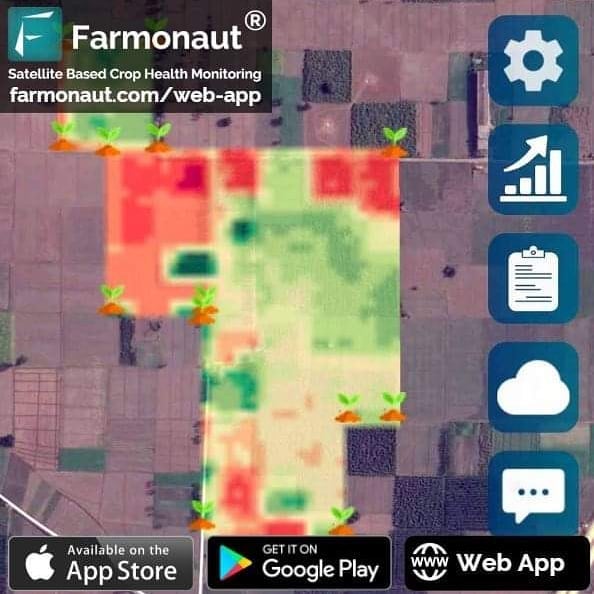
NDMI Index Explained: Understanding NDMI Values, Interpretation, and Meaning for Precision Agriculture
In the ever-evolving world of precision agriculture, understanding various vegetation indices is crucial for effective crop management. Among these indices, the Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) stands out as a powerful tool for assessing vegetation water content and overall plant health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the NDMI index, exploring its meaning, interpretation, and the significance of NDMI values in modern farming practices.
What is the NDMI Index?
The Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) is a remote sensing-derived index that provides valuable insights into the moisture content of vegetation. As a team of experts at Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of this index in precision agriculture and its role in optimizing farm management decisions.
The NDMI index is calculated using near-infrared (NIR) and short-wave infrared (SWIR) bands from satellite imagery. The formula for NDMI is:
NDMI = (NIR – SWIR) / (NIR + SWIR)
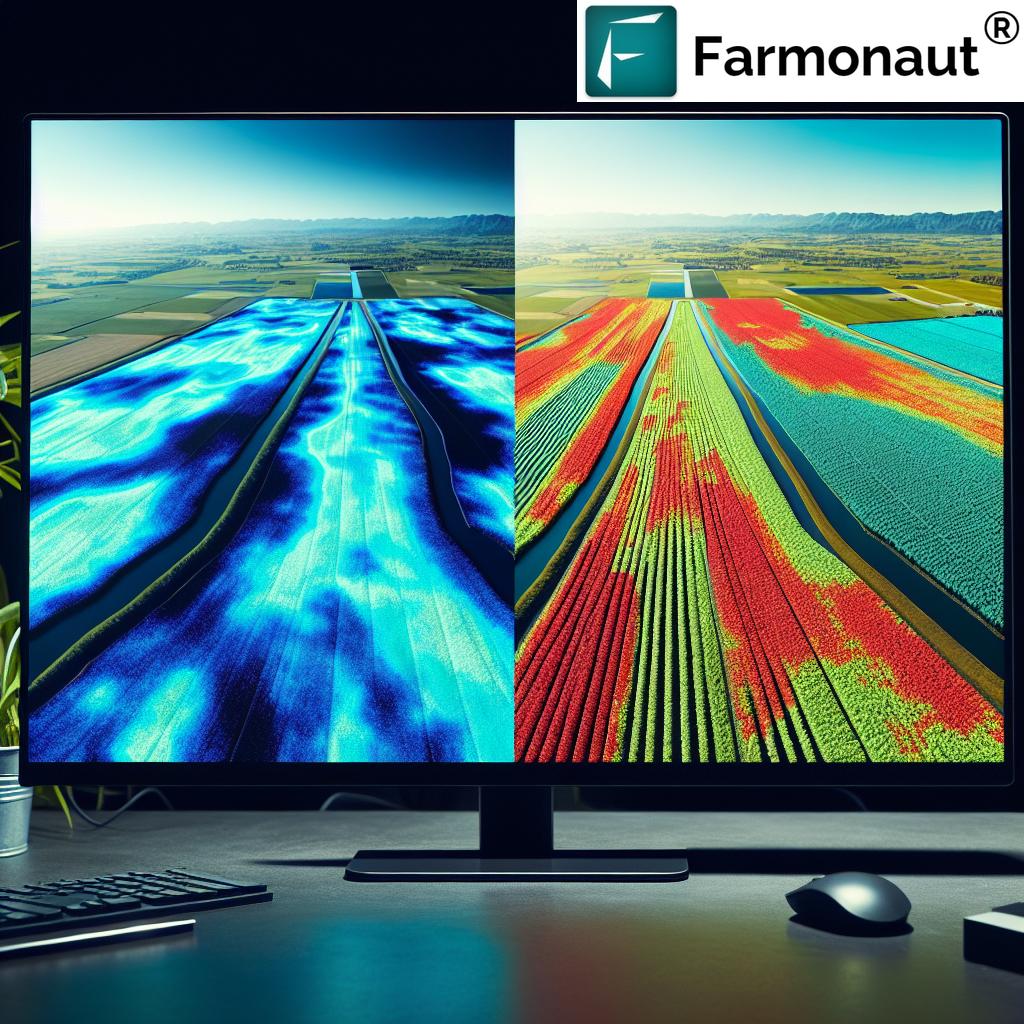
This calculation results in values ranging from -1 to 1, where higher values indicate higher vegetation water content.
