Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Peach Shortage Challenge
- Causes of the Peach Shortage
- Impacts of Peach Shortage
- 7 Key Solutions for Climate Impact on Peach Production
- 1. Developing Climate-Resilient Peach Varieties
- 2. Improved Orchard Management Practices
- 3. Enhanced Pest and Disease Management
- 4. Addressing Labor Shortages in Agriculture
- 5. Diversification and Alternative Crops
- 6. Sustainable Farm Resource and Carbon Management
- 7. Advanced Data-Driven Tools for Peach Crop Management
- Key Causes & Sustainable Solutions Table
- FAQ: Peach Shortage, Solutions, and Future Outlook
- Conclusion: Path to Peach Resilience
Peach Shortage: 7 Key Solutions for Climate Impact
Peaches have long held a cherished position in agricultural regions, particularly in the United States and states like Georgia, due to their sweet flavor, nutritional benefits, and contribution to local economies. However, a noticeable peach shortage has emerged in recent years, causing widespread concern among farmers, consumers, and the agriculture industry.
This shortage is driven by multiple factors: the effects of climate change on peaches, increased pest and disease prevalence, and persistent labor shortages in agriculture—all of which threaten the reliability of peach production.
In this in-depth article, we explore the causes and impacts of reduced peach crop yields and rising peach prices, and offer expertly backed solutions for peach crop loss. Our focus is on sustainable farming practices, climate adaptation, and the agricultural technologies (including those developed by us at Farmonaut) revolutionizing peach crop management and resilience.
Keywords: peach, shortage, peaches, labor, pest, shortages, production, farming, climate, practices, management, impacts, solutions, change, Georgia, diseases, fruit, reduce, agricultural, farmers, consumers, winters, trees, increased, loss, crop, pests, crops, economic, availability, prices, varieties, regions, years, causes, potential, weather, patterns, affecting, cultivation, warmer, insufficient, chill, hours, state, winter, warm, frosts, freeze, yields, workforce, financial, higher, fresh, supply, products, alternative, help, mitigate, orchard, implementing, enhance, approach, disease, adopting, strategies, addressing, nutritional, benefits, staple, particularly, United States, recent, concerns, among, industry, agriculture, forestry, unpredictable, erratic, dormancy, bloom, temperatures, projections, chilling, requirements, disrupting, spells, blooming, vulnerable, blooms, prevalence, compromising, insect.
Causes of the Peach Shortage
1. Climate Change and Unpredictable Weather Patterns
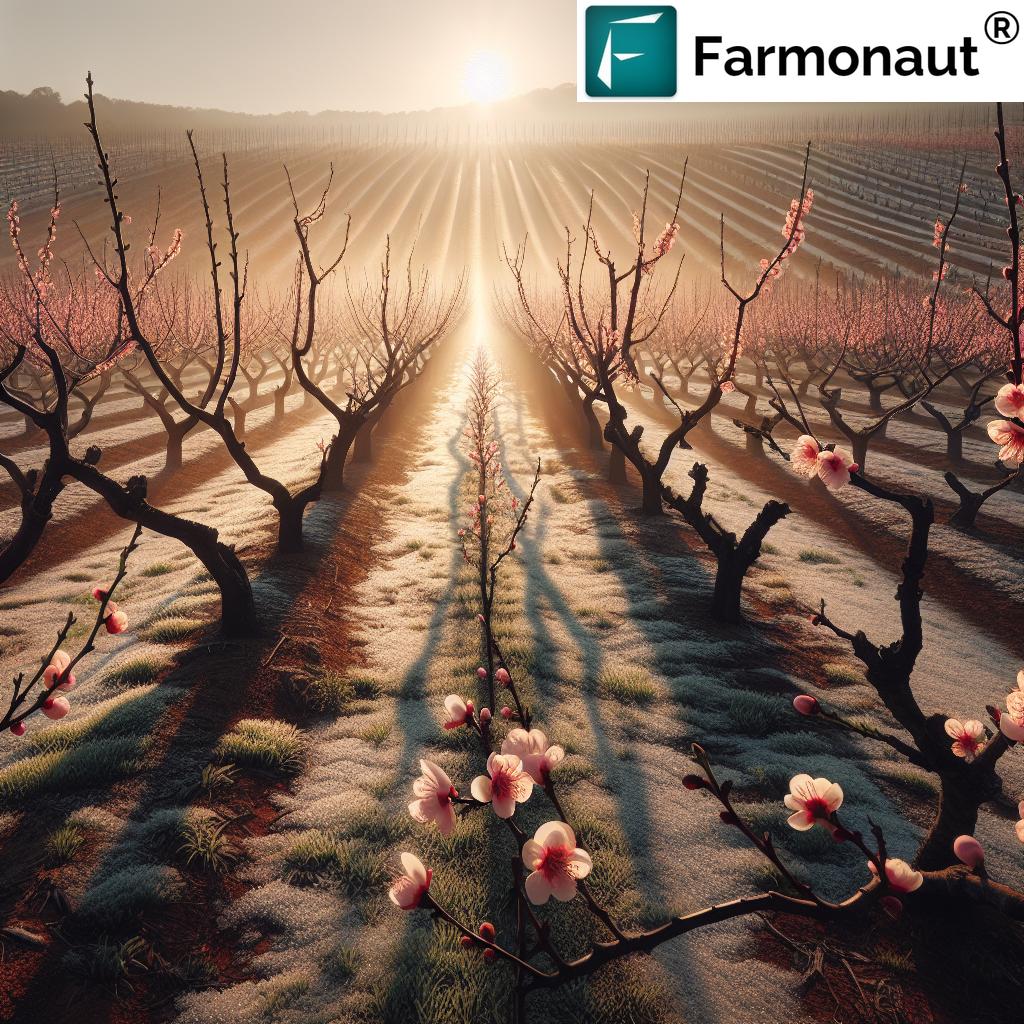
Climate change is the primary driver of the recent peach shortage. Erratic weather patterns have become more common, with warmer winters resulting in insufficient chill hours—the low-temperature periods crucial for peach trees to break dormancy and properly bloom in spring. In Georgia, for example, the state’s average fall and winter temperatures have increased by about 1°F over the last 125 years (epa.gov).
