Celebrating India’s Moon Landing: Chandrayaan-3’s Historic Achievement and Its Impact on Agriculture

On August 23, 2023, India made history as Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed on the Moon’s south pole region. At Farmonaut, we join the world in celebrating this monumental achievement by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). This blog post delves into the significance of this accomplishment, its potential impact on agriculture, and how space technology continues to revolutionize farming practices worldwide.
Table of Contents
- The Chandrayaan-3 Mission: A Brief Overview
- ISRO’s Journey to the Moon
- The Significance of Landing on the Moon’s South Pole
- Impact on Space Technology and Agriculture
- How Satellite Technology is Transforming Agriculture
- Farmonaut’s Role in Agricultural Innovation
- The Future of Space Exploration and Farming
- FAQs
1. The Chandrayaan-3 Mission: A Brief Overview
Chandrayaan-3, India’s third lunar exploration mission, marked a significant milestone in the country’s space program. The mission’s primary objective was to demonstrate a safe and soft landing on the lunar surface, conduct roving operations, and carry out in-situ scientific experiments.
Key components of the mission included:
- Lander module (Vikram)
- Rover (Pragyan)
- Propulsion module
The successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 not only showcased India’s technological prowess but also opened up new possibilities for scientific research and exploration of the Moon’s south pole region.
2. ISRO’s Journey to the Moon
ISRO’s lunar exploration program has been a testament to India’s growing capabilities in space technology. Let’s look at the key milestones in this journey:
- Chandrayaan-1 (2008): India’s first lunar probe, which made significant discoveries, including the detection of water molecules on the Moon’s surface.
- Chandrayaan-2 (2019): Although the lander crashed, the orbiter continues to function and provide valuable data.
- Chandrayaan-3 (2023): The successful soft landing on the Moon’s south pole region, making India the fourth country to achieve a soft landing on the lunar surface and the first to land near the south pole.
This progression demonstrates ISRO’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration and its ability to learn from past experiences to achieve greater success.
3. The Significance of Landing on the Moon’s South Pole
The successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 on the Moon’s south pole region is particularly significant for several reasons:
- Unexplored Territory: The south pole region of the Moon remains largely unexplored, offering new opportunities for scientific discoveries.
- Presence of Water Ice: This region is believed to contain water ice in permanently shadowed craters, which could be crucial for future lunar missions and potential human settlements.
- Unique Geological Features: The south pole area has distinct geological characteristics that can provide insights into the Moon’s formation and evolution.
- Strategic Importance: Landing in this challenging terrain demonstrates India’s technological capabilities and positions the country as a key player in future lunar exploration efforts.
The success of Chandrayaan-3 not only advances our understanding of the Moon but also paves the way for future missions that could utilize lunar resources for sustainable space exploration.
4. Impact on Space Technology and Agriculture
While the Chandrayaan-3 mission’s primary focus is lunar exploration, its success has far-reaching implications for various fields, including agriculture. Space technology and agriculture have a long history of synergy, with satellite-based systems playing a crucial role in modern farming practices.
Here are some ways in which advancements in space technology, like those demonstrated by Chandrayaan-3, can benefit agriculture:
- Improved Earth Observation Satellites: Technologies developed for lunar missions can be adapted to enhance Earth observation satellites, providing more accurate and detailed data for agricultural applications.
- Advanced Sensors: Sensors designed to study lunar soil and atmosphere can be modified to better analyze Earth’s agricultural lands, helping farmers understand soil composition and crop health more effectively.
- Resource Management: Techniques developed for managing resources in the harsh lunar environment can inspire more efficient resource management practices in agriculture, particularly in water-scarce regions.
- Climate Research: Studying the Moon’s atmosphere and surface can contribute to our understanding of Earth’s climate systems, which is crucial for long-term agricultural planning.
- Technological Innovation: The drive to solve complex problems in space missions often leads to innovations that can be applied to agricultural challenges on Earth.
