Biologicals in Agriculture: 7 Shocking Benefits Revealed!
“Biologicals can increase crop yields by up to 20% while reducing chemical pesticide use by 30%.”
Summary: Biologicals in Agriculture – A Comprehensive Overview
In recent years, we have witnessed a significant shift towards sustainable practices in global agriculture. At the core of this transformation lies the adoption of biologicals—natural solutions and products that leverage the power of microorganisms, plants, and natural processes to enhance crop growth, protect against pests and diseases, and improve soil health. This article offers a deep dive into biologicals in agriculture, exploring their classification, uptake, wide-ranging benefits, ongoing challenges, future trends, and how emerging technologies (like those offered by Farmonaut) empower farmers to optimize their integration and adoption.
Understanding Biologicals in Agriculture
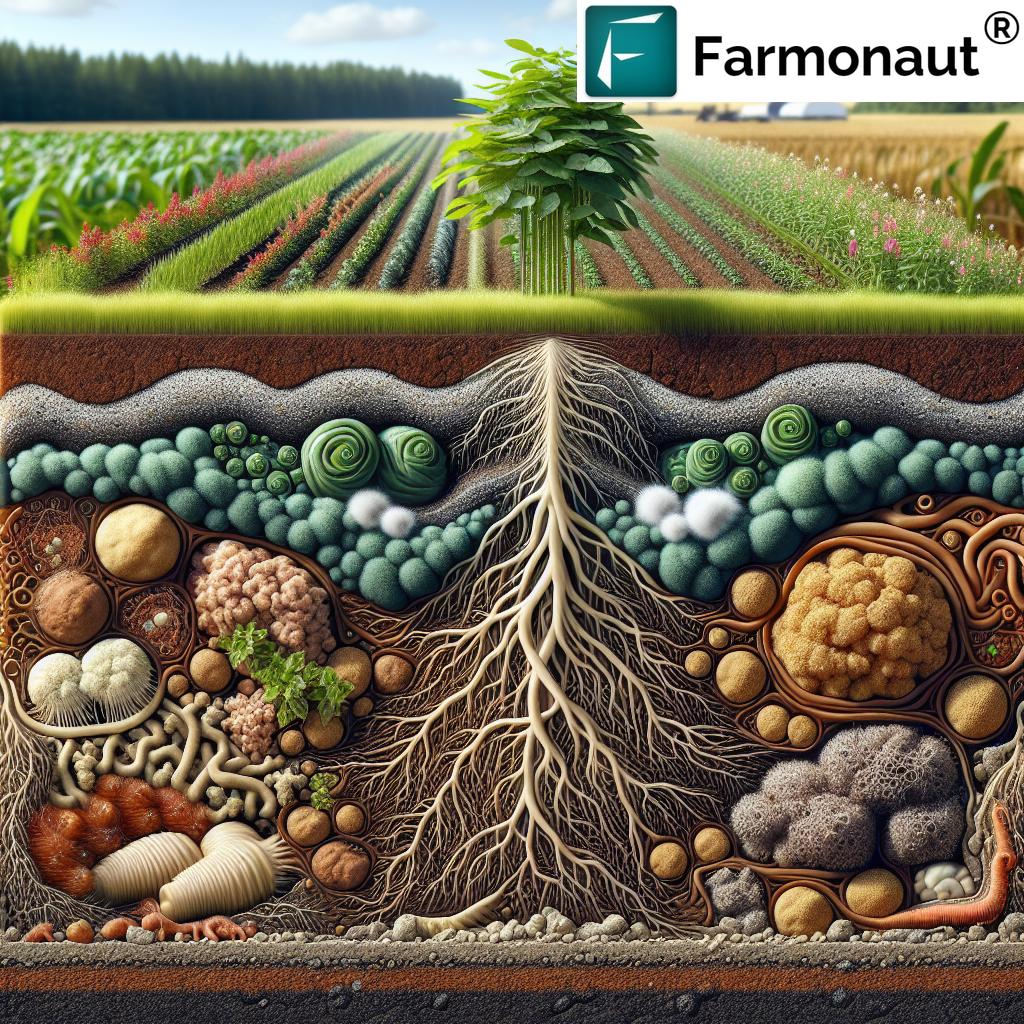
Biologicals are living organisms, their byproducts, or naturally derived substances used in agriculture to enhance plant growth, protect crops, and improve soil health. Unlike conventional synthetic chemicals, biologicals work by reinforcing or stimulating the natural processes and defenses present in ecosystems. These innovations play a vital role in sustainable farming practices by reducing reliance on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, decreasing residues in food, and promoting long-term soil fertility and agricultural productivity.
