Table of Contents
- Introduction: Almond Farming in California
- Trivia: California’s Global Almond Leadership
- 1. The Foundation: Smart Almond Orchard Planning & Maintenance
- 2. Water is Gold: Advanced Almond Irrigation Techniques
- 3. The Pollination Puzzle: Maximizing Almond Pollination by Bees
- 4. Soil Health Excellence: Fertility, Cover Cropping & Mulching
- 5. Sustainable Pest Management: Control, Reduction & Protection
- 6. Harvest Like a Pro: Optimizing Almond Harvesting Methods
- 7. Embracing Technology: Precision Farming & Resource Efficiency
- Sustainable Practices Impact Comparison Table
- Emerging Almond Industry Challenges & Adaptation
- Trivia: Sustainability Boosts Yields & Protects Nature
- Farmonaut Solutions: Supercharge Your Almond Farming
- FAQ: Almond Farming and Sustainability
- Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Almond Excellence
Almond Farmer Secrets: 7 Game-Changers for Huge Yields
“California produces over 80% of the world’s almonds, using advanced irrigation to save up to 33% more water per acre.”
Almond farming in California isn’t just a regional affair—it’s the heartbeat of the global almond industry. As farmers, agribusinesses, and agricultural enthusiasts, we know success hinges on a combination of tradition, innovation, and sustainability. Today, we’ll unlock the almond farmer secrets behind consistently huge yields, covering everything from water efficiency, pest and pollinator management, to digital technologies like Farmonaut—all through the lens of environmental stewardship.
Almond crops thrive in the hot, dry Mediterranean climates of areas like California’s Central Valley, making our ongoing commitment to sustainable practices and technological evolution central to both yield and survival. Let’s journey through the seven top strategies every almond farmer—whether managing a single orchard or a large agri-business—must know.
1. The Foundation: Smart Almond Orchard Planning & Maintenance
Almond Cultivation Practices Begin with the Basics
At the core of every productive almond farm lies exceptional orchard management. Our journey with almond cultivation in California starts with strategic planning and regular maintenance:
- Site Selection: Almond trees prosper in well-drained soils with ample sunlight. Areas like California’s Central Valley, with their Mediterranean climate, provide the perfect backdrop for orchard establishment.
- Orchard Design: Planting density, row orientation, and spatial layout all impact air circulation, exposure to sunlight, and ultimately, nut yields.
- Pruning: Regular pruning shapes tree structure, ensures light penetration, improves air movement (reducing disease), and fosters the development of productive fruiting wood.
- Soil Preparation: Pre-planting, we test and amend soils (for pH, nutrients), deep-rip compacted zones, and establish baseline organic matter—helping almond roots access water and nutrients efficiently.
Early investments in orchard planning and maintenance build robust roots for future productivity and resilience.
2. Water is Gold: Advanced Almond Irrigation Techniques
Almond Irrigation Techniques for Sustainability & High Yields
Water conservation in almond orchards is paramount—both for sustainability and business viability in drought-prone California. Modern almond farmers must master:
- Drip Irrigation Systems: The gold standard for efficient water use, drip methods deliver water directly to each tree’s root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Our orchards see up to 33% water savings per acre compared to flood or sprinkler systems.
- Soil Moisture Sensing: Monitoring real-time soil moisture helps us apply just enough water at precisely the right moment—no more, no less.
- Smart Scheduling: Aligning irrigation with tree water demand and weather forecasts further reduces waste and strengthens drought resilience.
- Fertigation: Combining drip with targeted nutrient delivery maximizes growth while minimizing leaching and environmental impact.
For orchards spanning hundreds of acres, Farmonaut’s Advanced Large-Scale Farm Management tools enable seamless monitoring of irrigation efficiency, alerting us to anomalies and helping us fine-tune water usage.
