Ag Machinery: 10 Modern Farming Innovations
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Types of Agricultural Machinery and Their Uses
- Comparison Table: Key Machinery Innovations
- Advancements in Modern Agricultural Machinery
- Farmonaut’s Role in Precision Agriculture and Machine Management
- Challenges Facing the Agricultural Machinery Industry
- Future Directions and Ongoing Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction: The Revolution of Agricultural Machinery
Agriculture is at the heart of human civilization, and the evolution of agricultural machinery has played a crucial role in shaping how we produce and supply food. Today, modern farming equipment is no longer just about horsepower and ruggedness; it’s about precision, intelligence, and sustainability.
As we continue to experience rapid technological advancements in agricultural machinery, the ways we perform tasks such as plowing, planting, fertilizing, and harvesting have become increasingly efficient, safe, and sustainable. Our world is witnessing machines capable of autonomous operation, enhanced data connectivity, and precise application of resources – all contributing to a smarter and more resilient future for agriculture.
Types of Agricultural Machinery and Their Uses
The agricultural machinery landscape is vast, encompassing a wide range of machines and equipment designed for specific tasks. These machines are the cornerstone of farming, forestry, and related industries, enabling us to enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and achieve sustainable and precise operations.
Let’s explore the core types of agricultural machines and their principal uses:
- Tractors: The backbone of modern agriculture, tractors are versatile machines used for plowing, tillage, planting, and hauling implements. With powerful engines, they serve as the main source of mechanical energy for many other attachments and tools.
- Plows: Used for primary tillage, plows break up and turn over the soil to prepare it for planting. Besides creating a new seedbed, they help incorporate organic matter and control weeds.
- Cultivators: Performing secondary tillage, cultivators stir and pulverize the soil for a smooth surface suitable for planting. Mounted or self-propelled, they also help with weed control.
- Harrows: Following plowing, harrows break up clods and create an ideal environment for seed germination. They come in disc or tine types, depending on soil conditions and crop requirements.
- Seeders and Planters: These machines plant seeds at precise depths and intervals, ensuring uniform emergence. Seeders are mainly for small seeds (example: wheat, canola), while planters work with larger seeds (corn, soybeans).
- Sprayers: Sprayers are crucial for applying pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers; they come in backpack, boom, or self-propelled forms for consistent distribution across crops.
- Harvesters: Crop harvesting equipment like combine harvesters efficiently gather grains, while specialized harvesters are designed for fruits and vegetables. These machines greatly improve productivity.
- Balers: After harvesting, balers compact straw, hay, or silage into transportable bales for easier storage and movement.
- Grain Dryers: By removing moisture from harvested grains, these machines prevent spoilage, safeguarding crop quality.
- Fertilizer Spreaders: These are used to distribute fertilizers evenly across fields for optimal crop growth.
Comparison Table: Key Machinery Innovations
To quickly contrast the most influential modern farming equipment innovations, we’ve summarized them in the table below. This resource highlights each innovation’s primary function, how much it boosts productivity, its sustainability profile, and the leading technology at its core.
| Innovation Name | Main Function | Estimated Productivity Gain (%) | Sustainability Impact | Key Technology Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Tractors | Driverless plowing, planting, spraying | 30-70% | High | AI, GPS, Robotics |
| Electric & Hybrid Machinery | Emission-free power for various tasks | 15-25% | High | Electric Engines, Battery Systems |
| Robotics in Agriculture | Precise tasks: weeding, pruning, harvesting | 20-50% | Medium/High | AI, Sensors, Machine Vision |
| Precision Agriculture Technology | Data-driven input management | 10-30% | High | GPS, Satellite, Remote Sensing |
| Smart Irrigation Systems | Efficient and automated water delivery | 20-50% | High | IoT, Sensors, Data Analytics |
| Advanced Planters/Seeders | Accurate seed placement | 12-18% | Medium | Mechanical Precision, GPS Mapping |
| High-Efficiency Combine Harvesters | Fast, loss-minimized harvesting | 25-40% | Medium/High | Automation, Sensing |
| Variable Rate Sprayers | Targeted pesticide & fertilizer application | 10-20% | High | Sensors, GIS, Data Analytics |
| Automated Balers | Efficient post-harvest residue management | 10-15% | Medium | Mechanical Automation |
| Grain Dryers with Smart Controls | Automated, energy-saving moisture control | 10-18% | High | IoT, Sensors, Thermal Controls |
Advancements in Modern Agricultural Machinery
Recent technological advancements have profoundly changed the landscape of agricultural machinery. By integrating robotics, sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), satellite monitoring, and electric/hybrid machinery, we now experience farming systems that simultaneously maximize efficiency, minimize costs, and champion sustainable practices.
