Table of Contents
- Introduction to Germany’s Engine Technology Innovations
- Industry Trivia: Fuel Efficiency and Emissions
- Current Trends in Internal Combustion Engine Technology
- 7 Innovations Powering Cleaner Vehicles
- Feature Comparison Table: Seven German Engine Innovations
- Challenges & Benefits for Cleaner Internal Combustion Engines
- Alternative Fuels for Combustion Engines
- Hybridization and The Future of Diesel Engines
- Sustainable Automotive Technologies Made in Germany
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Farmonaut for Sustainable Fleet & Crop Management
Germany Engine Technology: 7 Innovations Powering Cleaner Vehicles
Meta Description: Discover Germany’s leading internal combustion engine technology innovations for cleaner vehicles—boosting efficiency, reducing emissions, and shaping sustainable mobility.
As we drive toward a sustainable future, internal combustion engine technology continues to evolve—contrary to those who call for its retirement. Germany, recognized as one of the world’s leading automotive hubs, continues to deliver groundbreaking engine innovations for vehicles of every class. These advancements are improving fuel efficiency in vehicles, reducing emissions, and setting new standards for cleaner, smarter mobility.
Current Trends in Internal Combustion Engine Technology
Mark Twain once wittily commented, “Reports of my death are greatly exaggerated.” That also rings true for the internal combustion engine (ICE). While electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction worldwide, experts agree that ICE systems—whether diesel or gasoline engines—will co-exist with EVs well into the next few decades. This is particularly significant in Germany, a place where the future of the automotive industry is forged through relentless research, development, and innovation.
The ICE has come a long way since its inception, and, thanks to modern technologies such as cylinder deactivation, direct injection, hybridization in the automotive industry, exhaust gas after treatment, and alternative fuels for combustion engines, it is cleaner, more efficient, and smarter than ever.
As the push for emissions reduction technologies grows alongside governmental standards (such as Euro 6 and the upcoming Euro 7), Germany’s automotive engineers and manufacturers have expanded their focus, not only on the advent of electric solutions, but also on making internal combustion engines more sustainable. With over 1.5 billion passenger vehicles on the road, and infrastructure lagging behind EV ambitions, the journey to a zero-emissions fleet is not as straightforward as it may seem.
Want to integrate precision field, crop, or fleet management into your agri-business? Explore Farmonaut’s Satellite APIs here. Discover full API Developer Documentation here.
7 Innovations Powering Cleaner Vehicles: Focus on Germany Engine Technology
Germany’s leading automakers—Mercedes-Benz AG, BMW AG, and Porsche AG—together with global suppliers and engineering giants, are combining cutting-edge engine design with green objectives and technological prowess. Let’s delve into the seven remarkable innovations shaping a cleaner future for internal combustion engines:
-
1. Cylinder Deactivation & Variable Valve Timing
Germany’s premium manufacturers have pioneered cylinder deactivation—an approach that allows engines to shut off some cylinders under low-load operating cycles, dramatically improving fuel efficiency in vehicles. When full engine power is not required, only necessary cylinders fire, reducing fuel use and emissions.
This is paired with sophisticated variable valve timing (VVT) systems that fine-tune the timing and duration of valve lift events to match demand. This results in lower pumping losses, better combustion control, and overall higher efficiency.
- Example: BMW’s Valvetronic and Mercedes-Benz’s recent M254 engine use both VVT and cylinder deactivation.
- Benefits: Up to 10% boost in fuel economy and significant CO2 emissions reduction.
-
2. High-Pressure Direct Injection & Compression Ratio Optimization
Next-generation internal combustion engines in Germany now utilize high-pressure direct injection systems with higher compression ratios, enabling more thorough fuel combustion. By precisely controlling the timing and amount of fuel injected directly into the cylinder, combustion is cleaner, power is increased, and incomplete burning is minimized.
- Example: BMW’s new patents, including a pre-chamber ignition system, provide more efficient and complete combustion of gasoline.
- Benefits: Added power, 8–15% improvement in fuel efficiency, lower nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
-
3. Turbocharging & Downsizing
Turbocharging with smaller, “downsized” engines is a proven way to maximize power output while limiting weight and fuel consumption. By forcing more air (and thus more fuel) into the combustion chamber, turbochargers allow for smaller displacement engines that achieve the same or greater power as larger, thirstier powertrains.
- Example: Nearly all modern German petrol and diesel engines, especially from Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes, utilize efficient turbos in 3- or 4-cylinder formats.
- Benefits: Enhanced power-to-weight ratio, as much as 20% fuel savings.
-
4. Advanced Exhaust Gas After-Treatment Systems
Managing tailpipe emissions is key for modern engine compliance with Euro standards. Germany is home to world-class after-treatment systems—selective catalytic reduction (SCR) for diesels, particulate filters, and advanced three-way catalysts for gasoline engines. These systems neutralize NOx, hydrocarbons, particulates, and CO.
