- Summary: Vertical Farming Revolutionizing Agriculture
- Understanding Vertical Farming: Concept & Systems
- Vertical Farms: 7 Shocking Benefits You Must Know!
- Comparison Table: Traditional vs. Vertical Farming Benefits
- Overcoming the Challenges of Vertical Farming
- How Farmonaut Empowers the Future of Agriculture
- The Future of Vertical Farming and Sustainable Food Production
- FAQs about Vertical Farming
- Get Started with Farmonaut
Vertical Farms: 7 Shocking Benefits You Must Know!
As our world’s population continues to rise, the demand for food is quickly escalating, placing immense pressure on traditional agriculture systems.
Vertical farming has emerged as a promising solution, offering innovative methods to produce food efficiently and sustainably, especially in urban settings.
In this article, we explore the vertical farming benefits that are revolutionizing urban food production, optimizing space, and addressing global challenges through controlled environment agriculture (CEA) and advanced hydroponic farming systems.
Understanding Vertical Farming: Concept & Systems
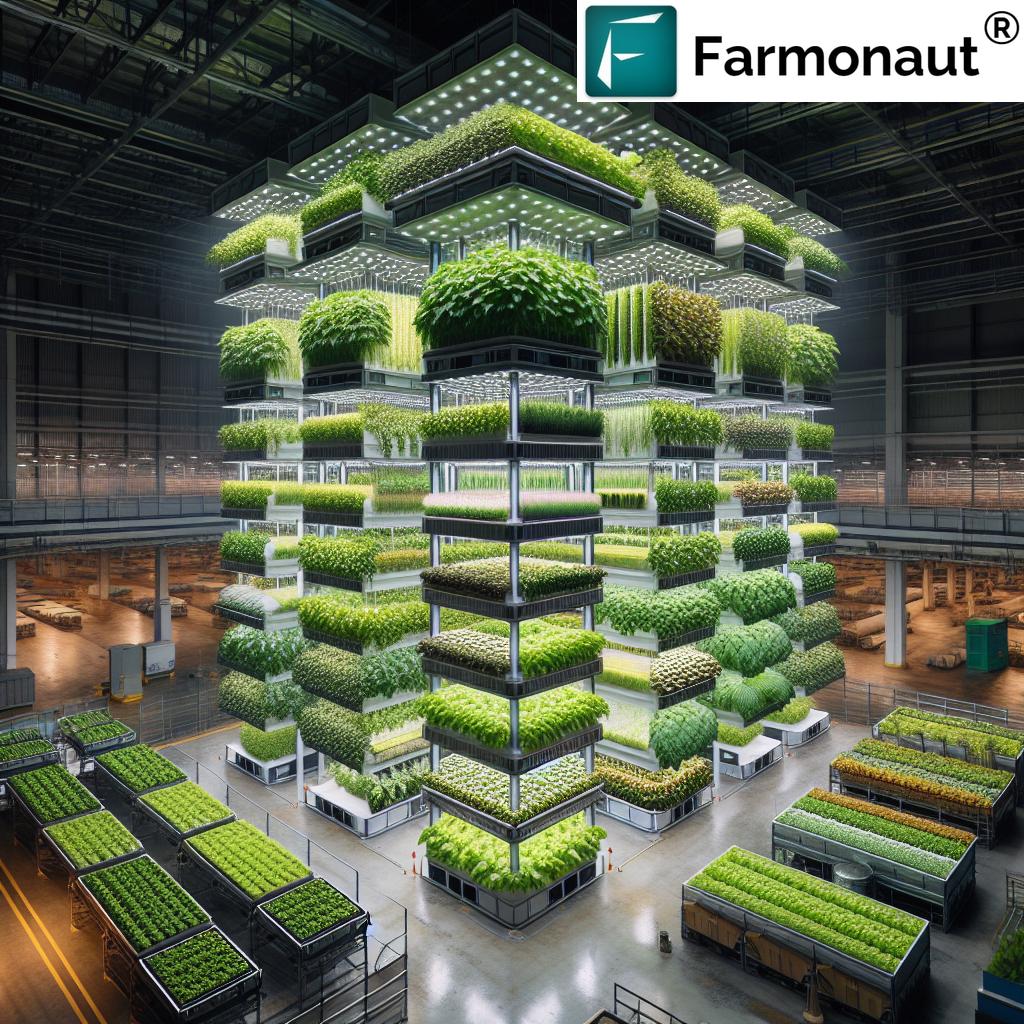
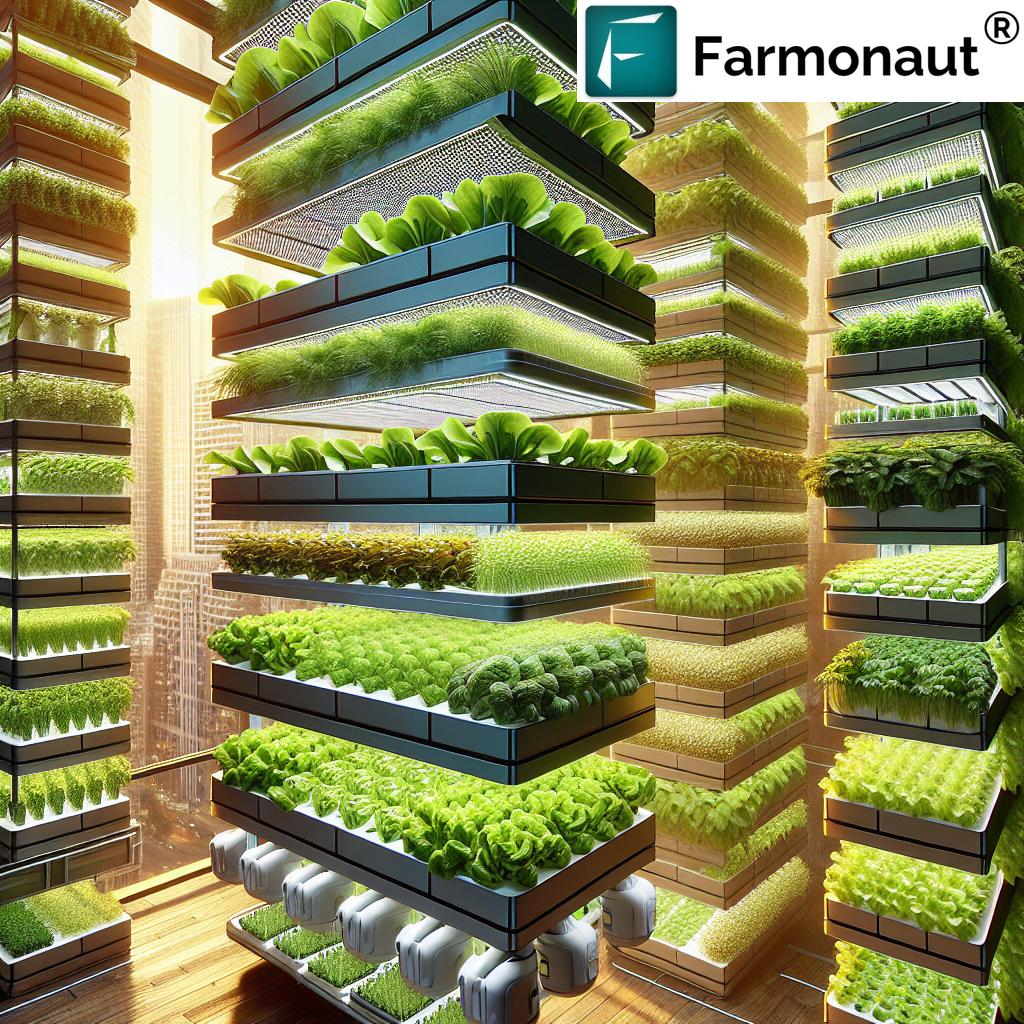
Vertical farming involves cultivating crops in stacked layers or vertically inclined surfaces, often integrated into structures like skyscrapers, shipping containers, and repurposed warehouses.