1. Autonomous Tractors: Redefining Power & Precision
Autonomous tractors lead the charge in technological innovation, being capable of operating with minimal or no human oversight. By leveraging AI, GPS, and robust data connections, these machines perform tasks like plowing, planting, and spraying independently. Not only do they address labor shortages, but they also guarantee precise, round-the-clock fieldwork, optimizing both inputs and yields.
- Efficiency: Substantial reduction in labor costs; autonomous tractors can lower expenses by up to 60%.
- Environmental Sustainability: Autonomous operation enables optimal resource usage and reduced emissions.
- Examples: John Deere’s self-driving tractors for precision spraying and planting, as showcased at CES (see latest developments).
2. Electric and Hybrid Farm Machinery for Sustainable Agriculture
The surge in electric and hybrid farm machinery signals a shift toward environmental sustainability. Modern tractors and machinery used for primary, secondary, and post-harvest processes are often powered by electricity or hybrid systems, drastically reducing greenhouse gas emissions and noise.
- Emission-Free: Electric tractors match the power of diesel models yet operate without emissions.
- Sustainability: Reduced operational costs and improved energy efficiency.
- Example: New Holland’s NH2 hydrogen-powered tractor, emitting only water vapor (learn more).
3. Robotics in Agriculture: AI and Automation Take the Lead
The role of robotics in agriculture is rapidly expanding. Today’s smart machinery is capable of pruning, weeding, and even delicate harvesting—tasks previously challenging to automate. AI-driven robotic systems maximize crop quality, minimize labor requirements, and precisely apply water, fertilizers, or pesticides.
- Precision: AI enables robots to monitor plant health, differentiate crops from weeds, and execute tasks with minimal resource use.
- Research: Ongoing research in autonomous pruning, as evidenced in orchards and vineyards (see recent research).
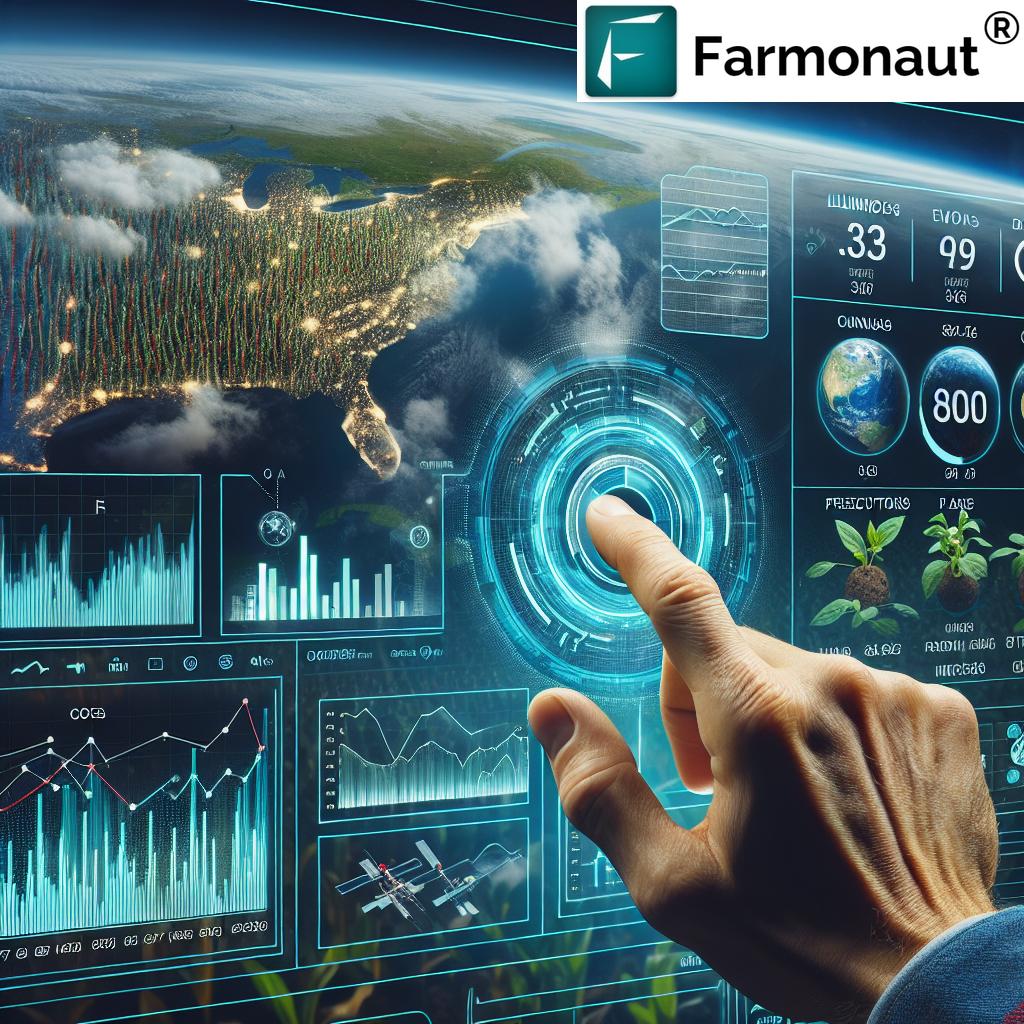
4. Precision Agriculture Technology: Data-Driven, Targeted Farming
Precision agriculture technology utilizes remote sensors, GPS mapping, and real-time data analytics to monitor field variability. This technology allows us to optimize input application for water, fertilizers, and pesticides, tailoring management for each section of land.
- Benefits: Significantly reduce costs, limit environmental impacts, and increase productivity by allocating resources where they are most needed.
- Sustainability: Precision systems cut input use and boost profitability while minimizing runoff and pollution.
5. Smart Irrigation Systems: Optimizing Water Use for Increased Efficiency
Modern smart irrigation systems tap into the Internet of Things (IoT), soil moisture sensors, and climate data to provide crops with the exact amount of water they need. Automated scheduling and real-time monitoring mean water isn’t wasted, and environmental impact is minimized.
- Water Efficiency: Reduce water usage by up to 50%, saving costs and supporting sustainable resources.
