Water Restoration: 7 Shocking Secrets to Boost Farm Yields
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Power of Water Restoration in Agriculture
- Trivia: Farm Yield Boost
- Understanding Water Restoration and Sustainable Practices
- Secret #1: Riparian Zone Restoration
- Secret #2: Agroforestry Benefits for Water Management
- Secret #3: Strategic Reforestation to Reduce Runoff
- Secret #4: Assisted Natural Regeneration Uncovered (ANR)
- Secret #5: Forest Landscape Restoration (FLR) Strategies
- Secret #6: Water-Smart Forest and Landscape Restoration Tools
- Secret #7: Engaging Local Communities and Traditional Practices
- Comparison Table: Water Restoration Techniques and Yield Impact
- How Farmonaut Empowers Water Restoration and Sustainable Farm Yields
- Trivia: Soil Erosion and Agroforestry
- Economic, Environmental Benefits and Challenges of Water Restoration
- FAQ on Water Restoration in Farming
- Conclusion: The Future of Water Restoration and Sustainable Agriculture
“Water restoration can increase farm yields by up to 20% through improved soil moisture and reduced erosion.”
Understanding Water Restoration and Sustainable Practices
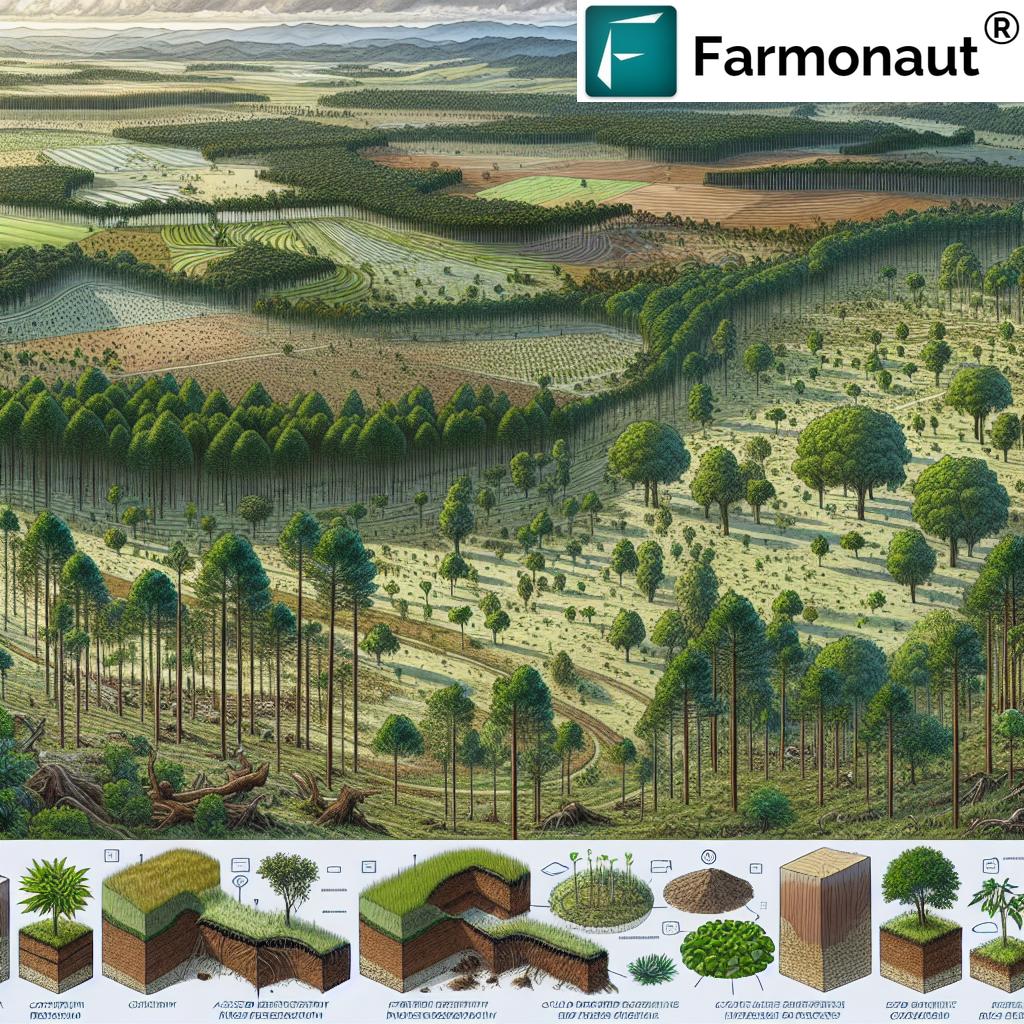
In today’s agricultural landscape, water restoration is more than a buzzword—it’s a lifeline for sustaining productivity, restoring ecological balance, and ensuring food security. As we face climate variability, soil degradation, and increasing water scarcity, adopting sustainable land management practices and innovative ecosystem restoration strategies becomes imperative.