Unlike traditional farming, which depends on arable land and external environmental conditions, vertical farms utilize controlled environments and soilless methods such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics.
- Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA): Allows us to adjust all environmental factors—light, temperature, humidity, CO2, and nutrients—for optimal growth.
- Hydroponic Farming Systems: Grow crops in nutrient-rich water, not soil, enabling efficient use of water and resources.
- Aeroponics: Delivers nutrients as a mist to roots, further increasing resource efficiency and minimizing waste.
- Aquaponics: Integrates fish farming with hydroponic crop production for symbiotic, sustainable systems.
These settings make possible year-round, local, and fresh produce even in densely populated urban centers where land availability is limited.
Vertical Farming Benefits: 7 Incredible Ways It’s Revolutionizing Agriculture
Let’s discover the 7 shocking benefits of vertical farms that every advocate of sustainable crop production must know!
1. Space Optimization and Maximized Yields
One of the most groundbreaking advantages is space optimization. By utilizing vertical space, these farms can produce an astonishing amount of food in urban areas with very limited land.
- Efficient Space Utilization: Imagine a 30-story vertical farm building with a 5-acre base yielding an annual crop comparable to 2,400 acres of traditional land!
- Location Flexibility: Urban vertical farms allow us to bring food production right into the proximity of population centers, eliminating the need to search for large tracts of arable land.
This remarkable use of space is reshaping the future of agriculture by enabling us to grow food efficiently where it’s needed most.
2. Water Efficiency and Sustainability
Vertical farming systems, especially those using hydroponics or aeroponics, are astoundingly water efficient—using up to 95% less water than traditional agriculture.
- Closed Loop Recirculation: These systems minimize water consumption by continually recirculating and reusing water.
- Reduced Waste: Minimizes water lost to evaporation, runoff, and inefficiency.
- Global Impact: In water-scarce regions or where drought is common, vertical farms offer a truly sustainable way forward.
By dramatically cutting water usage, we can secure a more sustainable and resilient food supply for generations to come.
3. Reduced Land Use and Environmental Footprint
Vertical farms enable us to produce food in urban environments, drastically reducing the need for arable land. This leads to:
- Preservation of Habitats: Less agricultural expansion means we can preserve forests, wetlands, and natural environments.
- Deforestation Reduction: By growing more on less land, vertical farming actively curbs deforestation, helping maintain biodiversity.
- Urban Integration: Farms can be integrated into under-used buildings, rooftops, or even in the heart of dense cities, transforming urban agriculture.
This shift supports a healthier planet and aligns with global sustainability goals.
4. Local, Fresh Produce & Lower Food Miles
By growing food within urban centers and in close proximity to where people live, vertical farms keep food fresher and slash the carbon emissions from transport (food miles).
- Shorter Supply Chains: Produce goes directly from farm to market or table in hours, not days—especially suitable for leafy greens and herbs.
- Greater Nutritional Value: Fresher produce means nutrition is at its peak, and food waste is minimized.
- Reduced Spoilage: Transport-related spoilage drops dramatically, further increasing overall food production efficiency.
This empowers cities and urban areas to become partially self-sufficient in fresh produce supply.