- Example: Mercedes-Benz’s BlueTEC diesel engines and Euro 6d/Euro 7-ready models feature cutting-edge SCR and particulate filter tech.
- Benefits: Up to 97% particulate reduction, compliance with strictest emission norms.
-
5. Hybridization in Automotive Industry
Hybrid engines blend the best of internal combustion with electric drive—either as mild-hybrids (MHEV), plug-in hybrids (PHEV), or full hybrids. Electric motors manage low-speed or stop/start motion, while combustion engines take over at higher loads or for battery recharging. Germany has seen a renewed focus on hybridization for both passenger and commercial vehicles, dramatically improving urban efficiency and lowering average emissions.
- Example: Mercedes-Benz plans to reintroduce V8s as mild-hybrid systems. Porsche combines performance and eco-focus in its plug-in hybrid models.
- Benefits: Up to 30% fuel consumption reduction (urban driving), significant drop in CO2 output.
-
6. Hydrogen Powered Engines and Alternative Fuels
Hydrogen combustion and alternative fuels like ammonia, methanol, biodiesel, and E-fuels are in active development and testing in Germany for both on-road and heavy-duty applications. Hydrogen-powered internal combustion engines (H2-ICE) offer rapid refueling and familiar refueling infrastructure, while burning cleanly. The Liebherr Group’s ammonia engine is another example, tapping into fuels with higher energy density for use in marine and mining sectors.
- Example: Tenneco develops H2-ICE components; Cummins X15 engine supports multiple future fuels including hydrogen.
- Benefits: Drastic CO2 reduction, supports transition in sectors where battery power is still impractical.
-
7. Friction Reduction & Lightweight Engine Components
Mechanical friction saps energy, increases wear, and reduces thermal efficiency. To overcome these challenges, Germany’s top engineers are deploying low-friction coatings, advanced lubricants, tougher piston rings (e.g. Tenneco’s DuroGlide), and lightweight materials like high-strength aluminum alloys and composites. These enhancements collectively enhance output, efficiency, and reliability.
- Example: Porsche’s two-piece, 3D-printed pistons with internal oil channels for improved cooling and reduced weight.
- Benefits: As much as 10% reduction in internal engine friction, up to 15% gains in long-term efficiency, and lower maintenance requirements.
Feature Comparison Table: Germany Engine Innovations for Cleaner Vehicles
| Innovation Name | Description | Estimated Fuel Efficiency Improvement (%) | Estimated Emissions Reduction (%) | Technology Type | Applicable Vehicle Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Deactivation & Variable Valve Timing | Selective cylinder shutdown and adaptive valve timing optimize combustion and efficiency. | 5–10% | 10–12% | Mechanical/Control Systems | Passenger Cars, Light Trucks |
| High-Pressure Direct Injection & Compression Ratio Optimization | Precise fuel delivery and higher compression for more complete combustion. | 8–15% | 8–18% | Fuel Delivery/Combustion | All Vehicles |
| Turbocharging & Downsizing | Smaller engines with turbochargers boost power while reducing fuel use. | 15–20% | 14–20% | Forced Induction | Passenger, Commercial, Trucks |
| Advanced Exhaust Gas After-Treatment | SCR systems, particulate filters, and catalysts minimize tailpipe emissions. | 2–5% | Up to 97% (particulates) | Emissions Control | Diesel, Gasoline, Hybrid, Heavy-duty |
| Hybridization | Integrating electric motors with ICEs to optimize operation and recover energy. | 15–30% | 20–30% | Hybrid Powertrain | All (esp. urban/passenger) |
| Hydrogen/Alternative Fuels | Using hydrogen, ammonia, or biofuels to fuel ICEs for near-zero CO2 output. | 5–15% | 70–100% (CO2, with full switch) | Alternative Fuels | Trucks, Heavy-duty, Off-Highway |
| Friction Reduction & Lightweight Components | Low-friction materials, advanced lubricants, and lighter parts enhance efficiency. | 5–10% | 5–10% | Materials Science | All Vehicles |
Key Challenges and Benefits for Cleaner Internal Combustion Engines
Germany’s engines are at the frontlines of balancing performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Key challenges include:
- Transition complexity: Integrating new technologies (hybridization, alternative fuels, advanced emissions systems) with existing infrastructure.
- Cost considerations: Adoption of high-tech components and fuel systems increases manufacturing and maintenance cost.
- Regulatory compliance: Evolving EU emissions standards (Euro 7), requiring significant investments and testing for compliance.
- User adoption: Convincing global consumers and fleet operators to choose cleaner vehicle models amid several mobility alternatives.
- Fuel infrastructure: Building scalable hydrogen, ammonia, or e-fuel refueling stations alongside EV charging networks.
