Smart Farming IoT: 7 Data Hacks Farmers Swear By
Meta Description: Discover the power of Smart Farming IoT. Learn the top 7 data-driven hacks farmers use to boost yields, optimize resources, and make agriculture more sustainable with precision technology.
“Over 70% of smart farms use IoT sensors to monitor soil moisture and nutrient levels in real time.”
Introduction: The Revolution of Smart Farming IoT
Welcome to the era of smart farming, where data, IoT devices, and automation unite to transform agriculture as we know it. We stand at the cusp of a profound shift, driven by the urgency to produce more food efficiently, reduce environmental impact, and make better use of finite resources. This shift is led by precision agriculture—a data-centric approach that leverages sensors, analytics, and connected systems across every aspect of farm management.
By integrating IoT technologies, smart sensors, and advanced analytics into daily agricultural practices, we as farmers, agronomists, and agri-businesses can make more informed decisions, optimize schedules, and improve crop yields while promoting sustainability. The focus keyword IoT in agriculture isn’t just a buzzword—it’s the core of a movement that’s reshaping farming for the 21st century.
Smart Farming Essentials: Key Components and Concepts
Before diving into the most impactful data hacks, it’s crucial to grasp the core components that underpin IoT in agriculture and smart farming. These pillars are what elevate modern farming beyond traditional practices:
- IoT Sensors and Agricultural IoT Devices: Deployed across fields, these sensors monitor soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels in real time. Real-time data collection enables us to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and disease prevention.
- Data Analytics & Machine Learning: Collected data is analyzed with analytics and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and spot problem areas. This enables not just reactive, but proactive and even predictive decision-making for timely interventions.
- Automated Machinery & Robotics: From autonomous tractors to drones and robotic harvesters, automated systems are reshaping labor and efficiency, reducing human error and overhead costs.
- Connectivity Solutions: Using reliable LPWAN, 5G, or hybrid networks ensures seamless data transmission—a must for decentralised sensor nodes and remote areas. Continuous connectivity is key for farm data analytics to be truly effective.
- Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting: Monitor and reduce your farm’s carbon emissions to meet sustainability goals. This service empowers agricultural businesses and farmers to accurately track, manage, and report their environmental impact, aligning with global sustainable farming practices.
- Farmonaut Blockchain-Based Traceability: Enhance food safety and transparency by tracing every stage of the agricultural supply chain, building consumer trust and ensuring compliance.
- Large-Scale Farm Management App: Perfect for agribusinesses and cooperatives, this platform delivers advanced management, analytics, and reporting tools via web and mobile, scaling with your operation.
- Fleet and Resource Management: Optimize your farm’s logistics, track farm vehicles and machinery, ensuring operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Satellite-Based Crop Loan and Insurance Verification: Streamline loan approvals and reduce fraud with satellite verification, making financial access easier for farmers.
Smart Farming IoT: 7 Data Hacks Farmers Swear By
Let’s explore the top seven data-centric hacks and strategies that are at the heart of smart farming and precision agriculture. By leveraging these tools and technologies, we can optimize our crop yields, reduce costs, and boost sustainability.
-
1. Real-Time Soil Moisture & Nutrient Monitoring
Deploying soil moisture sensors and nutrient probes gives us continuous, granular insight into soil health. When combined with satellite-based remote sensing—like that used on the Farmonaut platform—we get a comprehensive picture of moisture levels and vital nutrient parameters. This enables:
- Targeted irrigation management (no more guesswork, only data-driven water use).
- Optimal fertilizer scheduling, reducing wastage and costs.
- Early alerts for dry spells or nutrient deficiencies before they become critical.
Fact: According to Digi.com, moisture sensors can reduce water use by up to 30% and boost yields by 10–15%.
-
2. Automated Irrigation Solutions
Automated irrigation—driven by IoT sensor networks—matches watering schedules precisely to weather, crop type, and soil data. Using platforms like Farmonaut, farmers set up smart irrigation rules triggered by sensor thresholds or remote advisories.
