Kansas Winter Wheat Yield: 7 Proven Practices for Resilience
“Kansas winter wheat yields can drop by up to 30% during severe drought years, highlighting the need for resilient practices.”
Introduction: The State of Winter Wheat in Kansas
In the heartland of the United States, Kansas stands proudly as a top winter wheat producer, contributing significantly to the nation’s food supply. The wealth of golden wheat fields stretching across the Kansas plains is both a symbol of agricultural resilience and an ever-evolving challenge for farmers. With the state’s continental climate—characterized by hot summers, cold winters, and varying precipitation-—every season brings a unique blend of climatic conditions, economic factors, and agricultural challenges.
Kansas wheat production faces mounting complexity as soil health, climate impacts, yield trends, adaptation, and shifting market dynamics all play pivotal roles in shaping the future of this vital crop. From the pressures of drought, reduced harvests, dropping prices, and competition from other crops, to innovations in soil health practices for wheat and advanced agtech solutions like those offered by Farmonaut, Kansas wheat farmers are at a crossroads.
This comprehensive guide explores the intertwined forces shaping “Kansas Winter Wheat Yield: 7 Proven Practices for Resilience.” Discover actionable strategies from crop rotation benefits to adaptation strategies for farmers, all designed to support sustainable, profitable, and resilient wheat farming in Kansas.
Climatic Factors Impacting Kansas Winter Wheat
Continental Climate: What Sets Kansas Apart?
Kansas experiences a classic continental climate, with sharp seasonal contrasts. The state sees hot summers and cold, often snowy winters, with precipitation varying between regions. These patterns set the stage for both the potential and challenges of winter wheat Kansas.
- Planting Time: Winter wheat is typically planted in the fall, taking root before entering dormancy through winter’s chill.
- Resumption of Growth: In early spring, as conditions improve, wheat resumes growth before fields burst into gold around June, signaling harvest time.
- Precipitation Variance: Western Kansas is notably drier, while eastern regions see more rain, impacting yields and management strategies.
Recent Weather Extremes and Impact of Drought on Wheat Yields
The last decade has brought new extremes in weather events, particularly drought. In 2024, the U.S. winter wheat crop in Kansas was in one of its worst conditions ever recorded, with only 38% rated good or excellent by the USDA—well below analysts’ estimates. Drought intensified, affecting 58% of winter wheat areas—the highest since early 2023 (Reuters).
- Harvests have dropped in drought years, reducing both volume and quality.
- Severe conditions can cut yields by up to 30%—a devastating blow for farmer incomes.
- Wheat yield challenges from drought-driven crop failures mean increased financial pressures and reduced supply.
The necessity for adaptation strategies for farmers has never been clearer: climate-resilient practices are crucial to securing the future of Kansas wheat production.
Soil Health Practices for Wheat: The Foundation of Resilience
The vital, living layer beneath our feet—soil—is foundational to wheat yield, crop quality, and farm sustainability. Yet, years of industrial agriculture have degraded soil health in many Kansas fields, compounding the current problems caused by climate and market stresses.
Key Soil Health Practices for Wheat
- Crop Rotation: Rotating wheat with other crops (such as sorghum, soybeans, or legumes) helps break pest and disease cycles, restores soil fertility, and enhances organic matter.
- Reduced Tillage: Limiting tillage preserves soil structure, reduces erosion, and maintains soil moisture for improved resilience.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops maintains soil cover off-season, reduces nutrient runoff, boosts water retention, and promotes beneficial microbial activity.
- Soil Testing and Targeted Amendments: Regular testing allows for precision nutrient applications, correcting deficiencies and minimizing fertilizer waste.
Adopting soil health practices can boost Kansas winter wheat yields by 15%, supporting both sustainability and profitability.
Benefits of Healthy Soil:
- Improved Yields: Healthy soils deliver more reliable water and nutrients, leading to optimal wheat yields.
- Climate Resilience: Soils rich in organic matter can buffer against both drought and floods.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Healthier soils require fewer chemical inputs and are more environmentally sound.
