Enhancing Pacific Flyway Habitat: How Sustainable Farming Practices Support Wildlife Conservation and Drought Mitigation
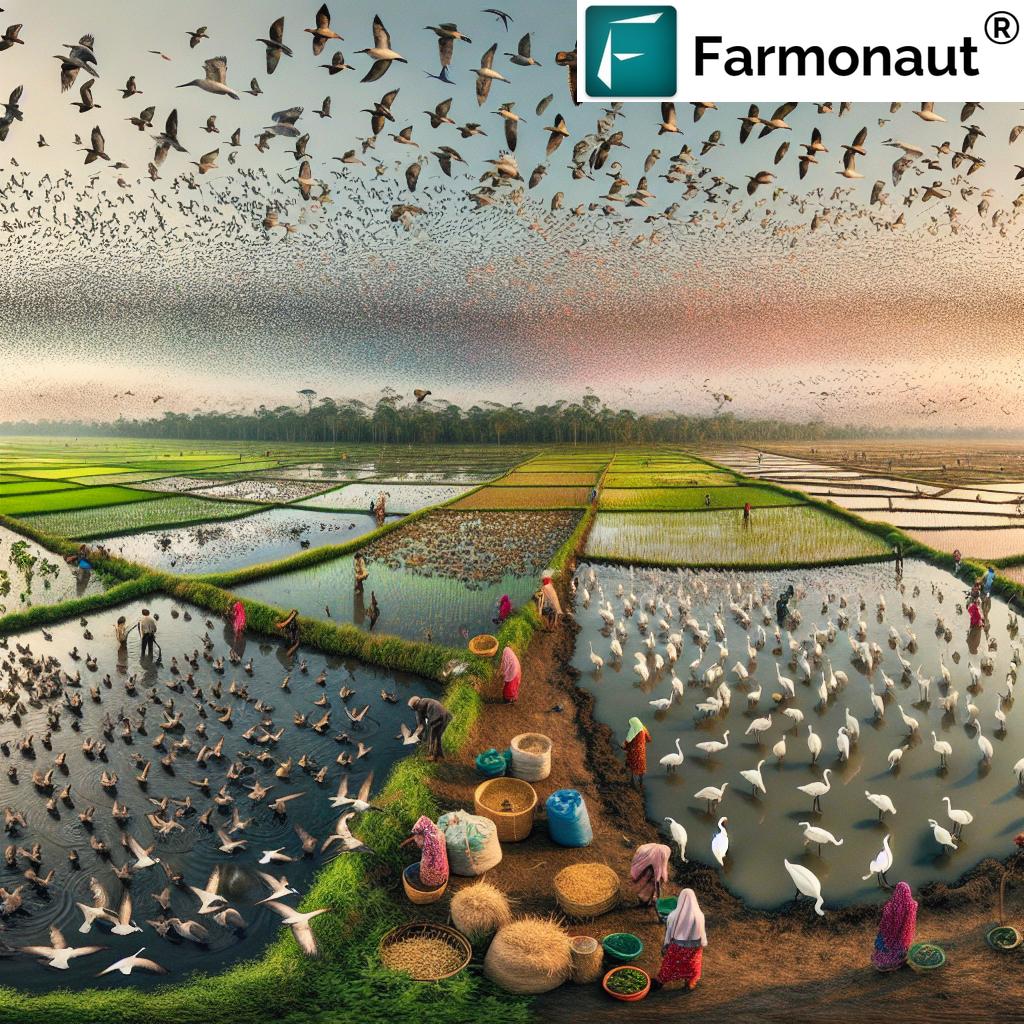

“The Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act incentivizes farmers to flood fields seasonally, supporting over 200 bird species along the flyway.”
In the vast tapestry of North American ecosystems, the Pacific Flyway stands as a crucial corridor for migratory birds, stretching from Alaska to Patagonia. This vital pathway, however, faces numerous challenges due to habitat loss and climate change. Today, we’re excited to explore a groundbreaking initiative that aims to address these issues while supporting sustainable agriculture: the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act.
This bipartisan legislation, reintroduced by U.S. Representatives Mike Thompson and Doug LaMalfa, represents a significant step forward in balancing the needs of wildlife conservation with the demands of modern agriculture. By expanding the Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program (CREP) to include qualified wetlands, this act offers a win-win solution for farmers and the environment alike.
