Regenerative Dairy: 7 Proven Practices for Healthy Soils
“Rotational grazing can increase soil organic matter by up to 30% in regenerative dairy systems.”
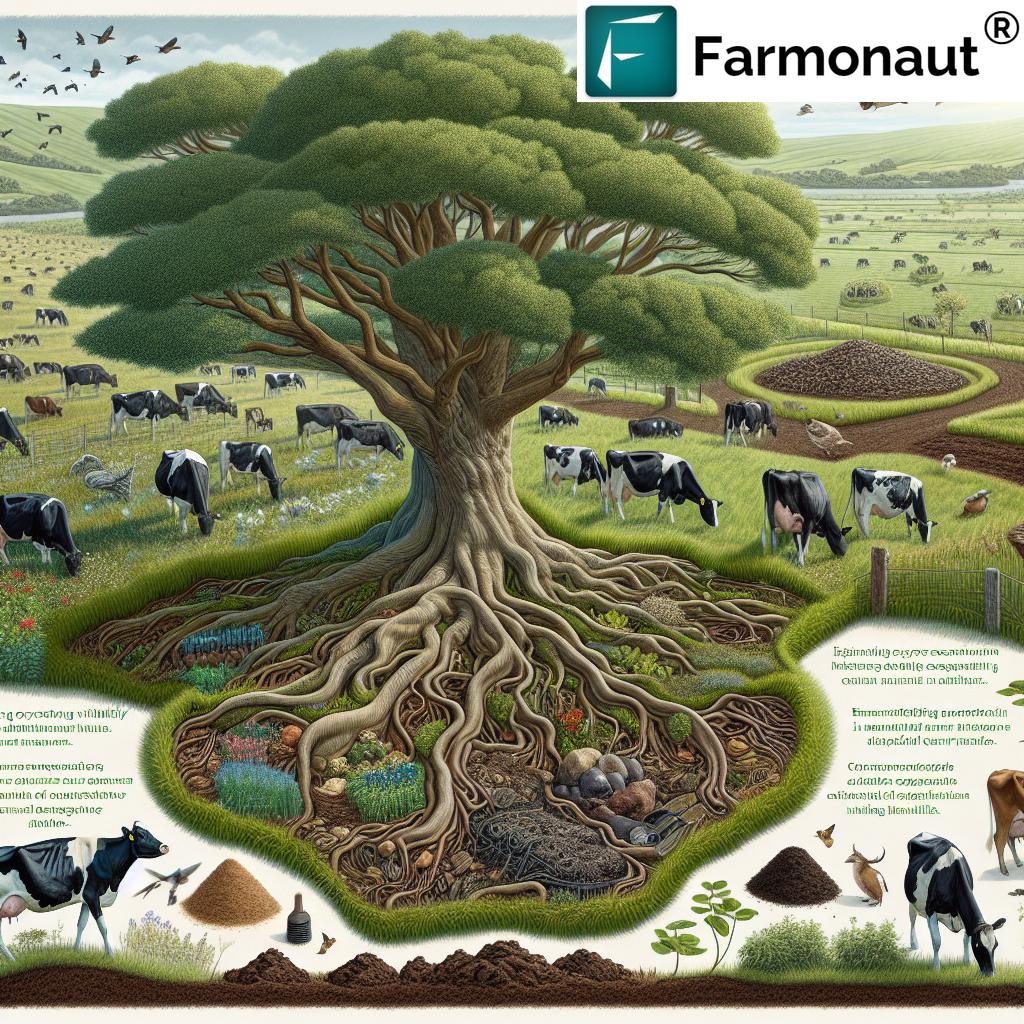
Introduction to Regenerative Dairy Farming
Regenerative dairy farming is revolutionizing the agricultural landscape, offering a holistic approach to restoring and enhancing the long-term health of soils, ecosystems, and animals. Unlike conventional systems, this innovative model integrates practices that boost soil fertility, promote biodiversity, ensure animal welfare, and sequester carbon. It paves the way for a resilient, sustainable dairy industry—one that responds to environmental challenges while maintaining economic viability and producing quality dairy products.
With a rising global demand for sustainably produced products and increasing awareness of climate change impacts, regenerative dairy practices present us with a strategic, future-proof solution. Throughout this guide, we will delve into the essential methods underpinning this movement—highlighting their benefits, practical application, and significance for healthy soils and thriving agricultural systems.