The effects of climate change on peaches are evident: by 2050, around 40% of winters in Georgia may be too warm to meet chilling requirements, directly threatening peach production in this iconic region.
- Unpredictable warm spells in late winter can trigger premature blooming.
- Subsequent frosts or sudden freezes can destroy vulnerable blooms, severely reducing crop yields. In 2023, a late-season freeze following early peach blooms in Georgia resulted in the loss of 90% of the region’s peach crop.
2. Pests and Diseases Impact on Peaches
Alongside climate disruptions, escalating problems with pests and diseases have been affecting peach yields and quality. The prevalence of insect infestations, such as the oriental fruit moth, and fungal diseases like brown rot, is increasing.
Changing weather patterns—including warmer, wetter conditions—create optimal environments for pests and pathogens to thrive, quickly spreading across peach orchards and causing extensive damage.
- Insect pests can compromise fruit quality and quantity during critical growth stages.
- Fungal diseases spread rapidly under humid conditions, leading to significant yield loss.
- Traditional chemical strategies are becoming less effective due to resistance and environmental concerns.
3. Labor Shortages in Peach Production
Effective peach crop management is labor-intensive. Tasks such as pruning, thinning, and timely harvesting all require a skilled workforce. Unfortunately, labor shortages have compounded the shortage problem.
These labor shortages in agriculture are driven by:
- Complex immigration policies restricting the availability of seasonal workers
- Increased operational costs deterring sufficient hiring
- Competition for agricultural labor across other, higher-paying industries
Labor scarcity results in reduced peach production efficiency, decreased quality and quantity of fruit, and occasionally, the loss of entire crops if harvesting is incomplete.
Impacts of the Peach Shortage
1. Economic Consequences & Peach Prices Increase
The 2023 freeze event in Georgia—following premature blooming and the resulting crop loss—has had dramatic economic impacts on growers and businesses alike.
- Peach farmers faced financial losses from up to 90% crop loss (cnn.com).
- Wholesale peach prices soared from $17–$20 per box to $40–$60 per box due to the shortage and increased demand.
- Small businesses, restaurants, and food processors were forced to pay higher prices or seek alternative fruit products.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions & Product Availability
The shortage affected more than just fresh peach supply. Shortfalls in crop yields have impacted the availability of processed goods like canned peaches, jams, and juices. Supply chain disruptions have far-reaching consequences, including stock shortages and increased costs for consumers.
- Estimates suggest a 20–30% decline in processed peach product availability in affected regions.
- Retailers and distributors experienced difficulties fulfilling orders, further disrupting the market.
