Agriculture Analysis: 7 Techs Transforming Farming
“Over 70% of global farmers are expected to adopt precision agriculture technologies by 2030.”
Agriculture remains the backbone of human civilization, shaping economies, sustaining populations, and stewarding vast landscapes. With the rapid advancement of agricultural technologies and the expanding reach of digital agriculture, the sector is undergoing an unprecedented transformation. This comprehensive overview explores agricultural analysis, highlights precision agriculture technologies, and delves into sustainable farming practices that are redefining how we analyze, manage, and optimize crop yields, soil health monitoring, and environmental impacts.
As stakeholders in modern agriculture—whether researchers, policymakers, agribusiness professionals, or tech providers like us at Farmonaut—it is critical to understand the multifaceted landscape of agricultural analysis. This knowledge enables us to support farmers in harnessing advanced data, optimize resource use, and promote sustainable development for a food-secure future.
The Importance of Agricultural Analysis
Agricultural analysis is the systematic evaluation of various factors affecting agriculture—ranging from soil health, climate conditions, crop performance, and market dynamics to environmental sustainability and resource management.
Why Is Agricultural Analysis Crucial?
- Optimizing Productivity: By understanding and interpreting datasets from soil, weather, crop, and farm operations, it becomes possible to optimize yields and increase productivity for both crops and livestock.
- Adopting Sustainable Practices: Agricultural analysis supports adoption of sustainable farming practices and climate smart agriculture—preserving biodiversity, reducing input waste, and maintaining soil fertility.
- Enhancing Economic Viability: Market and cost-benefit analyses enable farmers to identify the most profitable ventures and reduce economic risks.
- Guiding Policy Development: Comprehensive, data-driven insights inform policymakers and help design impactful support systems for the agricultural sector.
Key Methodologies in Agricultural Analysis
- Field Surveys & Data Collection: Data is gathered through soil sampling, crop scouting, and direct observation—offering empirical insight into soil health monitoring, pest pressure, and input needs.
- Remote Sensing in Agriculture & GIS: Satellite imagery and GIS allow for large-scale monitoring of crop health, soil moisture, and land use patterns, supporting timely decision-making and resource allocation. This is central to Farmonaut’s precision agriculture services as well.
- Statistical Modeling & Data Analysis: Advanced statistical tools help us analyze complex datasets, predict outcomes, discern yield patterns and assess environmental impacts.
- Economic Analysis: Evaluating financial feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and market trends, guides farmers and agribusinesses in making economically viable choices.
Integrating Technologies in Agricultural Analysis
Today’s precision agriculture technologies are revolutionizing how agricultural data is collected, processed, and translated into actionable strategies, making agricultural analysis both more comprehensive and accessible.
Comparative Overview: 7 Precision Agriculture Technologies
| Technology Name | Main Application | Est. Yield Improvement (%) | Soil Health Impact | Sustainability Benefit | Adoption Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Satellite Crop Monitoring | Crop health & stress detection | 15–30% | High—continuous soil status assessment | Efficient input use, reduced wastage | Growing rapidly |
| 2. AI-Based Advisory Systems | Personalized crop management | 10–25% | Moderate—targeted recommendations | Improves input efficiency | Fast adoption in advanced markets |
| 3. IoT Sensors | Real-time soil, weather, & irrigation monitoring | 12–20% | High—precise moisture/fertility mapping | Water and fertilizer conservation | Rapid & expanding |
| 4. Robotics & Automation | Automated planting, weeding, harvest | 15–28% | Low—indirect via reduced soil compaction | Reduces labor reliance, fuel use | Adoption rising in large farms |
| 5. Blockchain Traceability | Supply chain transparency | 5–10% | Low—traceability not direct soil impact | Reduces fraud, supports organic labels | Limited but increasing |
| 6. Variable Rate Technology (VRT) | Optimized fertilizer & pesticide application | 12–20% | High—reduces buildup/contamination | Minimizes input waste, runoff | Strong in commercial farms |
| 7. Drone Remote Sensing | High-res crop monitoring, mapping | 10–15% | Moderate—localized diagnostics | Early detection, site-specific care | Expanding in developing regions |
Agriculture Analysis: 7 Technologies Transforming Farming
Precision agriculture technologies are reshaping the future of agricultural analysis, empowering farmers to harness the best of science and digital innovation for their fields. Here, we analyze seven pivotal technologies that drive yield optimization, soil health monitoring, and resource efficiency:
-
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring
Leveraging satellite imagery and multispectral analysis, this technology delivers comprehensive insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and crop stress in real-time. It allows for large-scale monitoring and precise targeting of irrigation, fertilizers, and pest controls. Remote sensing in agriculture not only supports yield optimization but also enables cost-effective decision-making by pinpointing problems early and at scale.
