Leafhopper Control: 7 Shocking Ways to Save Your Crops
“Leafhoppers can reduce crop yields by up to 50% if not controlled with integrated pest management strategies.”
Introduction: Understanding the Threat of Leafhoppers
Leafhoppers—those remarkably small, but devastatingly impactful insects from the family Cicadellidae—represent a significant threat to agriculture, farming, and forestry worldwide. Our crops are not just threatened by their sap-sucking feeding habits, but also by their powerful ability to transmit various plant pathogens. From potatoes suffering curly top virus, to beet crops facing growth stunting and discoloration, understanding how to implement robust leafhopper control is crucial to ensuring crop health, maximizing yields, and achieving sustainable production.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) has become the gold standard for leafhopper management in agriculture. By combining cultural, biological, chemical, and technological controls, we can minimize infestations, reduce chemical dependence, and protect both our farms and our environment.
This comprehensive guide will explore the biology, monitoring methods, and the most innovative and effective leafhopper control strategies—including how technology from Farmonaut empowers us to safeguard our food, fiber, and forests.
Identification and Biology of Leafhoppers
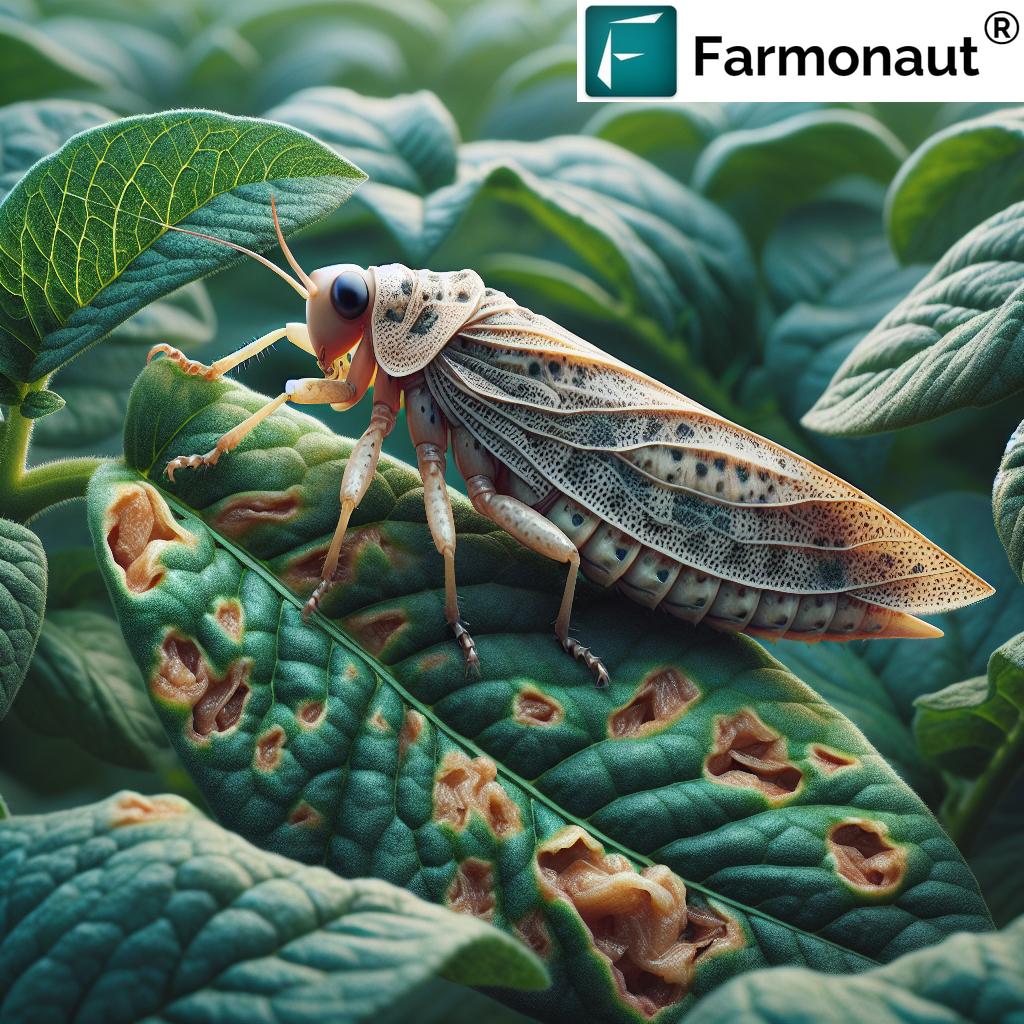
Our approach to leafhopper management begins with a deep understanding of their biology and life cycle. Leafhoppers are not a single species, but rather a broad family (Cicadellidae) consisting of hundreds of species—each with their own favored host plants and local distribution. However, they share common features and behaviors that facilitate targeted interventions.
