Sustainable Gardening: 7 Hacks for Healthier Soil!
“Healthy soil contains up to 1 billion bacteria per gram, supporting robust plant growth and biodiversity.”
Introduction: Embracing Sustainable Gardening for a Healthier Planet
In an era of rapid climate change and increasing resource scarcity, sustainable gardening practices are more crucial than ever. As gardeners, farmers, and environmental stewards, our mission is to create thriving ecosystems that not only serve our immediate needs but also protect and enrich our environment for generations to come.
At the heart of these efforts is the soil—the living foundation supporting plants, microorganisms, and a vast web of life. Cultivating resilient, eco-friendly gardens means prioritizing soil health, efficient water use, and promoting biodiversity. By integrating advanced technologies, such as those provided by Farmonaut—a leading agro-tech company specializing in real-time crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisory, and carbon footprinting—our approach to sustainable gardening becomes smarter and more accessible.
Let’s delve into the most effective and practical sustainable gardening hacks that enhance soil fertility, conserve precious resources, and build resilient garden ecosystems!
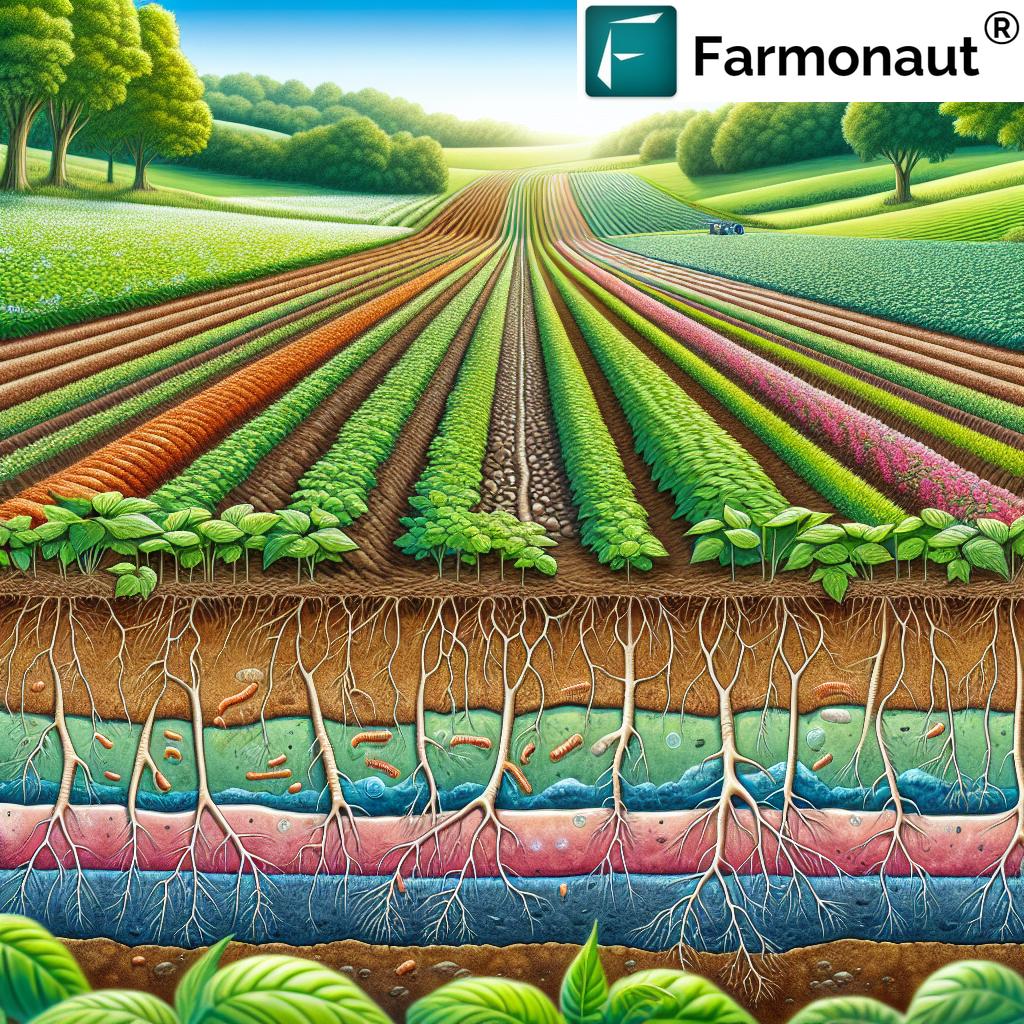
1. The Foundation: Soil Health and Conservation
Soil health is the cornerstone of every sustainable gardening approach. Healthy soil is not just dirt; it is a vibrant ecosystem teeming with beneficial microorganisms, organic matter, nutrients, and complex structure supporting robust plant growth, biodiversity, and water retention. By prioritizing soil health and conservation, we’re investing in the long-term productivity, sustainability, and resilience of our gardens.
