Unlocking Wisconsin’s Agricultural Potential: The Vital Role of Antigo Silt Loam in Sustainable Crop Production
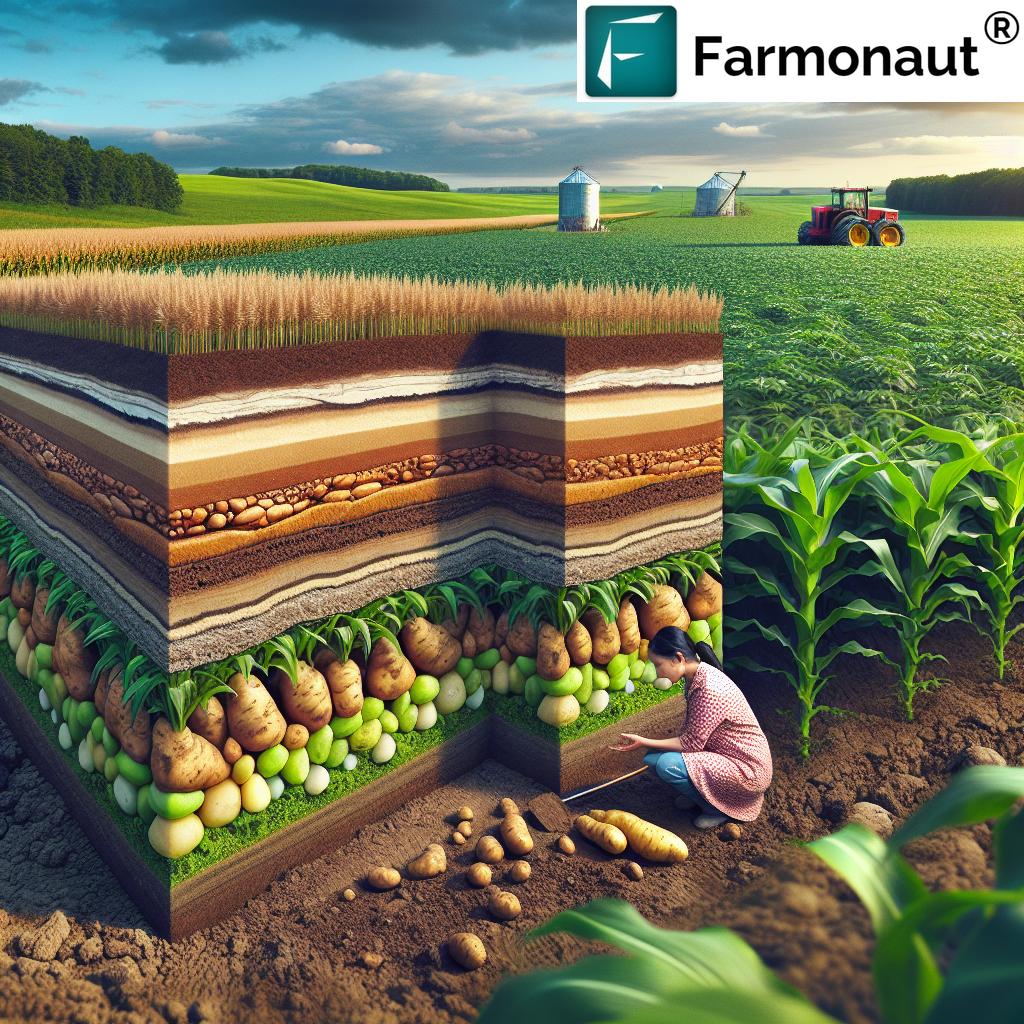
“Antigo Silt Loam, Wisconsin’s state soil, covers an impressive 300,000 acres across Wisconsin and parts of Minnesota.”
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of Wisconsin’s hidden treasure – the Antigo Silt Loam. As we delve into the world of agronomy and soil science, we’ll uncover how this unique soil type plays a crucial role in shaping the agricultural landscape of America’s Dairyland. At Farmonaut, we’re passionate about sustainable agriculture and leveraging technology to enhance crop production. Join us as we examine the properties, formation, and impact of Antigo Silt Loam on Wisconsin’s farming practices and environmental conservation efforts.
The Genesis of Antigo Silt Loam: A Glacial Legacy
Antigo Silt Loam, Wisconsin’s state soil, is a testament to the powerful forces of nature that shaped the region thousands of years ago. This remarkable soil type owes its existence to the glacial activity that occurred during the last Ice Age. As massive ice sheets retreated, they left behind a complex mixture of sediments that would eventually form the foundation of Wisconsin’s agricultural prowess.
The glacial soil formation process that created Antigo Silt Loam is a fascinating journey through time:
- Glacial deposits: As glaciers moved across the landscape, they ground up rocks and minerals, depositing a diverse mix of materials.
- Loess accumulation: Fine, wind-blown silt (loess) settled on top of these glacial deposits, creating the characteristic silty texture.
- Weathering and soil development: Over thousands of years, these deposits underwent weathering and biological processes, forming distinct soil horizons.
