Mastering Cotton Protection: Understanding Bollworm Types and Pink Bollworm Life Cycle for Farmers
As leaders in agricultural technology, we at Farmonaut understand the critical challenges faced by cotton farmers worldwide. One of the most persistent threats to cotton crops is the bollworm, a destructive pest that can significantly impact yield and quality. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of bollworms, with a particular focus on the pink bollworm life cycle and various bollworm types. Our goal is to equip farmers with the knowledge and tools necessary to protect their cotton crops effectively.
Understanding Bollworms: A Farmer’s Nemesis
Bollworms, often referred to as “ball worms” by some farmers, are a group of lepidopteran insects that pose a severe threat to cotton crops. These pests can cause extensive damage to cotton bolls, leading to significant economic losses for farmers. Let’s explore the main types of bollworms that cotton farmers need to be aware of:
- Cotton Bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera)
- Pink Bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella)
- Spotted Bollworm (Earias vittella)
- American Bollworm (Helicoverpa zea)
Each of these bollworm species has unique characteristics and life cycles, but they all share a common trait: their potential to devastate cotton crops if left unchecked.
The Pink Bollworm: A Closer Look
Among the various bollworm species, the pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) is particularly notorious for its destructive potential and complex life cycle. Understanding the pink bollworm life cycle is crucial for implementing effective control measures.
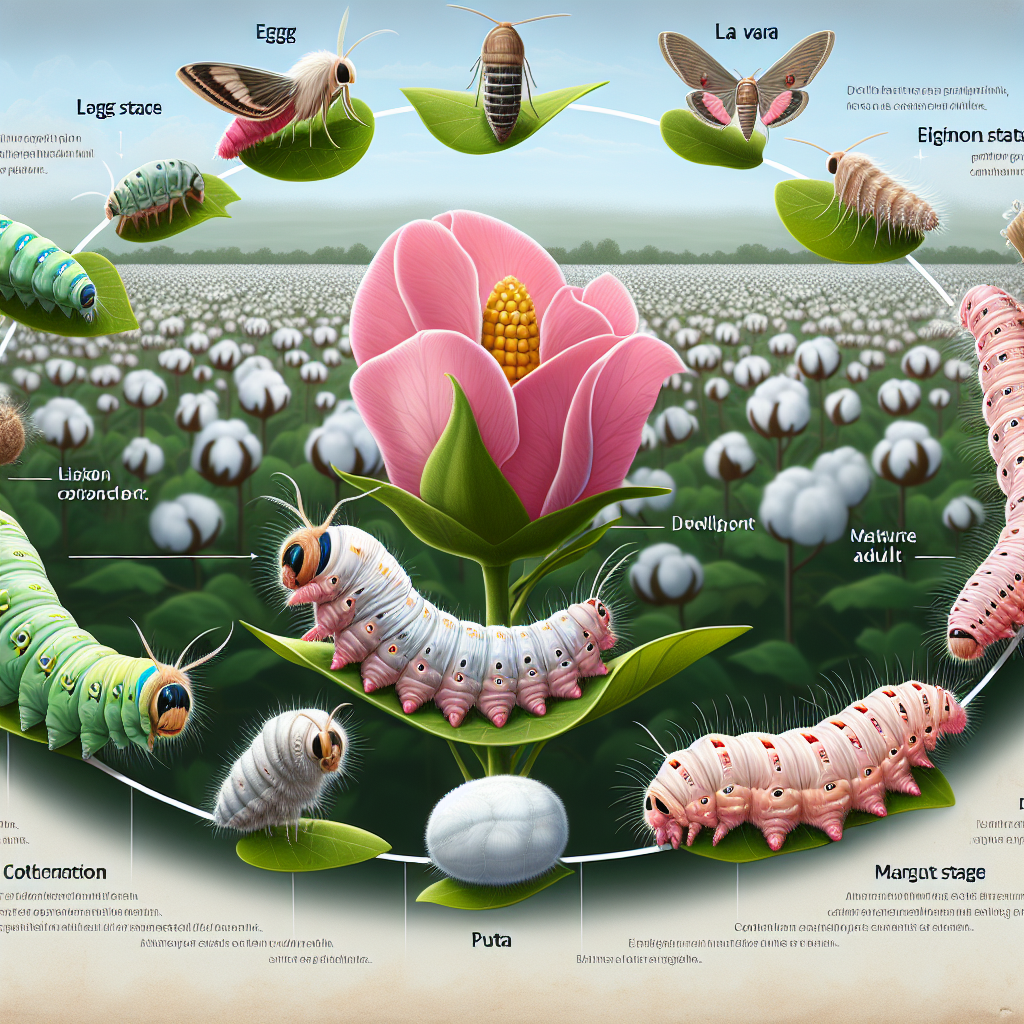
Pink Bollworm Life Cycle: From Egg to Adult
The pink bollworm goes through a complete metamorphosis, consisting of four distinct stages:
- Egg Stage: Adult female moths lay tiny, oval-shaped eggs on cotton plants, typically on the undersides of leaves or on young bolls.