- Adaptability: Smart systems continuously adapt to changing soil and weather conditions.
6. Variable Rate Technology (VRT) in Spraying and Spreading
Variable rate sprayers and spreaders adapt the application rates of fertilizers and pesticides in real time, based on soil and crop data. This ensures inputs are only applied where necessary, enhancing sustainability.
7. High-Efficiency Harvesters and Combines
Innovations in harvesting equipment now offer seamless cutting, threshing, and cleaning of grains with minimal crop loss. Automation, in-cab controls, and advanced cleaning systems deliver optimal productivity and quality.
- Productivity: Modern combines harvest larger areas faster and with greater efficiency.
- Grain Quality: Gentle handling preserves more marketable crop.
8. Automated Balers for Post-Harvest Handling
Today’s balers use automation to efficiently collect, compact, and tie crop residues, transforming them into neat bales for storage or transportation. Their improved design reduces labor needs and speeds up field clearance.
9. Grain Dryers with Smart Moisture Control
Integrated smart controls and sensors in grain dryers monitor moisture levels to prevent under- or over-drying, preserving crop quality and reducing energy costs.
10. AI-Integrated Fleet and Resource Management Systems
Fleet management has become seamless with AI-powered software and sensor integration. Platforms like Farmonaut enable real-time tracking and maintenance of agricultural vehicles—helping us manage usage, safety, and overall machine efficiency.
- Benefit: Optimizes deployment, cuts downtime, and lowers operational costs.
- Explore: Farmonaut Fleet Management offers efficient, satellite-enabled oversight for any size operation.
Farmonaut’s Role in Precision Agriculture and Machine Management
At Farmonaut, our mission is to make precision agriculture affordable and accessible worldwide. We recognize the tremendous impact that smart machinery and technological solutions can have on agricultural success, and we empower farming communities with actionable data to complement their investment in modern machines and systems.
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: We use multispectral satellite imagery to provide real-time insights on vegation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and crop status, enabling users to maximize efficiency and yield.
- AI Advisory Systems: Jeevn, our AI-powered advisor, offers instant, personalized guidance on field management, irrigation, pest and weed control, and more.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Transparency is essential. Our solution ensures every step in the supply chain is secure and visible—learn more about traceability here.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Track, maintain, and optimize your agricultural machinery—from tractors to harvesters—with our fleet management solution.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Monitor your operational emissions with Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool and take actionable steps toward sustainability.
