Regenerative Farming: Transforming UK Agriculture with Sustainable Practices and Farmonaut’s Agritech Solutions
“Regenerative farming practices in the UK have reduced input costs by up to 40% for some farmers.”
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of regenerative farming in the United Kingdom. As we delve into this transformative approach to agriculture, we’ll uncover how innovative practices are reshaping the landscapes of England, Scotland, and Wales. Join us on this journey to understand how regenerative farming is not just a trend, but a vital solution for the future of UK agriculture.
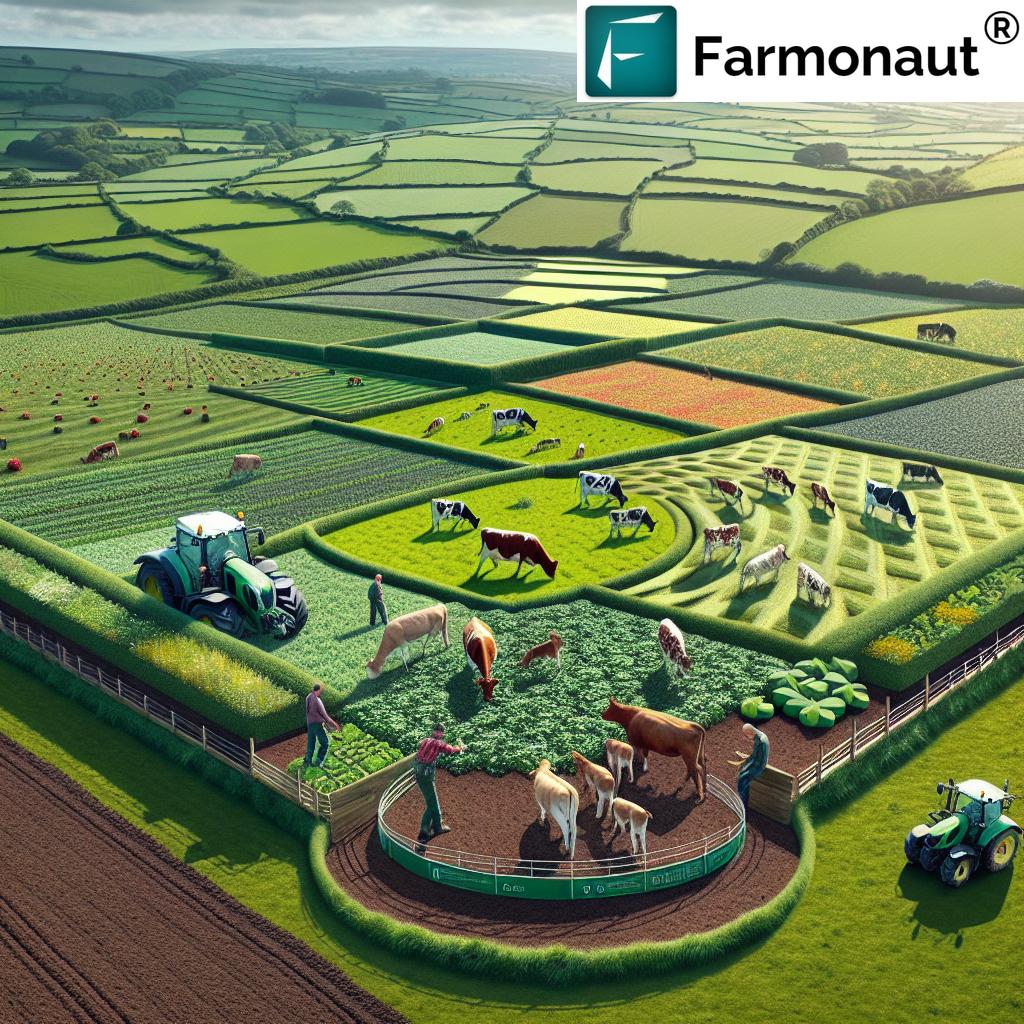

Understanding Regenerative Farming
Regenerative farming is a holistic approach to agriculture that focuses on improving soil health, enhancing biodiversity, and restoring ecosystems. This method goes beyond sustainability by actively regenerating the land, making it more resilient and productive over time. In the UK, where agricultural practices have shaped the landscape for centuries, the shift towards regenerative farming is particularly significant.
