- Regenerative Farming Techniques: 7 Game-Changing Secrets
- What Is Regenerative Farming?
- Key Principles of Regenerative Farming
- The 7 Game-Changing Regenerative Farming Techniques
- Comparative Impacts Table
- Farmonaut: Satellite-Powered Precision for Regenerative Agriculture
- Benefits of Regenerative Farming Practices
- Challenges and Considerations for Shifting to Regenerative Methods
- FAQs: Regenerative Farming Techniques and Farmonaut
- Get Started with Proven, Affordable Satellite-Powered Farm Solutions
- Conclusion: The Path Forward for Sustainable Agriculture
Regenerative Farming Techniques: 7 Game-Changing Secrets
Meta Description: Regenerative farming techniques represent a holistic approach to agriculture, aiming to restore and enhance the health and biodiversity of farming ecosystems. Unlike conventional methods that often degrade soil and biodiversity, regenerative practices focus on rebuilding soil organic matter, increasing biodiversity, and improving water cycles, all while reducing reliance on chemical inputs.
“Regenerative farming can increase soil organic matter by up to 21% in just five years.”
Regenerative farming practices are transforming the way we think about agriculture and our global ecosystems. By shifting our approach from simply sustaining to actively restoring our farming landscapes, we gain far more than higher yields. We build soil health, increase biodiversity, and improve water retention. In this guide, we’ll reveal the seven most impactful, science-backed secrets underpinning modern regenerative farming techniques—with detailed examples, explanations, and actionable tips.
We are in an era where climate risk, degraded soils, and resource limitations challenge farmers everywhere. But through focused regenerative practices, it’s proven possible to restore soil fertility, sequester more carbon, build drought and flood resilience, and improve farm profits over time. Our journey into these transformative techniques will give you practical insights and data you can trust.
What Is Regenerative Farming?
Regenerative farming is a philosophy and practice that aims to restore soils, ecosystems, and farm productivity by working in harmony with natural cycles. Unlike conventional agriculture—which often relies on intensive tilling, monocultures, and chemical fertilizers or pesticides—regenerative techniques rebuild organic matter in the soil, enrich biodiversity, and improve structure for long-term resilience and productivity.
- Emphasizes minimizing soil disturbance (no-till farming methods)
- Uses cover crops to prevent erosion and add fertility
- Promotes biodiversity in agriculture through varied crops and animal species
- Focuses on maintaining living roots and continuous ground cover
- Leverages natural nutrient cycling, reducing need for synthetic inputs
- Integrates livestock systems for manure-based soil enrichment
By deliberately improving soil structure, retention, infiltration, and ecosystem health, this approach leads to robust, sustainable, and profitable agriculture systems.
Key Principles of Regenerative Farming Practices
Successful regenerative agriculture rests upon several guiding principles. As we explore the seven game-changing techniques, keep in mind how every method contributes to at least one of these principles, supporting soil health, biodiversity, and strong ecosystems.
- Minimizing Soil Disturbance: Frequent tilling breaks soil structure, destroys organic matter, and disrupts microbial life. Reducing or eliminating tillage (no-till) preserves structure and allows roots & organisms to thrive.
Source: CBF.org - Maintaining Soil Cover: Keeping fields covered with vegetation or organic materials suppresses weeds, reduces erosion, and protects against heat and compaction.
Source: CBF.org - Enhancing Biodiversity in Agriculture: Introducing a diversity of crops and animal species (e.g., crop rotation, intercropping, and agroforestry systems) builds pest resilience, supports pollinators, and creates balanced, productive ecosystems.
Source: CBF.org - Keeping Living Roots Year-Round: Living roots in the soil support microbial communities, enhance structure, increase water infiltration, and provide continuous nutrient cycling.
Source: CBF.org - Integrating Livestock: Managed grazing and integration of livestock adds natural manure for soil fertilization, breaks pest cycles, and stimulates plant regrowth.
Source: CBF.org
“Fields using regenerative techniques retain up to 40% more water compared to conventional farms.”
The 7 Game-Changing Regenerative Farming Techniques
Let’s break down each proven, research-backed regenerative farming technique, highlighting why it matters, the science behind it, and practical steps for implementation. These are the essential tools to restore your soil, water, and yield potential—whether you are managing a small organic field or a large-scale agricultural enterprise.
