Crop Stress: 7 Hacks to Boost Your Yield Fast!
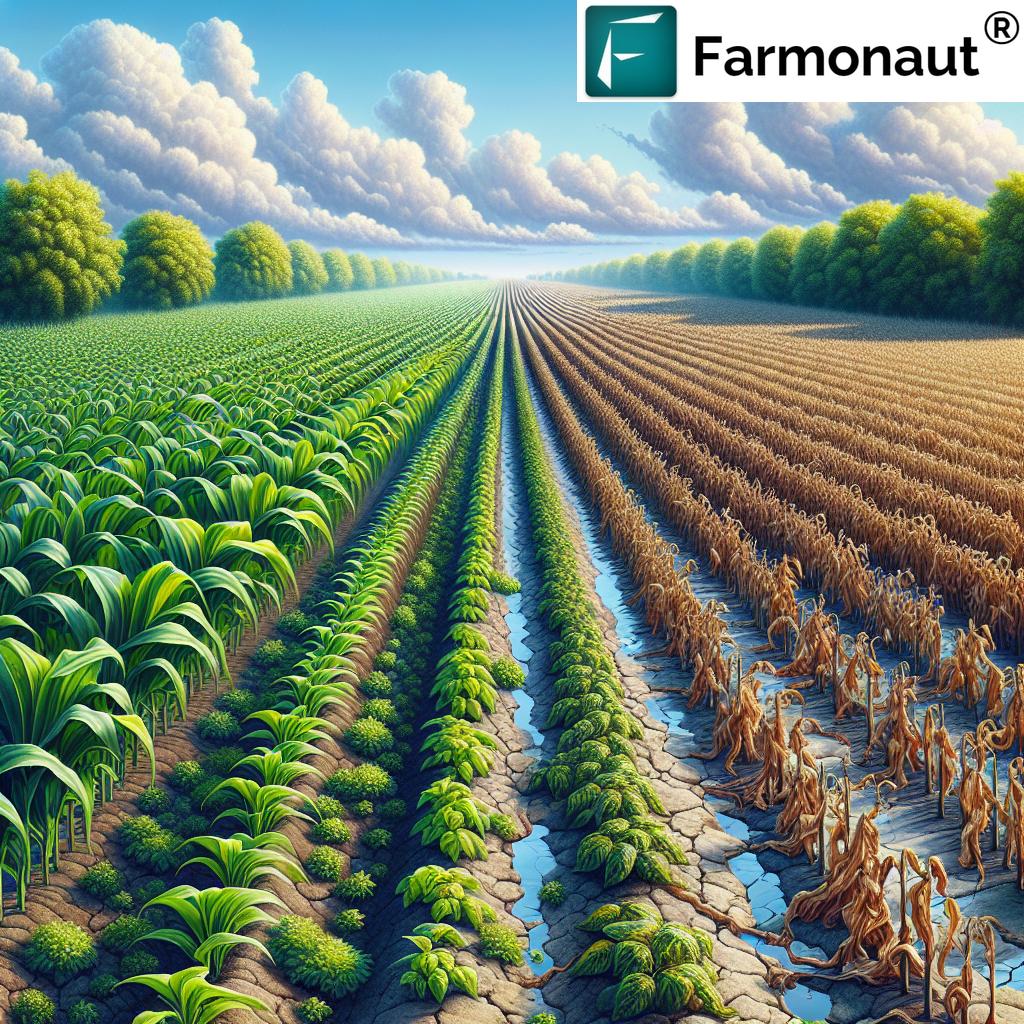
Modern agriculture faces an urgent challenge: crop stress—any external factor that adversely affects the growth, development, and yield of our plants. For us as farmers, agronomists, and agricultural businesses, understanding crop stress management has become essential for optimizing yields, improving soil health, and achieving sustainable farming outcomes.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the types, causes, effects, detection methods, and management strategies for crop stress. We’ll also highlight new, actionable crop stress detection technologies, precision agriculture techniques, and how Farmonaut’s solutions can empower your farm or agribusiness to achieve greater productivity and resilience.
Types, Causes, and Effects of Crop Stress
Crop stress is broadly divided into two major categories: abiotic stress and biotic stress. Recognizing the different types, causes, and effects of crop stress allows us to design targeted management strategies for improving yield, mitigating damage, and fostering sustainable agriculture.