Key principles of regenerative farming include:
- Minimizing soil disturbance
- Maintaining soil cover
- Increasing plant diversity
- Integrating livestock
- Reducing synthetic inputs
These practices work together to create a more balanced and productive agricultural system that benefits both farmers and the environment.
The Rise of Regenerative Farming in the UK
Across England, Scotland, and Wales, farmers are increasingly adopting regenerative practices. This shift is driven by several factors:
- Rising costs of conventional farming inputs
- Increasing awareness of environmental issues
- Government policies supporting sustainable agriculture
- Consumer demand for environmentally friendly products
From the rolling hills of Oxfordshire to the rugged landscapes of Scotland, regenerative farming is proving its worth in diverse agricultural settings.
Key Regenerative Farming Practices Transforming UK Agriculture
1. Adaptive Multi-Paddock Grazing
Adaptive multi-paddock grazing is revolutionizing livestock management in the UK. This method involves dividing pastures into smaller paddocks and rotating animals through them more frequently. The benefits are numerous:
- Improved grassland health and productivity
- Enhanced soil structure and fertility
- Increased carbon sequestration
- Better animal health and productivity
In Scotland and Wales, where sheep and cattle farming are prevalent, adaptive multi-paddock grazing is helping farmers manage their grasslands more effectively while reducing feed costs.
2. Crop Rotation and Diversification
Arable farmers across England are embracing diverse crop rotations to break pest and disease cycles, improve soil health, and reduce reliance on synthetic inputs. This practice involves:
- Rotating between different crop families
- Including cover crops and green manures
- Integrating legumes for natural nitrogen fixation
By diversifying crops, farmers are seeing improvements in soil structure, increased organic matter, and enhanced biodiversity on their land.
3. No-Till and Minimum Tillage
Reducing or eliminating tillage is a cornerstone of regenerative farming. In the UK, where conventional plowing has been the norm, the shift to no-till or minimum tillage practices is significant. Benefits include:
- Improved soil structure and water retention
- Increased soil organic matter
- Reduced erosion and nutrient runoff
- Lower fuel and labor costs
Farmers in areas prone to erosion, such as hilly regions in Wales and Scotland, are finding these practices particularly beneficial.
The Role of Technology in Regenerative Farming
Innovative agritech solutions are playing a crucial role in supporting the transition to regenerative farming. Farmonaut, a leading agricultural technology company, offers advanced tools that align perfectly with regenerative principles.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring provides farmers with real-time insights into vegetation health, soil moisture levels, and other critical metrics. This technology enables precise decision-making regarding irrigation, fertilizer usage, and pest management, aligning with regenerative farming’s goal of optimizing resource use.
Key features of Farmonaut’s technology include:
- NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) mapping for crop health assessment
- Soil moisture monitoring to optimize water use
- AI-driven advisory system for personalized farm management
- Carbon footprint tracking to support sustainable practices
These tools are accessible through Farmonaut’s web and mobile applications, making it easy for farmers to integrate technology into their regenerative farming practices.
For developers and businesses looking to integrate Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data into their own systems, the company offers API access. You can explore the API and refer to the API Developer Docs for more information.
Economic Benefits of Regenerative Farming
One of the most compelling aspects of regenerative farming is its potential to improve farm economics. UK farmers adopting these practices are seeing:
- Reduced input costs for fertilizers and pesticides
- Improved crop resilience leading to more stable yields
- Potential for premium prices for regeneratively produced goods
- Diversified income streams through ecosystem services
As input costs rise, the economic case for regenerative farming becomes increasingly strong. Farmers using Farmonaut’s technology are finding it easier to track and optimize their resource use, further enhancing the economic benefits of regenerative practices.
“Adaptive multi-paddock grazing can increase soil organic matter by 3-5% within 3-5 years of implementation.”
Environmental Impact and Biodiversity
Regenerative farming practices are having a profound impact on the UK’s agricultural landscapes. The benefits extend far beyond the farm gate:
- Improved soil health and carbon sequestration
- Enhanced water quality in rivers and streams
- Increased biodiversity, including beneficial insects and wildlife
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions from farming activities
In areas like Oxfordshire, where intensive agriculture has historically impacted wildlife habitats, regenerative practices are helping to restore ecological balance.