3. Cultural, Social, and Consumer Impacts
Peaches are more than a crop; they symbolize community and tradition, especially in Georgia—The Peach State. Traditional festivals, family recipes, and local economies all depend on robust peach production. Prolonged shortages threaten not only income but also regional pride and culinary heritage.
- Annual peach festivals saw lower turnout and limited activities due to lack of fresh peaches.
- Consumers shifted to alternative fruits, with lasting effects on purchasing habits and regional food diversity.
Peach Shortage: 7 Key Solutions for Climate Impact
Amid these ongoing challenges, the agricultural sector is actively exploring solutions for peach crop loss—focusing on sustainability, adaptation, and innovation. Below, you’ll find detailed explanations of practices and tools that can help reduce crop loss, address labor shortages in agriculture, manage pests and diseases, and build climate resilience into every level of peach production.
1. Developing Climate-Resilient Peach Varieties
Climate-resilient peach varieties are a cornerstone of agricultural adaptations to climate change. Plant scientists and horticulturists are focusing on breeding cultivars that require fewer chill hours to break dormancy, can withstand erratic winter temperatures, and are less susceptible to spring frosts.
- Such varieties may bloom later, avoiding premature exposure to cold snaps.
- Lower chilling requirements help ensure reliable yields even as warm winters become more common.
- Collaboration between researchers and growers is key to adopting these improved genetics at scale.
For instance, breeders in the United States are developing cultivars for Georgia and other regions prone to warm winters and sudden cold spells, specifically addressing uncertainty in future climate projections.
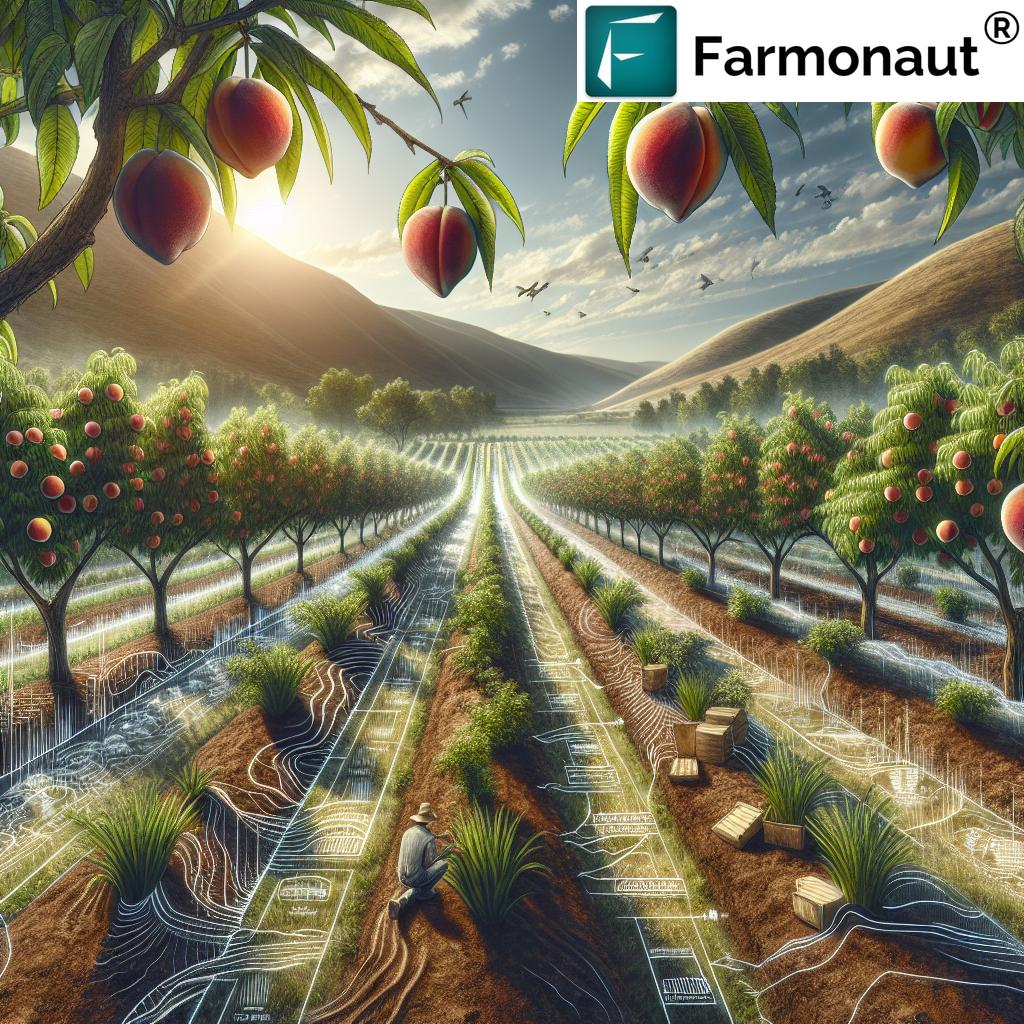
2. Improved Orchard Management Practices
Modern orchard management practices can significantly reduce loss from climate impact. High-density planting—placing more trees per acre—allows for earlier and more stable yields, while carefully scheduled pruning and thinning improves airflow and reduces disease pressure. Technologies such as precision irrigation and shade netting help mitigate extreme weather effects.