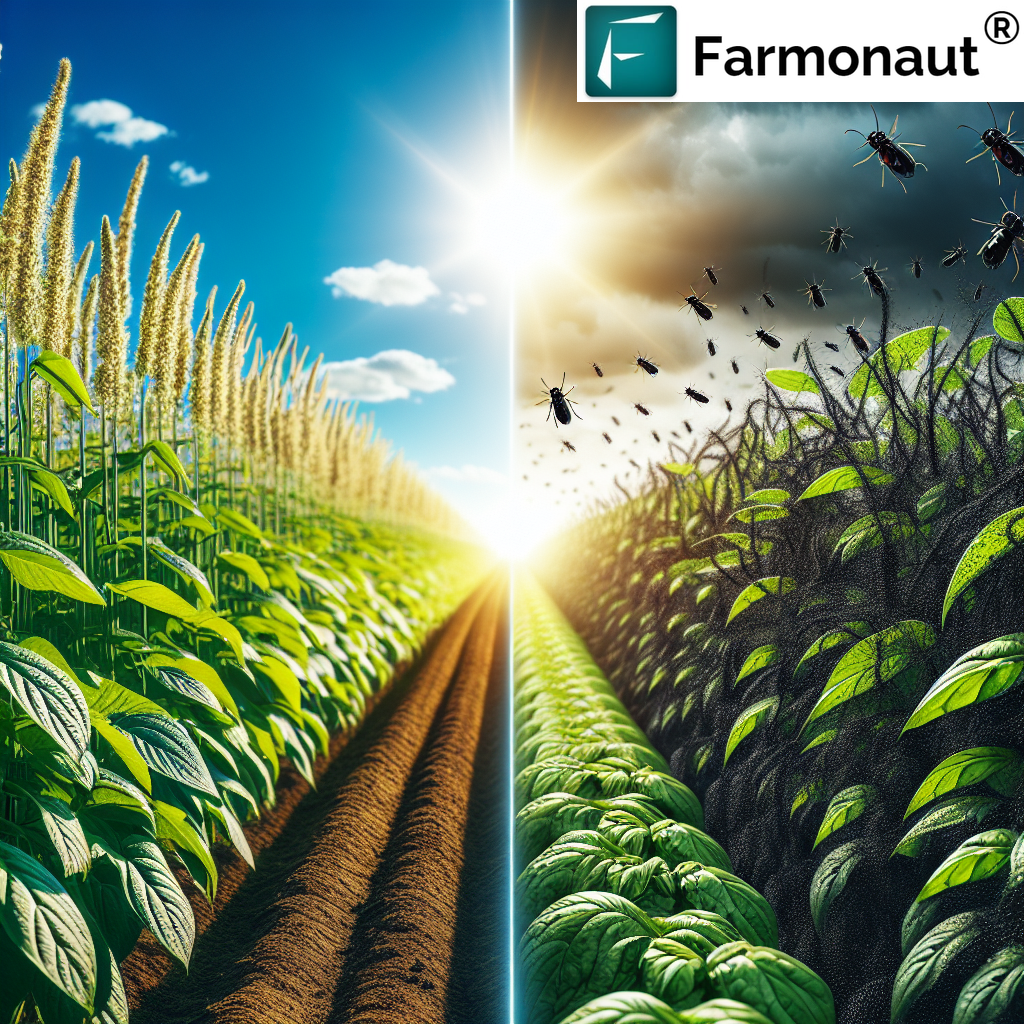
5. Pesticide-Free & Controlled Environment Agriculture
Vertical farms operate in controlled environments that are sealed from outside pests and diseases, meaning:
- No or Low Pesticides: Mostly pesticide-free cultivation leads to safer, healthier produce.
- Environmental Protection: Minimizes contamination of water, soil, and air.
- Food Safety: Consistent, high-quality crops with rigorous monitoring of nutrients and growth factors.
This makes indoor agriculture not only better for the environment, but also ideal for people seeking organic, uncontaminated diets.
6. Year-Round Sustainable Crop Production
With full environmental control, vertical farming enables continuous production, independent of weather, seasons, or climate disruptions.
- Uninterrupted Harvests: Reliable food supply every week, regardless of rain, drought, or frost.
