Mite Management Secrets: 7 Hacks Farmers Swear By
- Introduction: The Importance of Mite Management in Agriculture, Farming, and Forestry
- Types and Impact of Mites in Farming and Forestry
- Understanding Mite Infestations: Causes, Signs, and Risks
- Mite Management Secrets: 7 Proven Hacks for Farmers
- Hack 1: Embrace Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Sustainable Mite Control
- Hack 2: Harness Biological Control of Mites with Natural Predators
- Hack 3: Strengthen Cultural Practices to Disrupt Mite Life Cycles
- Hack 4: Precision Chemical Control—The Responsible Use of Miticides for Crops
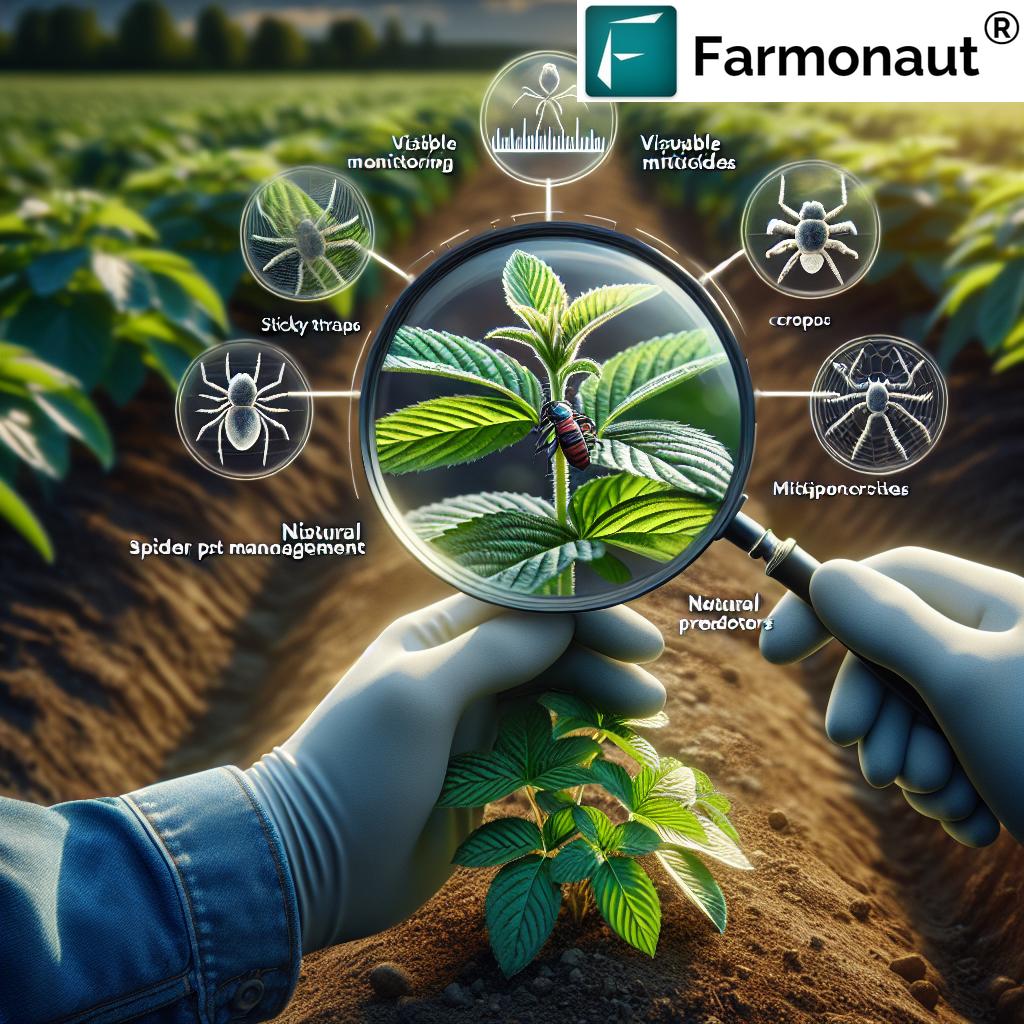
- Hack 5: Monitoring and Early Detection of Mites for Timely Action
- Hack 6: Conserve and Encourage Beneficial Organisms
- Hack 7: Adopt Precision and Data-Driven Mite Management with Farmonaut
- Comparative Effectiveness of Mite Management Strategies
- Frequently Asked Questions on Mite Management
- Conclusion: Ensuring Sustainable, Optimal Yields through Effective Mite Control
- Farmonaut Subscription Options
Mite Management in Agriculture, Farming, and Forestry: Why It Matters
Mites are microscopic arachnids that play various vital roles in our ecosystems. While some species of mites act as beneficial organisms, contributing to soil health and acting as natural predators, others can inflict significant damage to crops, plants, and even trees. In agriculture, forestry, and farming systems worldwide, unchecked mite populations are notorious for causing reduced yields, stunted growth, discolored foliage, and—if left unmanaged—large-scale economic losses across sectors such as palm oil, coconut, and poultry industries.