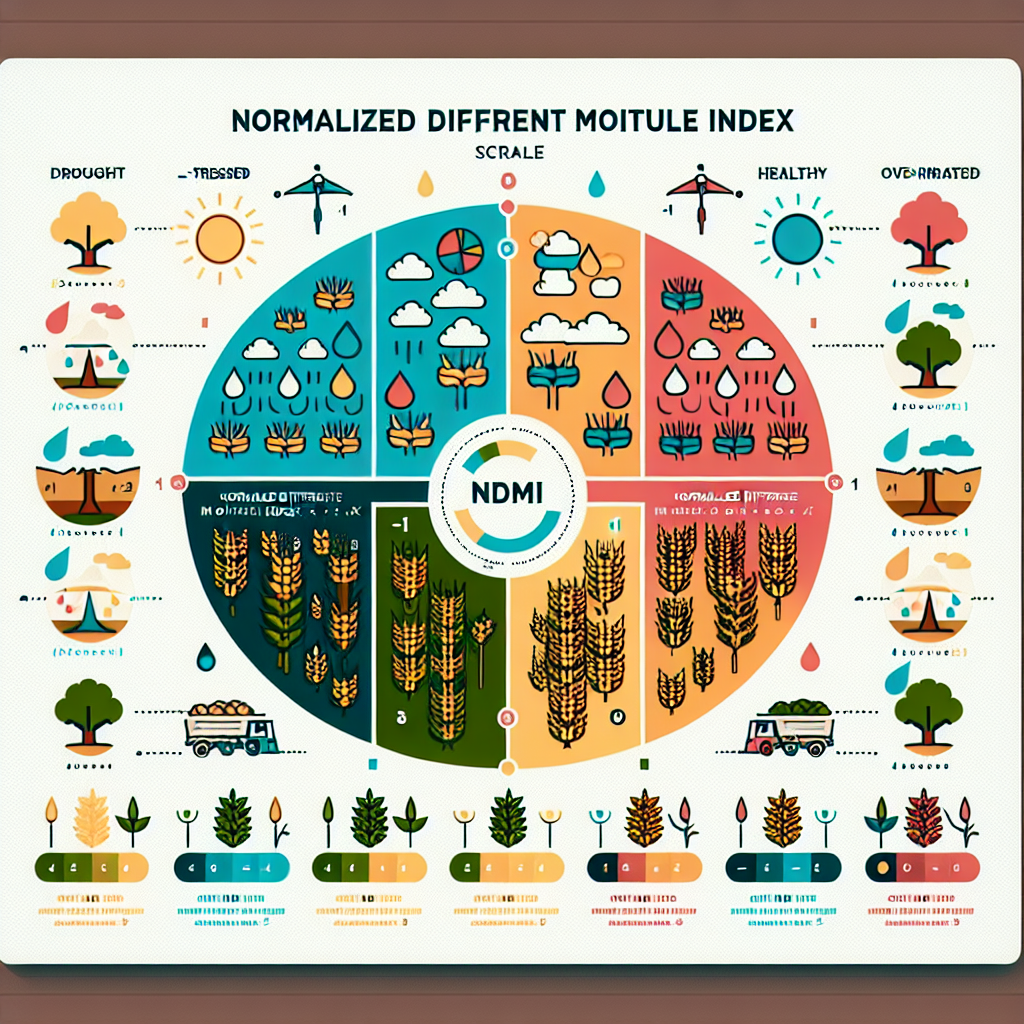
Understanding NDMI Values
Interpreting NDMI values is essential for extracting meaningful information about crop health and water stress. Here’s a general guide to understanding these values:
- -1 to 0: Indicates very low or no vegetation water content, often associated with bare soil, urban areas, or extremely stressed vegetation.
- 0 to 0.2: Suggests low vegetation water content, potentially indicating water stress in crops.