-
No-Till or Minimum-Till Farming Methods

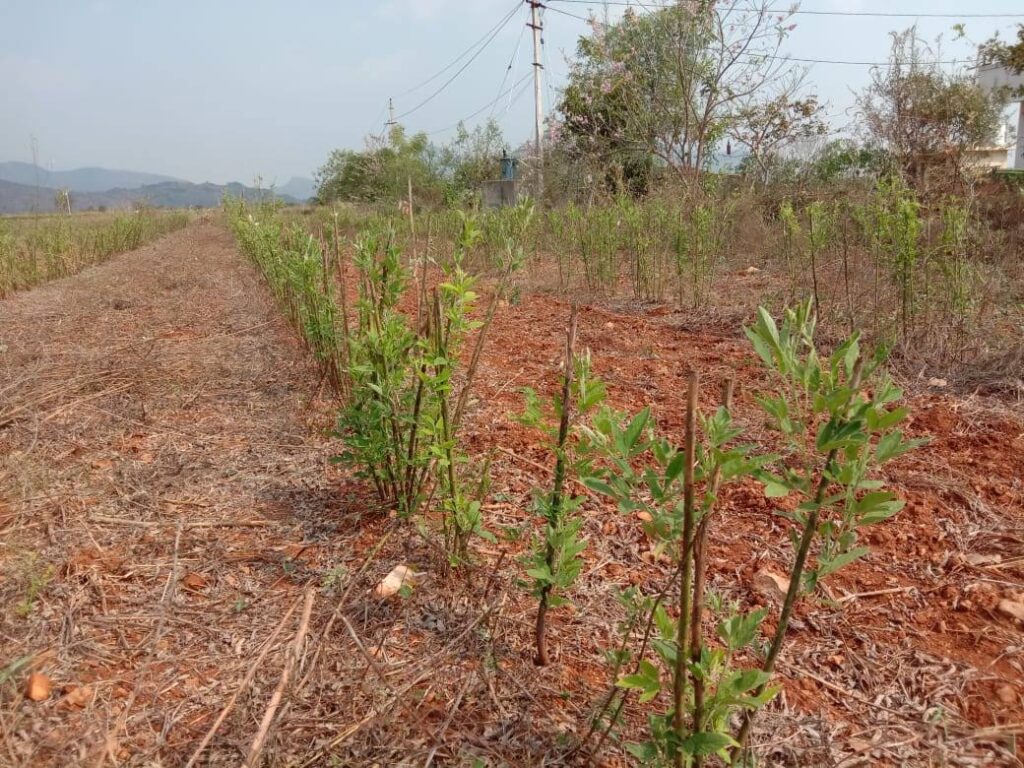
Traditional intensive tilling breaks apart soil aggregates, exposes organic matter to rapid decomposition, and disrupts beneficial soil organisms.
No-till farming methods instead keep soil layers intact—preserving structure, allowing water infiltration, and supporting robust microbial communities. Minimal surface disturbance also helps retain moisture and reduce erosion.
- Leads to quick soil health improvement (better structure, retention, organic matter)
- Reduces soil loss during heavy rains/flooding
- Boosts yield resilience during weather extremes
Tip: Consider direct seeding into cover crop residues. Regular field monitoring with platforms such as Farmonaut’s crop health insights can help optimize management and identify compaction/stress zones.
-
Cover Crops Benefits
Cover cropping means planting non-cash crops (often legumes or grasses) between harvests, in rotation, or even alongside main crops.
These cover crops benefits are immense:
- Prevent erosion by shielding soils
- Add organic matter (roots + residues feed soil fertility)
- Fix nitrogen (especially legumes), reducing synthetic fertilizers need
- Suppress weeds and pest cycles naturally
- Support an active, diverse soil food web
Mixes of legumes, grasses, and brassicas are proven most effective in boosting water retention in soil, improving cycling and nutrient availability, and restoring fertility.
Deep-rooted species like daikon radish or vetch can break compacted layers and bring nutrients up from subsoil. For near real-time field monitoring during cover cropping schedules, use a digital tool like Farmonaut.
-
Crop Rotation Techniques
Constantly growing the same crop (monocropping) depletes nutrients, increases pest pressure, and leads to disease cycles.
Crop rotation techniques mean alternating crops with different families, lifecycles, and root depths across seasons in a strategic pattern.- Breaks pest and disease cycles (less need for chemical control)
- Improves nutrient cycling as different crops pull up different minerals
- Reduces reliance on external inputs (fertilizers, pesticides)
- Enhances soil structure and supports microbes year-round
Example: Rotating corn/wheat-soybeans-alfalfa. Incorporating deep-rooted (living roots) crops followed by shallow-rooted crops optimizes soil restoration and fertility.
