10 Innovative Agricultural Technologies Changing Farming
“Precision agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 20% using data-driven decision-making.”
- Introduction
- Comparative Table: Top 10 Innovative Agricultural Technologies
- 1. Precision Agriculture
- 2. Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) & Vertical Farming Solutions
- 3. Agrivoltaics
- 4. Aeroponics
- 5. Cellular Agriculture
- 6. AI in Agriculture & Machine Learning
- 7. Robotics in Modern Farming
- 8. Blockchain in Agriculture
- 9. Nanotechnology in Agriculture
- 10. CRISPR Gene Editing
- Smart Irrigation Systems
- Bee Vectoring Technologies (BVT)
- Farmonaut: Accelerating Precision Farming
- Farmonaut Subscription Plans
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the face of growing climate change, resource scarcity, and heightened demands for sustainable food production, innovative agricultural technologies are transforming the way we farm. Across every continent, traditional farming practices are being revamped with the help of precision agriculture, advanced sensors, data analytics, and AI-powered tools. These advancements not only boost productivity and crop yields, but also promote efficiency, environmental stewardship, and resource optimization.
As we explore these key innovations, we will discover how tools like Farmonaut’s satellite-based farm management solutions and smart irrigation systems are revolutionizing the agriculture, forestry, and crop production sectors worldwide.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through 10 innovative agricultural technologies that are helping us meet the global challenges of food security, resource management, and sustainable growth.
Comparative Table: Top 10 Innovative Agricultural Technologies
| Technology Name | Primary Function/Benefit | Estimated Yield Improvement (%) | Estimated Cost Savings (%) | Environmental Impact | Adoption Rate (Global %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Agriculture | Data-driven decision-making, optimized input use | 10–20% | 8–15% | Reduces waste, lowers chemical usage | 15% |
| Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) | Stable, year-round, high-efficiency crop production | 20–30% | 10–25% | Reduces water use, limits pesticides | 7% |
| Agrivoltaics | Combines solar energy and farming | 5–15% | 10–20% | Produces renewable energy, reduces water evaporation | 1% |