- Larval Stage: Upon hatching, the larvae (caterpillars) immediately seek out cotton bolls to feed on. This stage is the most destructive part of the pink bollworm life cycle.
- Pupal Stage: After feeding for about 2-3 weeks, the larvae spin cocoons and enter the pupal stage, either within the cotton boll or in plant debris on the ground.
- Adult Stage: Moths emerge from the pupae, ready to mate and lay eggs, thus continuing the cycle.
The entire pink bollworm life cycle can be completed in as little as 30 days under optimal conditions, allowing for multiple generations within a single growing season.
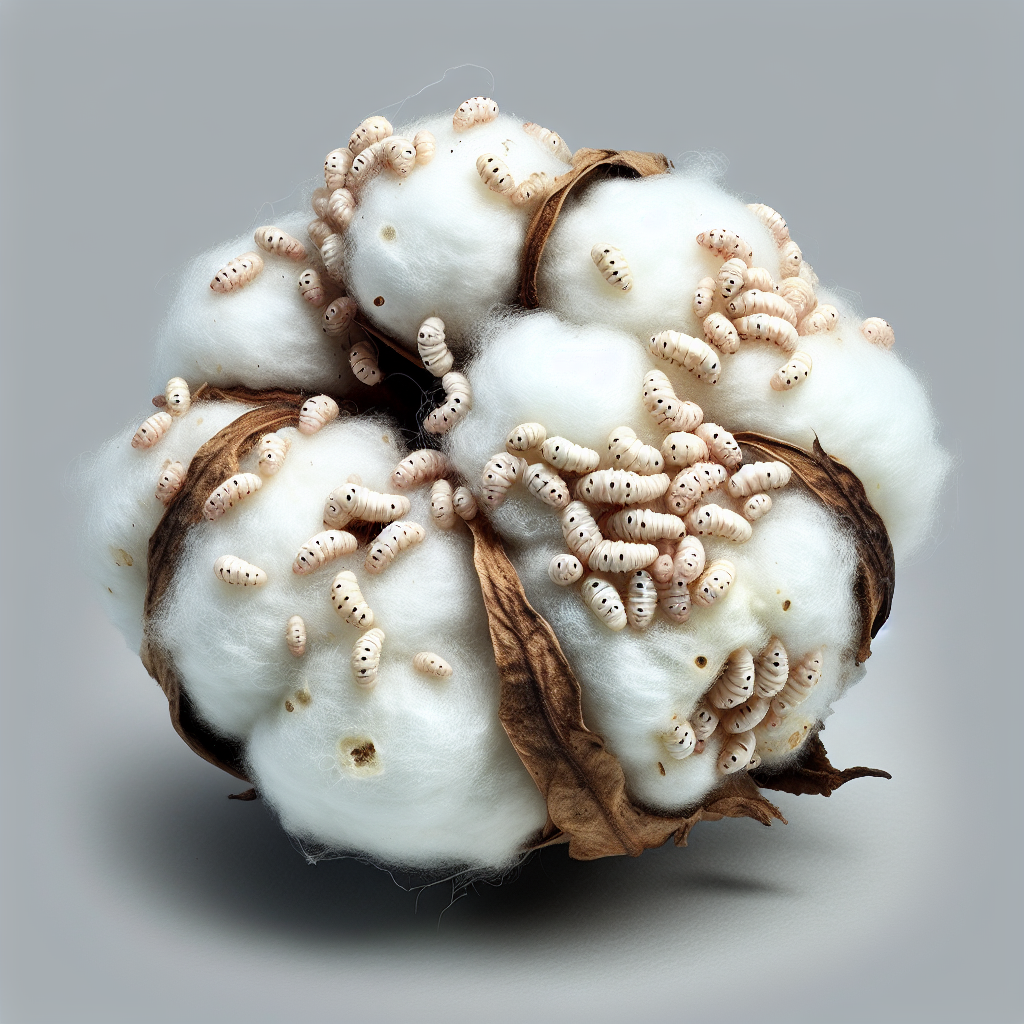

Spotting the Spotted Bollworm
While the pink bollworm often takes center stage in discussions about cotton pests, the spotted bollworm (Earias vittella) is another significant threat that farmers must be aware of. This pest, also known as the spiny bollworm, can cause extensive damage to cotton crops if not properly managed.
Characteristics of the Spotted Bollworm
- Adult moths have distinctive green forewings with white spots, hence the name “spotted bollworm.”
- Larvae are initially pale yellow but turn pink as they mature, with dark spots along their body.
- They primarily attack young bolls and squares, causing them to shed prematurely.