- High-density orchards maximize land use and buffer against weather-related setbacks.
- Sensors and data-driven insights optimize water, fertilizer, and nutrient usage.
- Tech-enabled monitoring allows early detection of disease and drought stress.
Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring supports these solutions by delivering real-time data on vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and crop stress. These insights empower farmers to implement targeted strategies for resource-efficient, resilient peach production.
Explore Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management platform to make advanced orchard management accessible for all farm sizes—track health, manage inputs, and optimize yields in one unified dashboard.
3. Enhanced Pest and Disease Management
With the increasing prevalence of pests and diseases due to climate change, integrated pest management (IPM) strategies are essential. Adopting a holistic approach to pest control and disease prevention minimizes environmental footprint while ensuring robust yields.
- Regular monitoring of pest populations using traps, field scouting, and AI-driven tools for early-warning systems
- Biological controls—e.g., beneficial insects or microbial agents—to reduce reliance on chemicals
- Targeted use of eco-friendly pesticides when thresholds are reached
Integrated approaches can help reduce the impact of pests and diseases on peaches, protecting both fruit quality and farm profitability while maintaining ecological balance.
Our Jeevn AI Advisory System delivers real-time, satellite-driven pest and disease advisory to farmers—empowering rapid decision-making for more resilient orchards and healthier crops.
4. Addressing Labor Shortages in Agriculture
Long-term solutions to labor shortages in agriculture are multifaceted:
- Policy reform could create legal pathways for hiring seasonal agricultural workers.
- Incentives, fair wages, and modernized working conditions can help attract and retain labor.
- Mechanization and automation—from optical harvesters to robotic pruners—reduce total dependency on manual labor in labor-scarce regions.
Labor-saving technology can make peach production more sustainable and cost-effective. However, balancing innovation with job protection will be crucial to community stability and legacy skills retention.
Our Fleet Management tools support efficient deployment and scheduling of machinery, helping producers stretch limited workforce resources much further during key harvest and management periods.
5. Diversification and Alternative Crops
One robust strategy to mitigate economic risk is the diversification of crops and farming systems. By integrating alternative fruits or agroforestry (blending orchards with timber or other agricultural crops), farmers can:
- Reduce reliance on a single, vulnerable crop
- Maintain stable income even if peach yields are compromised
- Enhance biodiversity—helping control pest cycles and improve orchard health
This approach has shown that diversified agro-ecosystems withstand environmental shocks much better than monocultures. It is particularly useful in regions facing repeated weather or pest-induced disruptions.
Discover how Plantation & Forest Advisory Services support crop diversification—guiding landowners in blending trees and crops for optimal environmental and financial return.
6. Sustainable Farm Resource and Carbon Management
Greater sustainability in resource use and carbon tracking is central to building future crop resilience. Resource management includes optimizing irrigation, fertilizers, and land use, while carbon footprinting helps reduce environmental impacts and aligns farms with emerging policy expectations and consumer demands.
Best practices include:
- Utilizing soil and weather data for water-smart irrigation scheduling
- Applying inputs only when and where needed, decreasing waste and runoff
- Adopting renewable energy or low-emission machinery to minimize farm carbon emissions
Our Carbon Footprinting solution allows you to track, measure, and manage your agricultural emissions in real time—helping you unlock incentives and stay ahead in sustainability compliance.