As we aspire towards more sustainable, environment-friendly pest control and higher crop productivity, it becomes essential to adopt effective mite management strategies. These approaches must focus on minimizing the harmful impact of mite pests, protecting beneficial species, and ensuring optimal yields while safeguarding our fragile agro-ecosystems.
Types and Impact of Mites in Farming and Forestry
We see a startling array of mites that can influence our agricultural systems, each with unique roles, impact, and control requirements. Mite management in agriculture requires us to first understand the primary target species.
-
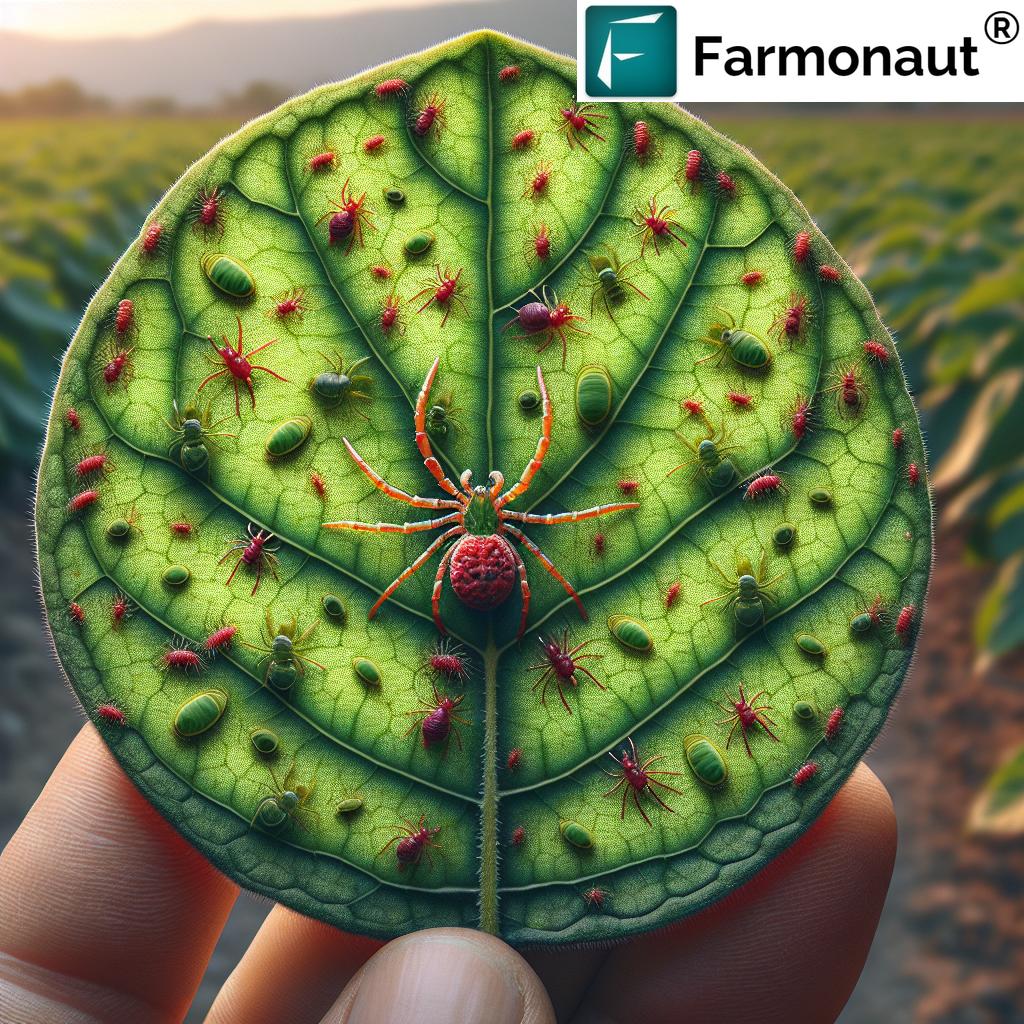
Spider Mites (Tetranychidae):
Description: Among the most notorious agricultural pests, spider mites (Tetranychus spp.) feed by puncturing plant cells, leading to stippling, yellowing, and leaf drop. Infestations can rapidly escalate, resulting in stunted growth, poor development, and reduced yields.