Key Identification Features
- Small, slender bodies, typically 3-15 mm in length
- Green, yellow, or brown coloration—sometimes with vivid patterns or speckling
- Strong hind legs adapted for fast and high jumping
- Wings held roof-like over the back in adults
- Eggs are laid inside plant tissue, often in rows
- Nymphs resemble adults, but are wingless during early stages
Life Cycle and Generational Turnover
- Incomplete metamorphosis—progressing from eggs, to nymphs, to adults
- Duration of life cycle varies by species and environmental conditions
- Many species are capable of producing multiple generations per year, especially in warm climates
This means that monitoring populations and intervening at critical points in the life cycle is essential for minimizing infestation and damage. As we move through each integrated pest management approach, remember the importance of targeting not just adults, but also eggs and nymphs for the highest efficacy.
Signs of Leafhopper Damage and Their Impact
Recognizing early signs of leafhopper damage is essential for quick intervention. Leafhoppers cause harm in two primary ways:
- Direct Feeding: Piercing-sucking mouthparts drain plant sap, causing visible and physiological damage.
- Transmitting Plant Diseases: Vectoring viruses and other pathogens, leading to systemic infections.
Typical Symptoms of Leafhopper Activity
- Leaf curling
- Chlorosis (yellowing) or discoloration
- Stunted growth, especially notable in potatoes and beet crops
- Browning or necrosis at leaf margins
- Diminished plant vigor and yield
Specific diseases spread by leafhoppers, such as Beet Curly Top Virus (BCTV) and beet leafhopper-transmitted virescence agent (BLTVA), can devastate entire fields if unchecked. The economic thresholds for intervention vary by crop and region, making monitoring and timely action vital.
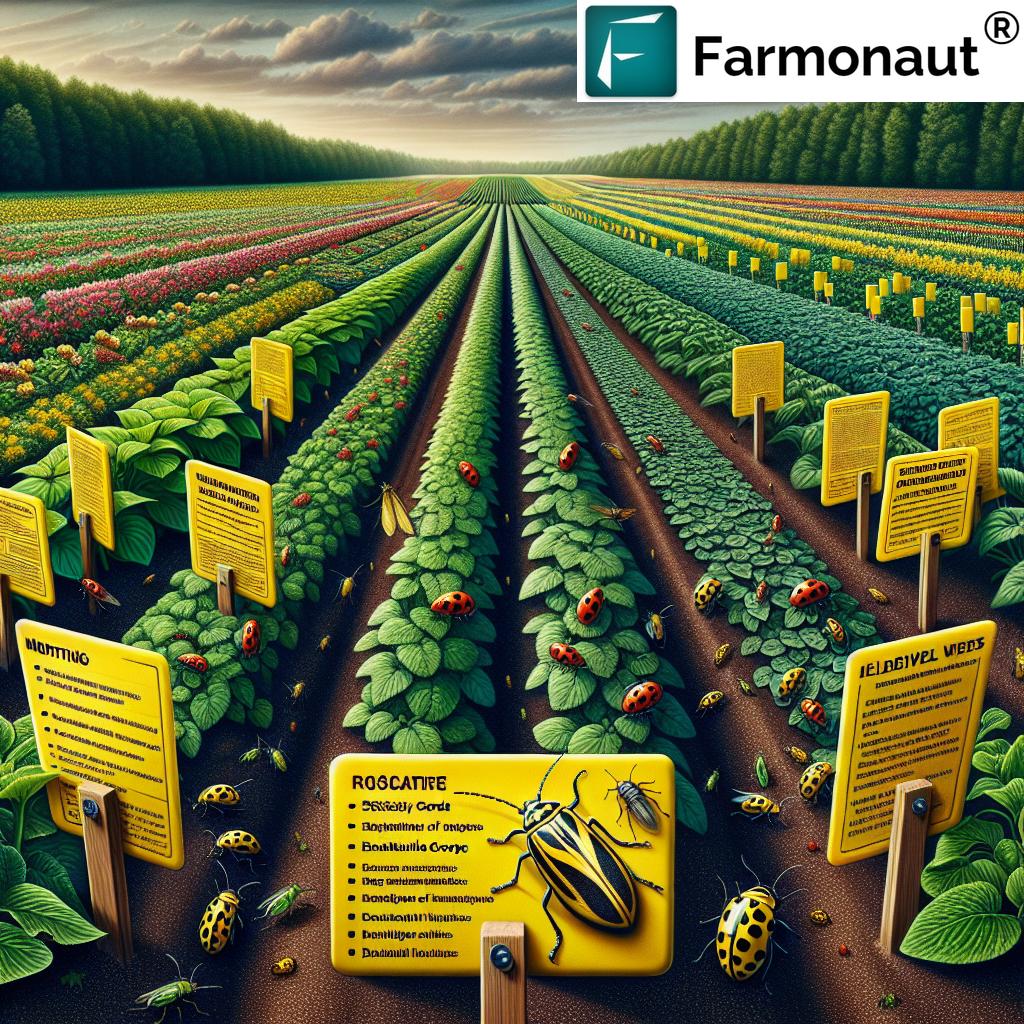
Leafhopper Monitoring Methods: Early Detection Is Key
How do we know when leafhoppers are present—and when to act? The answer lies in vigilant, systematic leafhopper monitoring methods. Regular monitoring is foundational to all integrated pest management for leafhoppers and enables cost-effective, targeted responses.
Effective Monitoring Strategies
- Visual Inspections: Check for signs of leaf curling, stunting, and discoloration on susceptible crops like potatoes and beets.
- Yellow Sticky Cards: Deploy these traps 5-10 feet from field edges; check and replace weekly to estimate population trends and migration.
- Sweep Nets: Sweep vegetation in a standardized manner to physically collect adults and nymphs for identification and counting.