- Rapid Growth Cycles: Optimized light, CO2, and nutrients allow for faster crop growth and potentially more harvests per year.
- Food Security: This consistency bolsters resilience against climate change and natural disasters.
Indoor agriculture in the form of vertical farms will play a major role in ensuring stable global food production into the future.
7. Energy-Efficient Farming Methods and Smart Integration
While energy consumption can be a concern in vertical farms (due to lighting and climate control), advancements in LED lighting and use of renewables are making indoor agriculture systems more energy efficient than ever.
- Precision Lighting: LEDs provide crops exactly what they need, reducing waste and minimizing operational costs.
- Smart Monitoring: IoT devices, AI, and remote sensors optimize all resources and automate adjustments for maximum efficiency.
- Resource Management: Automated control of water, nutrients, and climate using realtime data.
Smart, data-driven technology is the future—connecting growers with actionable insights for sustainable crop production.
Monitor your environmental footprint using Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tool—get real-time data on emissions and drive your farm’s journey towards true sustainability!
Comparison Table: Traditional vs. Vertical Farming Benefits
| Benefit | Traditional Farming (Estimated Value or Qualitative Impact) | Vertical Farming (Estimated Value or Qualitative Impact) |
|---|---|---|
| Land Usage (Acres/ton produced) | ~1-2 acres/ton (depends on crop, location) | 0.05-0.10 acres/ton (10–20x yield per area) |
| Water Consumption (Liters/ton produced) | 200,000–300,000 L/ton | 6,500–15,000 L/ton (up to 95% less) |
| Pesticide Use (kg/year) | 10–50 kg per acre/year (variable) | Near 0 (minimal/none needed) |
| Crop Yield (Tons/acre/year) | ~3–4 tons average | 30–40 tons (leafy greens; 10–20x higher) |
| Carbon Footprint (kg CO2e/ton) | ~3,000–5,000 | Up to 70% reduced (*with renewables/photoLEDs) |
| Food Miles (km/produce shipped) | 1500–3000+ km (often inter-state/country) | 10–50 km (within cities or metro regions) |
| Production Cycle | Seasonal, 1–2 cycles/year (climate dependent) | Year-round, 6–10+ cycles/year (full control) |
| Crop Variety | Wide, including grains, tubers | Leafy greens, herbs, some fruits (variety expanding with technology) |
As we see in this comparison table, vertical farming benefits dramatically outpace traditional methods in many core sustainability and efficiency metrics.
Ensure supply chain transparency with Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Product Traceability—empowering secure, verified farm-to-market tracking for your produce!
Overcoming the Challenges of Vertical Farming
While vertical farming is revolutionizing agriculture, it is not without its challenges. We must address these to ensure long-term viability.
- High Initial Capital Costs: Startup costs for lighting, climate systems, structures, and automation remain significant, often deterring smaller farms. (Over time, falling prices for LEDs and automation mitigate this.)
- Energy Consumption: Indoor environments require more electricity, especially for lighting and cooling. However, energy-efficient farming methods and renewable energy are advancing rapidly.
- Technological Complexity: Running CEA systems requires knowledge in engineering, horticulture, and data analytics. Skilled staff and robust tech support are vital.
- Limited Crop Variety: While the current variety is largely leafy greens, herbs, and some fruits, ongoing research is expanding what’s possible.
- Pollination Issues: In sealed environments, manual or artificial pollination is often required, raising operational costs for certain crops.
The future of agriculture will rely on technological advances and strategic adaptation to overcome these hurdles—ensuring both sustainability and profitability.
For larger operations, Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Solutions offer advanced monitoring and precision data analytics—enabling smarter, scalable farm administration and operational control.