5. How Satellite Technology is Transforming Agriculture
Satellite technology, a cornerstone of space exploration, has become an indispensable tool in modern agriculture. At Farmonaut, we leverage this technology to provide innovative solutions for farmers and agribusinesses. Here’s how satellite technology is revolutionizing farming practices:
5.1 Crop Monitoring and Health Assessment
Satellites equipped with multispectral sensors can capture images in various wavelengths, allowing for detailed analysis of crop health. This technology enables:
- Early detection of crop stress due to pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies
- Monitoring of crop growth stages
- Assessment of vegetation density using indices like NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index)
By providing timely information on crop health, satellite technology helps farmers take proactive measures to protect their yields.
5.2 Precision Agriculture
Satellite data plays a crucial role in precision agriculture, allowing farmers to optimize their resource use. This includes:
- Variable rate application of fertilizers and pesticides
- Targeted irrigation based on soil moisture data
- Optimization of planting and harvesting schedules
These practices not only increase efficiency but also reduce the environmental impact of farming activities.
5.3 Weather Forecasting and Climate Monitoring
Satellite-based weather forecasting provides farmers with accurate, localized weather information, enabling them to:
- Plan farming activities more effectively
- Prepare for extreme weather events
- Make informed decisions about irrigation and crop protection
Long-term climate data from satellites also helps in understanding climate change patterns and their potential impact on agriculture.
5.4 Land Use and Crop Mapping
Satellite imagery allows for large-scale mapping of agricultural lands, providing valuable information on:
- Crop types and distribution
- Land use changes over time
- Estimation of crop yields at regional and national levels
This data is crucial for agricultural planning, policy-making, and food security assessments.
5.5 Soil Moisture and Water Management
Satellites can measure soil moisture levels across vast areas, helping in:
- Drought monitoring and prediction
- Irrigation planning and water resource management
- Understanding the impact of climate change on water availability
This information is particularly valuable in regions facing water scarcity challenges.
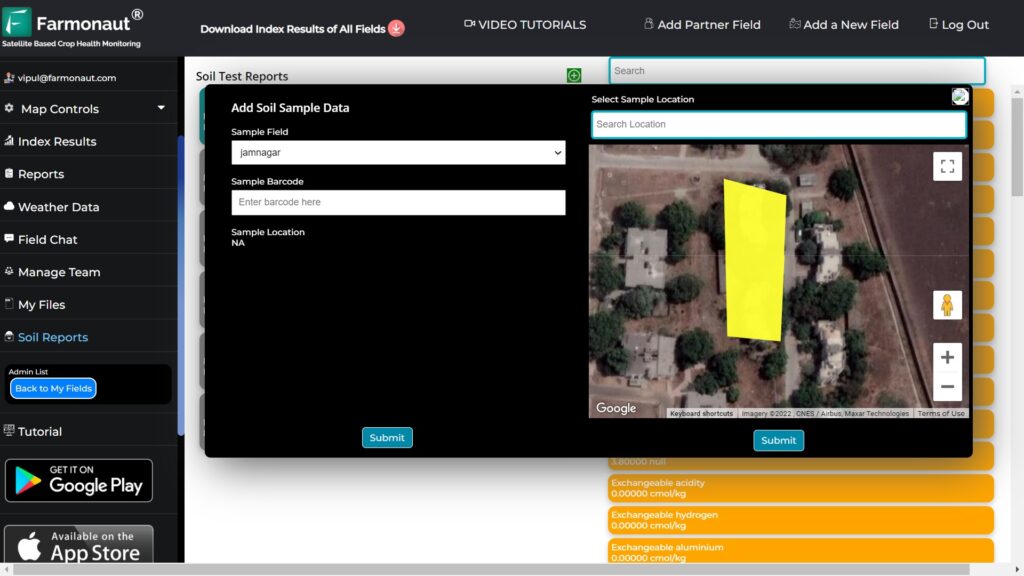
6. Farmonaut’s Role in Agricultural Innovation
At Farmonaut, we are at the forefront of integrating satellite technology with agricultural practices. Our platform leverages advanced satellite data to provide farmers and agribusinesses with actionable insights. Here’s how we’re contributing to agricultural innovation:
6.1 Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Our platform uses multispectral satellite images to monitor crop health, providing farmers with:
- Real-time vegetation health indices (NDVI)
- Soil moisture level assessments
- Early detection of crop stress and anomalies
This information enables farmers to make timely interventions, optimizing crop yields and reducing resource wastage.