- Reduces labor required for manual watering
- Conserves water (sustainability) while preventing over-irrigation
- Boosts crop growth by always maintaining optimal moisture conditions
Did you know? “Precision agriculture can reduce fertilizer use by up to 20% through automated data-driven application systems.”
-
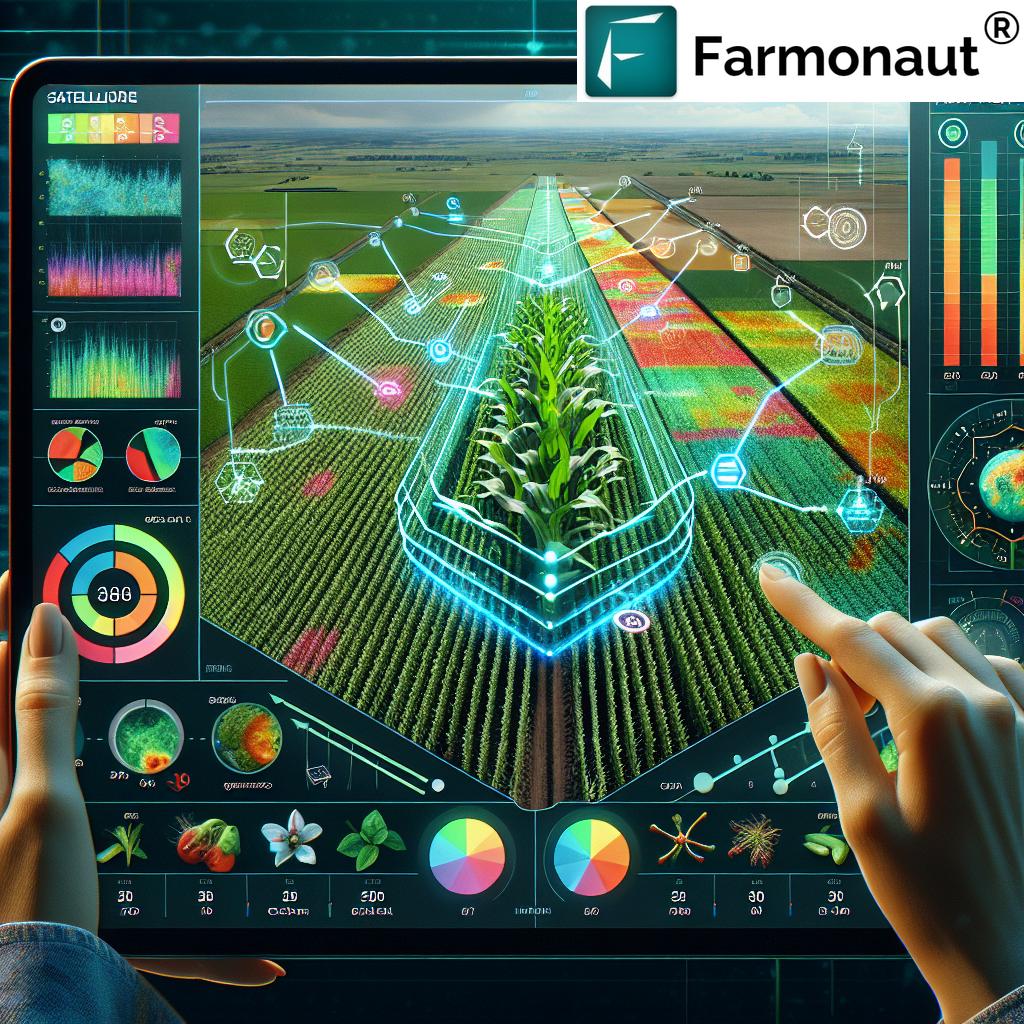
3. Precision Crop Monitoring Systems
Vegetation indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), analyzed via multi- and hyperspectral satellite imagery, allow fine-grained crop health monitoring. Farmonaut’s satellite-based platform delivers this data directly to mobile, web, and API endpoints.