Kansas Wheat Yield Challenges: Climate, Market, and Economics
Climate-Induced Challenges
- Frequent and extreme weather events (drought, heatwaves, late freezes, and heavy storms).
- Highly variable precipitation within and between seasons.
- Shifts in cropping calendars due to unpredictable climate patterns.
Economic Factors Affecting Wheat Farming
- Market volatility: In 2024, wheat market prices have reached five-year lows due to global oversupply.
- Rising input costs: Seeds, fertilizer, fuel, and equipment are all more expensive, squeezing profit margins.
- Competition: Corn and soybeans offer better returns, encouraging field abandonment and reduced acreage for wheat (Reuters).
- Insurance dependency: Many farmers depend on crop insurance to manage risk, as losses threaten financial stability.
Market Dynamics and Wheat Supply
- Global supply surplus drives prices even lower.
- High costs for transport, gasoline, and farm repairs eat away at thin profits (Reuters).
- Many operations are financially unsustainable, leading to an ongoing decrease in wheat farms and increased reliance on insurance.
These intertwined factors make resilience strategies for Kansas wheat production more critical than ever.
“Adopting soil health practices can boost Kansas winter wheat yields by 15%, supporting both sustainability and profitability.”
7 Proven Practices for Resilient Kansas Wheat Yields
Responding to the convergence of climatic, soil, economic, and market challenges, innovative conservation practices in agriculture have demonstrated clear benefits for yield resilience. Below, we outline the seven most effective, science-based strategies that Kansas wheat farmers should consider.
-
Crop Rotation: Boosting Soil and Yield Stability
Crop rotation benefits for wheat extend far beyond pest and weed control. Including soybeans, legumes, or sorghum in annual rotations enhances soil fertility, disrupts pathogen cycles, and increases wheat’s tolerance to variable climatic conditions. In Kansas, diversified rotations can deliver up to a 12% yield increase while replenishing soil nutrients.
-
Conservation Tillage: Protecting Soil Structure and Moisture
Reducing tillage intensity preserves soil structure, improves water retention, and decreases erosion. Practices like no-till or strip-till allow organic matter to accumulate and promote beneficial microbes—crucial for Kansas’ drought-prone areas.
-
Cover Cropping: Year-Round Soil Protection
Planting rye, clover, or vetch between cash crops offers a living shield for Kansas soils. Cover crops lock in moisture, suppress weeds, and boost soil organic carbon—an essential part of resilience. Some studies indicate yield benefits up to 8% when cover cropping is optimized in the rotation.
-
Soil Testing and Targeted Fertilization
Precision agriculture, guided by regular soil tests, delivers nutrients only where needed. This results in cost savings, improved crop growth, and reduced environmental risk. Accurate fertilization is especially vital when prices are squeezed and every input must count.
-
Drought-Resistant Wheat Varieties
Given the impact of drought on wheat yields, selecting modern, region-adapted varieties is vital. Drought-tolerant genetics support stable yields under water stress and can help mitigate economic and climatic yield challenges.
