Agriculture Technology Management: 7 Smart Innovations Transforming Farming
Introduction: The Era of Agriculture Technology Management
In today’s rapidly evolving agricultural landscape, it is essential for farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers alike to stay ahead by embracing smart technologies that enhance efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. From precision agriculture to IoT in agriculture and innovative crop monitoring with drones, modern agriculture technology management is redefining how we approach farming practices and address challenges in food production, resource management, and environmental conservation. If you’re seeking ways to optimize management and build a better future for your fields, understanding the latest smart farming solutions is crucial.
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% using data-driven decision-making.”
What Is Agriculture Technology Management?
Agricultural technology management (AgTech) encompasses the strategic integration of cutting-edge technologies into farming, forestry, and related operations to improve productivity, sustainability, and management efficiency. This multidisciplinary field combines principles from engineering, biology, and environmental science, addressing complex challenges in food production, resource management, and environmental conservation.
By leveraging precision agriculture, smart farming solutions, IoT in agriculture, and other advanced approaches, AgTech enables farmers to make more informed, data-driven decisions, optimize resources, and enhance crop yields while promoting environmental sustainability.
7 Smart Innovations in Agricultural Technology & Management
The future of farming is smart, data-driven, and sustainable. Discover these seven major innovations revolutionizing field management, crop production, and operational efficiency worldwide. Each of these technologies empowers farmers to tackle modern challenges and thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
“Smart farming solutions have reduced water usage in agriculture by nearly 30% through advanced monitoring systems.”
1. Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Farm Management
Precision agriculture stands at the forefront of the AgTech movement, employing data-driven management strategies to optimize every aspect of field operations. Utilizing GPS, remote sensing, advanced analytics, and IoT-based systems, this approach enables farmers to account for variability in soil fertility, crop health, and resource usage across different areas of a single field.
- RTK GPS (Real-Time Kinematic): Provides centimeter-level accuracy for planting, irrigation, and fertilization tasks. Precise positioning ensures inputs are applied in the right location, maximizing crop response and minimizing waste.
- Satellite Imaging & Sensors: Satellite and ground-based sensors monitor soil moisture, crop vigor, and identify plant stress, helping to spot variability and improve resource allocation.
- Yield Mapping & Variable Rate Technology: Collects data on yield and soil throughout the season, enabling variable-rate application of seeds, water, and chemicals for optimized productivity.
This approach not only enhances efficiency and improves yields but is instrumental in reducing environmental impact. By only applying the needed amount of water, fertilizer, or pesticide on precise locations, inputs are minimized and runoff is significantly reduced, supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
2. IoT in Agriculture and Automation
The revolutionary Internet of Things (IoT) has redefined how data is collected and transmitted on farms. Across modern farming operations, IoT in agriculture connects devices and systems—ranging from soil moisture sensors and weather stations to automated machinery—to provide a continuous stream of actionable insights.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use of sensors for soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health. These devices help farmers make timely decisions to mitigate threats or optimize resources.
- Automated Systems: Equipment like autonomous vehicles (tractors, harvesters) and automated irrigation systems execute tasks such as planting, harvesting, fertilization, and pest control with minimal human intervention.
- Remote Operations: IoT-powered controls allow for remote monitoring and management, reducing labor and fuel costs and enabling farms to run more efficiently and flexibly.
The impact of IoT in agriculture management is profound: it not only reduces costs and waste but also improves reliability of farming practices—enabling immediate response to variable field conditions.
For advanced monitoring using satellite and weather-based data for irrigation, resource, and operations management, see our Large Scale Farm Management Solution.
3. Artificial Intelligence & Data Analytics in Farming
Harnessing the analytical power of AI in farming and advanced machine learning algorithms, today’s agricultural technology platforms can process vast amounts of field and crop data. These intelligent systems provide insights into soil conditions, pest/disease risks, and even forecast future yields.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models analyze weather, soil, historical, and sensor data to anticipate challenges including pest outbreaks, disease, or yield declines. This allows for informed, proactive interventions.