Monitoring is best done weekly during the peak growing season to catch population spikes before they become overwhelming. If counts exceed crop-specific thresholds, it’s time to implement additional control measures.
“Monitoring fields weekly can decrease leafhopper infestations by 30%, protecting plant health and boosting productivity.”
Comparison Table: 7 Shocking Leafhopper Control Methods
To empower our decision-making process, let’s compare the leading leafhopper control methods across practical criteria. This strategy table provides estimated averages, cost implications, and suitability by crop type so we can select the ideal approach for specific situations.
| Leafhopper Control Strategy | Estimated Effectiveness (% Reduction in Infestation) | Cost per Acre (USD) | Environmental Impact | Implementation Time (Days) | Suitability for Crop Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural Controls | 30-40% | $5-$25 | Low | 7-21 | All major field crops, vegetables |
| Biological Controls | 20-35% | $10-$50 | Low | 14-30 | Vegetables, alfalfa, orchards |
| Chemical Insecticides | 50-80% | $15-$80 | Medium/High | 1-7 | Field crops, high-value vegetables |
| Physical Controls | 20-30% | $20-$70 | Low | 2-10 | Vegetables, nurseries |
| Planting Resistant Varieties | 35-65% | Varies* | Low | Varies* | Beet, potato, corn, others |
| Timely Planting & Field Sanitation | 25-45% | $5-$20 | Low | 7-30 | All crops |
| Technology-Based Management (e.g., Satellite, AI) | 40-60% | $10-$60 | Low | Instant to 14 | All crops |
*Varies depending on seed price and variety availability.
Leafhopper Control: 7 Shocking Ways to Save Your Crops
Let’s delve deeper into each method—understanding what it is, how it works, and where it fits into our integrated pest management approach for leafhopper infestations.
1. Cultural Controls: Proactive IPM Fundamentals
Cultural controls form the backbone of sustainable leafhopper control in agriculture, farming, and forestry. These techniques minimize the likelihood and severity of pest outbreaks by modifying the cropping environment and management practices.
- Crop Rotation: Interrupts the life cycle by alternating non-host crops
- Maintaining Crop Health: Vigorous, well-fertilized and properly irrigated plants can withstand minor infestations better
- Removing Volunteer Plants and Weeds: Eliminates alternate hosts—critical since many leafhoppers breed on wild or weedy plants before moving to our fields
In each growing region, adopting these proactive measures is not just effective for leafhopper management in agriculture, but also enhances soil quality, reduces pathogen carryover, and promotes overall plant health.