6.2 AI-Powered Advisory System
Our Jeevn AI advisory system combines satellite data with artificial intelligence to deliver:
- Personalized farm management recommendations
- Real-time weather forecasts and alerts
- Crop-specific guidance on pest management and fertilizer application
This AI-driven approach helps farmers make data-informed decisions, improving overall farm productivity and efficiency.
6.3 Blockchain-Based Traceability Solutions
We’ve integrated blockchain technology to enhance transparency in agricultural supply chains:
- Tracking products from farm to consumer
- Ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud
- Building consumer trust through transparent supply chain information
This technology is particularly valuable for industries requiring strict quality control and traceability, such as organic farming and premium agricultural products.
6.4 Resource and Fleet Management
Our platform offers tools for efficient management of agricultural resources:
- Optimization of farm machinery usage
- Tracking and management of agricultural fleets
- Improving logistics and reducing operational costs
These features help agribusinesses streamline their operations and increase overall efficiency.
6.5 Carbon Footprint Monitoring
In response to growing environmental concerns, we provide tools for:
- Tracking and monitoring carbon emissions in agricultural operations
- Identifying opportunities for reducing environmental impact
- Supporting sustainable farming practices
This feature helps agribusinesses meet sustainability goals and comply with environmental regulations.
7. The Future of Space Exploration and Farming
As we celebrate the success of Chandrayaan-3, it’s exciting to consider the future possibilities at the intersection of space exploration and agriculture. Here are some potential developments we might see in the coming years:
7.1 Advanced Earth Observation Technologies
Future satellites may feature even more sophisticated sensors and imaging technologies, providing:
- Higher resolution imagery for more detailed crop analysis
- Enhanced spectral capabilities for better detection of crop stress and soil properties
- Real-time monitoring capabilities for immediate response to agricultural challenges
7.2 Space-Based Agriculture
As we look towards long-term space exploration and potential colonization, space-based agriculture will become crucial:
- Development of techniques for growing crops in extraterrestrial environments
- Adaptation of Earth crops to low-gravity conditions
- Creation of closed-loop agricultural systems for sustainable space habitats
7.3 Resource Extraction from Celestial Bodies
Future missions may focus on extracting resources from the Moon or asteroids, which could benefit agriculture on Earth:
- Mining of rare earth elements for advanced agricultural technologies
- Extraction of water ice for space-based agriculture and potential use on Earth
- Development of new materials with applications in agricultural equipment and infrastructure
7.4 Climate Change Mitigation Strategies
Space technology will play a crucial role in understanding and mitigating the effects of climate change on agriculture:
- More accurate climate modeling and prediction
- Development of climate-resilient crop varieties based on data from space missions
- Potential geoengineering solutions inspired by planetary science
7.5 Integration of AI and Space Technology
The combination of artificial intelligence and space technology will lead to even more powerful tools for agriculture:
- AI-driven analysis of vast amounts of satellite data for precise agricultural insights
- Autonomous farming systems guided by satellite data and AI decision-making
- Predictive models for crop yields, pest outbreaks, and market trends based on global data
How Farmonaut Satellite System Compares to Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
| Feature |
Farmonaut Satellite System |
Drone-based Monitoring |
IoT-based Monitoring |
| Coverage Area |
Large scale (regional to global) |
Medium scale (local) |
Small scale (field level) |
| Data Collection Frequency |
Regular (based on satellite revisit time) |
On-demand (requires manual flight) |
Continuous (real-time data) |
| Initial Investment |
Low (subscription-based) |
High (equipment purchase) |
Medium (sensors and network setup) |
| Operational Complexity |
Low (cloud-based platform) |
High (requires skilled operator) |
Medium (requires maintenance) |
| Weather Dependency |
Low (can penetrate clouds) |
High (affected by wind, rain) |
Low (continuous operation) |
| Data Analysis |
Advanced (AI-powered insights) |
Moderate (requires additional processing) |
Basic (real-time data streams) |
| Scalability |
High (easily scalable to large areas) |
Low (limited by flight time and regulations) |
Moderate (requires additional sensors for expansion) |
As the table illustrates, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers unique advantages in terms of coverage, scalability, and advanced data analysis, making it an ideal choice for large-scale farm monitoring and management.