- Early detection of diseases or pest outbreaks
- Pinpointing zones of crop stress or nutrient problems
- Tracking leaf temperature, canopy condition, and chlorophyll concentration
Integrate Farmonaut satellite data directly into your preferred agri systems via our API.
Review the
API Developer Docs
for detailed guidance. -
4. Livestock Health Monitoring and Tracking
Wearable IoT devices enable continuous tracking of livestock health metrics, including body temperature, heart rate, and movement. Early alerts detect deviations from normal patterns, minimizing disease outbreaks and improving animal welfare.
- Enables proactive responses for sick animals, reducing losses and treatment costs
- Automates fractional adjustments in feeding and breeding schedules based on animal data
-
5. Smart Greenhouse Technology
IoT-enabled greenhouses monitor environmental temperature, humidity, light intensity, and CO₂. Farmonaut and similar satellite data platforms enable remote oversight and alerting for large-scale greenhouse operations.
- Climate is automatically adjusted (e.g., vents open, lights dim/brighten)
- Yields and quality become far less variable, unaffected by external weather
- Supports round-the-clock cultivation and precision harvesting
-
6. Automated Pest Control and Disease Detection
IoT-connected cameras and machine learning models spot pest incursions or disease symptoms early. Automated sprayers or traps are triggered only when needed, vastly reducing chemical use.
- Lower ecological footprint by minimizing pesticide drift and run-off
- Protects beneficial insects, promoting ecosystem health
- Timely interventions mean less crop damage and higher marketable yields
-
7. Supply Chain Optimization & Blockchain Traceability
Modern IoT devices track produce from field to table, ensuring transparency and safety. Blockchain-based traceability, as offered by Farmonaut, ensures every step—from harvest, transport, storage, to final sale—is logged, tamper-proof, and instantly verifiable.
- Ensures food safety and rapid recall in case of contamination
- Improves quality control and provenance authentication for export markets
- Consumers gain confidence through transparent supply chain practices
Comparative Benefits Table of IoT Data Hacks in Smart Farming
| Data Hack Name | Estimated Resource Savings (%) | Potential Yield Increase (%) | Implementation Difficulty | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture Sensors | 25–35% Water | 10–15% | Low | Up to 35% Water Saved |
| Automated Irrigation | 20–40% Water & Labor | 10–18% | Medium | Reduces CO₂ via energy efficiency |
| Drone Imaging & Satellite Crop Monitoring | 15–30% Fertilizer & Chemical | 12–20% | Medium | Cuts chemical runoff up to 25% |
| IoT Livestock Health Monitoring | 15–25% Labor, 8–12% Feed | 5–10% | Medium | Improves welfare, reduces loss/waste |
| Precision Pest & Disease Detection | 20–30% Pesticide Use | 8–12% | Medium | Reduces chemical impact, higher food safety |
| Smart Greenhouse Technology | 30–50% Energy/Chemical | 15–30% | High | Year-round cropping & low CO₂ |
| Supply Chain Optimization & Blockchain Traceability | 5–15% Waste & Losses | 0–5% | Medium | Reduces untracked loss, improves consumer trust |
Farmonaut Technology: The Future of Satellite-Driven Smart Farming
With Farmonaut’s advanced, satellite-based management solutions, we see a new level of affordability, accessibility, and accuracy enter precision agriculture. Farmonaut’s unique blend of multispectral satellite data, AI, and blockchain powers fast, actionable insights for any farm across the globe, whether you manage a single plot or thousands of hectares.