| Aeroponics | Soilless, high-density plant growth | 15–25% | 12–20% | Minimal water use, less land required | 2% |
| Cellular Agriculture | Lab-grown food products, animal alternatives | N/A (alternative products) | Varies | Lowers emissions, reduces land use | <1% |
| AI & ML in Agriculture | Predictive analytics, yield forecasting | 5–22% | 5–20% | Optimizes resource use, reduces waste | 11% |
| Robotics | Automates planting, harvesting, weeding | 7–18% | 15–30% | Reduces labor, limits inputs | 4% |
| Blockchain Technology | Secures traceability and transparency | 2–10% | 3–12% | Reduces fraud, ensures food safety | <1% |
| Nanotechnology | Improves nutrient delivery, early disease detection | 5–12% | 7–15% | Reduces chemical usage, enhances protection | 3% |
| CRISPR Gene Editing | Enhances crop traits, resilience | 10–25% | 5–15% | Tailored to climate and pest resistance | 1% |
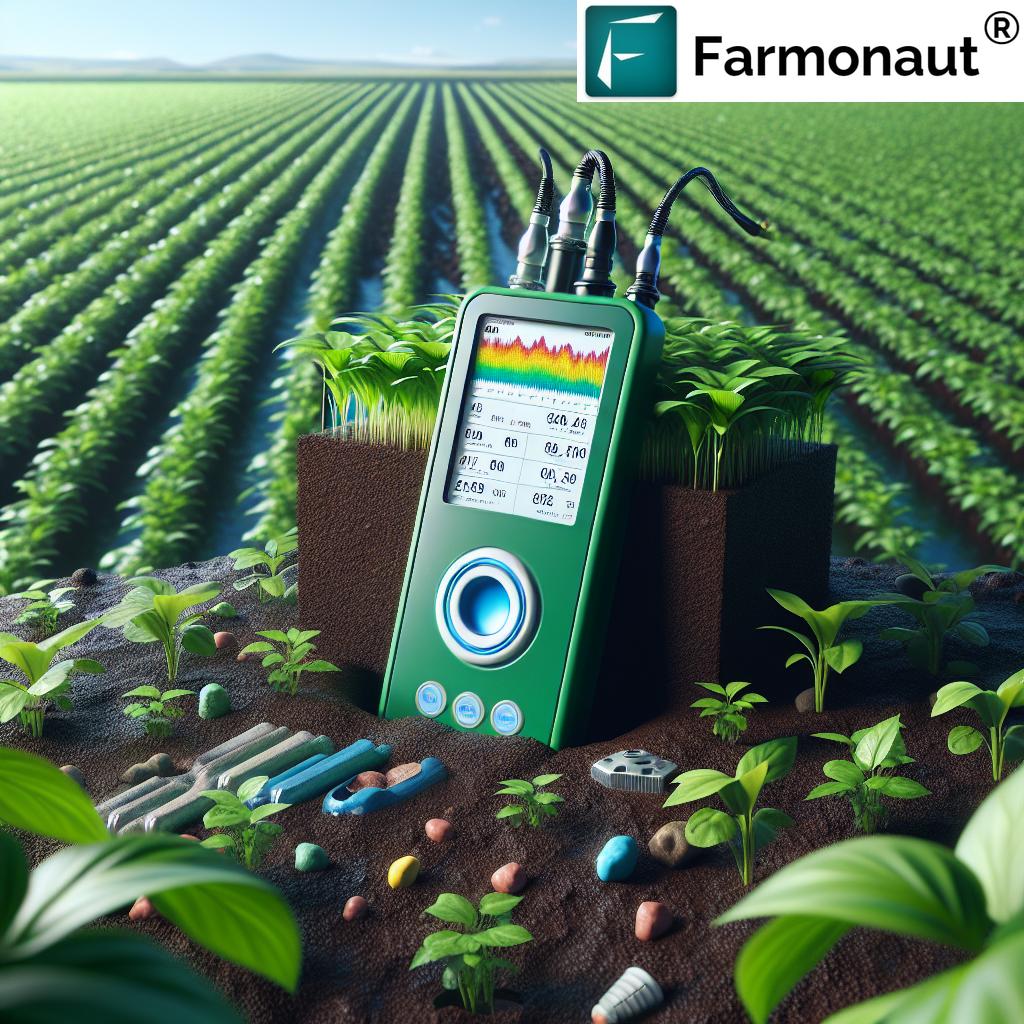
1. Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Decisions Transforming Yields
Precision agriculture is at the forefront of the digital transformation in farming. Utilizing advanced tools such as GPS, IoT sensors, remote sensing, and actionable data analytics, we can monitor and manage field variability in real-time.
How does it work? By integrating sensor data on soil moisture, nutrient levels, crop health, and weather with geospatial mapping, farmers can:
- Deliver targeted irrigation and fertilization (enabling resource efficiency and minimizing waste)
- Reduce usage of pesticides and fertilizers, limiting environmental impact
- Increase crop yields by as much as 20% (supported by agricultural data analytics)
- Ensure precise management of labor, time, and machinery
Major platforms, like Farmonaut, make precision agriculture accessible to all farmers, regardless of operation scale:
- Farmonaut’s Crop Health Monitoring—Monitor crop health using multispectral satellite images (NDVI) for nutrient and moisture optimization, weed and pest detection, and yield projection.
- Farmonaut API—Integrate satellite and weather data into custom tools for seamless, automated farm management.
- API Developer Docs—For agritech and research teams building next-gen solutions.
By optimizing inputs and labor, precision agriculture delivers sustainable productivity gains, aiding environmental stewardship while countering climate change and resource scarcity.