- Organic matter: Incorporating compost and organic debris feeds soil microbes, fosters nutrient cycling, and enhances soil structure.
- Minimal tillage: Reducing soil disturbance protects delicate soil aggregates, preserves carbon content, and minimizes erosion.
- Mulching: Applying an organic layer atop soil conserves moisture, regulates temperature, suppresses weeds, and helps prevent erosion.
Frequent soil testing helps identify pH levels, nutrient deficiencies, and compaction issues—empowering us to tailor interventions for maximum health and fertility. As sustainable gardeners, our commitment to soil conservation sets the stage for all other ecological practices.
2. Composting: Recycling to Enrich Soil and Foster Sustainability
Composting is the process of breaking down organic matter—like kitchen scraps, yard clippings, and crop residues—into rich, fertile humus. Incorporating compost into gardening systems recycles waste and returns essential nutrients to the soil, which:
- Enriches soil fertility and feeds beneficial microorganisms
- Improves soil structure, aiding aeration and moisture retention
- Promotes disease resistance and plant health
- Reduces dependence on synthetic fertilizers
For best results, balance “greens” (nitrogen-rich) and “browns” (carbon-rich) materials, keep the pile moist but not soggy, and turn the heap regularly to aerate. The result is a nutrient-packed amendment that transforms poor, lifeless soils into productive, healthy beds.
Farmonaut supports this approach by helping gardeners monitor soil health and optimize nutrient management by providing API and AI-based insights for crop vigor and fertility recaps.
“Mulching can reduce garden water evaporation by up to 70%, conserving moisture and promoting sustainable gardening.”
3. Mulching: Moisture Conservation and Weed Suppression
Mulching is a time-tested sustainable gardening practice with far-reaching benefits. By applying a layer of organic mulch (such as straw, leaves, or wood chips) around plants and across garden beds, we’re not only conserving moisture but also:
- Suppressing weeds and reducing competition for nutrients
- Regulating soil temperature to protect roots
- Preserving soil structure and reducing erosion from rainfall or wind
- Enhancing soil health as the mulch breaks down into valuable organic matter
These qualities make mulching indispensable in organic gardening, permaculture plots, and home gardens. For urban gardeners or those with limited time, mulch also minimizes maintenance needs. Mulching is integral for both commercial farming systems and community gardens prioritizing water conservation in regions like California, Australia, or southern India.
4. Minimal Tillage: Conservation Tillage Methods for Healthy Soil
Conservation tillage methods, like no-till, strip-till, or reduced till, are vital for protecting and preserving soil health. These approaches involve minimizing soil disturbance to:
- Preserve soil structure and valuable earthworm channels
- Reduce erosion caused by wind and rain, promoting sustainable soil use
- Maintain organic surface residues that nourish soil life
- Promote moisture retention and improve water infiltration
- Support the sequestration of carbon, mitigating climate change impacts
Tools such as no-till planters enable direct seeding into undisturbed soils. This has become a cornerstone in sustainable agriculture and regenerative gardening globally. For modern gardeners and large-scale farmers alike, minimal tillage fosters resilient ecosystems with higher biodiversity, fewer chemical inputs, and long-term productivity.
Satellite technologies, like those delivered through Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management platform, allow for monitoring of soil structure, crop cover, and moisture—all of which are critical when adopting conservation tillage techniques.
5. Cover Cropping Strategies for Soil Health
Cover cropping is a proven strategy for maintaining soil vitality between growing seasons or alongside primary crops. By planting leguminous cover crops—such as clover, vetch, or alfalfa—gardeners can:
- Fix nitrogen naturally in the soil, reducing need for synthetics
- Suppress weeds, cutting down on herbicide use or hand labor
- Prevent erosion by maintaining continuous living cover
- Feed beneficial soil organisms and improve overall structure
After their season, these crops can be gently turned into the soil (green manure), recharging organic content and freeing up nutrients for upcoming plantings. Cover cropping techniques are especially important when converting large fields, vegetable gardens, or urban green spaces to sustainable methods.
For gardeners seeking precision and optimization, Farmonaut provides resource management features including scheduled notifications for planting, irrigation, and cover crop termination based on satellite observations—making integration of cover crops easier and more effective.