Core Principles of Regenerative Dairy
At the heart of regenerative dairy farming lies a commitment to improving soil health in dairy farms and restoring ecological harmony. These principles underpin all regenerative dairy systems:
- Soil Health First: Prioritizing the enhancement of soil structure, organic matter, and biological activity.
- Biodiversity: Actively promoting diversity on dairy farms—from crops to wildlife, insects, and microorganisms.
- Carbon Sequestration in Agriculture: Using farming practices that draw down and store atmospheric carbon in soils and plants.
- Animal Welfare: Ensuring cows and other animals experience natural behaviors and well-being through low-stress environments and ethical care.
- Economic Resilience: Reducing dependence on external inputs, fostering efficient resource use, and tapping into new market opportunities for sustainably produced dairy products.
“Cover crops in dairy farms can reduce soil erosion by as much as 50% annually.”
Regenerative Dairy: 7 Proven Practices for Healthy Soils
Let’s explore the seven foundational practices in regenerative dairy farming that improve soil health, enhance biodiversity, and ensure productive, resilient systems:
-
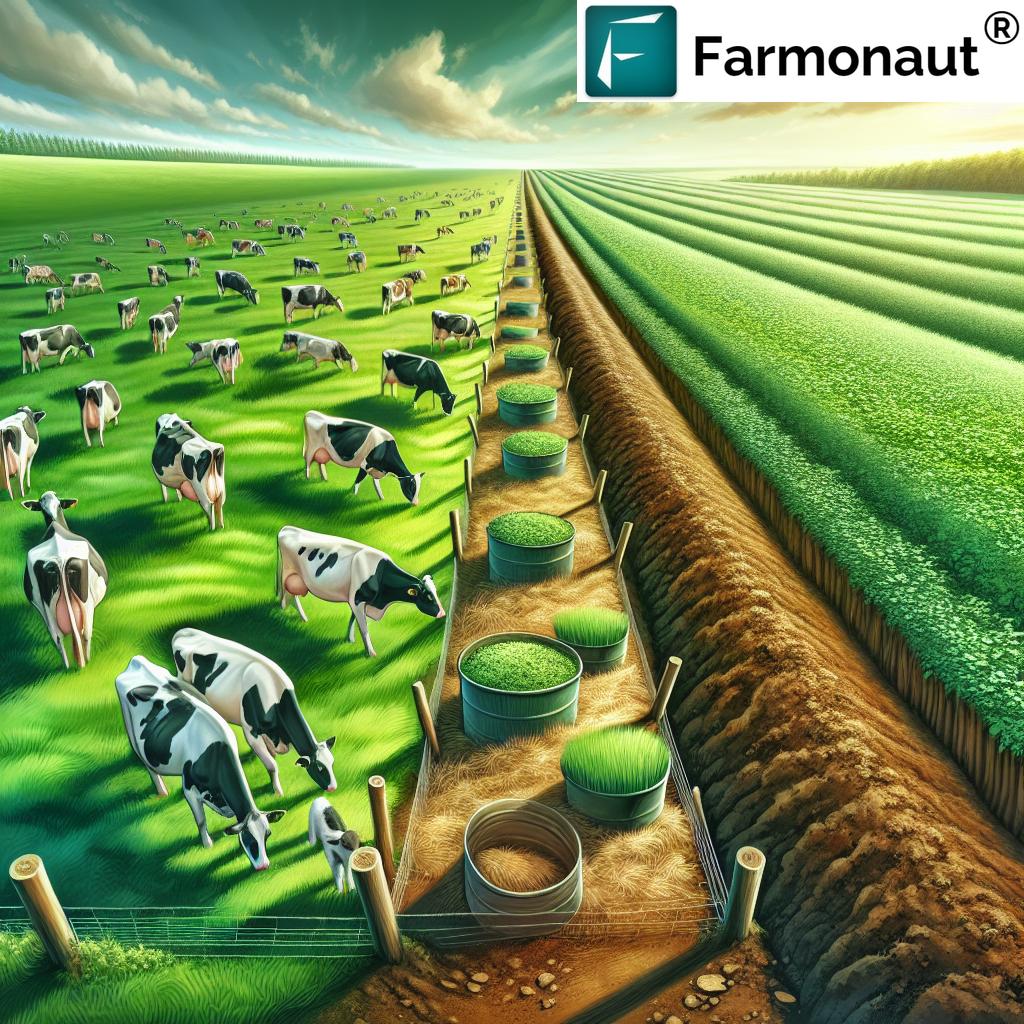
1. Rotational Grazing for Cows
Rotational grazing involves moving dairy cows briskly between different pasture areas—allowing periods of rest and regrowth for the grasslands. This prevents overgrazing, supports soil regeneration, and enhances productivity. Healthy pastures:
- Maintain high levels of organic matter
- Allow soil organisms to flourish, supporting overall biodiversity on dairy farms
- Reduce erosion, improving soil structure and boosting water infiltration
Fun Fact: Well-managed rotational grazing can increase soil carbon sequestration and pasture productivity significantly. It aligns with nature’s cycles, reducing the need for synthetic inputs.