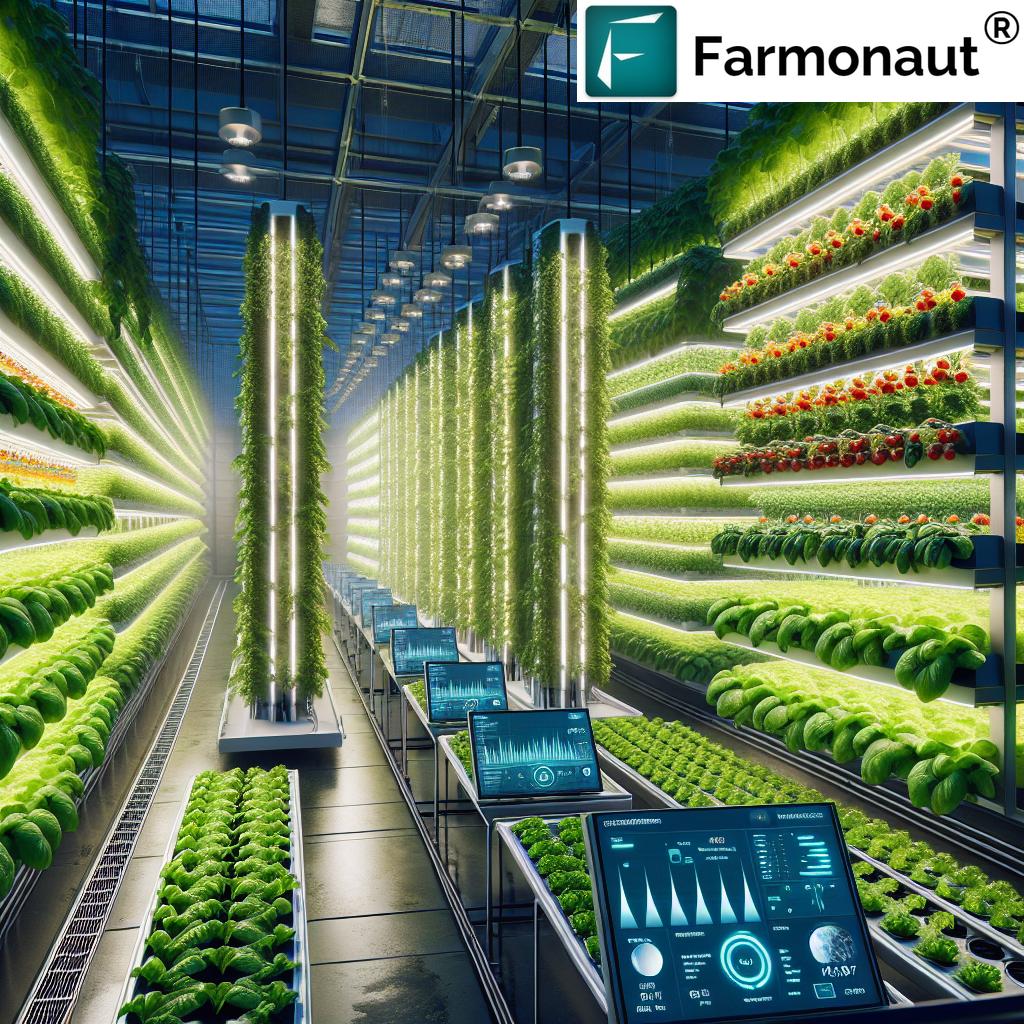
2. Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) & Vertical Farming Solutions
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) enables us to cultivate crops in regulated environments—from greenhouses to climate-controlled vertical farming towers. By managing light, humidity, temperature, and CO2 levels, we create optimal growth conditions, boosting productivity and enabling year-round harvests.
Vertical farming solutions take this further by stacking layers of crops in compact indoor facilities, maximizing space in urban areas where land is limited. Benefits include:
- Up to 95% reduction in water usage (vs traditional farming)
- Minimal pesticide requirement due to controlled environments
- Stable, predictable yields regardless of external weather factors
- Sustainable production in cities, reducing transportation emissions and delivery time
With CEA, advancements in hydroponics and aeroponics, urban agriculture can thrive—even in areas facing water stress, soil depletion, and changing climates.
If you manage large-scale farming, Farmonaut’s Large-Scale Farm Management Platform streamlines operations, satellite monitoring, and efficiencies across distributed landholdings.