Understanding the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act
The Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act is designed to expand conservation efforts on agricultural lands, supporting wildlife habitats and promoting sustainable farming practices. At its core, this legislation seeks to include qualified wetlands in the Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program, offering incentives for farmers to engage in seasonal field flooding.
Key aspects of the act include:
- Voluntary land retirement program
- Protection of environmentally sensitive land
- Decrease in soil erosion
- Restoration of wildlife habitat
- Safeguarding of ground and surface water resources
By promoting these environmentally sensitive management practices on working croplands, the act addresses crucial issues such as soil erosion prevention, wetland habitat conservation, and drought mitigation in agriculture.
The Role of Farmers in Wildlife Conservation
One of the most innovative aspects of this legislation is its recognition of the vital role that farmers, particularly rice growers, play in creating and maintaining wetland habitats for numerous species along the Pacific Flyway. This approach not only improves soil conditions but also safeguards ground and surface water resources.
Congressman Mike Thompson emphasizes, “Many wildlife species rely on wetland habitat created by California’s farmers, including our rice growers. With the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act, we can expand USDA support for our local growers, offering resources so qualified farmers can flood their fields in the off-season to both improve soil conditions and support the Pacific Flyway ecosystem.”
This innovative approach to agricultural land management strikes a delicate balance between the needs of farmers, wildlife, and ecosystem preservation while keeping agricultural lands productive and environmentally sustainable.
The Impact of Seasonal Field Flooding
Seasonal field flooding is a cornerstone of the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act. This practice offers numerous benefits for both wildlife and agriculture:
- Creates temporary wetland habitats for migratory birds
- Improves soil health by promoting nutrient cycling
- Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers
- Helps control pests naturally
- Contributes to groundwater recharge
By incentivizing farmers to engage in seasonal flooding, the act creates a mosaic of wetland habitats that support a diverse array of wildlife while simultaneously improving agricultural productivity.
Drought Mitigation and Water Resource Management
In the face of recurring droughts and water scarcity, the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act takes a proactive approach to water resource management. As Congressman Doug LaMalfa points out, “Drought is always just around the corner, and we have to make the most of the water we get to benefit farms, people, and wildlife.”
The act promotes smart water use through:
- Efficient irrigation practices
- Water conservation techniques
- Groundwater recharge through seasonal flooding
- Protection of surface water resources
These measures not only help farmers navigate dry periods but also contribute to the long-term sustainability of water resources in the region.
“Rice farmers in the Pacific Flyway region can create up to 500,000 acres of surrogate wetlands through sustainable farming practices.”
Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program: A Closer Look
The Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program (CREP) is a voluntary land conservation program that allows states to partner with the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) to address specific state and nationally significant conservation concerns. Under the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act, CREP’s scope would be expanded to include qualified wetlands, offering new opportunities for conservation and sustainable land management.
Key benefits of CREP include:
- Financial incentives for farmers participating in conservation efforts
- Technical assistance for implementing conservation practices
- Long-term protection of environmentally sensitive lands
- Improved wildlife habitats and ecosystem services
By leveraging CREP, the act ensures that farmers have the support and resources they need to implement sustainable practices that benefit both their operations and the environment.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
As we embrace sustainable farming practices to support wildlife conservation and drought mitigation, technology plays a crucial role in optimizing these efforts. Companies like Farmonaut are at the forefront of this agricultural revolution, offering advanced satellite-based farm management solutions that complement the goals of initiatives like the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act.
Farmonaut’s platform provides valuable services such as:
- Real-time crop health monitoring
- AI-based advisory systems
- Blockchain-based traceability
- Resource management tools
These technologies enable farmers to make data-driven decisions that optimize resource use, improve crop yields, and support sustainable practices. For instance, Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring can help farmers implement precise irrigation strategies, aligning with the water conservation goals of the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act.
Benefits for Farmers and the Environment
The Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act offers a range of benefits for both farmers and the environment. Let’s take a closer look at these advantages:
| Conservation Aspect | Farmer Benefits | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Seasonal Field Flooding |
– Financial incentives – Improved soil health – Natural pest control |
– Increased wildlife habitat – Enhanced biodiversity – Water resource replenishment |
| Wetland Habitat Conservation |
– USDA support for conservation efforts – Potential for ecotourism opportunities |
– Protection of endangered species – Maintenance of ecological balance |
| Soil Erosion Prevention |
– Long-term soil fertility – Reduced input costs |
– Improved water quality – Carbon sequestration |
| Drought Mitigation |
– Increased resilience to dry periods – Efficient water use |
– Sustainable water management – Climate change adaptation |
This comprehensive approach ensures that farmers can maintain productive agricultural operations while contributing significantly to environmental conservation efforts.
