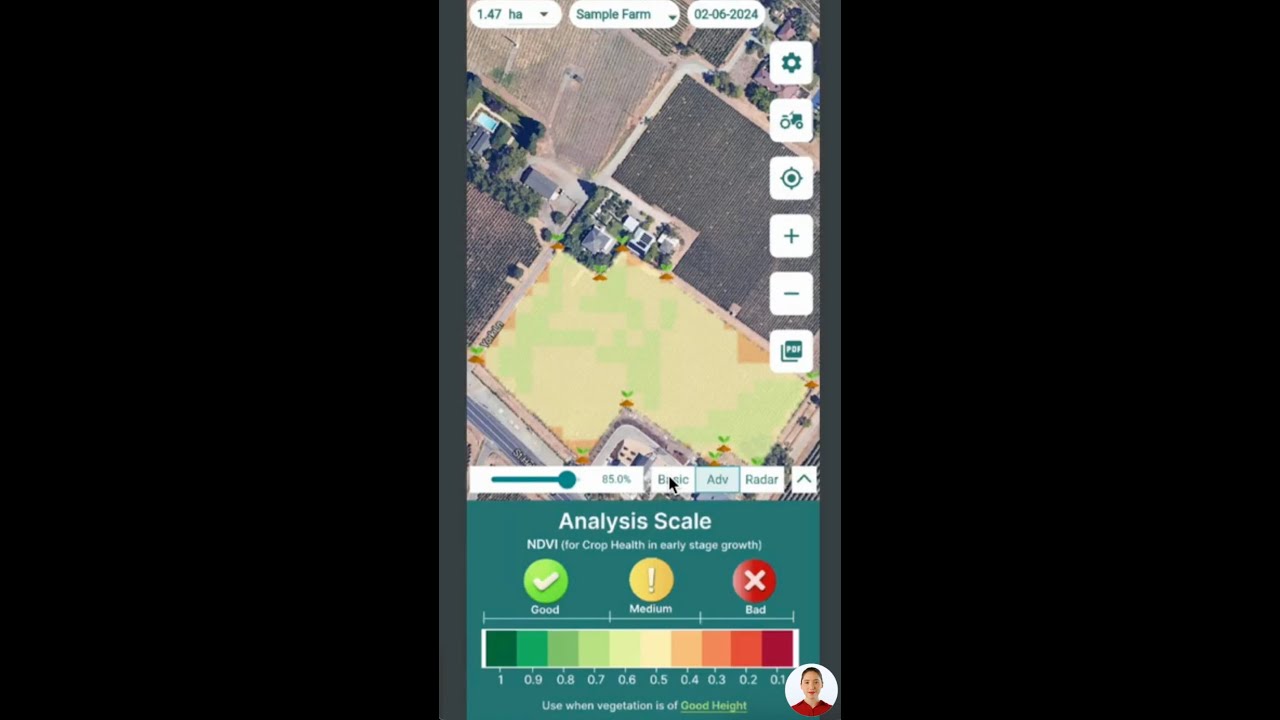
- Advanced crop health monitoring: Multispectral satellite images reveal real-time crop vigor, soil moisture, and plant stress, allowing tailored interventions for both annual and perennial species.
- Jeevn AI Advisory: Our AI-driven tool delivers dynamic, personalized advice. This ensures your crops and trees receive the right measures at the right time, enhancing yields even in diverse forest farming systems.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Show global markets your commitment to sustainability and product origin authenticity with secure traceability from field to consumer. Learn more
- Resource Management & Fleet Tracking: Efficiently manage tools, vehicles, and farm equipment across spread-out landscapes with Farmonaut Fleet Management.
- Carbon Footprinting Support: Track and report your farm’s carbon emissions or sequestration in real-time and make compliance with environmental standards easier.
Accessible via Android, iOS, and Web Apps, plus easy API and API Developer Docs, Farmonaut makes integrating technology into your agroforestry practice seamless—transforming tradition with innovation.
7. Challenges and Considerations in Agroforestry Implementation
While the benefits of agroforestry are substantial, practical challenges remain for many farmers and communities:
- Knowledge and Education:
- Transitioning to agroforestry requires new knowledge of crop, animal, and tree species selection as well as best management practices.
- Access to training and extension services is essential. This is where precision technology and online advisory platforms are invaluable.