At the same time, the benefits are substantial:
- Cleaner air quality due to drastically reduced emissions (NOx, particulates, CO, hydrocarbons).
- Improved energy efficiency and reduced operating cost for both public and private transport.
- Support for sustainable fuels and the use of renewable energy in fuel production helps in mitigating overall climate impact.
- Retention of existing ICE infrastructure reduces transition friction for industries and consumers.
Alternative Fuels for Combustion Engines: From Ammonia to Hydrogen
Pioneering alternative fuels for combustion engines, Germany’s automotive sector is actively developing and testing new energy carriers to replace traditional gasoline and diesel—without abandoning familiar internal combustion systems.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen powered engines function either as fuel cell EVs or as internal combustion engines burning hydrogen, emitting only water vapor. Critical research and infrastructure expansion are ongoing to support hydrogen adoption in heavy-duty and commercial vehicles.
- Ammonia: With far higher energy density than lithium-based batteries, ammonia is a promising fuel, especially for marine and mining applications where weight is a premium.
- E-fuels and Biofuels: Synthetic gasoline, diesel, and methane produced from renewable sources are designed as direct replacements for fossil fuels, supporting an easier transition and reducing life cycle CO2 footprint.
- Biodiesel & Methanol: Enable cleaner, flexible operation for commercial and agricultural engines.
Innovations such as engine part-load optimization, advanced wear-resistant coatings, and AI-driven engine calibration are further supporting the shift toward these fuels.
Hybridization in Automotive Industry and the Future of Diesel Engines
Hybridization is playing a transformative role across all markets. By running ICEs in their most efficient operating window and using electricity for low-load conditions, German automakers are extracting more value from every ounce of fuel. Research such as the Ricardo Magma xEV project demonstrates huge brake thermal efficiency improvements of up to 45% through optimal electrification strategies.
The future of diesel engines will be dictated not by obsolescence, but by continued improvement. Diesel’s unmatched energy density and cost-effectiveness for heavy-duty, agricultural, and marine applications ensure it will remain vital, especially when combined with renewable blends and after-treatment solutions.
Euro emissions standards—especially Euro 7—are pushing the industry to approach near-zero impact emission levels. Life-cycle assessment (LCA) now plays a larger role in automotive design, considering all emissions from product sourcing to disposal.
Sustainable Automotive Technologies Made in Germany
Let’s summarize the environmental impact, sustainable technologies, and digital transformation revolutionizing Germany’s automotive industry:
- Smart Engine Control: Artificial intelligence, digital twin testing, and predictive controls maximize performance and lower resource use.
- Advanced Materials: Lightweight, high-strength alloys and composites reduce weight, lowering both fuel consumption and emissions for every vehicle type.
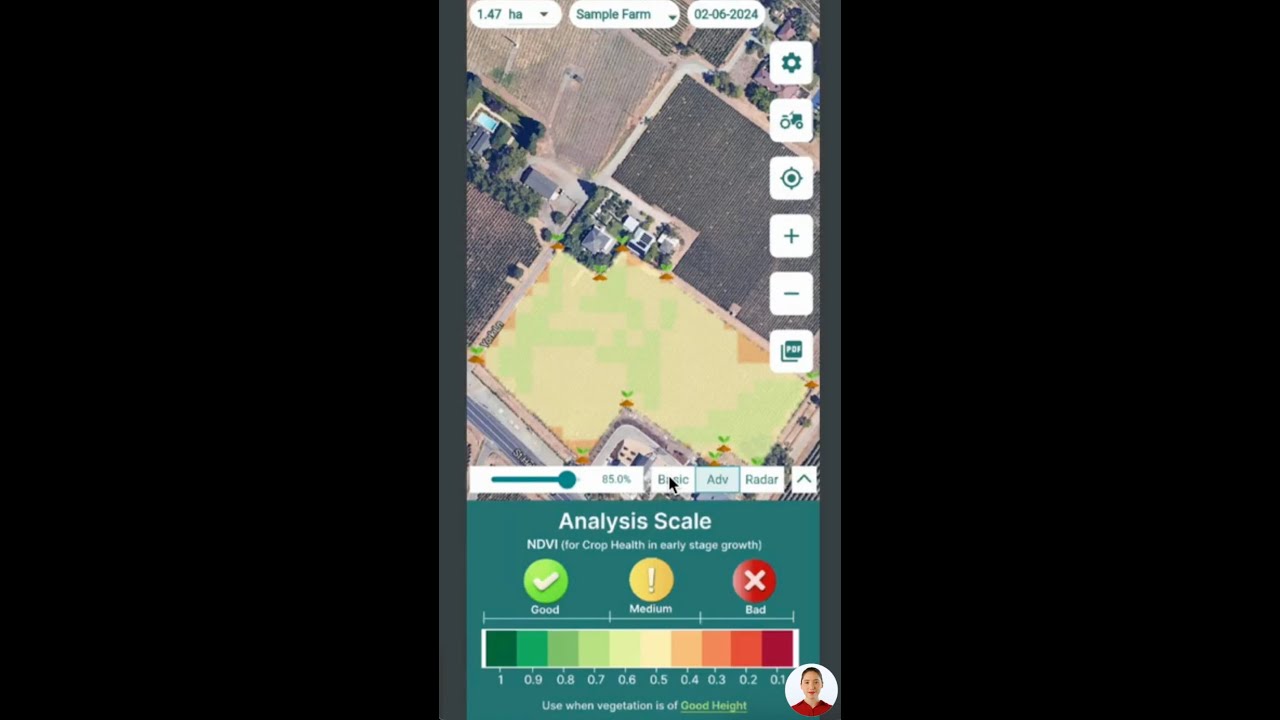
- Integrated Fleet Management: Real-time monitoring and optimization of vehicle fleets for better resource utilization and carbon footprint control. Farmonaut’s Fleet Management platform is a leading digital tool for agricultural and commercial vehicle operations management, reducing costs and environmental impact through satellite-based routing, safety, and analytics.