But what exactly is water restoration? Broadly, it’s the process of rehabilitating and enhancing water resources within agricultural, farming, and forestry systems to restore ecosystem health. Our goal is to improve water quality, regulate hydrological cycles, restore degraded landscapes, and establish robust, resilient farming environments for future generations.
Why is this important for us? Water—whether as rainfall, streams, rivers, or groundwater—is the foundation for healthy soils, thriving plants, and vibrant landscapes. Practices like riparian zone restoration, integrating trees via agroforestry, and controlled land management can improve water quality in agriculture, increase the storage capacity of our soils, and reduce harmful runoff.
As caretakers of the land, we can unlock transformational benefits by following the seven secrets detailed in this guide for water restoration and sustainable ecosystem restoration strategies.
The 7 Shocking Secrets to Boost Farm Yields with Water Restoration
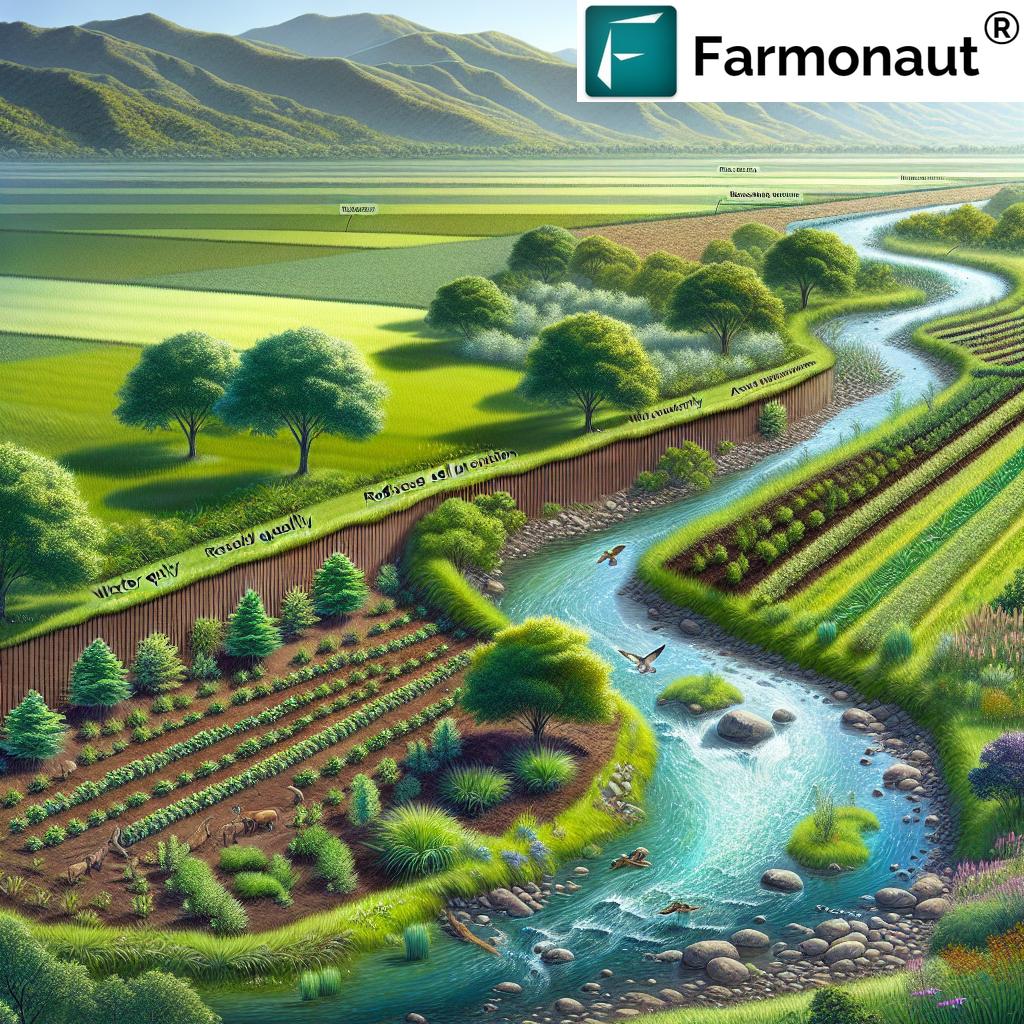
1. Riparian Zone Restoration: Nature’s Water Filters
Riparian zone restoration is one of the most powerful yet often overlooked methods to improve water quality in agriculture and stabilize our landscapes.
Riparian zones are the interfaces between land and water bodies—like streams, rivers, ponds, and wetlands. These areas act as natural buffers, protecting water bodies from pollution, erosion, and sedimentation while creating habitats for diverse wildlife species.
- Reestablishing Native Vegetation: Planting native trees, shrubs, and grasses helps stabilize soil, absorb excess nutrients, and filter out pesticides or fertilizers before they reach waterways.
- Protecting Zones from Overgrazing/Deforestation: Limiting livestock access and preventing clearing of vegetation keep the soil in place, reducing sedimentation and maintaining ecosystem stability.
- Providing Habitat and Biodiversity: A healthy riparian ecosystem supports a wide array of wildlife, insects, and beneficial microorganisms.
By restoring these critical interfaces, we help prevent nutrient runoff, reduce soil erosion in farming, and create a self-sustaining system that improves water quality and boosts farm productivity.