- Resource Optimization: Algorithms suggest the optimal planting strategies, irrigation schedules, and input levels to maximize production while conserving resources.
- Automated Disease & Pest Detection: Image-based AI tools scan imagery from drones or satellites and detect early signs of crops under stress or pest attack more accurately than the naked eye.
By embracing AI in farming, farmers and agribusinesses can make data-driven decisions faster—boosting crop health, efficiency, and profitability through timely, precise interventions.
Explore Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Traceability Solution for integrating AI and data analysis across the agricultural supply chain for improved transparency and trust.
4. Crop Monitoring with Drones & Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
Aerial crop monitoring with drones and UAVs has become vital for field scouting, data collection, and targeted interventions. Drones equipped with multispectral and thermal cameras generate high-resolution images and data, allowing for unprecedented monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, and resource needs.
- Efficient Field Scouting: Drones quickly survey vast areas, providing detailed visualization to guide ground crews for necessary action.
- Variable Rate Applications: Used for precise delivery of fertilizers, pesticides, or biologicals, drones minimize input waste and environmental harm.
- Early Detection: High-resolution aerial data detects vigor differences, pest infestation, or water stress often invisible to the human eye.
This modern technology helps reduce manual labor, optimize input applications, and enhance the sustainability and efficiency of farming operations.
To understand satellite-driven crop monitoring, check out Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory Features within our application.
5. Integrated Pest Management in Agriculture (IPM)
Integrated pest management in agriculture (IPM) is a holistic, eco-friendly approach using a mix of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools to manage pests, minimize pesticide use, and protect the environment.
- Biological Control: Introduction of natural pest enemies (predators, parasitoids) aids long-term suppression without chemicals.
- Aerial Release by Drones: Recent innovations enable drones to deploy beneficial insects over crops—a scalable, eco-conscious alternative to spraying chemicals.
- Precision Application: Data-driven IPM pinpoints exactly where intervention is needed, lowering pesticide exposure and safeguarding soil and water health.
IPM strategies, when enhanced by technology, are key to sustainable crop protection and yield preservation.
Farmonaut’s Fleet Management Solution can assist agribusinesses and service providers in tracking farm fleets and organizing aerial or ground-based IPM campaigns efficiently.
6. Nanotechnology & Nanosensors
Nanotechnology in agriculture presents powerful solutions for micro-level monitoring and resource management. Nanosensors—tiny devices often less than 100 nanometers across—can detect changes in soil nutrient levels, pH, or contaminant presence with high precision.
- Immediate Diagnostics: Embedded nanosensors deliver real-time information on soil health, alerting farmers of deficiencies for targeted fertilization.
- Sustainability: By guiding the precise application of fertilizers and reducing runoff, nanotechnology promotes environmental conservation.
- Advanced Materials: Innovative nanomaterials like graphene can detect nitrate and phosphate concentrations—key drivers of plant growth and environmental impact.
These breakthroughs are propelling agricultural technology and practices toward a more data-rich, sustainable future.
Want to know more about how modern satellite and AI-based analytics support precision and sustainability in farming? Explore our Carbon Footprinting capability for measuring and managing environmental impact at scale.
7. Vertical Farming Technology & Controlled Environment Agriculture
Vertical farming technology and controlled environment agriculture (CEA) empower crop production even in dense urban environments or regions with limited arable land.
- Hydroponics & Aeroponics: These soil-less techniques use nutrient-enriched water or mist, significantly reducing water use and giving plants the precise resources they need.
- Stacked Growth: Crops are cultivated in vertically stacked layers, maximizing yield per square foot and freeing up land for other uses.
- Climate Control: Fully managed light, temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels create conditions for year-round, consistent production—insulating farming against weather extremes.
This approach drastically reduces the carbon footprint of food transportation, prevents soil degradation, and bolsters efficiency in food production.