Implementing Sustainable Farming Practices
Implementing sustainable farming practices in line with the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key strategies that farmers can adopt:
- Precision Agriculture: Utilize technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring to optimize resource use and reduce environmental impact.
- Cover Cropping: Plant cover crops during off-seasons to improve soil health and prevent erosion.
- Integrated Pest Management: Implement biological pest control methods to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides.
- Water-Efficient Irrigation: Adopt drip irrigation or other water-saving technologies to conserve water resources.
- Habitat Corridors: Create and maintain wildlife corridors on farmland to support biodiversity.
By adopting these practices, farmers can align their operations with the goals of the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act while improving their farm’s productivity and sustainability.
The Economic Impact of Sustainable Agriculture
While the environmental benefits of the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act are clear, it’s essential to consider the economic impact on farmers and local communities. Sustainable agriculture practices promoted by the act can lead to:
- Reduced input costs through efficient resource use
- Potential premium prices for sustainably produced crops
- Diversification of income through ecotourism opportunities
- Long-term soil health leading to sustained productivity
- Increased resilience to climate-related challenges
Moreover, the act’s support for local farmers helps maintain the economic vitality of rural communities while contributing to broader conservation goals.
Challenges and Future Considerations
While the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act offers numerous benefits, it’s important to address potential challenges in its implementation:
- Balancing food production with conservation efforts
- Ensuring equitable access to program benefits for all farm sizes
- Adapting to changing climate patterns and their impact on wetland habitats
- Coordinating efforts across multiple states along the Pacific Flyway
- Monitoring and measuring the long-term impact of conservation practices
Addressing these challenges will require ongoing collaboration between farmers, policymakers, conservationists, and technology providers like Farmonaut to ensure the act’s success and long-term sustainability.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring and Compliance
As we implement the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act, technology will play a crucial role in monitoring compliance and measuring the impact of conservation efforts. Farmonaut’s satellite-based solutions offer powerful tools for this purpose:
- Remote Sensing: Monitor land use changes and wetland conditions across large areas.
- Data Analytics: Analyze trends in wildlife populations and habitat quality.
- Blockchain Traceability: Ensure transparency in conservation practices and resource use.
- AI-Powered Insights: Provide recommendations for optimizing conservation efforts.
These technological solutions can help ensure the effective implementation of the act while providing valuable data for future policy decisions.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Agriculture and Wildlife
The Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act represents a significant step forward in harmonizing agricultural practices with wildlife conservation and environmental sustainability. By incentivizing farmers to adopt practices like seasonal field flooding and wetland conservation, the act creates a win-win scenario for both agriculture and ecology.
As we move forward, the integration of advanced technologies like those offered by Farmonaut will be crucial in maximizing the impact of these conservation efforts. From satellite-based monitoring to AI-driven insights, these tools empower farmers to make data-driven decisions that benefit both their operations and the environment.
The success of this initiative will depend on the continued collaboration between farmers, policymakers, conservationists, and technology providers. Together, we can create a sustainable future where productive agriculture coexists with thriving wildlife habitats along the Pacific Flyway and beyond.

FAQs
- What is the Pacific Flyway Habitat Enhancement Act?
It’s a bipartisan legislation that expands the Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program to include qualified wetlands, offering incentives for farmers to engage in seasonal field flooding and other conservation practices. - How does this act benefit farmers?
Farmers receive financial incentives, support for implementing sustainable practices, and resources to improve soil conditions while contributing to conservation efforts. - What role do rice farmers play in this initiative?
Rice farmers are particularly important as their fields can create surrogate wetlands when flooded seasonally, providing crucial habitat for migratory birds along the Pacific Flyway. - How does the act address drought concerns?
The act promotes efficient water use, groundwater recharge through seasonal flooding, and protection of surface water resources, helping to mitigate the impacts of drought. - What technologies can support the implementation of this act?
Advanced technologies like Farmonaut’s satellite-based monitoring, AI advisory systems, and blockchain traceability can help farmers implement and track conservation practices effectively.