This unique origin story has endowed Antigo Silt Loam with properties that make it exceptionally well-suited for agriculture. Its glacial heritage provides a balance of minerals, organic matter, and soil structure that supports diverse crop production across Wisconsin.
Antigo Silt Loam: The Backbone of Wisconsin Agriculture
Spanning 300,000 acres across Wisconsin and parts of Minnesota, Antigo Silt Loam has become the cornerstone of sustainable agriculture practices in the region. Its distribution across thirteen counties in Wisconsin showcases its significant influence on the state’s agricultural landscape. Let’s explore the key characteristics that make this soil type so valuable for crop production:
| Property | Description | Agricultural Impact | Environmental Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Retention Capacity | High ability to hold moisture | Improved drought resistance for crops | Potential for reduced irrigation needs |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in essential minerals | Enhanced crop growth and yield | Risk of nutrient leaching if overfertilized |
| Soil Structure | Well-aggregated particles | Good root penetration and aeration | Reduced soil erosion risk |
| pH Level | Slightly acidic to neutral | Suitable for a wide range of crops | Minimal need for lime application |
These characteristics contribute to the soil’s exceptional suitability for various crops, including corn, grains, and potatoes. The water absorption capabilities of Antigo Silt Loam are particularly noteworthy, as they provide crops with consistent moisture access, even during drier periods.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices and Antigo Silt Loam
At Farmonaut, we recognize the importance of sustainable agriculture practices in preserving soil health and maximizing crop yields. Antigo Silt Loam’s unique properties present both opportunities and challenges for farmers striving to implement environmentally conscious farming methods.
Soil management for crops is crucial when working with Antigo Silt Loam. Here are some key considerations:
- Crop rotation: Implementing diverse crop rotations helps maintain soil fertility and breaks pest cycles.
- Cover cropping: Planting cover crops during off-seasons protects the soil from erosion and adds organic matter.
- Reduced tillage: Minimizing soil disturbance helps preserve soil structure and beneficial microorganisms.
- Precision nutrient management: Tailoring fertilizer applications to crop needs reduces the risk of nutrient runoff.
These practices not only enhance the productivity of Antigo Silt Loam but also contribute to long-term soil health and environmental sustainability.
“Antigo Silt Loam influences agriculture across thirteen counties in Wisconsin, supporting diverse crops like corn, grains, and potatoes.”
Environmental Impact and Challenges
While Antigo Silt Loam offers numerous benefits for crop production, it also presents some environmental challenges that require careful management:
- Groundwater contamination risks: The soil’s high permeability can lead to faster movement of nutrients and pesticides into groundwater.
- Soil erosion: Despite its good structure, intensive farming practices can still lead to erosion, particularly on sloping lands.
- Carbon sequestration: Proper management of Antigo Silt Loam can enhance its capacity to store carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach to land management and the adoption of innovative technologies. At Farmonaut, we offer solutions that can help farmers monitor and manage their fields more effectively, promoting both productivity and environmental stewardship.
The Role of Technology in Maximizing Antigo Silt Loam’s Potential
In the era of precision agriculture, technology plays a crucial role in helping farmers make the most of Antigo Silt Loam’s unique properties. Farmonaut’s suite of tools and services can significantly enhance farm management practices on this soil type:
- Satellite-based crop health monitoring: Our advanced imagery analysis can detect early signs of stress in crops growing on Antigo Silt Loam, allowing for timely interventions.
- AI-powered advisory systems: Our Jeevn AI provides personalized recommendations tailored to the specific needs of crops grown on this soil type.
- Soil moisture tracking: Given Antigo Silt Loam’s water retention properties, our soil moisture monitoring tools can help optimize irrigation practices.
- Carbon footprint assessment: We offer tools to help farmers quantify and reduce their carbon footprint, leveraging Antigo Silt Loam’s potential for carbon sequestration.
By integrating these technologies, farmers can make data-driven decisions that maximize yields while minimizing environmental impact on Antigo Silt Loam soils.
Climate Change and the Future of Antigo Silt Loam
As we look to the future, it’s crucial to consider the potential impacts of climate change on Antigo Silt Loam and the crops it supports. Climate models predict several changes that could affect this valuable soil resource:
- Increased temperature: Warmer conditions could alter soil microbial activity and organic matter decomposition rates.
- Changes in precipitation patterns: More intense rainfall events may increase erosion risks, while prolonged dry spells could stress the soil’s water-holding capacity.
- Shifting growing seasons: Farmers may need to adapt their planting and harvesting schedules to new climate norms.
To address these challenges, we at Farmonaut are continually updating our models and recommendations to help farmers adapt to changing conditions. Our climate-smart agriculture tools can assist in making informed decisions about crop selection, planting dates, and resource management in the face of a changing climate.
The Economic Impact of Antigo Silt Loam on Wisconsin Agriculture
The presence of Antigo Silt Loam has significant economic implications for Wisconsin’s agricultural sector. This soil type contributes to the state’s status as a major producer of several key crops:
- Corn production: Wisconsin ranks among the top 10 corn-producing states in the U.S., with Antigo Silt Loam playing a crucial role in supporting high yields.