2. Biological Control of Leafhoppers: Harness Nature’s Allies
Biological controls use living organisms—mostly predators and parasitoids—which naturally attack and suppress leafhopper populations. An example is the introduction or conservation of lady beetles, lacewings, and parasitic wasps that target eggs, nymphs, or adults.
- Lady Beetles & Lacewings: Devour nymphs and soft-bodied leafhoppers
- Parasitic Wasps: Lay eggs inside or on leafhopper eggs/nymphs, killing them before adulthood
- Minimize Harmful Pesticide Use: To conserve these beneficial insects, avoid broad-spectrum insecticides
These methods align perfectly with integrated pest management for leafhoppers and serve as a cornerstone for organic or low-input growers.
3. Chemical Insecticides for Leafhoppers: Threshold-Based Precision
While synthetic chemical insecticides can be very effective, they should be used judiciously—only after careful monitoring confirms that populations exceed locally established economic thresholds. Options include:
- Systemic and contact insecticides formulated for the target crop and pest
- Application after weekly scouting, starting post first harvest or cutting (alfalfa), and continuing until end of season if needed
- Rotating active ingredients to prevent resistance development
Always read and follow local label recommendations for safety and environmental stewardship. Residual sprays can control several generations, but overuse may trigger resistance or destroy non-target, beneficial organisms.
4. Physical Controls: Barriers and Deterrents
Physical methods for leafhopper control are often overlooked, but can play a crucial supporting role—especially in small-scale, high-value crops and nurseries.
- Reflective Mulches (Aluminum Foil/Plastic): The shiny surface disorients and deters leafhoppers from landing and settling
- Floating Row Covers: Exclude leafhoppers during critical establishment phases
- Sticky Traps: Not just for monitoring, but also for localized mass trapping of adults
Use these methods alongside cultural and biological controls for best results in integrated pest management for leafhoppers.
5. Planting Leafhopper Resistant Crop Varieties
Advances in breeding have yielded promising leafhopper resistant crop varieties for a range of field, vegetable, and orchard crops. Breeding resistance into susceptible crops like beets, potatoes, and corn promises substantial reductions in both feeding damage and disease transmission.
- Choose Resistant Seed Varieties: Confirm tolerance to local pest and disease pressures
- Consult Extension Recommendations: Regional extension offices or crop advisors can identify top-performing lines
- Less reliance on chemical interventions—lowering overall management costs
Integrating this approach with other IPM strategies can yield a sustainable, long-term reduction in leafhopper problems and withstand population surges.
6. Timely Planting and Field Sanitation for Preventing Leafhopper Diseases in Crops
Prevention is always better than cure—timing our sowing and maintaining field hygiene are core IPM strategies that have stood the test of time.
- Early Planting: Sow crops before leafhopper populations peak to minimize risk
- Remove Crop Residues & Weeds: Eliminates overwintering and breeding hosts
- Sanitize Field Equipment: Prevents inadvertent pest transfer between fields
A small investment in these preventive measures can yield major dividends in terms of crop protection and yield security.
7. Technology & Innovation: Satellite-Based Leafhopper Management
Innovation has added powerful weapons to our pest management arsenal. Farmonaut offers affordable, real-time satellite-based crop health monitoring—enabling us to detect biotic and abiotic crop stress before visible symptoms or yield loss occurs.
- NDVI Imagery: Detects areas of stress associated with leafhopper feeding, nymph feeding, or disease transmission long before human scouting would reveal a problem
- Weekly Monitoring and Automated Alerts: Monitor vast fields, orchards, or forests without exhaustive manual labor
- AI Crop Advisory: Receive precise, actionable advice on pest control timing, reducing unnecessary chemical use and maximizing ROI
- Traceability & Compliance: With blockchain-based traceability from Farmonaut, maintain full transparency on crop protection actions and inputs for supply chain integrity
- API-Driven Integration: Developers and agritech businesses can integrate Farmonaut’s satellite and weather API for custom, crop-wide pest monitoring solutions
Explore the transformation of your crop management using Farmonaut’s crop health monitoring technologies and experience the power of data-driven IPM!
Leverage carbon footprinting solutions by Farmonaut to monitor and manage the environmental impact of your IPM measures—aligning productivity with sustainability goals.
For those managing larger operations, Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management tools offer advanced analytics, resource management, and field-level insights to organize field teams and logistics during scouting and intervention.
If you’re an agribusiness or food processor, Farmonaut’s traceability suite ensures every intervention is recorded and available for blockchain-backed audit-trails, creating transparency and trust down the supply chain.