Abiotic Stress in Crops
- Drought Stress: When water availability is insufficient for plant needs, crops experience osmotic stress, reduced photosynthesis, stunted growth, and decreased yields. Severe cases can cause plant death.
- Salinity Stress: High salt concentrations restrict water uptake and nutrient absorption, leading to leaf burn and reduced productivity.
- Temperature Extremes: Low temperatures may cause frost damage and inhibit seed germination, while high temperatures can denature vital proteins and enzymes, causing heat stress and visible leaf damage.
- Light Stress: Both inadequate and excessive light affect photosynthesis and plant growth. Too much light can cause photoinhibition and chlorophyll breakdown, while too little reduces photosynthetic rates.
Biotic Stress in Crops
- Pest Stress: Insects, nematodes, and other pests feed on crops, causing damage to tissues, reduced photosynthetic area, and impaired development.
- Disease Stress: Fungi, bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens directly cause infections that hamper plant metabolism, stunt growth, and may result in complete crop loss.
- Weed Stress: Weeds fiercely compete with crops for sunlight, water, and nutrients, reducing both yield and quality.
How External Factors Trigger Crop Stress
Environmental conditions—such as drought, excessive rainfall, salinity, or abrupt temperature shifts—interact in complex ways with the field’s soil, plant genetics, agronomic practices, and pest/disease pressures.
- Drought: Reduced water availability impacts osmotic balance and plant cell turgor.
- Salinity: Soil with high salt levels acts like a sponge, pulling out water from plant roots through osmosis.
- High/Low Temperatures: Impact cell membrane stability, denature enzymes, and inhibit normal seedling and reproductive development.
- Pest/Pathogen Attack: Create wounds, sap resources, or disrupt plant functions.
Visible and Invisible Effects of Crop Stress
- Visible Symptoms: Leaf wilting, yellowing (chlorosis), necrosis (dead spots), stunting, or premature drop.
- Invisible/Internal Symptoms: Reduced photosynthetic activity, altered metabolic rates, increased susceptibility to secondary infections, and ultimately lower yields and weaker plant resilience.
Detection & Monitoring of Crop Stress
Traditionally, detection of crop stress relied on delayed, visual observation—by the time we spot wilting, yellowing, or stunted growth, significant damage may have already occurred. Now, with advanced sensors, imaging systems, and data-driven remote sensing, early intervention is increasingly possible.
Advanced Crop Stress Detection Technologies
- Remote Sensing in Agriculture: Satellite and drone-based imaging recognize stress-induced changes in the canopy’s light reflectance patterns—identifying drought, nutrient deficiency, or pest attack before we see visible symptoms.
- Spectral Imaging: Hyperspectral and multispectral cameras detect subtle stress signatures by measuring how plants reflect wavelengths of light.
- Thermal Imaging: These systems reveal changes in canopy temperature, which can indicate water stress, transpiration issues, or pest infestation.
- IoT Sensors: In-field sensor networks continuously monitor soil moisture, temperature, nutrient levels, and relay alerts on stress conditions in real time.
With these technologies, we can detect emerging stress factors, intervene before irreversible damage, reduce chemical inputs, and ultimately improve yields and sustainability.
Crop Stress Management Techniques & Impact Table
| Stress Management Hack | Description | Early Detection Technology Used | Estimated Impact on Yield (%) | Impact on Soil Health | Sustainability Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Irrigation | Utilizing real-time soil moisture data and targeted water application to minimize drought stress and wastage. | IoT Moisture Sensors, Remote Sensing | 8-15% increase | High | 5 |
| Advanced Remote Sensing | Satellite or drone-based monitoring detects stress early, guides interventions and resource allocation. | Satellite Imaging, Spectral & Thermal Cameras | 10–20% (via timely action) | Medium–High | 5 |
| Breeding Stress-Tolerant Varieties | Developing or selecting crop varieties with enhanced resistance to drought, salinity, and temperature stress. | Genotyping, Phenotyping, Field Data | 10–30% in susceptible areas | High | 5 |
| Integrated Pest Management | Combining biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical methods to control pests while reducing chemical reliance. | Pest Population Monitoring, Spectral Imaging | 5–12% | Medium | 4 |
| Soil Health Improvement | Using organic amendments, mulching, and conservation tillage to enhance soil structure, microbiome, and nutrient cycling. | Soil Sensors, Remote Sensing | 7–14% | High | 5 |
| Microbial Interventions | Application of beneficial microbes like Trichoderma or Pseudomonas sp. to improve growth and manage pathogen stress. | Lab Analysis, Field Monitoring | 5–10% | Medium–High | 4 |
| Precision Nutrient Management | Regular soil testing and data-driven fertilizer application to avoid deficiencies or excesses. | Soil Test Kits, Sensor Feedback, Imaging | 5–12% | High | 5 |
*Estimated values are for illustrative guidance. Actual impact depends on farm context, crop, and environmental conditions.