2. Agroforestry Benefits for Water Management: Integrating Trees with Farming
Agroforestry—the intentional integration of trees, crops, and sometimes livestock on the same land—is a cornerstone of sustainable land management practices.
When we combine trees with pasture and crops (silvopasture), we:
- Improve Soil Structure & Infiltration: The roots of trees break up compacted soils, enhancing drainage and allowing rainwater to seep deeper, replenishing groundwater stores.
- Reduce Surface Runoff & Nutrient Loss: Tree canopies slow rainfall, protecting topsoil and reducing the risk of fertilizer runoff.
- Create Microclimates: Trees offer shade, reduce evapotranspiration, and help conserve moisture—vital for drought resilience.
- Enhance Biodiversity: Agroforestry supports a more diverse ecosystem, boosting natural pest control and overall crop health.
Studies show that agroforestry benefits for water management include up to 50% reduction in soil erosion, plus substantial improvements in farm yield and resource conservation.
If you’re seeking to bring intelligence and precision to your farm’s landscape monitoring, explore Farmonaut’s Large-Scale Farm Management platform. This solution enables real-time monitoring, incorporating key agroforestry data, soil health metrics, and forest cover estimations to support smarter water management decisions across vast farming landscapes.
3. Strategic Reforestation to Reduce Runoff and Boost Groundwater
Reforestation and afforestation involve planting trees on degraded or deforested lands. These forests act as natural buffers that absorb rainfall, slow down surface water flow, and increase the storage and filtration capacities of our landscapes.
Restoring and planting native trees in targeted locations—especially flood-prone agricultural lands—can:
- Reduce surface water runoff by up to 30%, helping to mitigate flood risks
- Decrease soil erosion and sediment transport in waterways
- Improve soil moisture retention, enhancing plant root zone health
- Filter pollutants, improving water quality downstream
When we restore forests as part of a larger water restoration plan, we’re not only improving our yields but also protecting wider ecosystems and regenerating local aquifers.