Example use case: Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management platform,
uses satellite-based crop monitoring to help agribusinesses and large farms manage multiple fields efficiently. -
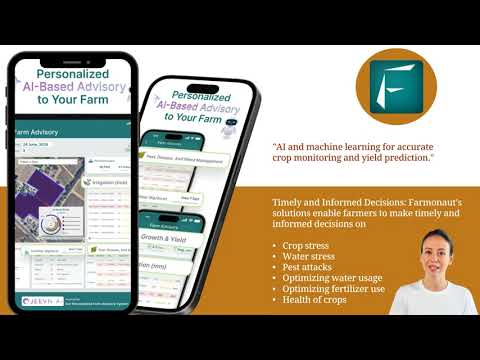
AI-Based Advisory Systems
Artificial Intelligence processes vast agricultural datasets, integrating climate patterns, soil characteristics, weather forecasts, and historical data for personalized crop recommendations. For instance, Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI-based advisory system provides cultivators with actionable advice—ranging from optimal sowing dates to customized nutrition and pest management plans—based on real-time analysis from satellites, the latest research, and on-ground inputs.
This not only improves productivity and yield prediction, but helps farmers adapt to climate change and changing market dynamics.
Benefit highlight:
AI-powered systems help close the knowledge gap for smallholder farmers by providing expert-level insights, even in remote or underserved areas. -
IoT Sensors and Connected Devices
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture brings a new era of real-time farm data management. Devices and sensors monitor environmental conditions—such as temperature, humidity, and soil moisture—and transmit this data for processing via mobile or cloud applications. This supports resource optimization, predictive irrigation, and timely interventions for both crops and livestock.
IoT is crucial for site-specific management, improving input efficiency, water conservation, and reducing environmental impacts.
-
Robotics and Automation
Autonomous vehicles and robots are revolutionizing field tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting. This reduces labor costs, eliminates human error, and increases the precision of input applications. Robotic solutions also help minimize soil compaction and enable farmers to manage larger areas more efficiently.
The integration of automation eases the growing challenges posed by labor shortages and rising production costs, ensuring greater efficiency and improved crop performance.
-
Blockchain-Based Product Traceability
Blockchain technology is transforming agricultural supply chains by enabling end-to-end traceability of products from farm to consumer. Every transaction and movement in the supply chain is recorded in an immutable ledger, ensuring transparency, authenticity, and safety.
For agrifood businesses and consumers, this is a game-changer in certifying organic/ethical produce, reducing fraud, and strengthening brand trust. Discover Farmonaut’s Traceability Platform for secure product provenance.
-
Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
VRT involves applying water, fertilizers, and pesticides with variable rates based on precise geospatial information. This targeted approach greatly enhances input use efficiency, prevents over-application, and reduces environmental contamination.
By embracing VRT, farmers can both optimize yields and ensure sustainability—a true representation of climate smart agriculture.
-
Drone Remote Sensing
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors offer rapid, on-demand remote sensing in agriculture. Drones capture detailed images for crop health analysis, mapping, and early detection of pest or disease outbreaks.