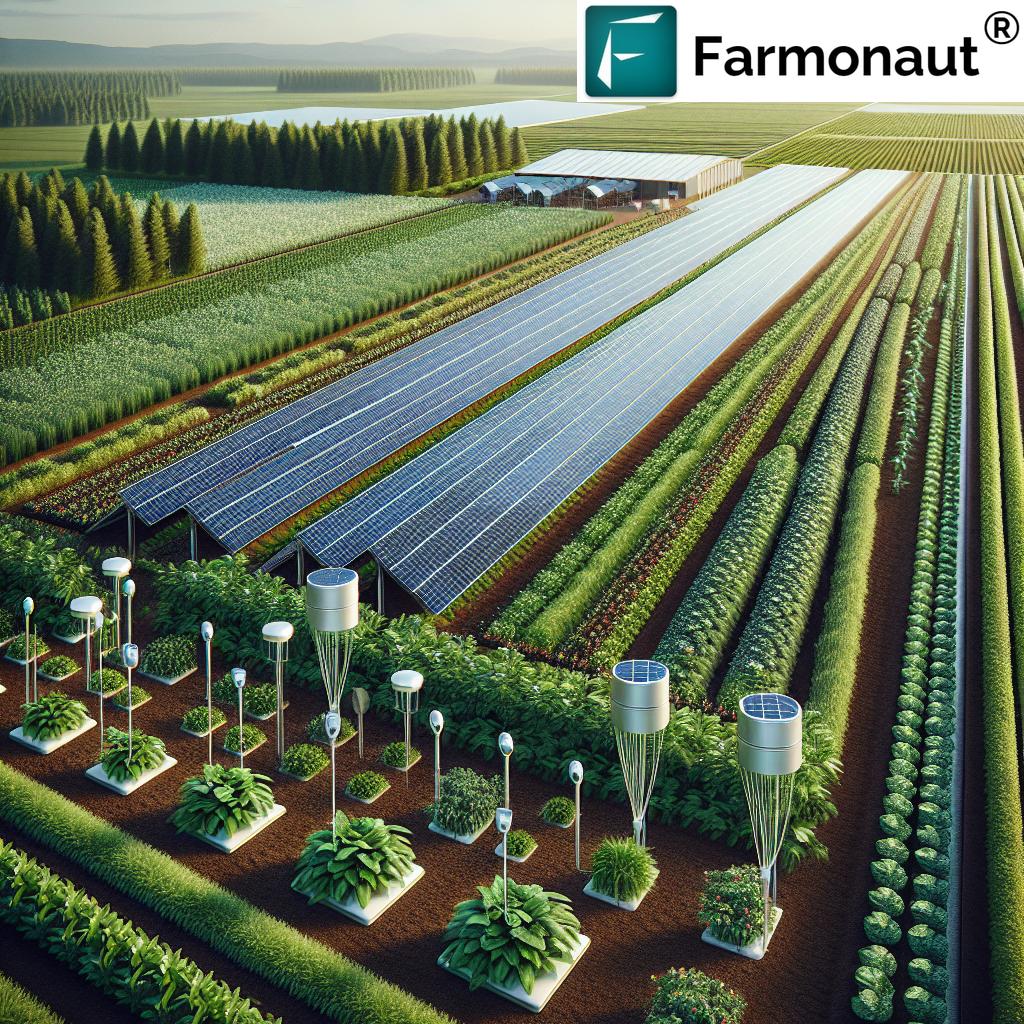
3. Agrivoltaics: Harnessing Solar Power & Growing Crops Together
As energy and food demands rise, agrivoltaics—the co-location of solar panels and agriculture—offers a truly innovative model for sustainable farm development. By installing solar panels above fields, we achieve simultaneous renewable energy production and crop cultivation, maximizing land resources.
Benefits include:
- Reduced soil moisture evaporation—shaded crops lose less water, requiring less irrigation.
- Shielding plants from extreme temperatures and weather changes, improving resilience and yields.
- Generation of clean energy for farm operations or sale to the grid, creating new revenue streams.
Research shows that crops such as lettuce, tomatoes, and strawberries can thrive under partial shade from solar panels. This system is particularly impactful for regions facing resource scarcity or seeking to reduce environmental impact by integrating renewable energy into food production.
4. Aeroponics: Next-Level Soilless Cultivation
Aeroponics represents a cutting-edge method in soilless, high-efficiency crop production. Plants are anchored in support structures while their roots dangle in the air, exposed and routinely misted by precision nutrient solutions.
Key advantages for the future of urban farming and high-density crop production:
- Extremely low water usage—up to 95% less than soil-based farming.
- Accelerated plant growth and higher yields, particularly for leafy greens, herbs, and specialty crops.
- Ability to deploy in urban centers, basements, or areas with depleted or contaminated soils.