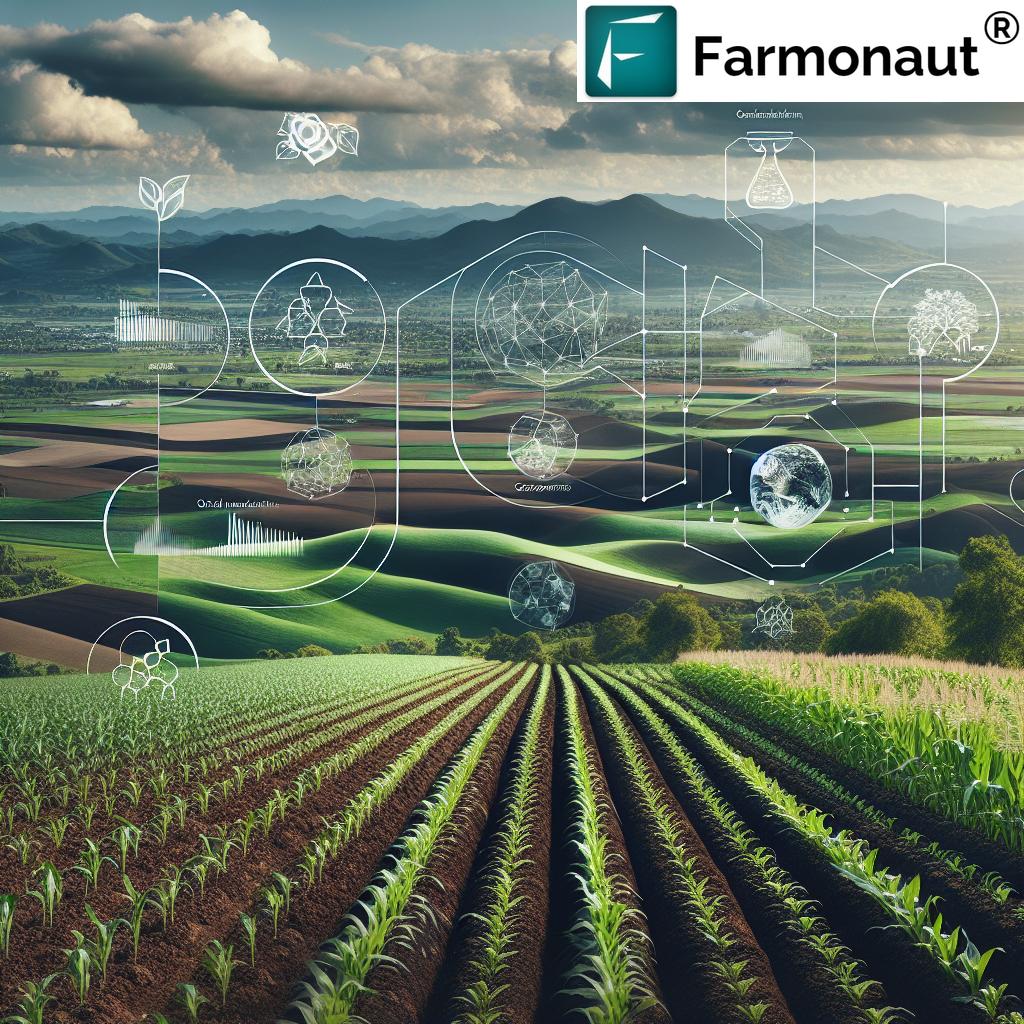
7. Advanced Data-Driven Tools for Peach Crop Management
Precision agriculture—powered by remote sensing, AI, and actionable analytics—is transforming peach crop management. Real-time monitoring, early warning of threats, and predictive yield models enable faster responses to weather, pests, and disease pressure, minimizing loss and maximizing efficiency.
- Satellite imagery tracks vegetation indexes, soil moisture, and spot issues across vast acres.
- AI-based advisory systems provide tailored guidance for timely interventions.
- Blockchain-based traceability ensures transparency, reduces fraud, and strengthens trust between farmers, suppliers, and consumers.
We at Farmonaut are committed to making cutting-edge agricultural technology accessible, affordable, and practical for farmers of all scales. Our platform empowers decision-making—helping producers adapt to climate change, optimize inputs, measure sustainability, and deliver verifiable, high-quality products.
- Start leveraging satellite imagery on Android, iOS, and Web for instantaneous, actionable insights—no advanced hardware required.
- Access API for seamless data integration: Farmonaut API Portal
- Develop advanced agritech solutions with our full developer documentation: API Docs
- Monitor product journeys for traceability: Blockchain Product Traceability
- Secure crop loans and insurance with satellite-based verification: Farmonaut Loan & Insurance Solutions
By harnessing these technologies, the agricultural community can reduce loss, increase efficiency, and secure peach supply chains—not just in Georgia or the United States, but globally.