Comparative Feature-Impact Table: 7 Smart Agriculture Innovations
| Innovation Name | Core Technology | Key Benefits | Estimated Increase in Efficiency (%) | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | GPS, Remote Sensing, Data Analytics | Optimized resource use, precise input application, data-driven decisions | 20–25% | 15–20% | Reduced runoff & emissions, water and fertilizer savings |
| IoT in Agriculture & Automation | IoT Sensors, Automated Machinery | Real-time monitoring, remote control, labor savings | 25–35% | 10–15% | 30% water savings, better energy use, less waste |
| AI & Data Analytics | AI, Machine Learning, Big Data | Predictive modeling, automated decision support, pest/disease alerts | 20–30% | 12–18% | Reduced input use, higher precision, fewer losses |
| Crop Monitoring with Drones/UAVs | Drones, Aerial Imaging, Remote Sensing | Rapid field scouting, targeted input application, early stress detection | 15–25% | 10–15% | Lower pesticide/fertilizer drift, reduced labor and fuel use |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Biological Control, Drones, Data Analytics | Reduced pesticide use, targeted pest management, ecosystem health | 16–22% | 10–14% | Significant decrease in chemical exposure and biodiversity preservation |
| Nanotechnology & Nanosensors | Nanosensors, Advanced Materials | Real-time soil/crop diagnostics, micro-level data for inputs | 12–19% | 6–12% | Reduces fertilizer overuse and environmental runoff |
| Vertical Farming Technology | Hydroponics, Aeroponics, Climate Control Systems | Year-round production, reduced land/water needs, urban food supply | 35–40% | >30% | Minimized environmental footprint, lower emissions, high resource productivity |
Developer? Explore detailed documentation here: API Developer Docs
Sustainable Agricultural Practices & Resource Management
As global pressure mounts for reduced environmental impact and maximized resource efficiency, sustainable agricultural practices are paramount. AgTech innovations are at the heart of this movement, facilitating responsible soil and water management, reduced waste, and improved management of both traditional and modern farming operations.
- Smart Irrigation: Soil moisture sensors and weather-driven controls optimize water usage, preventing overwatering and reducing waste—especially valuable in water-scarce regions.
- Targeted Inputs: Data from spatial or in-field sensors guides precise application of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides—lowering input consumption and ensuring only the needed amount is applied in each field zone.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Satellite and AI-based systems allow for real-time monitoring of emissions, helping farmers and agribusinesses set and meet sustainability targets.
- Soil & Crop Health Monitoring: Continuous remote monitoring (from satellites, sensors, or drones) provides actionable insights, supporting strategies for soil conservation, crop rotation, and cover cropping.
Sustainable approaches not only benefit the planet—they are increasingly a requirement for market access, regulatory compliance, and financial incentives.
Are you looking to track your farm’s carbon emissions and meet sustainability goals? Discover Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting Product to take your sustainability management to the next level.
Challenges in AgTech & The Future of Smart Farming Solutions
While the benefits of agricultural technology management and smart farming solutions are undeniable, widespread adoption does face obstacles:
- Initial Costs: Many advanced technologies require upfront investment, which may be a barrier for smallholder or resource-limited farmers.
- Technological Complexity: Operating, calibrating, and integrating hardware/software systems requires new skills and training.
- Connectivity: Reliable internet and power infrastructure is needed for real-time data collection, transmission, and automation—often lacking in rural or remote regions.
- Data Integration: Combining information from diverse sources and turning it into actionable insights remains a challenge.
The future of AgTech will be focused on scalability, accessibility, user-friendly design, and affordability. Research and innovative leaps in sensor miniaturization, edge AI, open API ecosystems, and mobile apps tailored for variable connectivity will further close the gap.
We envision a time where data-driven management and automation will be commonplace—from the largest commercial plantation to the smallest family farm—everywhere in the world.
To improve your access to affordable, accessible, and accurate precision agriculture tools, explore the range of flexible subscription options from Farmonaut below.