Crop Stress: 7 Hacks to Boost Your Yield Fast!
Management of crop stress isn’t just about treatment, but also about prevention, early detection, and building resilience into our agricultural systems. Here are seven powerful, practical strategies that combine modern technology and best agronomic practices to help us boost yields, protect soil health, and create truly sustainable farms.
1. Breeding & Selecting Resilient Varieties for Stress Tolerance
Long-term crop stress management starts with the genetics of our plants. Developing, selecting, and planting crop varieties with improved resistance to drought, salinity, pest, and disease pressures gives your farm an immediate defensive advantage.
- Drought-resistant varieties feature deep-root systems, efficient water use, and osmotic adjustment (the plant’s ability to maintain turgor with less water).
- Salt-tolerant plants can thrive in soils with elevated electrolyte concentrations by stabilizing cell membranes and maintaining nutrient uptake.
- Breeding for disease and pest resistance means selecting genotypes with robust natural defense pathways and resistance genes.
Tip: When evaluating seed options, focus on traits such as cell membrane stability, large seed size, vigorous early growth, or enhanced root architecture. These traits actively support survival under adverse environmental conditions and boost both resilience and yield.
2. Precision Agriculture Techniques for Optimal Resource Management
Precision agriculture leverages data, sensors, and analytics to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides in just the required amounts, at just the right time. This not only reduces wastage but actively prevents crop stress by mitigating the impact of drought, nutrient deficiencies, and pest outbreaks.
- Precision irrigation systems—using soil moisture sensors and weather data—apply water directly to where and when crops need it, conserving resources while reducing osmotic and drought stress.
- Variable rate nutrient application ensures that each area of your field receives optimized fertilizer, supporting even plant growth and stress resilience.
- Targeted pesticide application means that we only use inputs when and where necessary, lowering chemical load on the soil and surrounding environment.
Use Case: Farmonaut’s remote sensing solutions provide real-time feedback on soil and crop status, helping you enable and automate precision agriculture on your farm—without the need for expensive, on-field hardware.
Manage large and multi-field operations more efficiently, with satellite alerts and tailored advice.
3. Adopting Climate-Smart Agriculture
Climate-smart agriculture means choosing practices and technologies that increase our farm’s resilience to unpredictable and extreme weather events—including drought, heat waves, sudden temperature changes, or extended rainy periods.
- Adopt conservation tillage, agroforestry, or intercropping to create microclimates, enhance carbon sequestration, and limit soil erosion.
- Mix crop types and incorporate climate-smart varieties for adaptive resistance to new pests and diseases arising under climate change.
-
Monitor and manage carbon emissions from your farm to meet consumer, regulatory, and sustainability standards.
Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting tool quantifies and helps reduce your environmental impact through real-time emissions data and actionable guidance.
These approaches not only help maintain yield in uncertain conditions, but also enrich soil health and foster environmental sustainability.
4. Integrated Pest Management Strategies (IPM)
Repeated overuse of chemical pesticides can damage the ecosystem and create resistant pest populations, ultimately worsening crop stress. Integrated Pest Management strategies combine cultural methods, biological controls, mechanical tools, and minimal pesticide use to break pest cycles and promote resilience.
- Rotate crops each season and use intercropping to disrupt pest lifecycles and suppress weed pressure.
- Introduce beneficial organisms (predators or parasitoids) or microbial solutions as part of a biological control program.
- Apply pesticides only as a last resort—and always in a targeted, precise manner, minimizing harm to non-target organisms and the soil microbiome.
Technology Tip: Use Farmonaut’s satellite and spectral imaging tools to detect unusual canopy reflectance or spot specific pest/disease stress signals for faster, more targeted IPM actions.
5. Precision Nutrient Management
Nutrient deficiencies directly cause crop stress and reduce potential yields. Precision nutrient management ensures our plants always have balanced access to the key nutrients they require, without over-application that might harm the environment.