Key Causes of Peach Shortage and Sustainable Solutions
| Key Cause | Estimated Impact | Sustainable Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change (Warmer Winters, Erratic Weather) | 40% of winters in Georgia projected to be too warm by 2050; Up to 90% crop loss from late freezes observed in 2023; Estimated 20-30% decrease in yields regionally. | Develop climate-resilient peach varieties with lower chill requirements; Adopt high-density planting, precision irrigation, and temperature-monitoring tools. |
| Increased Prevalence of Pests & Diseases | Up to 25% yield loss in seasons with high pest/disease pressure; Higher chemical input costs. | Implement integrated pest management (IPM); Use biological controls and timely AI-driven advisories. |
| Labor Shortages in Agriculture | Delayed or incomplete harvesting and orchard maintenance; Loss of up to 15% of marketable fruit annually. | Adopt labor-saving mechanization; implement fair labor practices; deploy efficient fleet management systems. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | 20–30% reduction in peach product and byproduct availability in affected years; Increased wholesale and retail prices. | Diversify crops and supply chains; utilize blockchain-based traceability and advanced logistics management. |
| Economic Pressures & Price Increases | Peach prices increased 2–3x during shortages; significant financial strain for small farmers. | Leverage crop insurance and financial planning; use precision data to optimize input costs and reduce risk. |
Affordable Farm Management Subscriptions
Ready to empower your operation with affordable, advanced farm management? Start with a flexible Farmonaut subscription below:
FAQ: Peach Shortage, Solutions, and Future Outlook
-
Why are Georgia peaches in short supply in recent years?
Ongoing climate change has led to warmer winters, erratic weather patterns, and late-season freezes, drastically reducing the chill hours required for peach trees to bloom reliably. The 2023 late freeze alone wiped out roughly 90% of the state’s peach crop. Increased pest and disease pressure, along with labor challenges, further compromise yields, leading to recurring shortages.
-
How does climate change specifically affect peach production?
Key impacts include insufficient chilling hours, premature blooming (making trees vulnerable to spring frosts), and prolonged pest and disease cycles. Warmer falls and winters in Georgia, for example, threaten the region’s historic suitability for peaches.
-
Are peach prices going to keep rising?
During severe shortages, wholesale and retail peach prices can double or triple, affecting both consumers and businesses. While specific prices will depend on next season’s yields, effective adoption of solutions outlined here should help stabilize supply and moderate price increases over time.
-
What can farmers do to adapt to the new climate reality?
Invest in climate-resilient peach varieties, embrace advanced orchard management techniques, enhance pest and disease monitoring, diversify crops, and adopt precision agriculture technologies to gain real-time insights into crop health and resource needs.
-
How can consumers support sustainable peach farming?
Choose peaches and peach products from producers that implement sustainable practices; support local growers; and seek out agricultural brands that invest in traceability and responsible sourcing.
-
How does Farmonaut help address the peach shortage?
We provide satellite-based monitoring, AI-driven advisories, and resource management tools that inform timely interventions, optimize inputs, and track environmental impacts. Our services improve productivity, reduce resource wastage, and help peach farmers adapt to climate impacts—affordably and at scale.
-
Is it possible to make the peach industry resilient against future shortages?
While no solution eliminates all risks, a combination of improved genetics, smarter farm management, technology adoption, and market diversification can markedly enhance resilience—securing the future of peaches in Georgia and beyond.
Conclusion: Path to Peach Resilience
The peach shortage is a multifaceted agricultural challenge. Climate change introduces unpredictable threats; pests, diseases, and labor shortages further disrupt established practices. The impacts span economic, cultural, and supply chain dimensions—with consumers and entire communities feeling the effects.
Yet, solutions are emerging, encompassing the development of climate-resilient peach varieties, adoption of advanced orchard management, integrated pest and disease management, enhanced workforce approaches, and smart diversification.
As we move forward, leveraging affordable agricultural technologies—including those offered by us at Farmonaut—will be pivotal. Real-time crop monitoring, AI insights, resource optimization, and transparent product traceability together offer a path to securing peach supply for generations to come, both in Georgia and across global peach-producing regions.
By embracing sustainable farming practices, data-driven solutions, and community support, we can reduce risk, maintain availability, and preserve the iconic, sweet taste of fresh peaches—even amidst the challenges of climate change.