- Carbon Footprinting Tools: Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution lets agribusinesses and governments actively monitor and reduce the carbon impact of their vehicle operations, supporting compliance and sustainability.
- Product Traceability: Learn more about Farmonaut Product Traceability for blockchain-secured, transparent supply chains—ensuring that the environmental credentials of vehicles and fuels are verifiable.
- Large-scale Farm & Plantation Management: Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Solution supports coordinated vehicle, crop, and resource management at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions: Germany Engine Technology & Cleaner Vehicles
1. Will internal combustion engines be phased out in Germany soon?
No. Most experts believe that internal combustion engine technology will remain relevant in Germany and worldwide for at least the next 30 years. This is due to existing vehicle fleets, fuel infrastructure, and the crucial performance of ICEs in heavy-duty and off-highway applications. Technology improvements continue to reduce emissions and improve efficiency.
2. What are the latest clean engine technologies for passenger vehicles?
The latest German innovations include cylinder deactivation, variable valve timing, hybridization, advanced exhaust after-treatment, hydrogen powered engines, and use of renewable fuels.
3. Is hybridization better than going fully electric?
Hybridization offers flexibility—useful especially where electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure is less developed. It improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions in stop-start urban environments, while retaining the range and fast refueling of combustion power.
4. Can diesel engines still be clean and efficient?
Absolutely. The future of diesel engines includes after-treatment technology, use of renewable fuels, and hybrid approaches — all helping to minimize emissions and maximize fuel savings, especially for trucks, rail, marine, and agricultural vehicles.
5. What role will hydrogen play in the future?
Hydrogen is a major enabler of alternative fuels for combustion engines. H2-ICEs, fuel cells, and hybrid systems powered by green hydrogen offer long range and rapid refueling, critical for sectors where EV batteries and charging are still limiting.
Farmonaut: Empowering Cleaner Vehicle Management for Agriculture and Enterprise
We endorse sustainable and efficient vehicle management not just in mobility, but across every sector—including agriculture. Farmonaut, a leader in agricultural technology, provides comprehensive fleet management and carbon footprinting solutions, leveraging satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, and real-time data analytics.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tool empowers agribusinesses to optimize vehicle usage, cut costs, and minimize emissions.
- Crop Area Estimation & Advisory: Automate field-level decision-making and resource allocation for greater productivity and sustainability — see Large Scale Farm Management.
- Blockchain Traceability: Secure traceability ensures credible and transparent vehicle and input supply chains.
- Carbon Footprinting: Carbon monitoring enables real-time emission tracking for regulatory compliance and sustainable goals.
- Crop Loan and Insurance: De-risk agricultural finance with satellite-verification for loans and insurance products.
With Farmonaut, we can drive a cleaner, more intelligent, and sustainable future across agriculture and beyond.
Summary: The Road Ahead for Internal Combustion Technology and Cleaner Vehicles
The legacy and future of Germany’s internal combustion engines demonstrate that technology, when steered by rigorous innovation, can give old powertrains a new lease on life. The seven innovations outlined above—ranging from cylinder deactivation to hydrogen-powered operation—prove that ICEs can be cleaner and more efficient, making a crucial contribution in our shared journey toward sustainable mobility.
As electric vs combustion vehicles continues to be debated, our collective focus should be on maximizing the thermal efficiency improvements and minimizing environmental impact using all available tools—hybridization, advanced materials, alternative fuels, and intelligent operational controls.
If you’re invested in sustainable technology for agriculture, fleet management, or environmental compliance, explore Farmonaut’s solutions to bring the power of digital transformation, resource efficiency, and transparency into your operation—today and into the cleaner future.