- Conduct regular soil testing using in-field sensors or lab kits to detect deficiencies and guide fertilizer strategy.
- Use variable-rate application tools to deliver nutrients—organic or synthetic—only where and when they’re needed.
- Incorporate foliar feeding or targeted amendments in response to identified issues, helping plants recover faster and reducing input wastage.
Farmonaut’s platform provides satellite-derived nutrient status maps and AI-driven advisory—so you can allocate resources efficiently and minimize preventable stress events.
6. Soil Health Improvement Practices
Healthy soil is the unshakable foundation of stress-free, high-yield crops. We must adopt soil health conservation practices that:
- Mulch or cover-crop to reduce surface evaporation, protecting moisture in drought-prone environments.
- Harvest and store rainwater for supplemental irrigation during dry spells.
- Enhance organic matter (compost, cover crops, minimum tillage) to invigorate soil microbial life, improve structure, and boost resilience against abiotic and biotic stress factors.
Did you know? Satellite imagery and soil reflectance data can non-invasively assess your soil health, suggest improvements, and even benchmark your field versus regional averages.
Traceability tools from Farmonaut validate and capture your soil-friendly, sustainable cultivation practices—backing up your farm’s environmental claims with blockchain-powered data.
7. Microbial & Biotechnology-Based Interventions
The future of sustainable crop stress management is ‘living’. Beneficial microbes—such as Trichoderma, Pseudomonas species, and mycorrhizae—not only stimulate healthy root growth, but also suppress harmful pathogens in the rhizosphere.
- Apply known biocontrol agents to the soil or as seed treatments to reduce reliance on chemical interventions.
- Leverage recent advances in plant genetics and genome editing (such as CRISPR) to develop crops with built-in resistance to emerging pathogens.
Why it matters: Using microbial and biotech interventions reduces chemical residues, supports beneficial soil microbes, and delivers robust, sustainable protection against biotic and abiotic stress.
Crop Stress Detection Technologies: Remote Sensing, Imaging, and IoT
Timely, actionable data is at the core of modern crop stress management. Here’s a look at cutting-edge technologies available today:
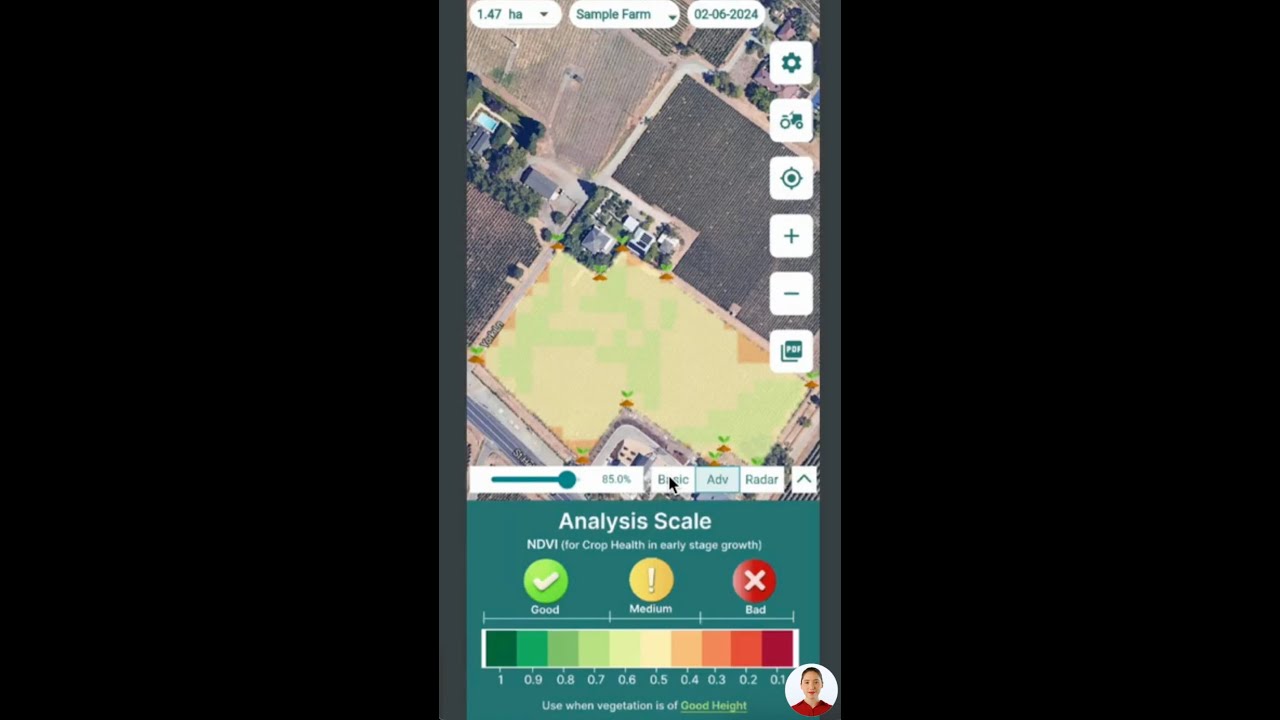
- Remote Sensing in Agriculture: Satellite-based tools like those on Farmonaut’s platform analyze NDVI, SAVI, NDWI (Normalized Difference Water Index), and more to rapidly detect changes in vegetation health or soil moisture.