Farmonaut’s Role in Advancing Agricultural Technology Management
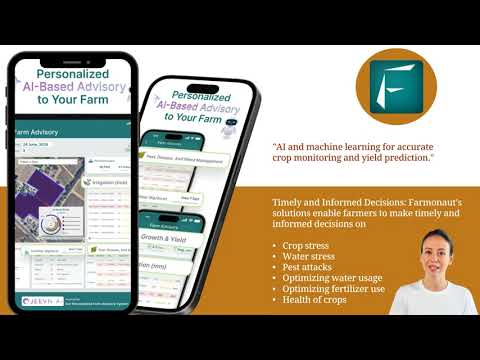
At Farmonaut, we are dedicated to transforming how farmers worldwide conduct management and monitoring of their operations. Our advanced, satellite-based farm management solutions and smart farming technologies are designed to make precision agriculture both affordable and accessible. Here is what sets our platform apart:
- Satellite-Based Crop Monitoring: We utilize high-resolution, multispectral satellite images to provide actionable insights into crop health, soil moisture, and resource usage. This enables informed, timely decisions for irrigation, fertilizer, and integrated pest management, enhancing yields and reducing waste.
- AI-Driven Advisory: Our Jeevn AI system delivers personalized recommendations and data-driven farm management strategies tailored to field and crop needs.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: To guarantee transparency and trust, our traceability solution ensures every product journey step is recorded and immutable from farm to consumer.
- Fleet and Resource Management: We offer tools for fleet optimization, logistics planning, and reduced operational costs for large agribusinesses.
- Carbon Footprinting: With real-time carbon emission data, our platform empowers agribusinesses to monitor, manage, and lower their environmental impact. This supports compliance and aligns with sustainable agricultural practices.
Our business model is subscription-based and scalable, serving individual farmers, cooperatives, large agribusinesses, and government agencies through flexible pricing and platform access (Android, iOS, browser, and API). Developers and businesses can also leverage real-time satellite and weather data via our API and API documentation.
We believe in empowering every stakeholder in the agricultural ecosystem—from the smallest farmers seeking affordable smart farming solutions, to commercial operations, corporate supply chains, and environmental stewards. Our mission is clear: making advanced agricultural technology inclusive, effective, and truly transformative.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Agriculture Technology Management
Q1: What is agriculture technology management (AgTech)?
Agriculture technology management is the integration of advanced technologies (like IoT, AI, drones, and satellite analytics) into farming practices and management systems to increase productivity, efficiency, and sustainability.
Q2: How does precision agriculture benefit farmers?
Precision agriculture uses data-driven insights and sensing technologies to apply the right inputs at the right time and place. This improves resource use efficiency, crop yields, and profitability—all while lowering environmental impact.
Q3: What is the role of AI in farming?
AI in farming or AI in agriculture processes vast agricultural datasets to identify crop health issues, forecast pest or disease outbreaks, and optimize planting or irrigation. It automates and enhances farm management decisions with high accuracy.
Q4: Can smallholder farmers access AgTech solutions?
Yes, especially as platforms like Farmonaut offer affordable, accessible solutions on mobile devices, with modular features suitable for any farm size.
Q5: How do drones support crop management?
Drones perform crop monitoring, soil analysis, and precise input delivery. They help detect issues early, identify variability, and allow targeted treatment—saving time, money, and resources.
Q6: What are the main sustainability benefits of AgTech?
Reduced chemical and water usage, lower emissions, improved soil health, and increased resource efficiency—all contributing to sustainable farming practices and long-term farm viability.
Q7: Where can I find the Farmonaut apps and services?
You can access the web application, Android and iOS apps using the links below. For satellite data API access, visit this page.
Conclusion: Embracing Smart Agriculture for a Sustainable Tomorrow
Agriculture technology management is not just a trend, but a revolution driving productivity, efficiency, and true sustainability in food and resource production systems globally. By integrating precision agriculture, AI in farming, IoT in agriculture, advanced crop monitoring with drones, and other smart innovations, we can address pressing challenges—ensuring security, resilience, and prosperity for communities everywhere.
With the right smart farming solutions and data-driven farm management tools, each stakeholder—farmer, agribusiness, or policymaker—has the opportunity to optimize yields, protect the environment, and build a brighter, more sustainable future for agriculture and the planet.
Ready to transform your field management? Explore Farmonaut’s solutions today and join the next generation of agricultural leaders.