How Farmonaut Empowers the Future of Sustainable Agriculture
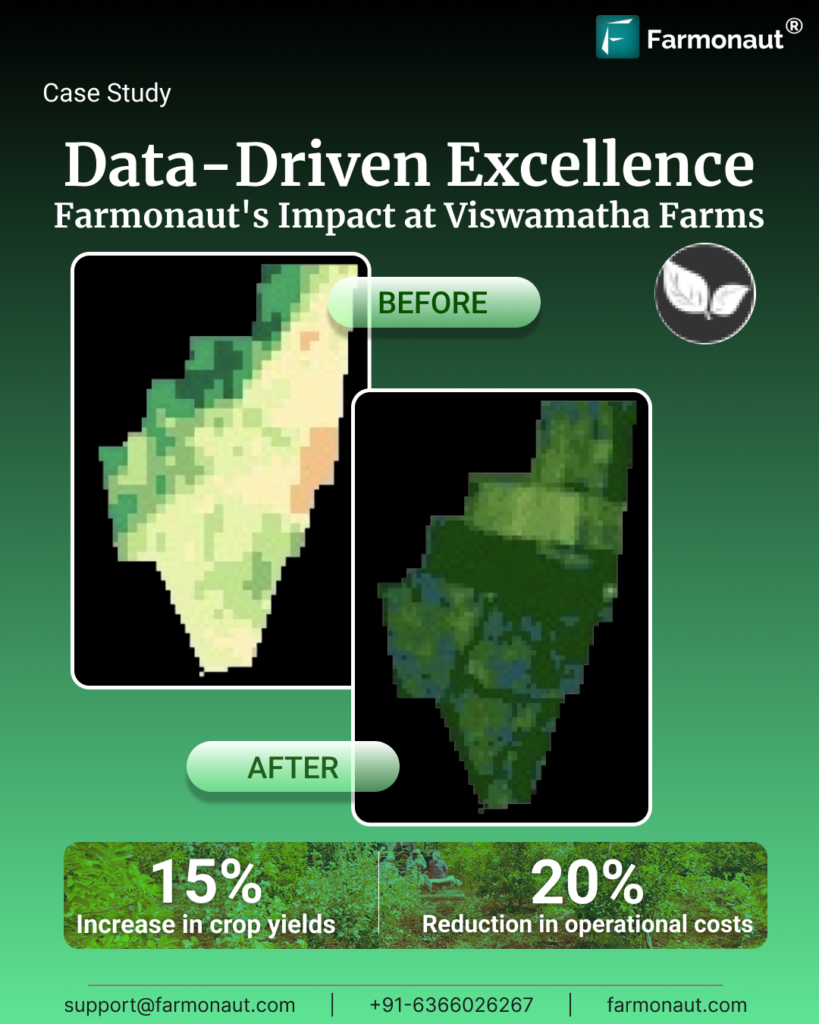
As vertical farming and precision agriculture expand globally, having access to reliable technology and data is vital. Farmonaut bridges this gap—revolutionizing agriculture through advanced satellite-based farm management solutions accessible worldwide via app, web, and API.
- Real-time Crop Health Monitoring: Farmonaut leverages satellite imagery and AI to deliver critical data—NDVI (Vegetation Index), soil moisture, and stress alerts—helping us make informed decisions on irrigation, nutrient application, and disease management.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Personalized, real-time crop advice, weather forecasts, and actionable strategies for farm success—right in your pocket.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Secure, transparent, tamper-proof records for food supply chains, boosting consumer trust and food safety.
- Fleet and Resource Management: For agribusinesses, track vehicles and optimize usage, slashing resource waste and controlling operational costs.
- Carbon Footprinting: Real-time farm emission tracking to ensure compliance and drive eco-friendly strategies. (Explore this on Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting page)
- API Access: Integrate Farmonaut’s satellite & weather data. Explore the API portal | Check developer docs
Secure crop loans and insurance easily through satellite-based verification with Farmonaut’s Crop Loan and Insurance Verification.
With highly affordable subscriptions, anyone—from smallholder farmers to multinational agribusinesses and government agencies—can utilize Farmonaut’s powerful precision agriculture platform for sustainable, data-driven decision-making.