For sustainable land management projects that include forest restoration and require expert digital advisory, check out Farmonaut’s Crop Plantation & Forest Advisory Services, which helps assess suitability, track growth, and optimize planting for reforestation across varying climates and geographies.
4. Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR): Unlocking Nature’s Resilience
Assisted natural regeneration (ANR) is a highly effective and low-cost strategy for water and land restoration. Instead of planting new trees, we support the land’s natural regrowth by:
- Protecting seedlings, stumps, roots, and naturally occurring vegetation from livestock and disturbances.
- Controlling invasive species, encouraging the proliferation of native flora.
- Reducing fire and illegal logging risks through regular management and patrolling.
ANR promotes biodiversity, enhances soil organic matter, improves water retention, and creates self-sustaining landscapes that naturally regulate water cycles and reduce erosion.
5. Forest Landscape Restoration (FLR): Integrating Large-Scale Ecosystem Restoration
Forest landscape restoration (FLR) goes beyond individual practices by taking a holistic, landscape-level view. It involves:
- Restoring the ecological integrity of whole degraded landscapes
- Integrating forests with agricultural systems and other land uses
- Engaging diverse stakeholders—from local farmers to regional planners
FLR improves water availability, regulates runoff, and enhances the delivery of vital ecosystem services like flood mitigation, carbon sequestration, and groundwater recharge. It is a cornerstone for sustainable land management worldwide, with proven results in both environmental health and rural livelihoods.
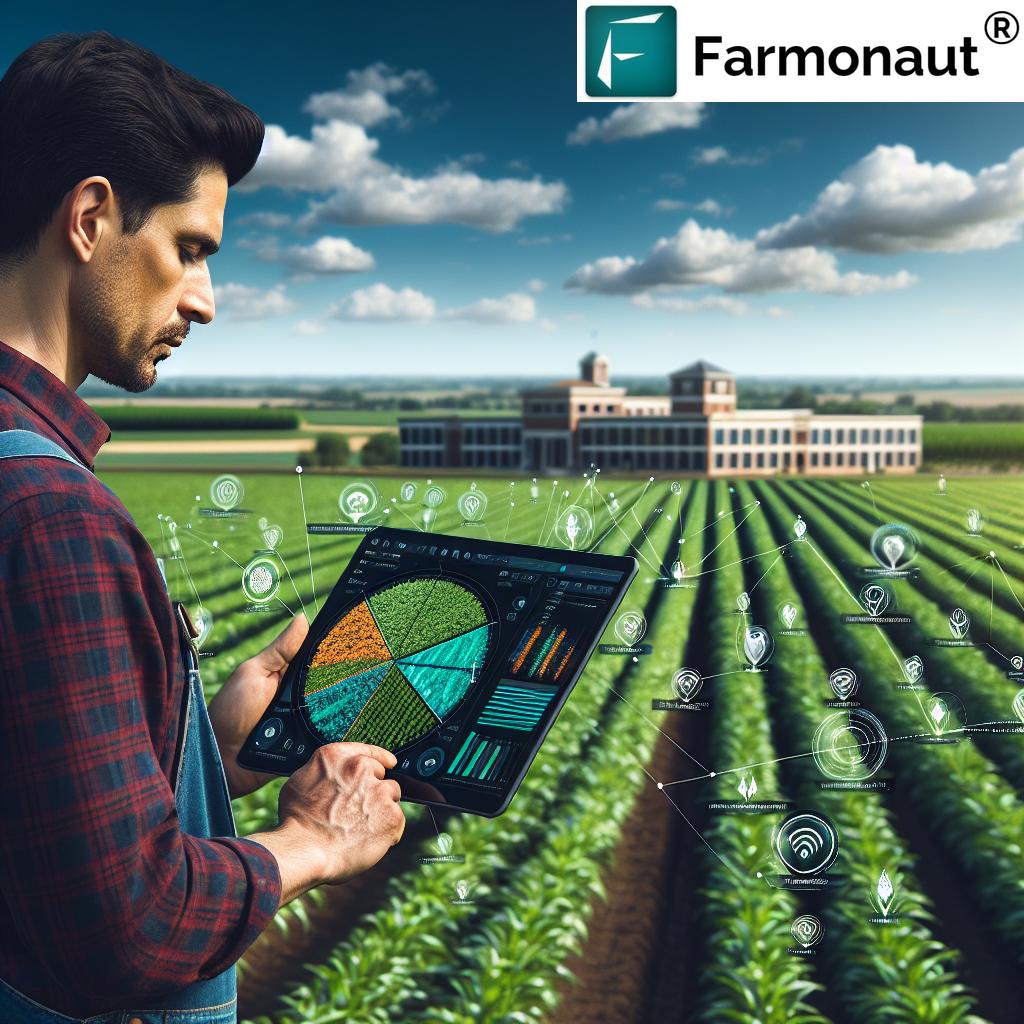
6. Water-Smart Forest and Landscape Restoration: Technology for a Sustainable Future
As the climate and water cycles become more erratic, integrating sophisticated assessment tools is crucial. Water-smart forest and landscape restoration methodologies utilize digital tools (like the W-FLR tool) to:
- Assess water risks—such as flood potential, drought stress, or runoff hazards
- Map water flows, infiltration, and soil moisture distribution
- Guide the integration of water management into restoration projects
Technology brings clarity and precision to restoration projects, ensuring that every intervention is planned not only for productivity but also for ecosystem and community resilience.
Using digital tools like Farmonaut’s platform, which offers APIs for satellite-based soil moisture and rainfall monitoring, allows us to make informed, water-smart decisions across entire regions and scales.
For developers and agri-tech leaders, the Farmonaut Satellite Weather API Developer Docs provide robust documentation to integrate water risk data and analytics into your own tools or research projects.
7. Engaging Local Communities and Traditional Practices: Wisdom for Water Sustainability
The knowledge and involvement of local communities are essential for successful water restoration. In many regions, traditional techniques—such as the “sowing and harvesting water” methods used in the Peruvian Andes—are proven ways to intercept, store, and make the most of scarce water resources.
By integrating such indigenous practices with modern science and tech, we:
- Enhance water infiltration, storage, and availability
- Promote ecosystem resilience during droughts or floods
- Preserve and revitalize native species and habitats
- Ensure the long-term sustainability of agricultural, forest, and pastoral systems
Our restoration strategies are most successful when communities are empowered, respected, and actively involved in designing and maintaining restoration projects.
Comparison Table of Water Restoration Techniques and Their Yield Impact
“Agroforestry practices reduce soil erosion by as much as 50%, significantly enhancing long-term ecosystem sustainability.”
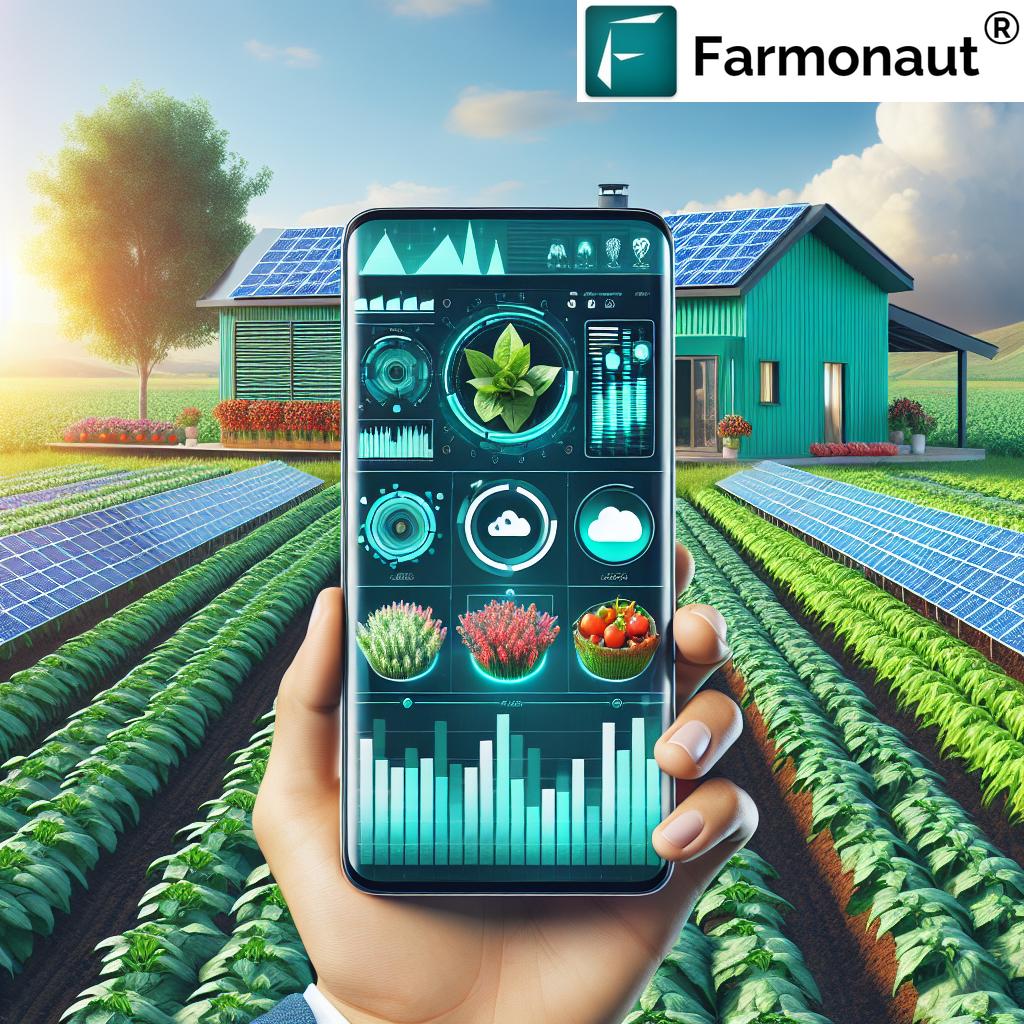
How Farmonaut Empowers Water Restoration & Sustainable Farm Yields
While several physical restoration techniques can boost yields, modern farm management today also depends on accurate, timely, and affordable data.