-
Satellite Crop Health Monitoring:
See NDVI, NDRE, soil moisture, and more—all visualized for quick crop health assessment. -
Jeevn AI Advisory:
Data-driven, personalized recommendations on everything from optimal irrigation to pest management, accessible via web, Android, iOS apps, or APIs. -
Blockchain Traceability:
Log every supply chain event for food safety, compliance, and consumer trust—especially valuable for high-value crops and export markets. -
Fleet & Resource Management:
Track and optimize fleet, machines, and logistics to improve efficiency and reduce overhead (Learn more). -
Carbon Footprinting:
Monitor emissions and work toward environmental targets (Start here).
Applications of IoT in Agriculture: Transforming Every Field
Let’s review key use cases where IoT in agriculture is making a measurable impact:
-
Precision Crop Monitoring:
IoT sensors track leaf health, temperature, moisture, and nutrient deficits. Machine learning models analyze sensor data, offering instant recommendations to keep crops flourishing.
Cite: blog.grape.solutions -
Automated Irrigation Management:
Soil moisture sensors connect directly to cloud-based platforms and irrigation controllers—watering only when needed, maximizing water conservation and crop growth.
Cite: telit.com -
Livestock Health Monitoring:
Wearable collars and smart ear tags monitor animal heart rates, temperature, and movement, delivering health alerts to farmers before visible symptoms emerge.
Cite: iotdesignpro.com -
Supply Chain Optimization:
From RFID tags to GPS trackers and blockchain, produce is monitored from harvest to sale. This transparency boosts food safety and satisfies regulatory and consumer demands for quality control.
Cite: thefarminginsider.com -
Smart Greenhouse Management:
Sensors and actuators control lighting, humidity, and ventilation, ensuring optimal crop growth with lower energy and labor inputs.
Cite: farmersprideinternational.org -
Pest and Disease Detection:
IoT-enabled cameras combined with analytics aid early detection, trigger automated traps, and alert farmers for precision intervention.
Cite: vitality.io
“Precision agriculture can reduce fertilizer use by up to 20% through automated data-driven application systems.”
Benefits of Smart Farming: Data-Driven Success
Our journey with smart farming IoT and precision technology delivers a cascade of benefits:
- Increased Yields: By making every drop of water and gram of fertilizer count, we can reliably boost yield per acre.
- Resource Optimization: Efficient use of irrigation, fertilizer, and pesticides leaves more profit in our pocket and minimizes waste.
- Environmental Sustainability: Cutting chemical, water, and energy use reduces negative impacts on ecosystems—key to sustainable farming practices.
- Labor Efficiency: Automation means we can devote time to strategy—not back-breaking manual tasks.
- Food Security and Quality: Continuous monitoring, traceability, and quality control lead to safer, higher-quality food delivered with confidence to market.
For more on tracking your farm’s environmental impact, see Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting Services—empowering sustainability through actionable data.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Farming IoT
While the promise of IoT in agriculture is transformative, we must acknowledge the real challenges that accompany this technological leap:
- High Initial Investment: Acquiring IoT devices, setting up data networks, and subscription platforms represent an upfront cost—especially significant for smaller farmers.
- Data Security and Privacy: The growing volume of farm data raises questions about privacy, data ownership, and protection from cyber threats.
- Connectivity Limitations: Lack of reliable internet in some rural areas can limit sensor deployment and automation. LPWAN and emerging 5G solutions offer promise for broader coverage.
- Technical Know-How: We need ongoing training and support to fully utilize and maintain this new generation of farming technology.
The good news? Thanks to platforms like Farmonaut, many barriers are dropping—making adoption, cost management, and ongoing training more practical than ever.
The Future: Where Is Smart Farming IoT Headed?
The next decade will see AI, machine learning, blockchain, and next-generation IoT sensors become even more affordable and accessible to the world’s farmers. Enhanced connectivity—via hybrid LPWAN, 5G, and satellite networks—will ensure reliable data flows, no matter how remote the location.
Farmonaut continues to push the envelope, bringing advanced analytics, automated advisories, and robust transparency into the hands of farmers and agribusinesses everywhere. Solutions will become ever more modular, scalable, and data-driven, enabling us to
meet global food demand sustainably while protecting our environment.