- Enables vertical stacking, dramatically increasing per-square-meter yields.
By enabling targeted delivery of nutrients, optimized irrigation, and year-round protection from weather and disease, aeroponics empowers sustainable food production in the most challenging environments.
5. Cellular Agriculture: Cultured Foods & a Sustainable Future
Cellular agriculture harnesses biotechnology to create lab-grown food products from animal and plant cell cultures—such as cultivated meat, milk, and eggs. By moving food production away from traditional livestock farming, cellular agriculture offers pathways to:
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water, and land usage
- Promote animal welfare and address ethical issues
- Deliver high-protein, customizable foods to meet global nutrition needs
As a next-generation alternative, these solutions may help feed a growing population with lower environmental costs, paving the way for sustainable food systems.
6. AI in Agriculture & Machine Learning Revolution
From weather prediction to crop disease detection, AI and machine learning are revolutionizing agricultural efficiency and decision-making. Expressions like “AI in agriculture“, “agricultural data analytics“, and “crop monitoring sensors” are not just buzzwords: they’re powering tangible advances on the ground.
Smart platforms analyze vast data streams, including satellite imagery, field sensors, and historical records, enabling:
- Automated yield forecasting and risk management
- Early pest, disease, and nutrient deficiency detection via image analysis
- Precise recommendations for irrigation, fertilization, and harvesting schedules
Farmonaut leads with its Jeevn AI Advisory System—empowering farmers worldwide to receive real-time, localized advice for boosting yields, efficiency, and resource use.
Access AI-driven insights directly on mobile and web platforms:
“Smart irrigation systems can reduce water usage in farming by as much as 30%.”
7. Robotics in Modern Farming: Automation for Greater Efficiency
Robotics and autonomous systems are fundamentally reshaping agriculture, forestry, and food production sectors. With computer vision and advanced guidance, robots can handle:
- Planting seeds with precise spacing (optimizing yields and reducing waste)
- Weeding and targeted pest control (minimizing chemical use)
- Fruit & vegetable harvesting with minimal crop damage
- Sorting and packaging for rapid market delivery
Robotic automation offers reliable solutions for labor shortages, reduces operational costs, and supports productivity improvements.
For large-scale operations, dedicated Fleet Management Tools are available—helping agribusinesses optimize equipment usage, reduce fuel waste, and track field operations efficiently.
8. Blockchain in Agriculture: Transparency & Traceability in Food Chains
The integration of blockchain technology into agriculture ensures food authenticity, safety, and transparency across complex supply chains. Blockchain records every stage—planting, harvesting, processing, transport, and retail—in an immutable digital ledger, enabling:
- Full product origin and journey transparency
- Protection against food fraud and tampering
- Stronger consumer trust in food safety and quality
For corporate supply chain managers, Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Traceability Solution offers seamless implementation, real-time tracking, and secure data integration with minimal setup.
9. Nanotechnology in Agriculture: Enhanced Crop Protection
By deploying nanoparticles and advanced nanosensors, nanotechnology takes crop management and plant protection to the next level. Applications include:
- Controlled-release fertilizers and pesticides—only delivered where and when needed, reducing chemical runoff and environmental harm
- Early detection of plant diseases with nanoscale sensors—enabling timely intervention and minimizing damage
- Enhanced absorption and efficacy of nutrients by plants, promoting higher yields
This technology supports sustainable farming practices, cleaner food, and reduced environmental impact worldwide.
10. CRISPR Gene Editing: Customizing Crops for Resilience
The rise of CRISPR gene editing is accelerating crop improvements, allowing us to:
- Enhance drought tolerance and pest resistance
- Increase nutritional value (e.g., vitamins, amino acids)
- Accelerate breeding of new varieties matched to evolving climate and regional needs
By altering DNA directly at targeted sites, CRISPR enables rapid, precise trait enhancement—even where traditional breeding would take decades. This approach makes crops more resilient and boosts food security globally.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Precision Water Use for Sustainable Farming
Smart irrigation systems leverage in-field sensors and weather data to deliver just the right amount of water, exactly when and where it’s required.
The advantages for farmers and the environment:
- Soil sensors monitor moisture levels in real-time, allowing data-driven decisions.