Sustainable Practices Impact Comparison Table
| Sustainable Practice | Estimated Water Savings (%) | Estimated Yield Increase (%) | Implementation Cost ($/acre, est.) | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | 25 – 33% | 8 – 15% | $750 – $1,800 | Reduces evaporation, lowers runoff, conserves water |
| Cover Cropping | 5 – 10% | 4 – 7% | $50 – $200 | Improves soil health, water retention, and biodiversity |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | 2 – 6% | 5 – 12% | $60 – $200 | Reduces chemical use, protects pollinators, enhances ecological balance |
| Soil Mulching & Composting | 5 – 12% | 2 – 6% | $100 – $250 | Boosts microbial activity, reduces erosion, improves moisture retention |
| Solar-Powered Pumping | — | 1 – 2% | $900 – $2,500 | Reduces energy emissions, cuts operational carbon footprint |
| Wildflower & Pollinator Habitat Planting | — | 2 – 5% | $20 – $80 | Supports bees & pollinators, improves pollination, strengthens yield |
| Digital Farm Management (e.g., Farmonaut) | 8 – 18% | 5 – 14% | $2 – $8/month/acre | Optimizes resources; reduces water, fertilizer, and chemical usage |
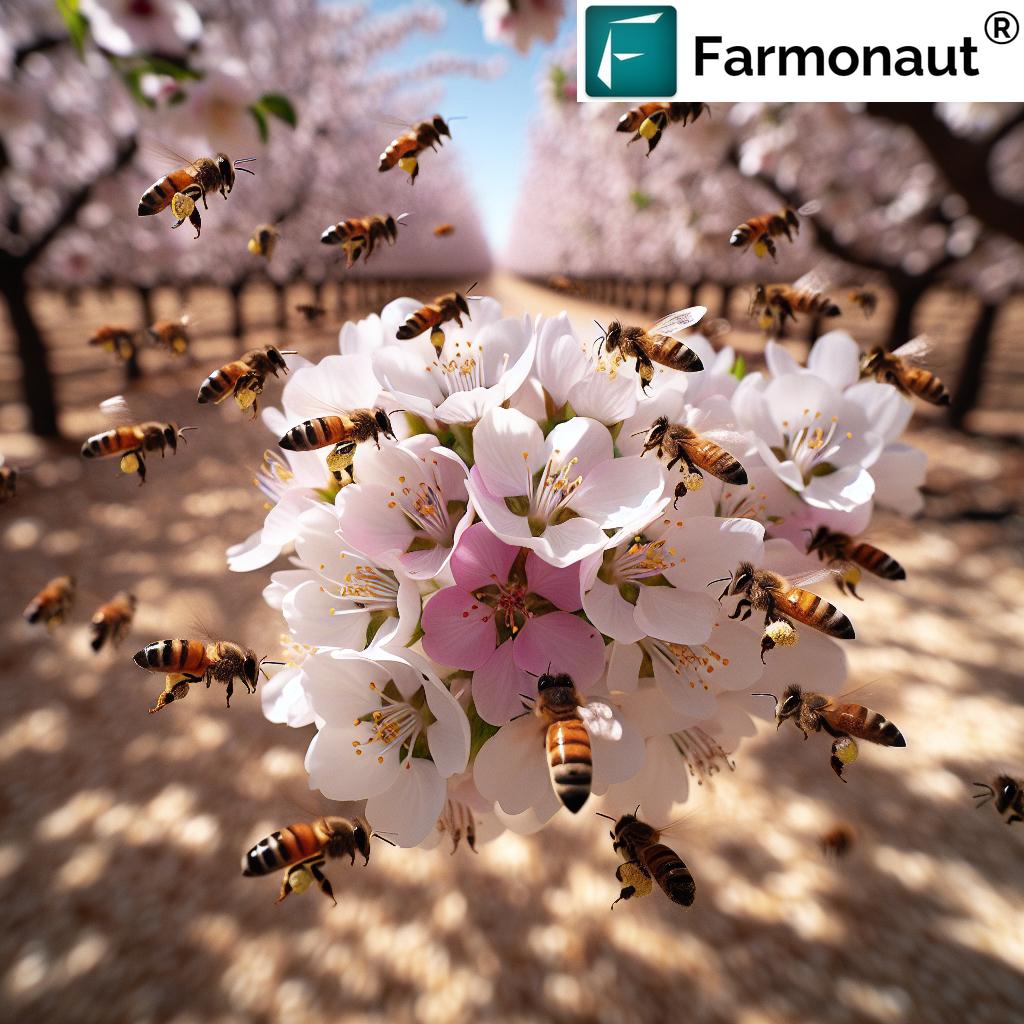
3. The Pollination Puzzle: Maximizing Almond Pollination by Bees
How Almond Trees Depend on Pollinators
Did you know? Almonds are not self-pollinating! Every tasty nut we enjoy is thanks to relentless bees and their hardworking beekeepers. Here’s how we ensure effective almond pollination by bees:
- Hive Rentals: By partnering with beekeepers who rent hives, we ensure ample pollinator presence during the blooming season. Timing hive arrival with almond bloom is crucial for full orchard coverage.
- Habitat Creation: Planting wildflowers and native vegetation around orchards supports bee health when the almond bloom ends. Healthy bees mean better fruit set & higher yields.
- Pesticide Safety: Adopting integrated pest management (IPM) minimizes exposure of pollinators to toxic chemicals, further protecting crop health and pollination efficiency.