-
Agroforestry Systems
Agroforestry is about integrating trees and shrubs into traditional crop or livestock systems. This creates multi-story farms mimicking natural forests, driving resilience and biodiversity benefits:
- Improves windbreak and microclimate for main crops
- Slows down water movement, enhances retention, infiltration
- Produces additional income (fruits, nuts, timber, medicine, honey)
- Offers habitat for beneficial insects and birds (pest control, pollination)
- Deep root systems draw up nutrients and increase total carbon stocks (carbon sequestration in soil)
Fun fact: Some studies show agroforestry improves total biodiversity by over 50 species per hectare!
-
Managed or Rotational Grazing
Integrating livestock with crops—or practicing managed grazing on dedicated pastures—transforms how nutrients cycle on the farm.
The secret: Rotating cattle, sheep, or poultry through smaller sections prevents overgrazing and allows vegetation to recover fully before animals return.- Encourages diverse vegetation and root mass
- Manure deposits fertilize the soil (natural nutrient cycling)
- Soil compaction is reduced; structure, retention, infiltration improve
- Boosts microbial communities and organic matter content
Digital tools now allow you to monitor pasture regrowth, optimize grazing rotation, and estimate carbon sequestration—see Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting for real-time carbon tracking.
-
Compost and Organic Amendments
Applying on-farm compost is among the fastest ways to build soil organic matter and microbial diversity. Composting transforms waste—crop residues, animal manure, food scraps—into nutrient-rich humus.
- Recycles farm waste into valuable fertility
- Adds stable organic matter to improve aggregation, water retention, structure
- Feeds mycorrhizal fungi and beneficial bacteria
- Reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers
A healthy compost program means better yields, top-quality produce, and an important step toward full regenerative agriculture systems.
-
Integrated Pest and Weed Management (IPWM)
Building biodiversity, interplanting with companion species, supporting beneficial insects, and using physical controls (mulching, rotating, managing field margins) all reduce chemical inputs and pest reliance.
- Utilizes trap crops and flowering borders for pollination and natural predators
- Reduces chemical disturbance that harms microbial life
- Leads to more resilient cropping systems, less resistance build-up
For in-season pest and disease monitoring from anywhere, AI-powered tools like Farmonaut’s Jeevn Advisory System provide alerts, trends, and recommendations, minimizing chemical inputs and yield loss.
Comparative Impacts Table: Regenerative Techniques vs. Key Sustainability Outcomes
| Technique | Est. Increase in Soil Organic Matter (%) | Water Retention Improvement (%) | Biodiversity Boost (species/ha) | Typical Time to See Results (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Till Farming | 8–15% | 20–35% | +10–20 | 2–5 |
| Cover Cropping | 9–12% | 30–40% | +20–30 | 1–3 |
| Crop Rotation | 6–10% | 18–27% | +15–25 | 2–3 |
| Agroforestry | 10–21% | 25–37% | +40–50 | 3–7 |
| Managed Grazing | 12–18% | 28–36% | +18–30 | 2–5 |
| Composting | 7–13% | 15–22% | +12–17 | 1–2 |
| IPWM (Integrated Pest/Weed Management) | 5–8% | 12–19% | +10–20 | 1–2 |
*Source: Industry averages & published research estimates. Actual values vary by region, weather, crop, and specific practices.
Farmonaut: Satellite-Powered Precision for Regenerative Agriculture
To fully unlock the power of regenerative farming practices, actionable data is essential, from understanding soil moisture trends to crop health, carbon sequestration progress, and optimal input timing. Farmonaut makes this advanced, scalable, and precise innovation accessible to every user—from smallholders to large agribusinesses.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health: Farmonaut delivers field-level satellite insights (NDVI, soil moisture, crop vigor) so we can improve yields and spot variability before it reduces productivity.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Real-time, AI-driven advisory enables targeted pest, disease, and input decisions—vital for reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals while boosting plant resilience.
- Blockchain Traceability: Secure, tamper-proof farm-to-market supply chain records for produce, driving consumer trust and supporting premium traceability solutions.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Streamline vehicle,input, and field operations—cutting costs for larger farms and simplifying reporting. Discover all capabilities at Fleet Management.
- Carbon Footprinting: Monitor and act on your farm’s real-time emission data, and verify improvements in carbon sequestration as you transition to regenerative techniques (carbon footprinting).
- Loan/Insurance Verification: Access smoother, fraud-resistant crop loan and insurance with satellite-confirmed farm data.
- Farm Management at Scale: Government and large producers can consolidate, plan, and monitor huge land areas efficiently: see Large Scale Farm Management for institutional tools.
- API Access: Integrate satellite data and weather intelligence directly into your agri-business apps—use Farmonaut API and review the API Developers Docs for custom solutions.