-
2. Cover Cropping Benefits
Cover crops (like rye and clover) are sown during off-seasons to protect soil from erosion, enhance organic matter, and provide habitat for beneficial insects. The cover cropping benefits include:
- Reducing soil erosion by up to 50%
- Fixing nitrogen in the soil (especially with legumes such as clover)
- Improving soil structure and moisture retention
- Increasing population of beneficial insects and birds, fortifying farm resilience
Pro Tip: Dairy farmers can incorporate cover crops into crop rotation systems for sustained soil fertility and health.
-
3. Composting and Manure Management
On regenerative dairy farms, composting and manure management turn waste into a valuable asset. Composting manure:
- Increases soil organic matter
- Enhances nutrient cycling for crops and pastures
- Improves water retention capacity
- Reduces emissions (vs. unmanaged manure) and supports carbon sequestration
Repeated, responsible application of composted manure enriches the soil and lowers reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
Explore carbon footprinting solutions for dairy farms -
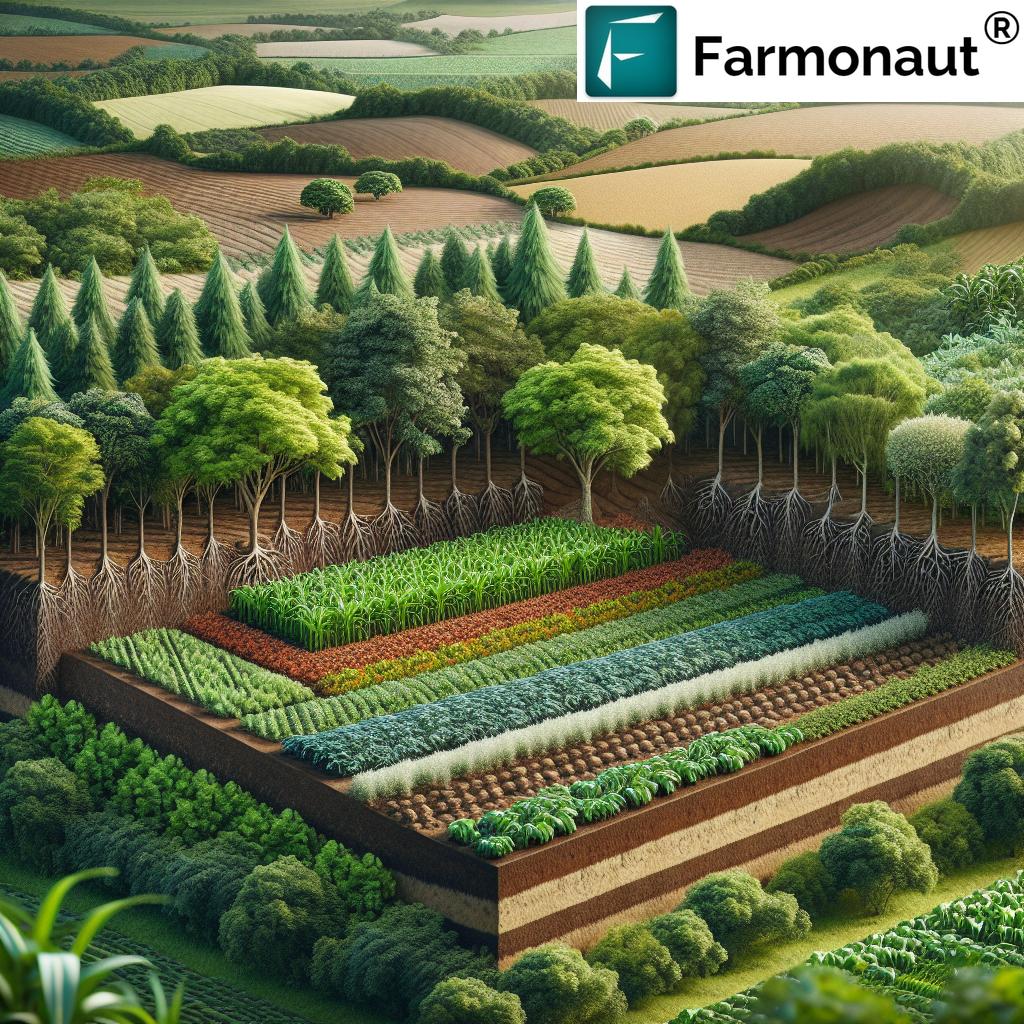
4. Agroforestry in Dairy Systems
Agroforestry means integrating trees and shrubs into pasture and cropping systems. Trees:
- Provide shade and windbreaks for cows, reducing heat stress and promoting welfare
- Support wildlife habitats, bird populations, and biodiversity on dairy farms
- Decrease wind erosion and enhance environmental resilience
- Sequester significant amounts of carbon
Tip: Varieties like willow, poplar, or native fruit trees offer food, shelter, and economic benefits.
Learn about precision mapping and advisory for agroforestry projects -
5. Minimizing Soil Disturbance
Healthy soils depend on minimal mechanical disturbance. Practices include no-till and reduced-till systems:
- Preserve beneficial soil microbiomes and fungi networks