Farmers in California and beyond know: strong pollinator support is the backbone of sustainable almond farming and future industry success!
4. Soil Health Excellence: Fertility, Cover Cropping & Mulching
Soil Is the Secret Engine of Yield
Yield and resilience in sustainable almond farming flow from the ground up. Healthy soils support robust tree growth and increase water and nutrient efficiency:
- Soil Testing: Ongoing soil analysis allows us to deliver just the right balance of macro- and micronutrients.
-
Cover Cropping: Planting legumes or grasses between orchard rows:
- Reduces erosion and compaction,
- Improves water infiltration,
- Boosts beneficial soil microbes and organic matter.
- Mulching and Composting: Applying mulch and compost not only recycles nutrients but also enhances soil moisture retention, moderates temperature, and staves off weeds.
With satellite-based crop health monitoring from Farmonaut, we track soil moisture and the vegetative health of our orchards, allowing for even more targeted soil management. This reduces waste and boosts yields while reducing our environmental impact.
5. Sustainable Pest Management: Control, Reduction & Protection
Balancing Pest Control with Environmental Considerations
Pests and diseases threaten both yield and environmental sustainability. Our almond orchard management emphasizes these integrated management strategies:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): We combine biological control (natural predators like lacewings and ladybugs), cultural practices (timely pruning, sanitation), and limited, targeted use of crop protection chemicals.
- Scouting & Monitoring: Frequent scouting for pest hot spots (with help from precision platforms like Farmonaut’s satellite imagery) means faster identification and smarter interventions.
- Disease Prevention: Good air circulation, proper pruning, and leaf litter management reduce fungal pressures—from root rot to blossom blight.
- Minimizing Bee Exposure: Timing and selection of pest control measures is coordinated to protect pollinator health and avoid harming the bees vital for almond pollination.
These strategies are not only better for the environment—they also help us meet stringent local, state, and global standards for sustainable almond farming while increasing yields.
6. Harvest Like a Pro: Optimizing Almond Harvesting Methods
Maximizing Quality, Efficiency, and Resource Use
Almond harvesting methods in California have evolved to prioritize both efficiency and quality. Once hulls split, mechanical shakers gently shake trees, the nuts drop to the ground, and are collected for processing. Let’s break down the process:
- Determining Ripeness: We monitor almond development closely; optimal harvest time is when hulls begin to split, maximizing both yield and quality.
- Mechanical Shakers: Gentle, site-appropriate shaking drops nuts cleanly, reducing tree stress and physical damage to crops.
- Cleanup & Collection: Swift nut collection prevents losses to pests, diseases, and ground moisture. Using efficient mechanical sweepers and pickers reduces labor input and time.
- Processing: Cleaned and graded almonds are sent to processors for hulling, shelling, quality sorting, and packaging for global markets—from the EU to Asia.
As labor shortages and rising costs squeeze the agricultural sector, orchard owners are increasingly exploring automation and optimized machinery scheduling—which platforms like Farmonaut’s Fleet Management help coordinate across large-scale orchards for peak efficiency during the critical harvest window.
7. Embracing Technology: Precision Farming & Resource Efficiency
How Digital Tools Like Farmonaut Transform Almond Production
Today, the key to high almond yields and robust environmental performance is precision farming. Digital platforms empower us to:
- Monitor Crop Health in Real-Time: Leveraging satellite imagery and AI (NDVI, soil moisture), we quickly spot stress zones, nutrient deficiencies, and irrigation problems—long before they show up visually.
- Personalize Crop Advisory: With tools such as Jeevn AI Advisory, growers receive real-time advisories, weather forecasts, and management tips based on actual orchard data.
- Enhance Resource Use: Targeted interventions—water, nutrients, and pest control—reduce costs and improve environmental outcomes.
- Automate Compliance & Traceability: Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Product Traceability ensures almond batches are fully traceable, meeting consumer and regulatory demand for transparency.
- Environmental Impact Tracking: Managing carbon footprint and emissions enables California almond growers to position their product as truly sustainable.
Access these digital innovations through the Farmonaut app (Web, Android, iOS) or API. Developers can get started with our API Developer Docs for integrations tailored to orchards, supply chain, crop health, and more.
Emerging Almond Industry Challenges & Adaptation
Navigating Water, Climate, Labor, Trade & Pest Pressures
The almond industry is thriving, but our success brings unique challenges, especially in California:
- Water Availability: Almond farming remains water-intensive. The state’s ongoing droughts require us to combine advanced water-efficient systems with real-time satellite monitoring to cut waste.