Target crops: Alfalfa, cotton, soybeans, tomatoes, fruits, and more.
Learn more about spider mites -
Bulb Mites (Rhizoglyphus spp.):
Description: Important pests of bulbous plants like onions, garlic, and tulips, these mites disrupt roots and storage organs. The result: poor plant development and decreased quality of the harvested products.
See research on bulb mites -
Red Palm Weevil Mites (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus):
Description: Associated with the destructive red palm weevil, these mites exacerbate damage to palm trees, leading to steep economic losses in coconut and palm oil industries. -
Poultry Mites (Dermanyssus gallinae):
Description: Infesting poultry farms, these mites feed on the blood of birds, causing stress, reduced egg production, and—if uncontrolled—even bird death.
Poultry mite impact research
Understanding these common types of mites and their damage is the foundation for building an integrated pest management plan tailored to your unique agricultural ecosystem.
Understanding Mite Infestations: Causes, Signs, and Risks
Mite infestations can arise rapidly—especially under dry, hot, and dusty conditions—and can become persistent if left unchecked. As stewards of our land, we must recognize and interrupt the factors that foster mite outbreaks in farming, forestry, and plantation crops:
- Drought or Irrigation Stress: Stressed plants are more susceptible to mite feeding and reproduction.
- Frequent Use of Broad-Spectrum Pesticides: This can eliminate natural predators of mites, causing pest populations to rebound.
- Weed Reservoirs: Weeds act both as hosts and hiding places, letting mite populations build up unnoticed.
- Dense Crop Canopies: Poor airflow and thick foliage create humid microclimates that attract mites.
Signs of Mite Infestation:
- Stippling or small yellow/white spots on leaves
- Yellowing & patchy discoloration
- Webbing (especially with spider mites and red spider mite infestations)
- Premature leaf drop and general loss in plant vigor
- Stunted growth and deformed fruits or bulbs
Early identification of these signs is critical for monitoring and early detection of mites, which enables us to act swiftly and limit damage before populations explode.
Fleet Management with Farmonaut can aid large plantation and farm operators in organizing regular on-ground monitoring schedules, improving surveillance against pests and diseases.
Mite Management Secrets: 7 Proven Hacks for Farmers
Now let’s unlock the secrets farmers swear by—the essential pest management strategies for crops that provide effective mite management, including spider mite control, across modern agriculture and forestry systems. By employing an IPM approach (Integrated Pest Management), we not only improve yields and sustainability, but also secure the long-term health of our agro-ecosystems.
Hack 1: Embrace Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Sustainable Mite Control
Integrated pest management for mites is the foundation of modern, sustainable pest control. It involves using a combination of biological, cultural, chemical, and monitoring strategies in a logical, layered approach, reducing reliance on any single method.
- Integrates diverse control tactics, preserving environmental and economic sustainability.
- Reduces the risk of pesticide resistance and protects non-target beneficial organisms.
- Ensures optimal yields by addressing the whole ecosystem rather than just the pest.
With IPM, we don’t just “spray and pray.” Instead, we rely on ongoing assessment, adopting the lowest-impact solution that is effective against mite populations. Strategic use of monitoring (see Hack 5) plays a central role.
Farmonaut’s crop plantation, forest, and advisory tools help your team plan IPM strategies with real-time, field-specific insights for enhanced action against mites and other pests.
Hack 2: Harness Biological Control of Mites with Natural Predators
Biological control is recognized as one of the most environmentally safe and effective mite management solutions available. By harnessing the power of natural predators of mites and pathogenic organisms, we can regulate pest populations with minimal impact on non-target species or human health.
-
Predatory mites: Species such as Phytoseiulus persimilis and Neoseiulus californicus are voracious predators of spider mites. They can quickly reduce populations by preying on eggs, larvae, and adult mites, providing an in-field army to protect our crops.