- Protect soil structure, increase water retention, and reduce erosion
- Limit the loss of organic matter and aid carbon sequestration in agriculture
Adopt low-disturbance tillage to keep soils productive, fertile, and resilient.
-
6. Application of Compost
Consistent application of compost (from farm or local sources) is at the heart of restoring soil health:
- Boosts microbial activity and soil fertility
- Slow-release of nutrients for sustained crop and pasture growth
- Supports moisture retention and reduces reliance on synthetic inputs
- Helps build up soil organic matter year after year
Compost is a cornerstone for improving soil health in dairy farms.
-
7. Polyculture and Diverse Forage Systems
Polyculture forage systems involve planting a diversity of grasses, legumes, and herbs in pastures. This approach:
- Increases resilience to drought, pests, and diseases
- Enhances feed diversity and nutrition for cows
- Supports a wider array of pollinators and beneficial insects
- Promotes robust root systems and aboveground productivity
The result? Greater animal health, more biodiverse habitats, and improved soil structure.
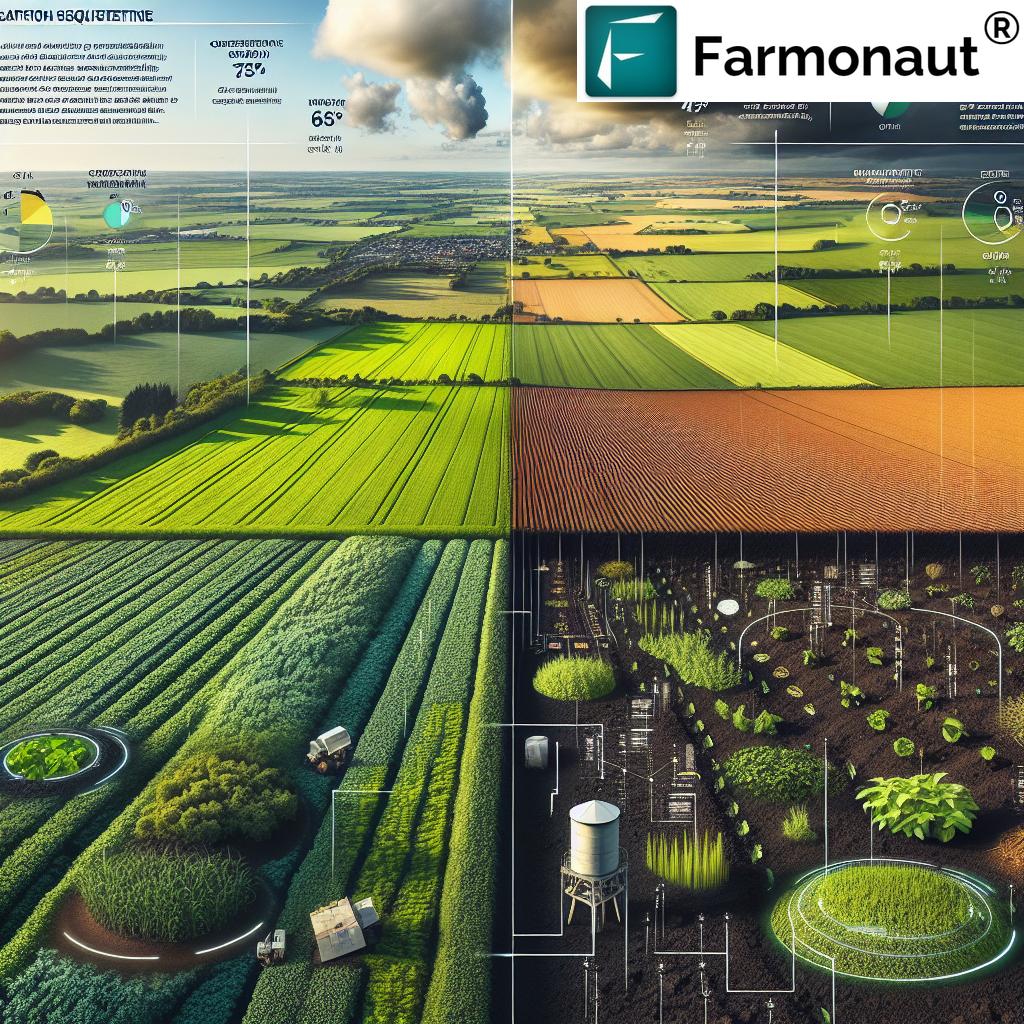
Practice Comparison Table: Regenerative Dairy Farming Methods
| Practice Name | Description | Soil Health Benefit | Biodiversity Impact | Est. Implementation Cost | Est. Yield Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotational Grazing | Moving cows across different pasture areas to allow rest and regrowth. | Improves organic matter, prevents compaction, enhances structure. | High (supports grassland flora & fauna diversity) | Low–Moderate | 10–30% |
| Cover Crops | Planting non-cash crops like clover/rye to cover soil during off-season. | Reduces erosion, adds nutrients, improves moisture retention. | Moderate–High (supports insects and birds) | Low | 8–18% |