- Irrigation automatically adapts to rainfall, evaporation rates, and crop stage—minimizing water waste.
- Up to 30% reduction in water usage (significant for regions facing water scarcity).
- Limits disease risk from over-watering and reduces fertilizer runoff.
Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting Solution empowers agribusinesses to monitor and optimize environmental impact and water use. These insights help us reduce carbon emissions and ensure compliance with sustainability goals.
Bee Vectoring Technologies (BVT): Nature-Based Crop Protection Agents
Bee Vectoring Technologies (BVT) harness the natural foraging behavior of bees to deliver biological crop protection agents right to the flowers, precisely where they are needed.
This innovative method supports both environmental and productive outcomes by:
- Minimizing chemical pesticide usage (reducing residues, runoff, and impact on pollinators)
- Improving pollination and increasing crop yields
- Enabling targeted application, promoting healthy plants and sustainable farming
Integrating BVT into standard farm routines promotes both crop health and pollinator vitality, supporting environmental stewardship at every level.
Farmonaut: Accelerating Precision Farming for the 21st Century
As we’ve explored, innovative agricultural technologies are revolutionizing farming, forestry, and crop production worldwide. Farmonaut stands at the forefront of this transformation, empowering farmers, agribusinesses, governments, and corporate supply chains with accessible, data-driven solutions:
Key Farmonaut Technology Solutions:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Multi-spectral imagery for real-time crop growth, health, and soil moisture analysis—enabling targeted irrigation, fertilization, and pest management.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Personalized, AI-driven recommendations concerning crop health, weather forecasting, and farm management.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Transparent, secure tracking of agricultural products from field to consumer.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Tools for plantation management, logistics optimization, and asset tracking—cutting down operational costs and improving on-farm efficiency. Explore fleet capabilities here.
- Carbon Footprinting: Advanced insights into emissions and resource consumption to promote sustainability for all agriculture stakeholders.
With an intuitive Android app, iOS app, and web platform, Farmonaut delivers precision agriculture and field analytics directly to your fingertips.
Discover the advantages for advisory, research, supply chain transparency—or accelerated loan and insurance verification for financiers—on our Farmonaut crop, plantation, and forest advisory platform.
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Our flexible subscription model makes precision agriculture affordable and accessible—scalable for small farmers, cooperatives, agribusinesses, and institutions worldwide. Monitor your fields via the web, API integration, or mobile apps.
FAQ: Innovative Agricultural Technologies
What is precision agriculture?
Precision agriculture uses advanced technology, including satellites, IoT sensors, data analytics, and GPS, to optimize crop management, reduce input waste, and increase yields. Platforms like Farmonaut make it affordable and accessible for farmers of every scale.
How does smart irrigation improve efficiency?
Smart irrigation systems use soil and weather data to apply precise water amounts, reducing waste by up to 30% and promoting sustainable agriculture, especially in water-scarce regions.
What are the benefits of blockchain in agriculture?
Blockchain technology ensures food transparency, traceability, and authenticity. Every supply chain step is recorded, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing consumer trust.
What is the difference between vertical farming and traditional farming?
Vertical farming stacks crops in controlled, indoor environments using less land, water, and chemicals, with higher yield per square meter. It eliminates many constraints faced in traditional outdoor farming.
How does Farmonaut enable sustainable farming practices?
Farmonaut empowers users with real-time crop health monitoring, AI-based advisories, resource management, blockchain-supported traceability, and carbon footprint analytics for sustainable, efficient farming operations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Sustainable Farming
As we’ve seen, the adoption of innovative agricultural technologies—from precision agriculture and AI-powered analytics to controlled-environment agriculture and blockchain in agriculture—is revolutionizing the way we grow food, manage resources, and protect the environment. By leveraging advanced systems for monitoring, resource allocation, traceability, and sustainability, we can meet the challenges of climate change, water scarcity, and global food security.
Agricultural stakeholders—from individual farmers to large corporate producers and supply chains—are empowered to make smarter, more informed decisions. Tools like Farmonaut bring precision, real-time data, and transparency to every field, revolutionizing farming one pixel and one insight at a time.
The future of agriculture lies in embracing technology, prioritizing sustainability, and using actionable data to feed a growing world population—efficiently, responsibly, and with care for our planet.