The spotted bollworm’s life cycle is similar to that of the pink bollworm, but it tends to have a shorter development time, potentially leading to more generations per season.
Integrated Pest Management: A Holistic Approach to Bollworm Control
At Farmonaut, we advocate for an integrated pest management (IPM) approach to control bollworms effectively. This strategy combines various methods to minimize pest damage while reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. Here are some key components of an effective IPM program for bollworm control:
- Monitoring and Early Detection: Regular field scouting and the use of pheromone traps can help detect bollworm infestations early.
- Cultural Practices: Implement practices such as crop rotation, early planting, and thorough post-harvest field sanitation to disrupt the bollworm life cycle.
- Biological Control: Encourage natural predators and parasitoids that feed on bollworm eggs and larvae.
- Bt Cotton Varieties: Consider planting genetically modified cotton varieties that express Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) proteins, which are toxic to many bollworm species.
- Chemical Control: When necessary, use targeted insecticides as part of a broader IPM strategy, being mindful of resistance management.
Leveraging Technology for Bollworm Management
At Farmonaut, we believe in harnessing the power of technology to revolutionize pest management in cotton farming. Our satellite-based crop monitoring system offers several advantages over traditional methods:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large-scale (100s to 1000s of hectares) | Limited (10s of hectares per flight) | Limited (Depends on sensor placement) |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular (Every 3-5 days) | As needed (Labor-intensive) | Continuous (But localized) |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low | High (Drone purchase required) | Medium to High (Sensors needed) |
| Ease of Use | High (Cloud-based platform) | Medium (Requires trained operator) | Medium (Technical setup required) |
| Data Analysis | Advanced AI-driven insights | Manual interpretation often needed | Limited to sensor data |
Our satellite-based system provides comprehensive, large-scale monitoring that can detect early signs of bollworm infestation across vast cotton fields. By analyzing multispectral imagery, we can identify areas of stress in cotton plants that may indicate pest activity, allowing for timely and targeted interventions.
The Farmonaut Advantage in Bollworm Management
Our advanced agricultural technology platform offers several key benefits for cotton farmers battling bollworms:
- Early Detection: Our satellite imagery can detect subtle changes in crop health that may indicate bollworm activity before it’s visible to the naked eye.
- Precision Application: By identifying specific areas of infestation, farmers can apply pest control measures more precisely, reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Historical Data Analysis: Our platform stores historical crop data, allowing farmers to identify patterns in bollworm outbreaks and plan preventive measures for future seasons.
- Integration with Weather Data: By correlating pest activity with weather patterns, we help farmers anticipate and prepare for potential bollworm outbreaks.
- AI-Powered Recommendations: Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized recommendations for bollworm management based on real-time crop data and expert knowledge.
To experience the power of Farmonaut in managing bollworm infestations and other agricultural challenges, visit our app page or download our mobile app for Android or iOS.
Bollworm Resistance Management: A Critical Consideration
As we continue to battle bollworms in cotton production, it’s crucial to address the issue of pest resistance to control methods, particularly to Bt cotton and chemical insecticides. Resistance management is an essential component of long-term bollworm control strategies.
Strategies for Managing Bollworm Resistance
- Rotate Bt Cotton Traits: Use different Bt cotton varieties with distinct modes of action to prevent the development of resistant bollworm populations.
- Implement Refuge Areas: Plant non-Bt cotton or other host crops in designated refuge areas to maintain susceptible bollworm populations.
- Practice Insecticide Rotation: Alternate between insecticides with different modes of action to reduce selection pressure on bollworm populations.
- Monitor for Resistance: Regularly test bollworm populations for signs of developing resistance to Bt toxins or commonly used insecticides.
- Integrate Multiple Control Methods: Combine cultural, biological, and chemical control methods to reduce reliance on any single approach.
The Role of Climate Change in Bollworm Management
Climate change is having a significant impact on pest dynamics, including those of bollworms. As agricultural technology experts, we at Farmonaut are closely monitoring these changes and adapting our solutions accordingly.
Climate Change Effects on Bollworm Populations
- Extended Growing Seasons: Warmer temperatures may lead to longer growing seasons, potentially allowing for more bollworm generations per year.
- Altered Geographic Distribution: Changing climate patterns may shift the geographic range of bollworm species, introducing them to new areas.
- Increased Overwinter Survival: Milder winters could improve the survival rates of overwintering bollworm populations.
- Changes in Crop-Pest Synchrony: Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns may affect the timing of bollworm emergence relative to crop development stages.
Our satellite-based monitoring system and AI-powered analytics are uniquely positioned to track these climate-induced changes in bollworm behavior and distribution. By providing real-time data on crop health and environmental conditions, we help farmers adapt their bollworm management strategies to these evolving challenges.