6. Water Conservation in Gardening
Water conservation in gardening is not only about sustainability—it’s about necessity, particularly in regions facing drought or water restrictions. Efficient irrigation and water-smart design are essential for healthy plants and ecological balance. Here are key techniques:
- Drip irrigation systems: These deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, and ensuring deep, effective hydration.
- Rainwater harvesting: Collecting and storing roof runoff in barrels or cisterns provides an eco-friendly water source for gardens, reducing dependence on municipal supplies.
- Hydro zoning: Grouping plants with similar water needs optimizes irrigation schedules and conserves valuable resources.
- Mulching (as discussed above): Acts as a natural moisture barrier, dramatically curbing water loss.
Additionally, selecting drought-resistant or native species further reduces irrigation requirements. Satellite technology, like Farmonaut’s crop monitoring solutions, offers remote tracking of crop water status, optimizing irrigation management for everyone from small gardeners to large farming operations.
7. Biodiversity in Gardens: Plant Selection and Agroforestry Benefits
Biodiversity in gardens is a multi-layered safeguard for resilience, pollinator health, and natural pest control. Here’s how we can boost garden biodiversity:
A. Native Plant Selection
- Native species are adapted to local conditions, requiring less water, fertilizer, and chemical management.
- These plants provide habitat and nutrition for pollinators, wildlife, and beneficial insects.
- Native plantings encourage balanced, self-regulating ecosystems—minimizing the risk of invasive pests or diseases.
B. Growing a Variety of Plants
- Poly culture (growing a variety) supports resilience, beneficial predators, and ecosystem stability.
- Mixing vegetables, herbs, and flowers supports healthy insect populations and diverse soil biology.
C. Agroforestry Benefits
- Agroforestry—the practice of integrating trees and shrubs within garden or field systems—delivers shade, improves soil structure, stores carbon, and attracts both wildlife and beneficial insects.
- Examples: Alley cropping, silvopasture, and food forests. These approaches promote shade, organic matter cycling, and microclimate regulation.
Gardeners can use Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting solution to track the climate impact of agroforestry projects and individual land management decisions—an innovative step in quantifying the environmental benefits of sustainable gardening.
Integrated Pest Management & Natural Pest Control Techniques
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a cornerstone of sustainable, eco-friendly gardening. IPM combines multiple strategies to control pests—while minimizing reliance on chemical pesticides and safeguarding environmental and human health.
Key Components of IPM
- Biological control: Encouraging beneficial insects (like ladybugs, predatory wasps, and lacewings) to control pest populations naturally.
- Cultural practices: Crop rotation, interplanting, and sanitation reduce pest outbreaks and break lifecycle patterns.
- Physical controls: Using barriers (row covers), hand-removal, and traps for pests.
- Chemical controls—used as a last resort only: Selecting the least toxic, most targeted options to avoid harm to beneficial species.
Natural Pest Management Strategies
- Companion planting: Growing pest-repellent herbs and flowers among vegetable crops (e.g., marigolds with tomatoes).
- Planting “trap crops” to lure pests away from main yields.
- Frequent monitoring and manual removal of pest insects.
Farmonaut’s advanced satellite and traceability tools give gardeners, farmers, and agribusinesses the ability to monitor fields, quickly identify pest hotspots, and enhance precision pest management with robust data insights. These strategies are invaluable for keeping gardens and commercial fields productive while promoting biodiversity and environmental stewardship.
Climate Change Mitigation in Gardening
As environmental stewards, we must recognize the critical role sustainable gardening practices play in climate change mitigation. Each of the techniques described above—cover crops, agroforestry, mulching, conservation tillage—directly supports carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas reduction.
- Composting and cover cropping add organic carbon to soil, reducing atmospheric CO2.
- Agroforestry systems lock up carbon in woody biomass while providing ecosystem services like shade and wildlife habitat.
- Minimal tillage preserves soil carbon stocks and prevents erosion.
By measuring, reducing, and optimizing these mitigation strategies, gardeners can make a measurable difference in their environmental footprint. Access to Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting platform enables efficient tracking and smarter planning aligned with global climate targets.