- API Integration & Developer Support: We make satellite and weather data universally accessible for seamless app, research, and agribusiness integration. Explore our API and check out the developer docs.
- Large Scale Management: Our large scale management tool allows cooperatives, agribusinesses, and governments to monitor and manage extended farm operations remotely and efficiently.
Farmonaut’s scalable platform supports everyone from smallholder farmers to large-scale enterprises, offering subscription options for every need.
Key Challenges in the Agricultural Machinery Industry
Despite these breakthroughs, the agricultural machinery industry faces challenges that can impact the rate of adoption and innovation:
- High Initial Costs: Many advanced machines and systems require significant upfront investment, potentially putting them out of reach for some farming operations.
- Skill Requirements: There is an ongoing need for operators and farmers skilled in the operation, maintenance, and data interpretation associated with modern farming equipment.
- Economic Volatility: Fluctuating commodity prices and changing interest rates can impact machinery purchases and overall strategy (recent industry economic downturn).
- Technological Accessibility: Not all regions have the infrastructure or connectivity to support the latest autonomous or precision agriculture technology.
- Environmental Pressures: Balancing increased food production with environmental sustainability remains a global challenge.
The Future of Agricultural Machinery: Innovation, Adaptability, and Sustainability
Looking ahead, we anticipate continued development in agricultural machinery aimed at making farm work smarter, more accessible, and environmentally responsible. Major focus areas include:
- Further Autonomy: Ongoing refinement of fully autonomous tractors, harvesters, and drones—for even greater efficiency and adaptability. Companies like Deere are doubling down on autonomous tractors with fleets of new machines (read about their initiative).
- Sustainable Power: Transition toward electric, hybrid, and hydrogen-powered equipment.
- Smart Integration: Seamlessly linking sensors, satellite data, weather forecasts, and farm management platforms (such as Farmonaut) to create unified, data-driven farming systems.
- Accessible Precision: Efforts by countries such as China (five-year smart farming plan) aim to boost food output through accessible, smart farming technology.
- Environmental Accountability: Standardized carbon and resource footprint tracking—and making those metrics publicly available, as enabled by Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting product.
Sustained research, investment, and education will drive agricultural machinery toward a future where we efficiently, equally, and sustainably produce food for a growing population.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Agricultural Machinery
What is the most important advancement in agricultural machinery?
While there are many, autonomous tractors and precision agriculture technology collectively represent the biggest leap. They bring automation, data-driven decisions, and 24/7 efficiency to farming.
How do precision agriculture technologies improve sustainability?
They minimize resource usage by applying water, fertilizers, and pesticides only where needed, reducing environmental impact and boosting productivity.
What is the role of Farmonaut in managing agricultural machinery?
Farmonaut offers satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven advisories, blockchain traceability, carbon footprinting, and resource tracking, ensuring that investment in high-tech machines is maximized for operational efficiency and sustainability.
How can I integrate Farmonaut’s data with my existing farm management systems?
Farmonaut provides a robust API (see API), along with detailed developer documentation for smooth integration into any software or agribusiness system.
What are the main types of agricultural machines used today?
Key machine types include tractors, plows, cultivators, harrows, planters/seeders, sprayers, harvesters, balers, grain dryers, and fertilizer spreaders.
Are electric and hybrid machines affordable for small farms?
While costs remain higher than conventional equipment, prices are expected to decrease as adoption grows and technology matures. Farmonaut’s platform can assist small farms in maximizing return on investment by improving operational efficiency across all machinery.
How do I get started with Farmonaut?
Simply download our app for Android or iOS, or access directly via the web browser app. Choose a subscription plan or contact us for a custom solution.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Agricultural Machinery
From tractors and autonomous machines to smart irrigation systems and AI-guided sprayers, modern farming equipment is revolutionizing every step of the crop cycle. These advances don’t just increase yields, cut labor, and control costs—they are essential for building a food system that’s productive, sustainable, and resilient.
At Farmonaut, we believe that combining cutting-edge agricultural machinery with actionable insights, real-time monitoring, and seamless integration will help ensure global food security and environmental stewardship. Join our mission to enhance productivity, reduce resource wastage, and create a more sustainable future for agriculture—powered by innovative technology and empowered by data-driven farming.