- Imaging Technologies: Spectral, thermal, and fluorescence imaging detect early crop stress signals, e.g., heat signatures from water-stressed plants or color band changes from pest activity.
- IoT Sensor Networks: Soil, weather, and plant health sensors inform irrigation management in farming, nutrient application, pesticide spraying, and automatic alerting—enabling real-time intervention.
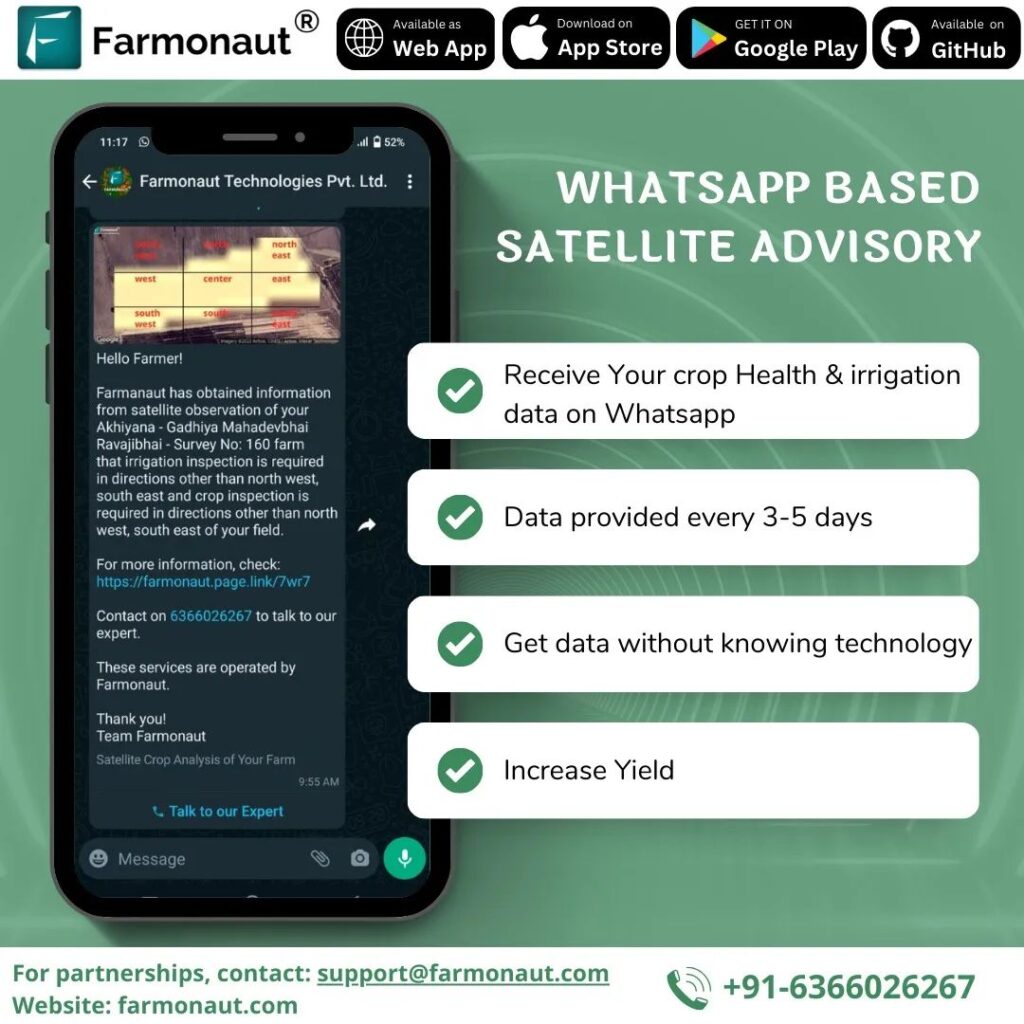
Insight: By combining remote sensing, AI-driven advisories, and dedicated mobile/web apps, Farmonaut is democratizing access to affordable precision agriculture for farmers and agribusinesses of all sizes.