Learn more about predatory mite species -
Entomopathogenic fungi: Fungi like Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana target mites by infecting and killing them, acting as a naturally occurring bioinsecticide.
Research on entomopathogenic fungi -
Bacterial agents: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) produces toxins that specifically kill certain mite species without harming other beneficial organisms.
Details on Bt and mite management
These methods make up the core of the biological control of mites and are especially desirable in organic systems or where pesticide resistance is a concern.
Combining natural enemies with regular monitoring and early detection of mites gives us the best chance at balanced, sustainable pest management.
Hack 3: Strengthen Cultural Practices to Disrupt Mite Life Cycles
Cultural control means refining our farming routines to suppress mite populations, making their environment less hospitable. Practical steps include:
-
Irrigation management: Maintain adequate soil moisture and avoid plant stress—healthy plants are less appealing to mites.
Tip: Satellite-based soil moisture monitoring from Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management platform can help schedule irrigation precisely, lowering water use and mitigating pest outbreaks. - Weed control: Eliminate weeds that could serve as alternate hosts or reservoirs for mites.
- Crop rotation: Rotating susceptible crops with non-hosts can break mite cycles and reduce persistent infestations over time.
- Use of resistant varieties: Opt for crop varieties with proven resistance where available.
These methods are central to pest management strategies for crops and contribute greatly to the health and resilience of the entire system.
Hack 4: Precision Chemical Control—The Responsible Use of Miticides for Crops
While cultural and biological controls form our first line of defense, there are situations where chemical control using miticides for crops is necessary—especially during severe outbreaks.
-
Selective miticides: Choose products like Abamectin or Spiromesifen that are proven effective against mites, while causing minimal harm to beneficial insects and other organisms.
Review selective miticide guidelines -
Organic pesticide options: Neem oil and insecticidal soaps are valuable tools for both organic and integrated systems.
Explore organic red spider mite treatment - Resistance management: Rotate different miticide classes to minimize the risk of resistance.
- Follow label directions strictly: Protect pollinators and natural enemies by spraying at optimal times and using targeted application methods.
Hack 5: Monitoring and Early Detection of Mites for Timely Action
Routine monitoring and early detection of mites is the lynchpin of effective mite management in agriculture. Here’s how we ensure no warning signs go unnoticed:
- Field scouting: Train your team to recognize early symptoms of mite feeding—stippling, yellowing, webbing, and leaf drop.
- Set action thresholds: Establish clear population levels at which interventions are necessary, preventing over- or under-treatment.
-
Leverage satellite-based monitoring: Farmonaut’s satellite crop health monitoring tools effortlessly flag areas of stress or canopy damage, enabling focused field checks and precise intervention.
API Developer Docs — Integrate this functionality into your farm management platforms.
By integrating real-time digital and traditional scouting, we build proactive, responsive solutions to manage outbreaks before widespread damage occurs.
Hack 6: Conserve and Encourage Beneficial Organisms
Often overlooked, conserving beneficial organisms fundamentally supports natural pest regulation and improves the effectiveness of biological control of mites.
- Avoid broad-spectrum pesticides: Minimize exposure of pollinators and natural enemies to chemicals.
- Enhance habitat: Plant flowering strips or install refuges to attract and sustain predatory mites, ladybugs, and other allies.
- Maintain field borders and diversity: Encourage predatory insects by keeping portions of your farm as natural as possible.
Such holistic approaches ensure our farms and forests benefit from an entire web of natural pest managers—driving sustainability and lowering costs.
Hack 7: Adopt Precision and Data-Driven Mite Management with Farmonaut
Finally, 21st-century mite management thrives best when supported by precise data and advanced technology platforms. This is where Farmonaut’s agricultural technology solutions create tangible differences:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Uncover mite hotspots and plant stress in real time over entire fields—triggering prompt, localized actions.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Get personalized, scientifically validated management recommendations for mite outbreaks and more—even predicting risk before symptoms appear.
-
Carbon Footprint Tracking: Compare the sustainability of alternative mite control methods, making it easier to comply with environmental regulations.
Monitor & Reduce Your Farm’s Carbon Footprint with Farmonaut -
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: Demonstrate the use of responsible, safe pesticides and pest management on your farm products from field to consumer.