Challenges in Leafhopper Management: Resistance & Environmental Impact
Despite our best efforts, leafhopper management poses ongoing challenges that must be acknowledged and addressed within any IPM framework.
- Resistance Development: Overuse or continuous use of a single class of insecticides accelerates selection for resistant populations.
- Environmental Impact: Non-selective chemical applications may eliminate beneficial insects, cause ecological imbalances, or leave damaging residues in soil and water.
- Economic Considerations: Integrating multiple strategies may require upfront investment in monitoring, premium seed varieties, or advanced tools—and returns manifest only across several seasons or in protected yields.
This is why data-driven, threshold-based intervention—minimizing chemical inputs while maintaining robust surveillance—is essential for modern, sustainable farming.
Farmonaut’s Role in Integrated Pest Management for Leafhoppers
Farmonaut is pioneering affordable, scalable solutions for every type of grower—from smallholder farmers in India to large-scale agricultural enterprises in North America. As champions of technology & innovation, our mission is to make precision agriculture accessible to all, empowering us to:
- Monitor fields in real-time using NDVI, soil moisture, and crop health indices derived from multispectral satellite imagery
- Adopt AI-driven advisory systems (Jeevn AI) to receive personalized pest management and weather guidance
- Ensure traceability of crop protection inputs and interventions via blockchain ledgers
- Track carbon footprint and resource usage to align IPM with environmental targets (Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting)
- Integrate monitoring and data with other software via our comprehensive developer API documentation
- Support secure and rapid satellite verification for crop loans and insurance, reducing fraud risk and easing farmer access to institutional support.
No matter your crop, region, or scale of operation, Farmonaut equips us with the data-driven insights and actionable tools needed for smart, sustainable, and profitable farming well into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions: Leafhopper Control
What are the best ways to identify leafhopper infestations in my fields?
Regular visual inspections, yellow sticky cards placed at the edge of fields (checked weekly), and sweep net sampling are all effective monitoring methods. Satellite-based crop health monitoring from Farmonaut can highlight stress patterns associated with early infestations—even before physical symptoms appear.
How can I prevent development of insecticide resistance in leafhopper populations?
Avoid repeated use of the same chemical class. Rotate products, only spray when monitoring shows economic thresholds are exceeded, and support interventions with cultural and biological controls to reduce overall insecticide reliance.
Are there truly leafhopper resistant crop varieties available?
Yes, breeding programs in regions like the US, Australia, and the EU have developed varieties of potato, beet, and corn with documented tolerance or resistance to important leafhopper-vectored diseases. Consult local extension for the best varieties adapted to your region.
How quickly should I implement controls after spotting leafhopper symptoms?
Act swiftly—ideally within days—if you notice stunting, leaf curling, or population spikes exceeding thresholds. Combining rapid cultural measures, targeted chemical controls, and AI-advised decision-making provides the best chance of saving crop yield.
How does Farmonaut integrate with my existing crop management process?
Farmonaut seamlessly overlays crop health data on maps of your fields. You receive visual alerts, NDVI imagery, and personalized advice via web, Android, or iOS apps—enabling rapid, informed interventions. For large-scale or enterprise users, API integration and traceability further streamline compliance, documentation, and sustainability efforts.
Conclusion: Protect Your Crops and Yields
Leafhoppers are small, but their impact on our agriculture, farming, and forestry systems can be enormous. By understanding their biology, recognizing the symptoms, and applying a smart combination of cultural, biological, chemical controls, and technological innovation, we can reduce infestations and safeguard plant health across all our crops.
Using Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management tools makes this battle significantly more winnable—putting cutting-edge data-driven decision solutions into the hands of all growers. Our commitment is to deliver affordable, scalable, and effective support to everyone in the agricultural value chain, from the first-time farmer to the world’s largest agribusiness enterprise.
Leafhoppers are impactful pests endangering crop yields worldwide through direct feeding and transmission of devastating plant diseases. Effective integrated pest management incorporates vigilant monitoring, cultural and biological controls, resistant crop varieties, and timely interventions with chemicals only when needed. Farmonaut’s affordable, satellite-based farm management suite empowers farmers, cooperatives, and agribusinesses to precisely track crop health and optimally allocate resources, leading to higher yields, reduced resource wastage, and sustainable agricultural practices. Protect your yields and secure your harvests with innovative technology and actionable data—discover Farmonaut today.