How Farmonaut Empowers Sustainable Crop Stress Management
Farmonaut is transforming how we manage abiotic and biotic stress in crops. By integrating satellite monitoring, AI, blockchain, and real-time data into an easy-to-use platform, Farmonaut unlocks actionable, affordable, and precise advisory for everyone across the agriculture value chain.
- Subscribe to Farmonaut for satellite-powered NDVI and moisture maps that pinpoint emerging stress before irreversible loss occurs.
- AI-driven Jeevn advisory provides crop-specific management strategies for irrigation, nutrients, and pest control—right on your phone.
- Blockhain-based traceability and carbon-footprinting let you prove your sustainable practices from seed to sale.
- Fleet and resource management tools cut field operation costs while optimizing equipment use and farm logistics.
- Integrate satellite and weather API into your own apps or research systems via robust developer documentation.
- Financial institutions can rely on Farmonaut for satellite-based farm verification—improving access to crop loans and insurance for farmers, and reducing fraud.
- All-in-one mobile, web, and API access makes next-gen crop management simple—even for smallholders.
Try Farmonaut’s comprehensive satellite-based crop health monitoring solutions:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is crop stress?
Crop stress is any external condition that negatively affects plant growth, development, or yield. It includes both abiotic factors like drought, salinity, and temperature, and biotic factors like pests, diseases, and weeds. -
How can I detect stress in my crops early?
Early signs of crop stress may not always be visible. Advanced methods—like remote sensing, spectral and thermal imaging, and in-field IoT sensors—allow us to detect stress triggers before visible symptoms appear. -
Which technologies are best for crop stress detection?
Satellite imagery, spectral cameras, crop canopy reflectance analysis, soil and moisture sensors, and AI-powered decision tools are currently the most effective approaches. -
How does precision agriculture help in managing crop stress?
Precision agriculture helps us use water, nutrients, and pest control products more efficiently—reducing crop stress, resource wastage, and environmental impact. -
What is the impact of crop stress on yield and soil health?
Unmanaged crop stress can reduce yields by over 20% and degrade soil health. Conversely, effective management increases productivity and enhances soil resilience over time. -
Can I use Farmonaut on my small farm?
Absolutely. Farmonaut solutions are designed to be affordable and accessible—even for individual smallholder farmers—via mobile and web apps. -
Is Farmonaut a seller of farm inputs or a regulatory body?
No, Farmonaut is not an online marketplace, equipment supplier, or regulatory agency. It provides precision agriculture software, satellite-based crop health monitoring, data-driven advisory, and related technologies.
Conclusion & Getting Started with Farmonaut
Crop stress management is integral to optimizing our farms for food security, environmental sustainability, and profitability. By understanding the various types, causes, and effects of crop stress, applying advanced detection methods, and integrating the 7 evidence-based hacks outlined above, we can increase yields, maintain soil health, and empower truly sustainable farming.
Farmonaut’s suite of remote sensing, AI advisory, and blockchain traceability tools brings these best practices to your fingertips. Whether you’re managing a family farm or overseeing thousands of hectares, you can now access affordable, actionable, and data-driven advice for every stage of the crop cycle.
- Empower your team with real-time crop health maps and AI-driven insights.
- Use advanced irrigation management in farming with IoT- and satellite-based alerts.
- Strengthen your sustainability credentials with carbon footprint monitoring, blockchain traceability, and regenerative soil health improvement practices.
Ready to boost yields and resilience on your farm?

Explore our platform today and take the next step towards sustainable crop stress management!
For large-scale management, tailored advisories, and real-time field insights, discover the specialized Farmonaut large scale & fleet management solutions.