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting Regenerative Practices
While the benefits of regenerative farming are clear, UK farmers face several challenges in adopting these practices:
- Initial costs of transitioning from conventional methods
- Learning curve associated with new practices
- Potential short-term yield reductions during the transition period
- Limited access to specialized equipment
To address these challenges, various support systems are emerging:
- Government grants and subsidies for sustainable farming practices
- Farmer-to-farmer knowledge sharing networks
- Partnerships with agricultural research institutions
- Innovative financing models for regenerative transitions
Farmonaut’s technology plays a crucial role in overcoming these challenges by providing data-driven insights that help farmers make informed decisions during the transition to regenerative practices.
The Future of Regenerative Farming in the UK
As we look to the future, regenerative farming is poised to play an increasingly important role in UK agriculture. Several factors are driving this trend:
- Growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainably produced food
- Policy shifts towards rewarding environmental stewardship
- Increasing pressure to reduce agriculture’s carbon footprint
- Advancements in agritech making regenerative practices more accessible
Farmonaut’s ongoing development of innovative solutions will continue to support farmers in their regenerative journey, making precision agriculture more accessible and affordable.
Comparison: Traditional vs. Regenerative Farming Practices in the UK
| Farming Practice | Traditional Method | Regenerative Method | Benefits of Regenerative Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Management | Intensive tillage, bare soil | No-till or minimum tillage, cover crops | Improved soil structure, increased organic matter, reduced erosion |
| Grazing Techniques | Continuous grazing | Adaptive multi-paddock grazing | Enhanced grassland health, improved soil fertility, increased carbon sequestration |
| Crop Rotation | Limited rotation, monocultures | Diverse crop rotations including cover crops | Improved soil health, natural pest control, reduced reliance on synthetic inputs |
| Biodiversity Impact | Often reduced biodiversity | Encourages biodiversity through habitat creation | Increased beneficial insects, improved ecosystem services |
| Water Usage | Often inefficient irrigation | Improved water retention, precision irrigation | Reduced water consumption, improved drought resilience |
| Farmonaut’s Support | Limited use of technology | Satellite-based crop monitoring, AI advisory | Data-driven decision making, optimized resource use, improved farm management |
Conclusion
Regenerative farming is more than just a set of practices; it’s a philosophy that’s transforming UK agriculture. By working with nature rather than against it, farmers across England, Scotland, and Wales are building more resilient, productive, and sustainable agricultural systems. The integration of innovative technologies, such as those provided by Farmonaut, is accelerating this transformation, making precision agriculture accessible to farmers of all scales.
As we face the challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, and food security, regenerative farming offers a path forward that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment. The future of UK agriculture is regenerative, and with continued innovation and support, we can create a more sustainable and prosperous farming sector for generations to come.
FAQ Section
Q: What is regenerative farming?
A: Regenerative farming is an approach to agriculture that focuses on improving soil health, enhancing biodiversity, and restoring ecosystems. It goes beyond sustainability by actively regenerating the land, making it more resilient and productive over time.
Q: How does regenerative farming differ from conventional farming?
A: Regenerative farming emphasizes minimal soil disturbance, diverse crop rotations, cover cropping, and integrated livestock management. It aims to reduce synthetic inputs and work with natural processes, unlike conventional farming which often relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Q: What are the main benefits of regenerative farming?
A: Key benefits include improved soil health, increased biodiversity, enhanced water retention, reduced input costs, more stable yields, and increased carbon sequestration, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Q: How can technology like Farmonaut support regenerative farming?
A: Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems provide farmers with real-time data on crop health, soil moisture, and other critical metrics. This enables precise decision-making, optimizing resource use in line with regenerative principles.
Q: Is regenerative farming economically viable for UK farmers?
A: Yes, many UK farmers adopting regenerative practices report reduced input costs, improved crop resilience, and potential premium prices for their products, making it an economically viable approach.
Q: How long does it take to see results from regenerative farming practices?
A: While some benefits can be seen within the first year, such as improved water retention, significant improvements in soil health and biodiversity typically become apparent within 3-5 years of implementing regenerative practices.
Q: Are there any government supports for regenerative farming in the UK?
A: Yes, the UK government is increasingly supporting sustainable and regenerative farming practices through various grants, subsidies, and policy initiatives aimed at promoting environmental stewardship in agriculture.
Farmonaut Subscriptions