- 0.2 to 0.4: Represents moderate vegetation water content, typical of healthy vegetation under normal conditions.
- 0.4 to 0.6: Indicates high vegetation water content, often seen in lush, well-irrigated crops or in areas with recent rainfall.
- 0.6 to 1: Very high vegetation water content, which may be observed in dense, healthy vegetation or areas with excessive moisture.
It’s important to note that these ranges can vary depending on the specific crop type, growth stage, and local environmental conditions.
NDMI Interpretation in Agricultural Context
The NDMI interpretation in agriculture provides valuable insights into crop health and water management. Here’s how we at Farmonaut utilize NDMI data to support farmers:
- Drought Detection: By monitoring NDMI values over time, we can identify areas experiencing water stress before visible symptoms appear, allowing for timely irrigation interventions.
- Irrigation Management: NDMI helps optimize irrigation schedules by indicating when and where crops require water, leading to more efficient water use.
- Crop Health Assessment: Changes in NDMI values can signal various plant health issues, including disease onset or nutrient deficiencies that affect water uptake.
- Yield Prediction: By analyzing NDMI trends throughout the growing season, we can contribute to more accurate yield predictions.
- Precision Agriculture: NDMI maps enable variable-rate irrigation and fertilization strategies, optimizing resource use across fields.
The Significance of NDMI in Modern Farming
Understanding the NDMI meaning in the context of modern agriculture is crucial for several reasons:
- Early Stress Detection: NDMI can reveal water stress in crops before it becomes visually apparent, allowing for proactive management.
- Resource Optimization: By providing insights into crop water content, NDMI helps farmers optimize irrigation and reduce water waste.
- Environmental Sustainability: Efficient water use based on NDMI data contributes to more sustainable farming practices.
- Economic Benefits: Timely interventions guided by NDMI can lead to improved crop yields and reduced input costs.
How Farmonaut Leverages NDMI for Precision Agriculture
At Farmonaut, we integrate NDMI analysis into our comprehensive satellite-based farm management solutions. Our platform provides farmers with:
- Regular NDMI updates for monitored fields
- User-friendly NDMI maps and visualizations
- AI-driven insights combining NDMI with other vegetation indices
- Customized alerts for significant NDMI changes
- Historical NDMI data for trend analysis
By leveraging these tools, farmers can make data-driven decisions to optimize their crop management strategies. To experience the power of NDMI and other advanced farming tools, try Farmonaut today.
NDMI vs. Other Vegetation Indices
While NDMI is a powerful tool for assessing vegetation water content, it’s often used in conjunction with other vegetation indices for a more comprehensive understanding of crop health. Here’s how NDMI compares to some other commonly used indices:
| Index | Focus | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDMI | Vegetation water content | Sensitive to canopy water content, useful for drought detection | Can be affected by soil background in sparse vegetation |
| NDVI | Vegetation greenness and density | Widely used, good for overall vegetation health | Can saturate in dense vegetation |
| EVI | Improved vegetation monitoring | Less sensitive to atmospheric conditions and soil background | More complex to calculate |
| NDWI | Open water features and water content in leaves | Useful for mapping water bodies and assessing leaf water content | Can be confused with built-up land in some cases |
At Farmonaut, we utilize a combination of these indices to provide a holistic view of crop health and field conditions.
Practical Applications of NDMI in Various Agricultural Sectors
The versatility of NDMI makes it valuable across different agricultural sectors. Here are some specific applications:
1. Row Crop Farming
- Monitoring water stress in corn, soybeans, and wheat
- Optimizing irrigation schedules for maximum yield
- Early detection of drought impacts on crop development
2. Orchard Management
- Assessing water needs in fruit trees and nut orchards
- Identifying areas of over- or under-irrigation
- Monitoring long-term tree health and stress levels
3. Viticulture
- Managing water stress for optimal grape quality
- Identifying variability in water content across vineyards
- Informing harvest timing based on vine water status
4. Pasture and Rangeland Management
- Assessing forage quality and quantity
- Monitoring grassland response to rainfall or drought
- Informing rotational grazing decisions
Integrating NDMI with Other Farmonaut Technologies
At Farmonaut, we don’t just provide NDMI data in isolation. We integrate it with our suite of advanced technologies to offer comprehensive farm management solutions:
- AI-Powered Advisory: Our Jeevn AI system combines NDMI data with other parameters to provide personalized crop management recommendations.
- Weather Forecasting: We correlate NDMI trends with weather forecasts to predict potential water stress events.
- Blockchain Traceability: NDMI data can be incorporated into our blockchain system, providing verifiable records of crop water status throughout the growing season.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: By optimizing water use through NDMI insights, farmers can reduce their carbon footprint, which is tracked and reported through our platform.