-
Precision Irrigation Techniques
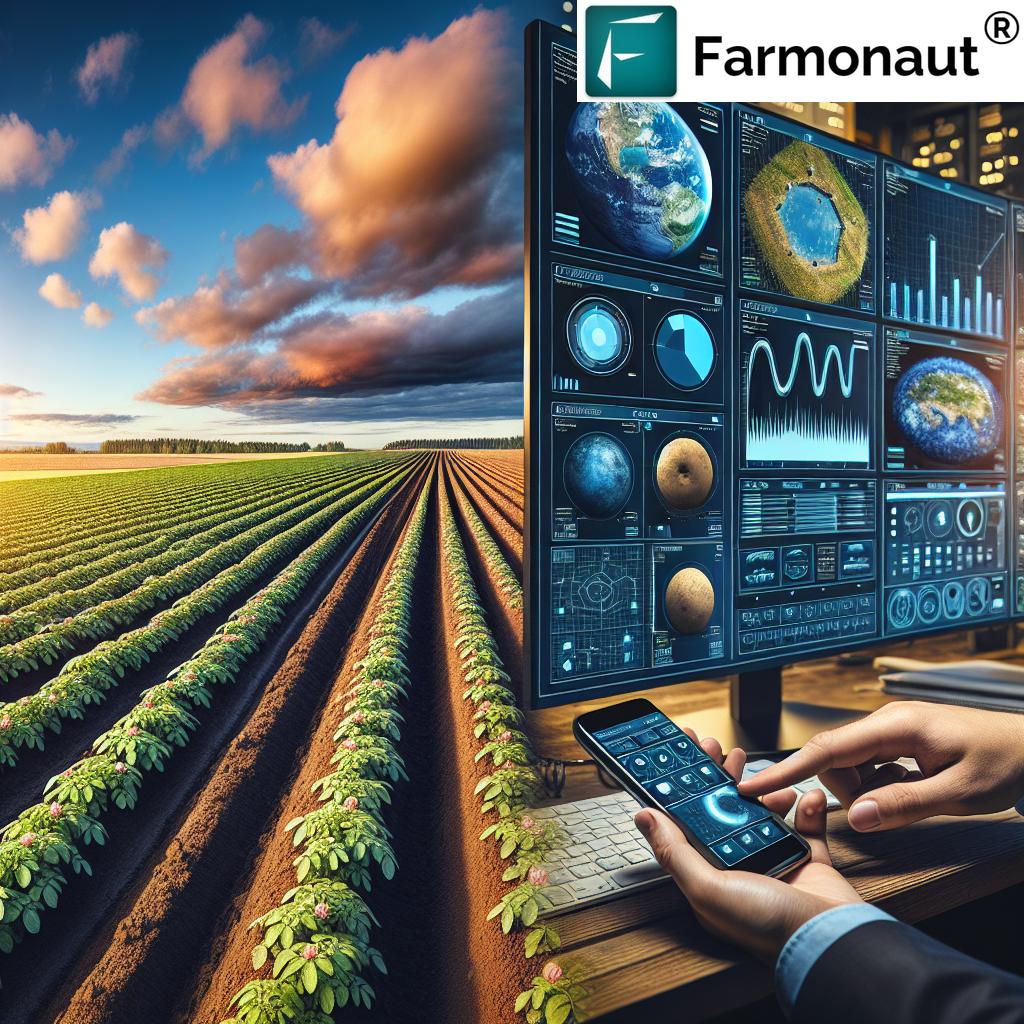
Whether through advanced scheduling, subsurface drip, or pivot systems, targeted irrigation saves water and maintains yield during dry spells. Technologies like soil moisture sensors and satellite monitoring (see: our Farmonaut platform) provide Kansas farmers with the data needed for optimal irrigation.
-
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
A blend of biological, mechanical, and chemical tools, IPM reduces pest damage while minimizing environmental impacts. Well-managed IPM can cut dependency on broad-spectrum pesticides and support soil health practices for wheat.