Sustainable Bollworm Management: Looking to the Future
As we continue to develop and refine our agricultural technology solutions, we’re committed to promoting sustainable practices in bollworm management. This includes:
- Precision Pest Management: Using our satellite imagery and AI analytics to enable highly targeted pest control interventions, minimizing unnecessary pesticide use.
- Ecosystem-Based Approaches: Promoting farming practices that enhance natural pest control mechanisms and biodiversity.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Empowering farmers with real-time, actionable insights to make informed decisions about bollworm management.
- Collaborative Research: Partnering with agricultural research institutions to develop innovative, eco-friendly bollworm control methods.
- Farmer Education: Providing comprehensive training and resources to help farmers implement best practices in bollworm management.
Conclusion: Empowering Farmers in the Fight Against Bollworms
Understanding the intricacies of bollworm biology, particularly the pink bollworm life cycle and the characteristics of pests like the spotted bollworm, is crucial for effective cotton crop protection. By combining this knowledge with advanced agricultural technology solutions like those offered by Farmonaut, farmers can significantly enhance their bollworm management strategies.
Our satellite-based monitoring system, AI-powered analytics, and comprehensive farm management tools provide cotton farmers with unprecedented insights into crop health and pest activity. This technology-driven approach, integrated with sound agronomic practices and sustainable pest management strategies, offers a powerful defense against the threat of bollworms.
We invite cotton farmers and agricultural professionals to explore the full potential of our platform in revolutionizing bollworm management and overall farm productivity. To learn more about our API services for developers and businesses, visit our API documentation page.
Join us in the journey towards more sustainable, efficient, and productive cotton farming. Together, we can overcome the challenges posed by bollworms and other agricultural pests, ensuring a more food-secure future for all.
FAQ Section: Bollworm Management in Cotton Farming
-
Q: What is the difference between a bollworm and a ball worm?
A: There is no difference. “Ball worm” is a colloquial term sometimes used to refer to bollworms. The correct scientific term is “bollworm,” which describes various moth larvae that attack cotton bolls and other crops. -
Q: How can I identify a pink bollworm infestation in my cotton field?
A: Look for signs such as small, irregular holes in cotton bolls, premature boll opening, and the presence of pinkish-white larvae inside the bolls. Our Farmonaut satellite monitoring system can also detect early signs of stress in cotton plants that may indicate pink bollworm activity. -
Q: What is the most effective way to control spotted bollworms?
A: An integrated pest management (IPM) approach is most effective. This includes regular monitoring, using pheromone traps, encouraging natural predators, planting resistant cotton varieties, and applying targeted insecticides when necessary. Our Farmonaut platform can help you implement and optimize these strategies. -
Q: How long does the pink bollworm life cycle take to complete?
A: The pink bollworm life cycle typically takes about 30-40 days to complete under optimal conditions. However, this can vary depending on environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. -
Q: Can Farmonaut’s satellite technology detect bollworm infestations before they become visible?
A: Yes, our advanced satellite imagery and AI analytics can detect subtle changes in crop health that may indicate early stages of bollworm infestation, often before visible symptoms appear. This allows for proactive management strategies. -
Q: How does climate change affect bollworm populations in cotton?
A: Climate change can lead to extended growing seasons, altered geographic distributions of bollworm species, increased overwinter survival, and changes in crop-pest synchrony. Our platform helps track these changes and adapt management strategies accordingly. -
Q: Are there any natural predators of bollworms that I can encourage in my cotton field?
A: Yes, several natural predators can help control bollworm populations, including parasitic wasps, lacewings, ladybugs, and certain bird species. Implementing habitat management practices can encourage these beneficial organisms. -
Q: How often should I monitor my cotton crop for bollworm activity?
A: Regular monitoring is crucial, especially during the flowering and boll formation stages. With Farmonaut’s satellite monitoring, you can receive updates every 3-5 days, complemented by weekly in-field scouting for best results. -
Q: Can bollworms develop resistance to Bt cotton?
A: Yes, bollworms can develop resistance to Bt cotton over time. It’s important to implement resistance management strategies, such as planting refuge areas and rotating Bt traits. Our platform can help you track the effectiveness of your Bt cotton and adjust strategies as needed. -
Q: How can I get started with Farmonaut’s bollworm management solutions?
A: You can start by visiting our app page or downloading our mobile app for Android or iOS. For more advanced features and API access, check out our developer documentation.
Subscribe to Farmonaut for Advanced Bollworm Management
Ready to take your bollworm management to the next level? Subscribe to Farmonaut’s advanced agricultural technology platform and gain access to cutting-edge satellite monitoring, AI-powered analytics, and personalized farm management tools.
By subscribing, you’ll join a community of forward-thinking farmers who are leveraging technology to combat bollworms and other agricultural challenges effectively. Take the first step towards more sustainable and profitable cotton farming today!