- Policy Support:
- Adoption hinges on enabling government policies and incentives.
- Supportive frameworks foster uptake and scaling of sustainable farming practices.
- Market Access:
- Agroforestry increases product diversity (timber, fruits, nuts, crops, animal products), but market chains may not be well established for all farm-forest products.
- Developing infrastructure and improving logistics, with technologies like blockchain-based traceability, support market access and ensure fair prices for farmers.
With the right policy support, market development, and knowledge-sharing, agroforestry will flourish, ensuring environmental, social, and economic benefits across landscapes.
8. Farmonaut’s Tools for Sustainable Farming and Agroforestry
Farmonaut is committed to supporting sustainable agriculture and agroforestry worldwide. Our advanced digital platform brings together:
- Satellite Crop Monitoring: For real-time stress alerts, moisture levels, and tracking crop health across diverse forested and cropped lands. This enables prompt and informed interventions for sustainable production.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Leverage actionable, personalized, and weather-informed insights for planning your crop rotations, succession, and integrating tree planting within farm systems.
- Resource Management: Manage irrigation, farm tasks, and machinery efficiently—crucial for farms practicing silvopasture or integrated livestock and crop production.
- Large Scale Farm Management: For expansive landscapes, the Farmonaut Agro-Admin App streamlines operations and boosts productivity. Ideal for agribusinesses and organizations managing hundreds of hectares or more.
- Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory: Receive guidance on crop and forest establishment, best practices, and monitoring—all in one platform. Start here
- Crop Loan & Insurance: Satellite-based verification speeds up loan and insurance processing, helping you invest confidently in long-term agroforestry systems. Learn more
For developers and agribusiness platforms, seamless API integration and comprehensive developer documentation make it simple to build custom digital services on top of Farmonaut’s industry-leading data.
9. FAQ: Localized Farming & Agroforestry Benefits
What is agroforestry, and how does it differ from conventional agriculture?
Agroforestry is the intentional integration of trees, crops, and sometimes livestock within the same area. Unlike conventional monoculture farming, agroforestry systems are diverse, combining multiple species to create productive, resilient, and environmentally sound landscapes.
What are some examples of products and income sources in agroforestry systems?
Agroforestry provides diversified income for farmers by producing timber, fruits, nuts, edible mushrooms, medicinal plants, honey, animal products, and sustainable wood-based products. This variety reduces economic risks and responds flexibly to market demands.
How does agroforestry contribute to climate change mitigation?
Trees in agroforestry systems sequester significant amounts of carbon in both their biomass and the soil. Perennial root systems enhance soil carbon storage, while diverse canopies buffer climate extremes and reduce the farm’s carbon footprint. Track and manage your farm’s carbon emissions with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solutions.
What role do digital technologies play in modern agroforestry?
Digital tools such as Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop and tree monitoring, AI-driven advisory systems, and blockchain traceability have revolutionized how we plan, manage, and market agroforestry products. From early-warning weather alerts to digital supply chain validation, precision technologies increase productivity and transparency.
What are the main environmental benefits of agroforestry?
- Enhanced biodiversity in agriculture through diverse species and habitats
- Soil conservation techniques that improve fertility and reduce erosion
- Water conservation and improved infiltration preventing floods and drought
- Climate resilience via carbon sequestration, microclimate regulation, and buffering against weather extremes
10. Conclusion: Toward a Resilient Agroforestry Future
Localized farming or agroforestry is more than a sustainable agricultural practice—it’s a transformative approach to land management that integrates the wisdom of the past and the promise of modern technology. By combining trees, crops, and livestock, and adopting new precision tools like those from Farmonaut, we are building truly resilient food systems for a changing world.
- We create environments that foster biodiversity, enhance soil health, and support rural livelihoods.
- We increase income stability and agricultural productivity through diverse, market-responsive products.
- We mitigate the impacts of climate change, sequester vast amounts of carbon, and contribute positively to the health of the planet.
- We honor traditional knowledge while leveraging cutting-edge data-driven insights.
Whether you are a farmer, agribusiness, policymaker, or sustainability advocate, now is the time to invest in agroforestry. Embrace the remarkable benefits of this holistic practice—supported by the science and digital innovation from Farmonaut—and help create a greener, more secure future for all.
Start your journey towards sustainable agriculture and resilient landscapes—discover Farmonaut today!