The Future of Vertical Farming and Sustainable Food Production
The future of agriculture is bright with the steady advancement of vertical farms and indoor agriculture. Trends shaping the evolution ahead include:
- Energy Integration: Renewables (solar, wind) and improved LED technology will make energy-efficient vertical farming standard.
- Broadened Crop Variety: As research progresses, ever more crops—beyond leafy greens—will become viable for vertical farming production.
- Automation and Robotics: AI-driven monitoring, automated harvest, and resource allocation will improve yields, reduce costs, and address labor shortages.
- Urban Integration: Cities worldwide will increasingly incorporate vertical farms into urban planning; even supermarkets may feature on-site urban agriculture for ultra-fresh produce!
- Food Security and Policy: Governments and institutions will invest heavily to ensure resilient future food supplies amid climate volatility.
- Smart Analytics: Data platforms (like Farmonaut) will inform every stage of production, from land selection to yield forecast and carbon tracking.
Together, these innovations will help the world feed its growing population efficiently—using fewer resources, less land, and with a far lighter environmental impact.
Optimize your agricultural logistics with Farmonaut’s Fleet Management Tools—reduce transportation waste, cut costs, and streamline your supply chain for better efficiency.
Unlock AI-assisted, real-time recommendations for your next sowing season with Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory Tools.
FAQs about Vertical Farming, Sustainable Production, and Farmonaut
Frequently Asked Questions
What is vertical farming and how is it different from traditional farming?
Vertical farming is a revolutionary food production method where crops are grown in vertically stacked layers, using controlled environment agriculture (CEA) systems such as hydroponics, aeroponics, or aquaponics. It enables optimal use of space, especially in urban centers, and operates year-round independent of outdoor climate conditions.
What are the main vertical farming benefits?
Key benefits include dramatic land and water savings, pesticide-free cultivation, higher yields, minimal food miles, and consistent supply of fresh, local produce. Vertical farming supports environmental sustainability by reducing deforestation, carbon emissions, and food waste.
What are the main challenges of vertical farming?
The top challenges are high initial capital costs, increased energy requirements, operational complexity, limited variety (mainly leafy greens), and artificial pollination needs. However, continual innovation in technology and systems design is rapidly addressing these.
Can vertical farming feed cities and support global food security?
Absolutely. While vertical farming can’t replace all forms of agriculture, it can supplement urban food production dramatically—especially for high-value, perishable crops—improving local food security and resilience.
How does Farmonaut help with vertical or traditional farming?
Farmonaut’s platform aids in both vertical and traditional agriculture by delivering real-time crop monitoring, AI-based advisory services, blockchain-based traceability, carbon footprint tracking, and efficient fleet management. Its accessible, affordable solutions empower smarter, more sustainable agriculture for users of all scales.
Where is Farmonaut available?
Farmonaut operates globally via its Android, iOS, and Web/Browse apps, as well as APIs. It’s tailored for individual farmers, agribusinesses, governments, and supply chain businesses.
How can I start using Farmonaut?
Download the Farmonaut Android app or iOS app, or use the web platform to access satellite-driven precision tools for your farm. Check our API docs for integration.
Get Started with Farmonaut: Shape the Future of Your Farm Today
Whether managing a single rooftop garden, piloting a vertical farm in your city, or scaling sustainable production across hundreds of acres—Farmonaut equips you with data-driven, cost-effective, and climate-smart solutions.
- Join a global community that’s transforming agriculture for a secure, sustainable future.
- Access the app or API from anywhere—on the field, in the office, or on the move.
- Monitor your crop health, manage resources, optimize yields, and reduce environmental impact—no matter the method you use.
Ready to revolutionize your approach to sustainable crop production?
The Farmonaut platform brings the next generation of smart farming tools—powered by satellite data, AI, and blockchain—straight to your fingertips. Embrace the future of agriculture today!