When integrated with other data streams, drone imagery helps refines precision agriculture interventions, delivering timely benefits to both smallholder and commercial farmers.
“Digital farming tools can increase crop yield analysis accuracy by up to 40% compared to traditional methods.”
Farmonaut’s Cutting-Edge Solutions in Digital Agriculture
As innovators in the agri-tech sector, we at Farmonaut are committed to making precision agriculture and digital farming accessible and affordable to farmers worldwide. Our platform fuses the power of satellite imagery, AI advisory systems, and blockchain technologies for comprehensive farm management.
- Real-Time Crop Monitoring: Our satellite-based platform provides insights into crop health, NDVI, and soil moisture—optimizing input management and increasing yields.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Delivers expert, location-specific advice—including crop selection, irrigation timing, and pest alerts.
- Blockchain Traceability: Enables transparent product tracking for supply chain integrity.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Our solutions empower businesses with efficient machinery usage and logistics optimization. Learn more about Farmonaut’s Fleet Management for enhanced operational oversight.
- Carbon Footprinting: We support sustainability goals through real-time carbon footprint tracking tools, helping agribusinesses comply with environmental standards and reduce emissions.
- Crop Loan & Insurance Verification: Our satellite-based system streamlines crop loan and insurance verification, reducing risk and increasing access to agricultural finance.
Experience next-gen agriculture with our Web, Android, and iOS apps, available globally in both English and Hindi. Discover more about how Farmonaut’s advanced technology delivers highly accurate, data-driven decisions for farms of any scale.
Try Farmonaut today! Web App | Android App | iOS App
Developers: Integrate satellite and weather data via our API and see the Developer Docs.
Sustainable Farming Practices & Precision Agriculture
Sustainable farming practices and precision agriculture technologies go hand-in-hand, addressing mounting global concerns—climate change, resource depletion, and food security. Examples include:
- Crop Rotation & Cover Cropping: Enhance soil structure, fertility, and biodiversity while reducing disease cycles and weed pressure.
- Conservation Tillage: Minimizes soil erosion, improves water retention, and promotes the growth of beneficial soil microorganisms.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combines biological, cultural, and chemical strategies for pest control, reducing overall pesticide use.
- Precision Input Application: When combined with digital agriculture platforms, helps reduce over-application of agrochemicals and maximizes environmental sustainability.
- Agroforestry Systems: Integration of trees into farm landscapes for ecological stability and diversified farm income.
The fusion of precision ag tools (from sensors to software platforms) enables farmers to minimize waste, enhance soil resilience, and ensure high yields for generations to come.
Agroforestry Systems & Regeneration: Integrating Trees for Sustainable Agriculture
Agroforestry systems merge principles of forestry with crop and livestock farming. By integrating trees onto agricultural land, they generate timber, fruits, nuts, and medicinal products while enhancing soil health and ecological balance. Key benefits of agroforestry analysis include:
- Stabilizing land and reducing erosion
- Improving infiltration and water regulation
- Providing habitat and food for wildlife—boosting biodiversity
- Capturing and storing atmospheric carbon—vital for climate smart agriculture
Farmer-Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR) is a cost-effective way to restore degraded lands, especially in dryland regions. This method promotes the regrowth of woody perennials, transforming barren soils into productive landscapes.
Pro Tip: Learn more about remote satellite detection for tree inventory and reforestation with Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory App.
Digital Agriculture & Data Management Trends
Digital agriculture refers to the application of advanced tools for collecting, analyzing, and sharing farm data. From big data analytics to cloud computing and seamless mobile integration, digital ag transforms every link in the agri-food value chain.
| Aspect | Impact on Modern Agriculture |
|---|---|
| Farm Data Management | Enables record-keeping, automates compliance, and supports continuous improvement at scale. |
| Cloud-Based Platforms | Allow seamless access to field data, alerts, and decision support tools from anywhere and any device. |
| Mobile Applications | Bring advisory, weather, and crop health monitoring directly to farmers, including those in remote areas. |
| API Integration | Enables researchers, financial institutions, and agribusinesses to embed powerful analytics into existing systems (see Farmonaut’s API). |
With digital tools like Farmonaut’s platform, farm data management is democratized, ensuring that even smallholder farmers can participate in the digital revolution. These solutions are crucial for enhancing productivity and for adapting to the evolving environmental and economic landscapes.