Comparison Table of Sustainable Gardening Hacks
To help you select the most effective interventions for your own green space, below is a comprehensive side-by-side comparison of each sustainable gardening practice discussed:
| Hack Name | Description | Estimated Soil Health Improvement (%) | Water Conservation Potential | Biodiversity Benefit | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composting | Recycles organic waste into fertile humus, boosting nutrients and soil life | 30-45% | Medium | Medium | Easy |
| Mulching | Organic cover that conserves moisture, regulates temperature, and suppresses weeds | 25-35% | High | Medium | Easy |
| Minimal/Conservation Tillage | Reduces soil disturbance, preserves structure, and cuts erosion | 20-30% | High | Medium | Moderate |
| Cover Cropping | Planting legumes/grasses off-season to protect, enrich, and restore soil | 30-40% | Medium | High | Moderate |
| Efficient Water Conservation | Drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and hydro zoning reduce water use | 10-20% | High | Low | Easy |
| Biodiversity and Agroforestry | Planting diverse crops and trees to support ecosystem balance | 25-35% | Medium | High | Challenging |
| IPM & Natural Pest Management | Reduces pest pressure using beneficial insects, barriers, and crop rotation | 15-25% | Low | Medium | Moderate |
How Farmonaut Empowers Sustainable Gardening Practices
Farmonaut is paving the way for sustainable gardening and agriculture through affordable, technological solutions. Here’s how the platform takes sustainable garden management to the next level:
- Satellite-Based Crop & Soil Health Monitoring: Measure vegetation health, soil moisture, and nutrient variability across your fields or gardens—empowering informed decisions to optimize planting, fertilization, and irrigation.
- AI-Powered Advisory (Jeevn AI): Receive real-time, personalized farm management insights, weather forecasts, and precision resource recommendations for healthier, more resilient crops.
-
Blockchain Traceability: Ensure transparent, secure record-keeping for crop journey “from field to fork”. Help increase trust for food safety and certification programs.
Learn more about Farmonaut’s Traceability Solutions. - Resource & Fleet Management: Seamlessly coordinate logistics, machinery, and input schedules with Fleet Management Tools—reducing operational costs and optimizing efficiency.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Quantify emissions and sequestration with Carbon Footprinting Tools. This is indispensable for anyone wishing to align their practices with environmental regulations and sustainability certifications.
- Financing & Insurance Support: Use satellite-based field verification for hassle-free crop insurance and loan approvals.
With simple and flexible apps for Android, iOS, and web browsers, or robust APIs (see API Developer Docs), Farmonaut brings advanced, easy-to-use, and scalable solutions to gardeners, farmers, and agri-enterprises worldwide.
Farmonaut Subscriptions
Choose a Farmonaut subscription that suits your land, crop, or business needs. Access up-to-date insights, monitor resources, or enable traceability— all at affordable rates for every scale of operation.
- Want to manage large-scale farming, forestry, or crop plantations sustainably? Farmonaut’s Advisory & Plantation Management platform delivers insights for precision agriculture, forest conservation, and biodiversity goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is sustainable gardening?
Sustainable gardening is an approach that prioritizes environmental health by enhancing soil fertility, conserving water, reducing chemical use, and promoting biodiversity. It integrates eco-friendly practices into gardening and farming systems, supporting both human needs and natural ecosystems.
Why is soil health so important in sustainable gardening?
Healthy soil forms the foundation of sustainable gardening. It nourishes plants, fosters biodiversity, preserves water, and sequesters carbon—supporting resilient and productive garden ecosystems while minimizing environmental impact.
How can I conserve water in my garden?
Implement drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and hydro zoning for efficient irrigation. Add mulches to curb evaporation and choose drought-tolerant, native plants to further minimize water needs.
What are some alternatives to chemical pesticides?
Integrated pest management (IPM), companion planting, biological pest control (encouraging beneficial insects), crop rotation, and manual removal all help reduce chemical dependence, supporting a balanced and healthy garden ecosystem.
How does Farmonaut support sustainable gardening?
Farmonaut provides satellite and AI-based tools for monitoring crop and soil health, optimizing water and nutrient management, tracking carbon footprint, and managing traceability and resources, thereby making sustainable gardening accessible and efficient for everyone.
Conclusion: Nurture Healthier Soil for a More Resilient World
By integrating sustainable gardening practices—from composting, mulching, and cover cropping to biodiversity promotion, water conservation, and advanced pest management—we empower our gardens, farms, and communities to thrive. These strategies enhance soil health, optimize resources, and support balanced ecosystems needed for the planet’s future.
Digital innovation, like those offered by Farmonaut, makes monitoring, data analysis, and sustainable management easier than ever before. Whether you’re cultivating a small urban plot or managing thousands of acres, you can play a pivotal role in building resilient, environmentally responsible food production systems. Let’s embrace regenerative action and nurture the foundation of life—our soil—for generations to come!