Enhance Transparency with Farmonaut Traceability Solutions -
API & Platform Access: Seamlessly integrate precision farming, scouting, and IPM modules into your organization’s management systems for efficiency at scale.
Learn more about Farmonaut API
Because Farmonaut solutions are affordable and accessible for all scales of farming—whether smallholder, large agribusiness, or government program—they empower anyone, anywhere, to make data-driven decisions for improved mite management and sustainable productivity.
Comparative Effectiveness of Mite Management Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Estimated Effectiveness (%) | Environmental Impact | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use of Natural Predators (Biological Control) | Releasing or encouraging predatory mites and beneficial insects to reduce pest numbers. | 60-80 | Low | Medium |
| Neem Oil Spray (Organic Chemical) | Applying neem oil to discourage feeding and disrupt mite development cycles. | 45-65 | Low | Low |
| Crop Rotation (Cultural) | Changing crop types seasonally to interrupt mite life cycles and breeding sites. | 40-60 | Low | Low |
| Targeted Miticide Use | Applying selective miticides with minimal impact on beneficial organisms. | 70-90 | Medium | Medium |
| Early Detection & Satellite Monitoring | Utilizing digital tools and regular scouting to identify outbreaks early. | 55-75 | Low | Low-Medium |
| Weed Management | Regular removal of weed hosts to disrupt mite habitats and population growth. | 35-55 | Low | Low |
| Habitat Management for Beneficials | Planting flower strips/refuges to support predatory insects and mites. | 50-65 | Low | Low |
This table helps us quickly compare mite management strategies by their effectiveness, sustainability, and cost, supporting informed farm decision-making for both smallholder farmers and large-scale agribusinesses seeking optimal yields.
Frequently Asked Questions on Mite Management
-
Q1: What are the signs of a mite infestation that I should look for first?
A: Early signs include stippling (tiny yellow or white spots) on leaves, webbing (with spider mites), yellowing or bronzing of foliage, premature leaf drop, and reduced plant vigor. Monitoring regularly ensures timely detection. -
Q2: Can I control mites without using chemical pesticides?
A: Absolutely. IPM strategies integrate methods such as biological control (releasing predatory mites or using entomopathogenic fungi), cultural control (irrigation, weed management, crop rotation), and early intervention to minimize chemical usage. -
Q3: Are all mites harmful to my crops?
A: No. While many mite species are pests, some are beneficial organisms that predate on harmful mites and insects. Protecting these natural allies is crucial for a balanced ecosystem. -
Q4: How often should I monitor for mites in my fields or orchards?
A: During peak susceptibility periods (e.g. dry/hot seasons), scout fields or orchards every 7–10 days, or more frequently if past infestations were severe. Digital tools like Farmonaut’s satellite health monitoring can increase efficiency and frequency. -
Q5: What is the safest way to use miticides for effective spider mite control?
A: Always select label-approved, selective miticides and rotate chemical classes to avoid resistance. Spray only when necessary, target the application, and avoid treating during pollinator activity. Follow local regulations closely. -
Q6: How does Farmonaut’s technology help in mite management?
A: Farmonaut provides satellite crop health monitoring, AI-based pest advisory, and API integrations that let farmers and agribusinesses detect stressed patches early, receive science-backed recommendations, and plan targeted interventions—improving sustainability and yield.
Conclusion: Ensuring Sustainable, Optimal Yields through Effective Mite Control
Mite management in agriculture is a nuanced, multifaceted effort that extends beyond mere chemical intervention. By understanding the complex interplay of types of mites, their ecological roles, and the factors that spark infestations, we as farmers, agribusinesses, and forestry managers can:
- Build robust, integrated management plans combining biological control of mites, smart chemical use, and strong cultural practices.
- Safeguard beneficial organisms and natural ecosystem services.
- Reduce environmental impact while ensuring optimal plant development and yields.
- Act rapidly and precisely using data-driven technologies such as Farmonaut’s satellite and AI-powered solutions.
By adopting these evidence-based mite management secrets, we collectively promote a more sustainable, productive, and environmentally considerate agricultural future—whether cultivating food crops, palm plantations, or forest trees.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Explore Farmonaut’s cost-effective subscriptions for individual farmers, cooperatives, enterprises, and government users. Track crop health, pest outbreaks, irrigation, resource allocation, carbon footprint, and traceability—all from your Android, iOS, or web app!