- Climate Change: Changing weather patterns and temperatures challenge tree dormancy, bloom timing, and pollination—making adaptability and data-driven decision-making essential.
- Labor Shortages & Mechanization: A shrinking agricultural workforce pushes us further into automation—from mechanical shakers to satellite-coordinated machinery and smart scheduling.
- Trade Policies: Global markets face turbulence from tariffs and trade disputes. Maintaining quality and sustainability credentials is vital to retaining export value.
- Pest and Disease Pressures: New pest species and disease outbreaks require ongoing research and adaptation. IPM, precision monitoring, and biodiversity are our best defense.
“Sustainable almond orchards can reduce pesticide use by 30%, boosting yields while protecting local pollinators and soil health.”
Farmonaut Solutions: Supercharge Your Almond Farming
Unlocking HUGE Yields with the Power of Precision & Technology
Farmonaut is redefining what’s possible in almond farming. By making satellite-based farm management affordable and accessible, we empower California almond producers (and global farmers!) with:
- Real-time Crop Health Monitoring: Detecting irrigation, disease, or nutrient issues as they develop, so we act—not react.
- Automated Advisory (Jeevn AI): Receive data-driven tips for all key stages—planting, irrigation, pest and disease control, harvesting, and beyond.
- Resource Management: Cut input costs and reduce environmental impact by targeting labor, fertilizer, and water exactly where and when needed.
- Full Supply Chain Traceability: Our Traceability Solutions add trust for global almond buyers and simplify crop loan and insurance verification, thanks to satellite evidence.
- Carbon Footprinting: Track and reduce CO2 emissions with our carbon accounting feature—essential for sustainability certifications.
Our platform delivers these benefits through easy-to-use web and mobile apps or via API integration for enterprises and developers. Explore scalable solutions for small and large orchards—without hefty upfront investments on field hardware!
FAQ: Almond Farming and Sustainability
What are the best almond cultivation practices for high yields?
Combining well-planned orchard layouts, regular pruning, efficient irrigation (drip systems), robust pest management (IPM), soil health (cover cropping, composting), and precision crop monitoring is the most effective route to maximizing both almond quality and yield.
How do almond farmers in California optimize water usage?
Growers use drip irrigation, implement soil moisture sensing, schedule irrigation efficiently, and use real-time satellite and weather data. These approaches collectively reduce waste and support drought resilience.
Why is pollination by bees so critical for almond orchards?
Almonds are not self-fertilizing. They require cross-pollination, mostly performed by honey bees and other pollinators. Strong pollinator presence means higher fruit set and substantial yield increases.
What are the main environmental impact concerns of almond farming?
The biggest concerns are water consumption, chemical input (fertilizers and pesticides), and emissions from energy use/machinery. Switching to water-smart irrigation, adopting IPM, and using renewable energy significantly reduces environmental impact.
How can technology help with almond orchard management?
Technology—especially satellite imagery, AI-based advisory, and resource management apps—enables us to detect problems early, direct inputs efficiently, and ensure full traceability and compliance for modern sustainable farming.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in almond farming?
IPM blends biological controls (predators, parasitoids), cultural practices, mechanical control, and minimized, smart pesticide use. This multi-pronged approach both protects almond crops and supports beneficial insects, including bees.
Does cover cropping really work in almond orchards?
Yes. Cover crops reduce soil compaction, increase infiltration, suppress weeds, enhance organic matter, and provide habitats for beneficial insects, thereby improving overall orchard health and yields.
How does Farmonaut’s technology fit into almond farming?
Farmonaut makes precision agriculture accessible with satellite crop health monitoring, AI-driven crop advisory, blockchain traceability, resource management, and carbon footprint tracking. This suite helps optimize yield, minimize costs, and achieve sustainability at every stage—from planting to harvest, whether for family-run or corporate almond orchards.
Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Almond Excellence
We’ve explored the proven secrets behind huge almond yields—from the basics of smart orchard design and water-efficient irrigation to bee-friendly pollination, healthy soils, smart pest control, modern harvesting methods, and precision digital management. These practices help not just to grow more almonds, but to do so responsibly, guarding our environmental legacy while remaining globally competitive.
Sustainable almond farming in California is an exemplary model: high productivity, export leadership, and a constant push to adapt to new industry challenges—from water shortages to labor and climate issues. Solutions like Farmonaut—democratizing satellite-based, precision management—support this journey towards a future where healthy orchards mean a healthy planet and resilient local communities.
Let’s continue embracing innovation, sharing knowledge, and putting sustainable practices at the center of our almond story—one orchard at a time.