Challenges and the Future of Agricultural Analysis
Emerging technologies and advanced methodologies promise a bright future for agriculture, but some significant hurdles remain:
- Data Management & Interoperability: The flood of agricultural data from satellites, drones, IoT, and field sensors requires robust systems for storage, integration, and real-time analysis.
- Access to Technology: Financial and infrastructure barriers still exist for many smallholder and marginal farmers, impacting adoption rates in rural and developing areas.
- Climate Change & Unpredictability: Intensifying weather extremes and shifting climate patterns threaten food security and economic viability for vulnerable regions.
- Policy & Regulatory Gaps: There’s a persistent need for policies that support innovation while ensuring environmental sustainability and social equity.
Future directions in agricultural analysis should focus on:
- Enhancing data interoperability and platform integration
- Creating affordable, accessible tech for farmers of all scales
- Prioritizing climate-resilient solutions and carbon tracking (see Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools)
- Encouraging open policy frameworks that value innovation, sustainability, and inclusion
Innovation in agricultural analysis is essential for bridging the gap between technology and field-level impact, ensuring a resilient and food-secure future.
Farmonaut Subscriptions
Our flexible, subscription-based model ensures affordable access for all types of users—smallholders, agribusinesses, government bodies, and researchers. Customize your solution by choosing services and hectare coverage as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is agricultural analysis and why is it important?
Agricultural analysis is the systematic examination of various factors affecting agricultural production, including soil health, crop performance, environmental conditions, and market dynamics. It helps farmers and agribusinesses optimize yields, improve sustainability, make informed decisions, and ensure long-term productivity and profitability.
2. How do precision agriculture technologies benefit farmers?
Precision agriculture technologies—like satellite crop monitoring, AI advisory systems, and IoT sensors—enable farmers to use inputs more efficiently, detect problems early, minimize resource wastage, and increase overall crop and livestock productivity.
3. What are sustainable farming practices?
Sustainable farming practices are methods that preserve soil health, promote biodiversity, conserve natural resources, and minimize environmental impacts. Examples include crop rotation, reduced tillage, integrated pest management, and agroforestry systems.
4. What is digital agriculture?
Digital agriculture leverages tools such as satellite data, mobile apps, AI, IoT, and cloud computing to optimize farm operations, improve data-based decision-making, and ensure efficiency across the agri-food value chain.
5. How does Farmonaut support modern agriculture?
Farmonaut delivers affordable, accessible digital agriculture solutions—offering satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven advisories, blockchain traceability, and comprehensive resource management tools for large-scale and individual farming.
Conclusion: The Future of Agricultural Analysis
Agricultural analysis stands at the threshold of an exciting digital revolution. As emerging technologies, precision agriculture practices, and digital platforms gain traction, farmers, policymakers, and agribusinesses are better equipped than ever before to tackle the sector’s greatest challenges. The integration of AI, remote sensing, blockchain, and other advanced methodologies enhances our understanding of soil health, supports climate resilience, and drives sustainable increases in yields.
We, at Farmonaut, believe that democratizing precision agriculture through cost-effective, accessible, and comprehensive solutions is the surest way to empower farmers and safeguard the future of food production. The journey towards truly sustainable agriculture involves ongoing innovation, responsive policies, and a continued commitment to environmental, economic, and social progress.
To join the agri-tech transformation, try our Web, Android, or iOS platform today, or explore our API for deep integration with your systems.
Together, we can shape the next era of farming, where agricultural analysis leads the way in advancing productivity, sustainability, and food security globally.