Comparative Practices Impact Table
| Practice Name | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Soil Health Impact | Climate Resilience Contribution | Cost Implication ($/acre) | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Rotation | 8-12% | High | High | Low | Enhances biodiversity, reduces input needs |
| Conservation Tillage | 6-10% | High | Medium | Low–Medium | Reduces erosion, stores carbon |
| Cover Cropping | 4-8% | High | High | Medium | Improves organic content, reduces runoff |
| Soil Testing & Fertilization | 2-6% | Medium | Low | Medium | Prevents run-off, efficient resource use |
| Drought-Resistant Varieties | 8-15% | Medium | High | Medium–High | Stabilizes yield, reduces irrigation need |
| Precision Irrigation | 10-18% | Medium | High | High | Saves water, reduces input waste |
| Integrated Pest Management | 3-5% | Medium | Medium | Low | Reduces chemical dependency |
Empowering Sustainable Agriculture with Farmonaut
Farmonaut is revolutionizing precision agriculture in Kansas and beyond, making advanced, satellite-driven insights accessible and affordable even to small-scale farmers. Our technologies are tailored to support Kansas wheat growers in facing today’s climatic and economic factors affecting wheat farming:
-
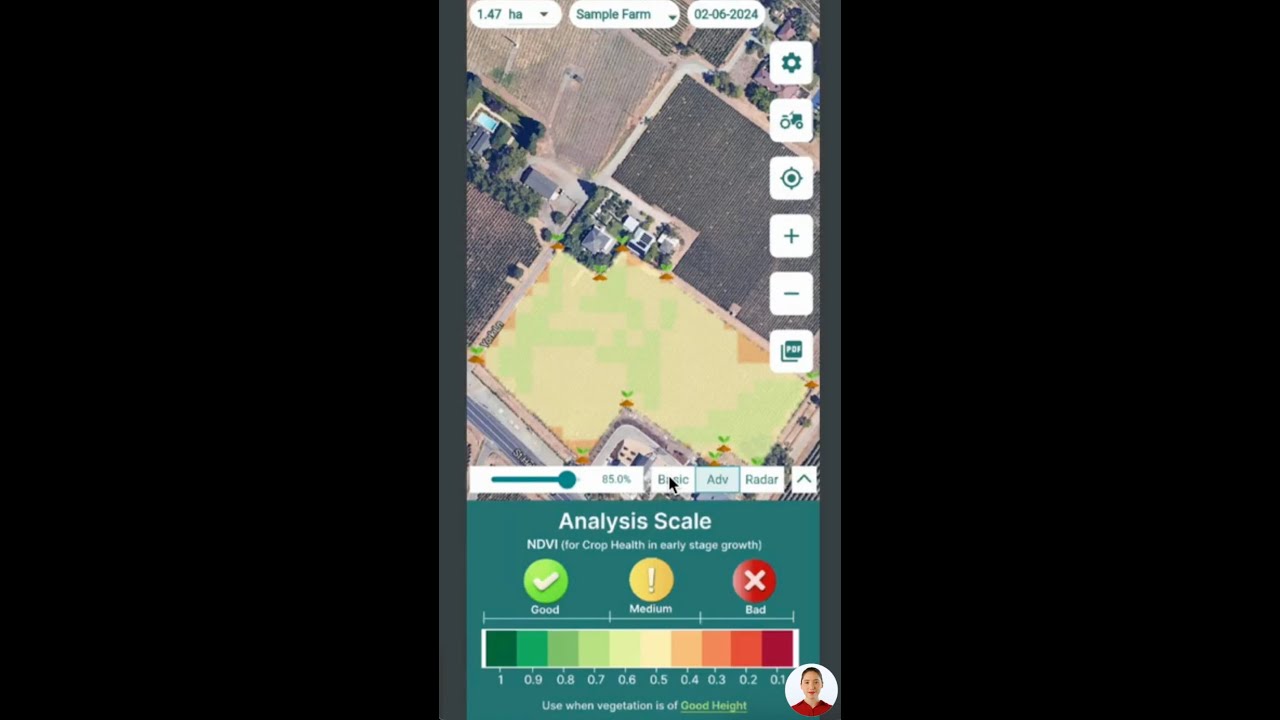
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring:
We deliver real-time visualization of crop health using multispectral imagery to track NDVI, soil moisture, and water stress. This empowers optimal irrigation, targeted nutrition, and timely intervention—vital for yield stability under climatic conditions and drought stress.
Try our web, Android, or iOS apps for actionable field insights. -
Jeevn AI Advisory System:
Advanced AI provides custom advice on crop management, fields with emerging issues, and best timing for fertilizer or pesticide application—helping increase yields and profitability. -
Blockchain-Based Traceability:
Our traceability solution ensures transparency across the entire wheat supply chain, beneficial for Kansas growers targeting premium or specialty markets. Learn more on our Product Traceability page. -
Fleet & Resource Management:
Tools to streamline operations, optimize logistics, cut fuel costs, and maintain field machinery. These help manage overhead in seasons of low prices or high costs.