Explore more about blockchain traceability and its implications for your brand’s trust and food safety at Farmonaut Product Traceability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is smart farming?
Smart farming is the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, data analytics, and automated systems to optimize agricultural processes, improve yields, reduce resource waste, and ensure sustainability.
How does IoT improve crop monitoring?
IoT sensors provide real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and crop health, enabling precision agriculture by identifying stress factors early and recommending the right interventions.
What are the benefits of satellite-based farm management?
Satellite data, as offered by Farmonaut, covers large areas in detail, provides frequent and objective monitoring, assists with decision-making, reduces manual scouting, and is highly scalable for any farm size.
How does Farmonaut ensure data privacy?
Farmonaut utilizes secure data handling protocols and keeps user data confidential. Blockchain traceability also assures data integrity throughout the supply chain.
Is smart farming only for large farms?
No. With platforms like Farmonaut, affordable smart farming solutions are now available for smallholder and medium-sized farmers too, providing access via app and web anywhere.
Can I integrate Farmonaut data with my own systems?
Yes. Farmonaut’s robust APIs (API documentation) let users pull satellite and weather data directly into custom farm management systems or analytics dashboards.
Does adopting smart farming require much technical expertise?
While a basic level of digital literacy is helpful, platforms like Farmonaut work to make interfaces simple, provide training and customer support, and integrate user-friendly advisories.
Farmonaut Subscription Options
Ready to transform your farm with data-driven decision-making? Farmonaut provides a range of affordable packages for individual farmers, agribusinesses, and government users. Track your fields, receive satellite-based health advisories, automate reports, and access APIs—via mobile, web, or custom integrations.
Choose the plan that fits your scale and requirements below and start leveraging the power of smart farming IoT:
Conclusion: Embrace the Smart Farming IoT Revolution
Smart farming, powered by IoT, precision data, and advanced analytics, is not just a passing trend—it’s the new foundation of sustainable agriculture. Through the top 7 data hacks outlined here, we’re empowered to make decisive, informed choices that advance yields, reduce costs, and promote environmental protection.
Farmonaut stands as a technology enabler for every farmer, co-op, and agribusiness ready to embrace data-driven agriculture. By leveraging satellite imagery, machine learning, blockchain, and user-friendly mobile/web apps, Farmonaut makes precision farming accessible, scalable, and affordable for all.
Are you ready to join the future of smart farming IoT? Download the Farmonaut app, start tracking your fields, and experience the benefits of data wisdom in every seed you plant.
Keywords utilized: iot, smart, data, farming, devices, crop, agricultural, resource, food, precision, agriculture, sensors, farmers, temperature, management, labor, systems, monitoring, water, technologies, practices, yields, machine learning, automated, connectivity, supply chain, safety, environmental, manual, internet, efficiency, sustainability, analytics, monitor, soil, moisture, humidity, levels, interventions, diseases, optimal, costs, reliable, areas, health, detection, damage, irrigation, crops, growth, livestock, track, optimization, transparency, quality control, greenhouses, conditions, benefits, growing, efficient, reduces, security, challenges, investment, privacy, adoption, leverages, things, productivity, integrating, informed, decisions, optimize, improve, components, deployed, fields, parameters, nutrient, collection, enables, precise, timely, collected, analyzed, identify, patterns, predict, outcomes, algorithms, forecast, harvest, times, requirements, facilitating, proactive, machinery, robotics, autonomous, tractors, drones, robotic, harvesters, tasks, planting, spraying, harvesting, solutions, communication, networks, lpwan, 5g, models, transmission, “smart farming”, “precision agriculture”, “IoT in agriculture”, “agricultural IoT devices”, “crop monitoring systems”, “automated irrigation solutions”, “livestock health monitoring”, “farm data analytics”, “smart greenhouse technology”, “sustainable farming practices”