Farmonaut stands at the forefront of sustainable agriculture with its advanced, satellite-driven solutions for water, soil, and yield management.
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Using multispectral satellite images, we enable farmers to analyze vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture levels, and key indicators of water stress. This real-time insight helps optimize irrigation, application of fertilizers, and pest control, thus reducing runoff and improving yields.
- AI-Driven Advisory via Jeevn AI: Farmonaut provides AI-powered, personalized recommendations for crop management, combining weather forecasts, soil status, and historic water patterns for precision farming.
-
Blockchain Traceability: Transparency is vital for sustainable supply chains. By ensuring secure, tamper-proof tracking of agricultural products, we support sustainability, reduce fraud, and enhance trust in food systems.
Learn how you can add transparency and trust with Farmonaut’s Product Traceability. -
Fleet & Resource Management: Efficient transport reduces resource loss, saves fuel, and ensures farm machinery is in the right place at the right time—minimizing operational costs and environmental impact.
See the impact for large-scale operations on Farmonaut’s Fleet Management. -
Carbon Footprinting: Tracking and reducing carbon emissions is now essential for market access and regulatory compliance, especially in markets prioritizing green agriculture.
Measure and improve your ecological impact with Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting services. -
Crop Loan & Insurance Support: Satellite-based verification makes loan approvals and farm insurance more dependable and less prone to disputes, enabling better access to financial resources.
Protect your investments using Farmonaut’s Crop Loan and Insurance Solutions.
By bringing together ground-level best practices in water restoration and advanced digital tools, we at Farmonaut empower farmers, agribusinesses, and entire communities to achieve sustainable productivity and ecosystem health.