Conclusion
The successful landing of Chandrayaan-3 on the Moon’s south pole is not just a triumph for India but a leap forward for humanity’s space exploration efforts. As we at Farmonaut celebrate this achievement, we’re reminded of the crucial role that space technology plays in advancing agriculture and ensuring global food security.
The synergy between space exploration and agricultural innovation continues to grow, offering exciting possibilities for the future of farming. From precision agriculture to climate resilience, the insights gained from space missions like Chandrayaan-3 have far-reaching implications for how we grow food and manage our planet’s resources.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to harnessing the power of satellite technology to revolutionize agriculture. Our platform brings the benefits of space technology directly to farmers and agribusinesses, enabling more efficient, sustainable, and productive farming practices.
As we look to the future, the possibilities are boundless. The success of Chandrayaan-3 inspires us to push the boundaries of what’s possible, both in space and on Earth. We’re excited to be part of this journey, contributing to a future where advanced technology and sustainable practices come together to feed the world and protect our planet.
Join us in this exciting journey towards a more innovative and sustainable agricultural future. Explore our services at
Farmonaut App, check out our
API services, or download our mobile apps for
Android and
iOS. For developers interested in integrating our satellite and weather data, visit our
API documentation.
FAQs
- Q: How does satellite technology benefit agriculture?
A: Satellite technology provides valuable data for crop monitoring, weather forecasting, soil analysis, and resource management, enabling precision agriculture and improving overall farm efficiency.
- Q: Can Farmonaut’s services be used for all types of crops?
A: Yes, Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring can be applied to a wide range of crops, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and cash crops like cotton.
- Q: How often is satellite data updated on the Farmonaut platform?
A: The frequency of updates depends on the satellite revisit time and the subscription plan. Typically, we provide updates every 3-5 days, with options for more frequent monitoring in some areas.
- Q: Is Farmonaut’s service available worldwide?
A: Yes, our satellite-based services are available globally, providing agricultural insights to farmers and agribusinesses around the world.
- Q: How does Farmonaut ensure the accuracy of its agricultural insights?
A: We use a combination of high-resolution satellite imagery, advanced AI algorithms, and ground-truthing to ensure the accuracy of our insights. Our systems are constantly refined based on user feedback and real-world data.
Ready to revolutionize your farming practices with satellite technology? Subscribe to Farmonaut today!
 On August 23, 2023, India made history as Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed on the Moon’s south pole region. At Farmonaut, we join the world in celebrating this monumental achievement by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). This blog post delves into the significance of this accomplishment, its potential impact on agriculture, and how space technology continues to revolutionize farming practices worldwide.
On August 23, 2023, India made history as Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed on the Moon’s south pole region. At Farmonaut, we join the world in celebrating this monumental achievement by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). This blog post delves into the significance of this accomplishment, its potential impact on agriculture, and how space technology continues to revolutionize farming practices worldwide.