| Agroforestry | Integrating trees within pasture/cropland to provide ecosystem benefits. | Improves structure; increases carbon sequestration. | Very High (wildlife, birds, pollinators) | Moderate–High | 10–20% |
| Manure Management | Composting animal manure and applying it as soil amendment. | Boosts organic matter, nutrient cycling, and water retention. | Moderate (soil organisms, fewer pollutants) | Low–Moderate | 6–15% |
| Minimizing Disturbance | Limiting tillage to protect soil structure & biological activity. | Preserves microbiome, improves infiltration. | Moderate (enhanced habitat stability) | Low | 7–14% |
| Compost Application | Spreading composted material to enrich soils. | Increases carbon, supports robust plant growth. | Moderate (soil food web, microorganisms) | Low–Moderate | 8–16% |
| Polyculture Forage | Growing diverse grasses, legumes, and herbs in pasture. | Diversifies root structure, maintains high fertility. | High (supports insects, pollinators) | Low | 8–15% |
Benefits of Regenerative Dairy Farming
By implementing sustainable dairy practices, the advantages for soils, livestock, the environment, and farmers themselves are profound:
-
Enhanced Soil Health:
- Increased organic matter, better water retention, and improved soil structure.
- Fertile soils reduce dependency on costly chemical fertilizers.
- Healthier soils are resilient against drought and flooding.
-
Increased Biodiversity on Dairy Farms:
- More plant, insect, and animal species; improved pollination and pest control.
- Greater ecosystem resilience, contributing to more stable and productive farms.
-
Carbon Sequestration in Agriculture:
- Soils become a critical climate solution, locking away atmospheric carbon.
- Regenerative practices can offset or reduce greenhouse gas emissions from dairy production.
-
Animal Welfare:
- Cows express natural grazing and social behavior in diverse, low-stress environments.