Discover our fleet management system for large farms and agribusinesses. -
Carbon Footprinting:
For those pursuing sustainable certification or wanting to minimize environmental impacts, our carbon tracking platform measures field-level greenhouse gas emissions.
Explore Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools for sustainable Kansas wheat production. -
API Access for Developers:
Integrate real-time satellite and weather data into your apps or services. Visit our API product page or review our API developer documentation. -
Verification for Crop Loans & Insurance:
Use our satellite-based monitoring for streamlined loan and insurance approvals on Kansas wheat fields. Check out our Crop Loan and Insurance Verification page.
Our mission is to empower farmers, agribusiness, and stakeholders with the insights needed to manage risk and boost both economic and environmental outcomes for Kansas wheat production.
Adaptation Strategies for Kansas Wheat Farmers
Kansas farmers must draw upon a toolbox of conservation practices in agriculture and innovative financial/market adaptations to survive and thrive in the coming decade. Here are practical ways to build long-term resilience based on current challenges and economic factors affecting wheat farming:
- Diversification: Many are incorporating alternative crops (corn, soybeans, sorghum) or livestock to spread risk, reduce reliance on single market prices, and maximize land value.
- Premium and Specialty Wheat: Shifting some acreage to high-quality, organically grown, or region-brand wheat for premium markets—for example, varieties with distinctive protein content or baking characteristics—can command better prices.
- Advanced Resource Management: Adopting precise monitoring via platforms like Farmonaut to enhance water, fertilizer, and pesticide efficiencies, thus cutting costs.
- Collaborative Approaches: Cooperatives, bulk input purchasing, and shared storage or logistics can further reduce operational costs and cushion against market volatility.
- Participating in Carbon and Traceability Programs: Emerging environmental and transparency standards can create new revenue streams; carbon footprinting programs and blockchain traceability bring value for eco-conscious markets.
- Leveraging Crop Insurance Data: Making full use of satellite-verified assessments (provided by our crop loan and insurance solutions) to ensure rapid, accurate payouts in adverse weather years.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most significant threats are drought and extreme weather events. Kansas’s climate is increasingly unpredictable, so adopting resilient practices like crop rotation, conservation tillage, and drought-resistant varieties is crucial.
Q: How do soil health improvements affect Kansas wheat?
Soil health practices for wheat—from increased organic matter to reduced tillage—can improve yields by 10–15%, lessen the impact of drought, and lower input costs. Healthy soil retains water and nutrients better and supports stronger plants.
Q: Can Kansas wheat farmers buffer themselves against low market prices?
Some adaptation strategies include diversifying with other crops or livestock, targeting premium/specialty wheat markets, and reducing operational costs with precision technologies (see: Farmonaut). Crop insurance also offers protection in difficult years.
Q: What technology can help boost Kansas wheat yields and manage risk?
Satellite-based tools and AI-driven advice (as found in the Farmonaut platform) support crop health monitoring, efficient irrigation, precise input use, and even insurance verification—resulting in higher yields and profitability.
Q: Are there additional environmental benefits to these resilience strategies?
Absolutely. Conservation-based wheat production reduces runoff, improves carbon sequestration, and enhances biodiversity—all crucial for sustainability.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Future for Winter Wheat Kansas
The path forward for Kansas wheat production is undeniably complex, shaped by the unpredictable climate, economic, soil, and market dynamics unique to the United States’ wheat heartland. However, embracing these 7 proven practices, alongside cutting-edge field monitoring, traceability, and resource management technology, unlocks the potential for a more resilient, profitable, and sustainable future.
Whether you’re a family farmer in western Kansas contending with drought, a large-scale operation juggling market volatility, or an advisor seeking data-driven crop solutions, a commitment to soil health and smart adaptation strategies is the surest path to sustained success for this iconic crop.
With robust conservation practices in agriculture—and advanced solutions like those we offer at Farmonaut—Kansas wheat farmers can continue to nourish both their land and their livelihoods, leading the nation in sustainable wheat farming for generations to come.