- Potato industry: The state is the third-largest potato producer in the nation, with many potato farms benefiting from the properties of Antigo Silt Loam.
- Diverse crop support: The soil’s versatility allows for the cultivation of various grains, vegetables, and forage crops, contributing to agricultural diversification.
By leveraging Farmonaut’s technologies, farmers can further enhance the economic potential of lands with Antigo Silt Loam. Our satellite-based crop monitoring and AI advisory systems can help optimize inputs, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
Explore Farmonaut’s API for advanced agricultural insights
Conservation Efforts and Policy Implications
Recognizing the importance of Antigo Silt Loam to Wisconsin’s agriculture and environment, various conservation efforts and policies have been implemented:
- Soil conservation programs: State and federal initiatives encourage farmers to adopt practices that protect and enhance soil health.
- Water quality regulations: Given the soil’s potential impact on groundwater, policies are in place to manage nutrient and pesticide applications.
- Research and extension services: The University of Wisconsin-Madison and other institutions conduct ongoing research on Antigo Silt Loam management.
Farmonaut supports these efforts by providing tools that enable farmers to comply with regulations while maximizing productivity. Our blockchain-based traceability solutions can also help in documenting and verifying sustainable farming practices on Antigo Silt Loam.
Access our API Developer Docs for integration insights
Innovations in Soil Science: Advancing Antigo Silt Loam Management
The field of soil science is continually evolving, bringing new insights and technologies that can enhance our understanding and management of Antigo Silt Loam. Some cutting-edge areas of research include:
- Microbiome studies: Investigating the complex communities of microorganisms in Antigo Silt Loam and their role in soil health and crop productivity.
- Precision soil mapping: Using advanced sensing technologies to create high-resolution maps of soil properties across fields.
- Biochar applications: Exploring the potential of biochar to improve soil structure, water retention, and carbon sequestration in Antigo Silt Loam.
- Nanotechnology in agriculture: Developing nanoparticles for targeted nutrient delivery and pest control, optimized for the specific properties of Antigo Silt Loam.
At Farmonaut, we stay abreast of these developments and incorporate relevant findings into our AI-powered advisory systems, ensuring that farmers have access to the latest scientific insights for managing their Antigo Silt Loam soils.
The Global Context: Lessons from Antigo Silt Loam
While Antigo Silt Loam is unique to Wisconsin and parts of Minnesota, the principles of its management offer valuable lessons for sustainable agriculture worldwide. As global food demand increases and climate change poses new challenges, the strategies developed for Antigo Silt Loam can inform practices in other regions:
- Adaptive management: The approach to managing Antigo Silt Loam under changing climate conditions can guide farmers in other areas facing similar challenges.
- Technology integration: The successful application of precision agriculture tools on Antigo Silt Loam demonstrates the potential for technology to enhance soil management globally.
- Balancing productivity and conservation: The efforts to maintain high yields on Antigo Silt Loam while protecting water resources provide a model for sustainable intensification.
Farmonaut’s global perspective allows us to apply insights gained from Antigo Silt Loam management to our services worldwide, helping farmers across different soil types and climates optimize their practices.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Sustainable Agriculture on Antigo Silt Loam
As we’ve explored throughout this post, Antigo Silt Loam is more than just Wisconsin’s state soil – it’s a vital resource that underpins the region’s agricultural success and environmental health. By understanding its unique properties, challenges, and potential, we can work towards a future where this soil continues to support thriving crops and ecosystems for generations to come.
At Farmonaut, we’re committed to supporting farmers, agronomists, and policymakers in making the most of resources like Antigo Silt Loam. Our advanced technologies and data-driven insights are designed to enhance decision-making, improve yields, and promote sustainable practices across all soil types.
As we face the challenges of climate change and growing food demand, the lessons learned from managing Antigo Silt Loam will be invaluable. By combining traditional wisdom with cutting-edge technology, we can unlock the full potential of our soils while preserving them for the future.
FAQ Section
- What makes Antigo Silt Loam unique among soil types?
Antigo Silt Loam is distinguished by its glacial origin, excellent water retention capacity, and balanced nutrient content, making it ideal for diverse crop production in Wisconsin. - How does Antigo Silt Loam contribute to sustainable agriculture?
Its properties support efficient water use, reduce erosion risks, and promote carbon sequestration, aligning with sustainable farming practices. - What are the main crops grown on Antigo Silt Loam?
Corn, potatoes, and various grains are the primary crops, benefiting from the soil’s fertility and structure. - How can farmers best manage Antigo Silt Loam for long-term productivity?
Implementing crop rotations, cover cropping, reduced tillage, and precision nutrient management are key strategies for maintaining soil health. - What role does technology play in managing Antigo Silt Loam?
Advanced technologies like satellite imagery, AI advisory systems, and precision agriculture tools help optimize crop management and resource use on this soil type.