- Healthier animals—fewer illnesses, improved productivity, longer productive lifespans.
-
Economic Resilience for Farmers:
- Reduced reliance on synthetic inputs cuts costs.
- Access to premiums for sustainably produced dairy products.
- Diversifying income through agroforestry or eco-tourism is often possible.
For those seeking reliable solutions for farm traceability and supply chain integrity, Farmonaut’s blockchain-based traceability system offers transparency from pasture to product—vital for certification and consumer trust.
Managing large holdings? Farmonaut Large Scale Farm Management provides satellite-driven analytics, resource allocation tracking, and automation tools for operational efficiency—whether for dairy farms or mixed agricultural systems.
Need advanced fleet management for agricultural machinery on your dairy? Explore Farmonaut Fleet Management for satellite-verified tracking, maintenance scheduling, and performance optimization.
Challenges and Considerations in Regenerative Dairy Farming
While the benefits are substantial, transitioning to regenerative dairy systems is not without obstacles:
- Knowledge Gaps: Adopting new methods requires education, trial, and adaptation for farmers accustomed to conventional systems.
- Initial Investments: Building infrastructure (like fencing for rotational grazing or tree planting for agroforestry) may need upfront capital.
- Transition Periods: Soils may take time to respond; yield increases and soil improvements are often gradual.
- Market Access: Not all regions have robust demand or premium pricing for sustainably produced products—this can affect farm economics.
- Policy and Support: Government or regional incentives can accelerate uptake, but their presence and effectiveness is variable.
Tip: Leveraging satellite-based verification for crop loans and insurance (via Farmonaut) can ease financial risk and streamline access to capital during your regenerative transition.
How Farmonaut Empowers Sustainable Dairy Practices
We at Farmonaut are dedicated to transforming agriculture by making precision, data-driven farming solutions accessible to all. Our technology suite supports regenerative dairy farmers in several crucial ways:
-
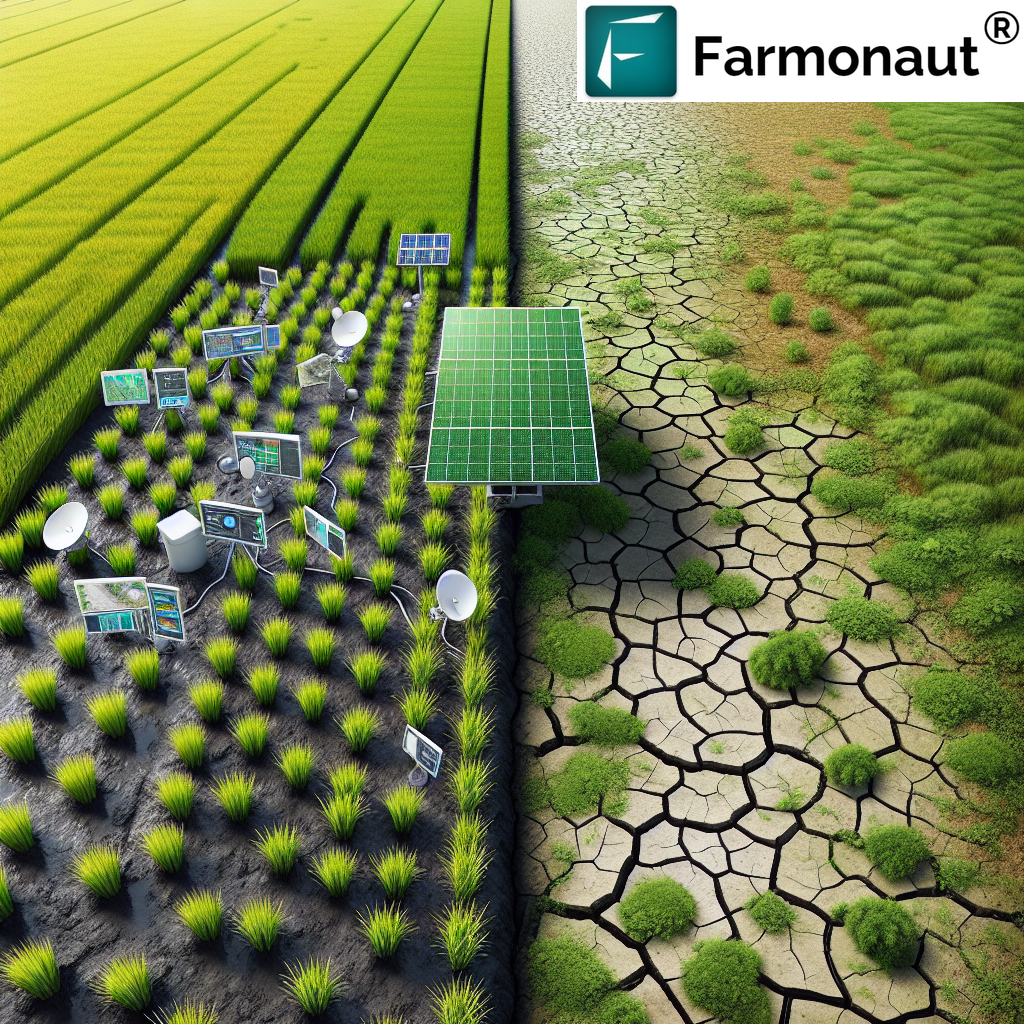
Satellite-Based Crop & Soil Monitoring:
We use multispectral satellite imagery to provide insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and progression of cover crops or pastures—helping you make informed, sustainable decisions. -
AI-Based Real-Time Advisory:
Our Jeevn AI system delivers personalized recommendations, weather forecasts, and early warnings, enabling resilient responses to climate and environmental stressors. -
Blockchain Traceability:
For transparency, our platform offers end-to-end blockchain-based traceability for dairy products, supporting food safety and sustainable sourcing. -
Resource & Fleet Management:
Track your machinery, optimize field logistics, and reduce input waste—advancing both financial sustainability and operational excellence. -
Carbon Footprint Tracking:
Our carbon footprinting tools support you in monitoring and mitigating emissions—essential for both compliance and environmental goals. -
API Integration:
Developers and researchers can access Farmonaut’s satellite and weather API and refer our Developer Documentation to embed precision data into their own dairy and livestock platforms.
Our mission is clear: integrate innovative technology and real-time data insights into traditional farming to empower farmers globally — profitably, efficiently, and sustainably.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is regenerative dairy farming?
Regenerative dairy farming is an agricultural approach that improves soil health, increases biodiversity, sequesters carbon, and enhances animal welfare through eco-friendly, restorative practices.
How does rotational grazing improve soil and animal health?
Rotational grazing for cows prevents overgrazing, allows grasses to recover, supports natural nutrient cycling, boosts soil organic matter, and decreases parasites—leading to healthier pastures and animals.
What are the best crops for cover cropping on dairy farms?
Popular cover crops include clover, rye, vetch, and radishes. These species add organic matter, fix nitrogen, and provide habitats for beneficial fauna.
How does composting help in regenerative dairy?
Composting and manure management recycle nutrients, boost soil structure, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, all while increasing yields and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Can I implement these practices on a small dairy farm?
Absolutely! Each regenerative practice can be scaled for small or large systems. Many benefits, such as improved soil and animal health, apply regardless of farm size.
How long before I see results from regenerative dairy farming?
Some improvements, such as animal health and reduced runoff, can appear within a single season, while full soil health restoration and increased yields often develop over several years.
Where can I find precision support and monitoring tools for my dairy farm?
Farmonaut’s platform delivers satellite-powered soil, crop, and resource monitoring tools for dairy farmers. Our mobile and web app, along with APIs, brings advanced insights to farms of every size.
Conclusion: Building Healthy Soils and Sustainable Dairy Systems
Regenerative dairy farming stands at the intersection of high productivity, environmental stewardship, and animal welfare. By integrating techniques such as rotational grazing, cover cropping, composting, and agroforestry, farmers can enhance soil fertility, boost on-farm biodiversity, and contribute to the global fight against climate change through meaningful carbon sequestration.
The journey may require patience and adaptation, but the results—improved soils, healthier animals, and greater farm resilience—are worth the investment for both current and future generations. For anyone ready to begin or accelerate this transformation, Farmonaut’s suite of affordable, advanced agri-tech tools can help optimize every aspect of your regenerative dairy system—from soil monitoring and animal welfare to resource management and landscape-level sustainability.
In facing the twin pressures of productivity and environmental responsibility, regenerative dairy practices are not just a trend—they are the essential blueprint for a resilient, sustainable future in farming.