To explore how these integrated solutions can benefit your farming operation, visit our API documentation or download our mobile app for Android or iOS.
The Future of NDMI in Precision Agriculture
As technology continues to advance, we anticipate several exciting developments in the use of NDMI for precision agriculture:
- Higher Resolution Imagery: Improvements in satellite technology will provide even more detailed NDMI maps, allowing for precise management of smaller field areas.
- Integration with IoT Devices: Combining NDMI data with ground-based soil moisture sensors will create a more comprehensive picture of crop water status.
- Machine Learning Advancements: AI algorithms will become more sophisticated in interpreting NDMI data, providing increasingly accurate and timely recommendations.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: NDMI data could directly inform smart irrigation systems, automatically adjusting water application based on real-time crop needs.
- Climate Change Adaptation: NDMI will play a crucial role in developing drought-resistant farming strategies as climate patterns shift.
Case Studies: NDMI in Action
While we don’t include specific case studies, it’s worth noting that NDMI has been successfully used in various agricultural scenarios worldwide. From drought monitoring in the American Midwest to precision irrigation in Mediterranean orchards, NDMI has proven its value in diverse farming environments.
Comparing Farmonaut’s Satellite System with Drone and IoT-based Farm Monitoring
While drones and IoT devices have their place in modern agriculture, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system offers unique advantages for farm monitoring:
| Feature | Farmonaut Satellite System | Drone-based Monitoring | IoT-based Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Area | Large scale (hundreds to thousands of hectares) | Limited by flight time and regulations | Limited by sensor placement |
| Frequency of Data Collection | Regular intervals (e.g., every 3-5 days) | As needed, but requires manual operation | Continuous, but localized |
| Cost Efficiency | High (no on-site equipment needed) | Moderate (equipment and operator costs) | Variable (initial setup costs can be high) |
| Data Processing | Automated, cloud-based | Often requires manual processing | Automated, but may require maintenance |
| Ease of Use | High (accessible via web and mobile apps) | Moderate (requires skilled operators) | Moderate (setup and maintenance needed) |
| Weather Independence | High (can penetrate clouds with certain bands) | Low (affected by wind and rain) | High (but sensors can be damaged in extreme conditions) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable across large areas | Limited by operational constraints | Requires additional sensors for larger areas |
While each system has its merits, Farmonaut’s satellite-based approach offers unparalleled scalability and cost-effectiveness for large-scale precision agriculture applications.
FAQs about NDMI and Precision Agriculture
Q: How often should I monitor NDMI values for my crops?
A: We recommend monitoring NDMI values at least weekly during the growing season. However, during critical growth stages or in periods of potential water stress, more frequent monitoring (every 3-5 days) can be beneficial.
Q: Can NDMI be used for all crop types?
A: NDMI is useful for a wide range of crops, particularly those sensitive to water stress. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on crop structure and growth habits. It’s often most effective for broad-leaf crops and less so for crops with very narrow leaves or sparse canopy cover.
Q: How does NDMI compare to ground-based soil moisture measurements?
A: NDMI provides a broader view of vegetation water content across an entire field, while soil moisture sensors give precise, point-based measurements. Both can be complementary – NDMI can guide where to place soil moisture sensors for more detailed monitoring.
Q: Can NDMI detect over-irrigation?
A: Yes, unusually high NDMI values can indicate over-irrigation. However, interpretation should consider recent rainfall, crop type, and growth stage.
Q: How does Farmonaut integrate NDMI data with other farm management tools?
A: Farmonaut’s platform combines NDMI data with other vegetation indices, weather data, and AI-driven analytics to provide comprehensive farm management insights. This integration allows for more nuanced and accurate recommendations.
Q: Is specialized equipment needed to use NDMI data from Farmonaut?
A: No, Farmonaut’s satellite-based system doesn’t require any on-farm equipment. All data is accessible through our web platform and mobile apps, making it easy for farmers to access NDMI insights from anywhere.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of NDMI for Smarter Farming
The Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) has emerged as a crucial tool in precision agriculture, offering valuable insights into crop water content and overall plant health. By understanding NDMI values, their interpretation, and meaning, farmers can make more informed decisions about irrigation, crop management, and resource allocation.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to making these powerful tools accessible to farmers of all scales. Our integrated platform combines NDMI analysis with other advanced technologies to provide comprehensive, actionable insights for modern agriculture.
Ready to experience the benefits of NDMI and other cutting-edge agricultural technologies? Try Farmonaut today and take your farming to the next level.
For more information on our API and developer resources, visit our API documentation.
Embrace the future of agriculture with Farmonaut – where precision meets productivity.