Economic and Environmental Benefits, Challenges, and Considerations
Key Benefits of Water Restoration:
- Boosts Farm Productivity: Improved water retention and soil quality mean better yields with lower input costs.
- Reduces Disaster Risks: By regulating hydrological cycles and controlling runoff, we mitigate flood or drought impacts.
- Delivers Ecosystem Services: Cleaner water, carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and resilient landscapes.
- Economic Value: Restoration investments can yield returns several times higher than the costs of inaction.
- Improves Community Livelihoods: Reliable water and healthy soils support secure, sustainable incomes for rural populations.
What are the Main Challenges?
- Funding Limitations: Restoration can require up-front investment and sustained maintenance.
- Land Tenure Issues: Success depends on local participation and stable, long-term land rights.
- Technical Skills Gaps: Knowledge of restoration techniques, monitoring, and adaptive management is needed.
- Tailoring Interventions: Not all solutions fit every region; strategies must be adapted to climate, soil, and community needs.
Our Perspective: Integrated Strategies for Lasting Impact
We believe that combining on-ground practices (like riparian restoration, agroforestry, and reforestation), digital decision-making support, and the wisdom of local communities creates the strongest foundation for long-term agricultural and ecological resilience.
The future of water restoration lies in holistic, data-driven, and people-centered strategies. Now, let’s address some of the most pressing questions about water and landscape restoration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Water Restoration in Farming and Forestry
What is water restoration in agriculture?
Water restoration involves a suite of strategies and best practices to rehabilitate and enhance water resources in farms and landscapes. It focuses on improving water quality, increasing availability, regulating hydrological cycles, and restoring ecosystem health—providing a foundation for sustainable agriculture and forestry.
How does riparian zone restoration help farms?
Riparian zone restoration restores the natural vegetation along rivers, streams, and other water bodies. This stabilizes riverbanks, filters run-off pollutants, reduces soil erosion, and provides habitats for wildlife—all of which contribute to higher crop yields and quality.
Why are trees important for water restoration?
Trees help restore water cycles by intercepting rainfall, increasing groundwater recharge, and slowing runoff. Agroforestry, reforestation, and afforestation practices are powerful tools to reduce soil erosion, retain soil moisture, improve water quality, and boost biodiversity on farms and degraded lands.
What is assisted natural regeneration (ANR), and how is it effective?
ANR is the process of protecting and managing existing natural vegetation and seedlings to encourage regrowth, rather than planting new trees. It’s cost-effective, preserves local biodiversity, and helps rehabilitate degraded landscapes rapidly.
How do digital tools like Farmonaut help in water restoration?
Platforms like Farmonaut leverage satellite imagery, artificial intelligence, and real-time data analytics to give farmers actionable insights into soil health, water stress, and yield optimization. These tools enable smarter irrigation, resource allocation, and landscape restoration—paving the way for efficient and scalable water management.
Can water restoration practices really increase farm yields?
Yes—numerous studies have shown that integrated water restoration can increase yields by up to 20% by improving soil moisture retention, reducing erosion, and supporting plant health via better water and nutrient management.
How can communities get involved in water restoration?
Community engagement is vital. By blending traditional knowledge (such as local methods for water harvesting and vegetation management) with scientific tools and restoration practices, communities can ensure the long-term sustainability and success of these efforts.
Conclusion: Embracing Water Restoration for Sustainable Farm Yields
The journey towards sustainable agriculture and thriving, resilient landscapes starts with smart water restoration strategies. By embracing the seven secrets—riparian restoration, agroforestry, reforestation, assisted natural regeneration, FLR, water-smart planning, and community involvement—we can transform degraded environments into productive, ecologically sound, and economically viable systems.
Tools like Farmonaut empower us to fuse tradition with technology—enabling informed decisions, maximizing yields, and ensuring our farms and forests remain healthy for generations to come. Whether you’re a smallholder, an agribusiness, or a policymaker, water restoration is your pathway to security, profitability, and a greener planet.
Let’s restore, protect, and nurture our water and lands—for today and tomorrow.