Ready to experience the future of affordable precision ag?
Benefits of Regenerative Farming Practices
Committing to regenerative agriculture systems offers immediate and long-term gains—not only for farmers and consumers, but also for our planet’s critical ecosystems. Let’s summarize the biggest payoffs:
- Soil Health Improvement & Building Soil Fertility: More organic matter means better structure, water/nutrient holding, and microbial life—all of which underpin yield gains and farming resilience.
- Biodiversity in Agriculture: Introducing diverse crops, livestock, trees, and cover species attracts pollinators and predators, balances pests, and creates a self-sustaining system.
- Water Retention in Soil: Richer soil with stable aggregates holds up to 40% more water, making farms drought-resistant and cutting irrigation costs.
- Carbon Sequestration in Soil: Every percent of added organic matter pulls more carbon from the air into the earth—crucial for climate mitigation and compliance.
- Reduced Inputs & Economic Resilience: Less spent on synthetic fertilizers, herbicides, and fuel means healthier farm finances—plus new income from diversified outputs like fruits, timber, and high-value traceable products.
- Environmental Protection: By minimizing runoff, soil loss, and pollution, regenerative methods protect water sources and downstream ecosystems.
Challenges and Considerations for Shifting to Regenerative Methods
Change is never simple—moving from conventional to regenerative approaches means rethinking habits, retraining, and sometimes managing risk during the transition. Here’s what to plan for:
- Potential initial drop in yields as soil biology recovers and weed/pest pressures shift
- Need for new equipment (such as no-till planters, compost turners)
- Learning curve in recognizing field variability and integrating complex rotations
- Support for accessing specialized seeds, livestock breeds, and cover crop options locally
- Marketing and price premiums—being able to access markets that value traceable, regenerative products
We recommend fully leveraging modern decision-support platforms (for example, Farmonaut’s advisory and remote sensing) to minimize uncertainty and optimize transitions.
Financial support and new markets are coming online, especially as governments and corporate buyers recognize the value of soil carbon, water management, and biodiversity on the global stage (Source: Reuters).
Get Started with Proven, Affordable Satellite-Powered Farm Solutions
Access all Farmonaut subscription packages, including options for individual farmers, cooperatives, and large agribusinesses. Flexible pricing, easy onboarding, and mobile/web access make it simple to start improving your soil health, maximize farm productivity, and monitor every field from anywhere.
FAQs: Regenerative Farming Techniques and Farmonaut
What is the difference between regenerative farming and organic farming?
While both emphasize eliminating chemical inputs and building soil health, regenerative farming techniques go further by aiming to restore ecosystem functions, actively improve soil fertility, and sequester carbon. Organic systems don’t always ensure increased soil organic matter and biodiversity the way regenerative practices do.
Can small farms or backyard gardeners use regenerative techniques?
Absolutely. From simple cover cropping and no-till beds to composting and diverse plantings, every garden or small plot benefits from increased organic matter, water retention, and biodiversity.
How quickly can benefits be seen after transition?
Most farmers observe improved soil structure and reduced run-off within 1–2 seasons. However, full restoration of organic matter, pest balance, and yield stability may take 3–7 years depending on location, soil history, and crops/livestock used.
How do Farmonaut’s technologies support regenerative farming?
Farmonaut empowers farmers by offering real-time crop health monitoring, soil moisture mapping, and AI-driven advisory. This supports timely decisions on irrigation, grazing, pest management, and fertility. Blockchain traceability verifies sustainable practices for premium market access.
Can Farmonaut solutions be scaled for large, multi-site agribusiness?
Yes. The platform is designed to meet the needs of single farms or large-scale operations with Enterprise Management, scalable satellite monitoring, and powerful analytics.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for Sustainable Agriculture
Regenerative farming techniques are the future of sustainable agriculture. By focusing on soil health improvement, water retention, biodiversity, and reduced reliance on chemical inputs, everyone—farmers, agribusinesses, and consumers—can contribute to reviving our planet’s most vital resources.
Whether you are just starting out on this journey or looking to scale up established regenerative practices, remember these seven game-changing secrets:
- No-till or minimum-till for soil integrity
- Diverse, seasonally matched cover cropping
- Strategic crop rotation
- Agroforestry systems for long-term resilience
- Managed grazing and livestock integration
- Composting to build living soils
- Integrated, biodiversity-based pest management
Combine these foundational techniques with the precision of Farmonaut’s satellite-driven management tools, and we can accelerate the transformation toward regenerative, profitable, and truly sustainable agriculture systems worldwide.