The surge in interest for agricultural biological products stems from diverse factors:
- Growing environmental awareness due to the negative impacts of synthetic chemicals on biodiversity, water, and soil
- Stringent regulations on residue limits and pesticide usage, especially for export-oriented crops
- Consumer demand for organic crop protection and safe food
- The need to address pest resistance to conventional inputs
- The global imperative to promote soil health and climate resilience in the face of changing weather patterns
“Over 60% of farmers using biologicals report improved soil health within just two growing seasons.”
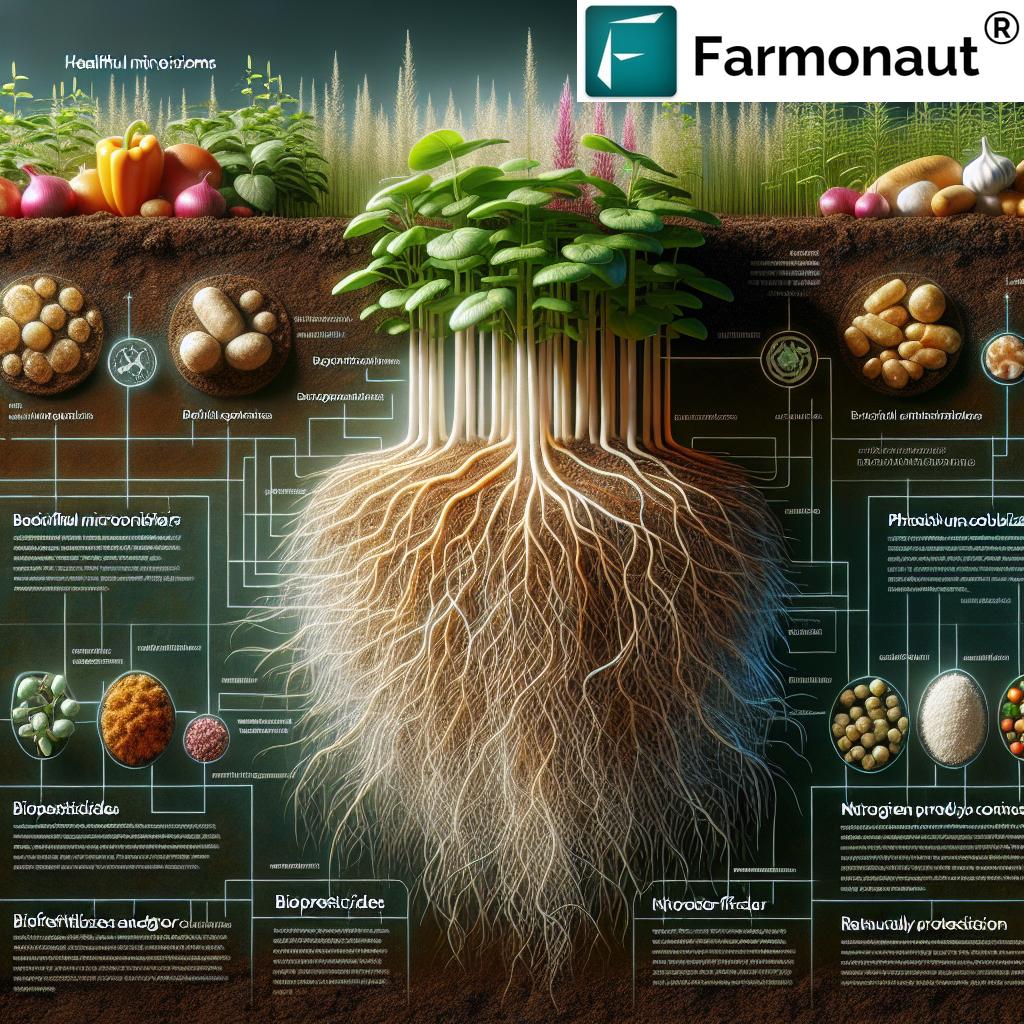
Types and Classification of Biologicals
Let’s deepen our understanding by categorizing biologicals in agriculture into primary groups based on their origin and usage. This helps us see their unique mechanisms and how they fit integrated sustainable farming practices.
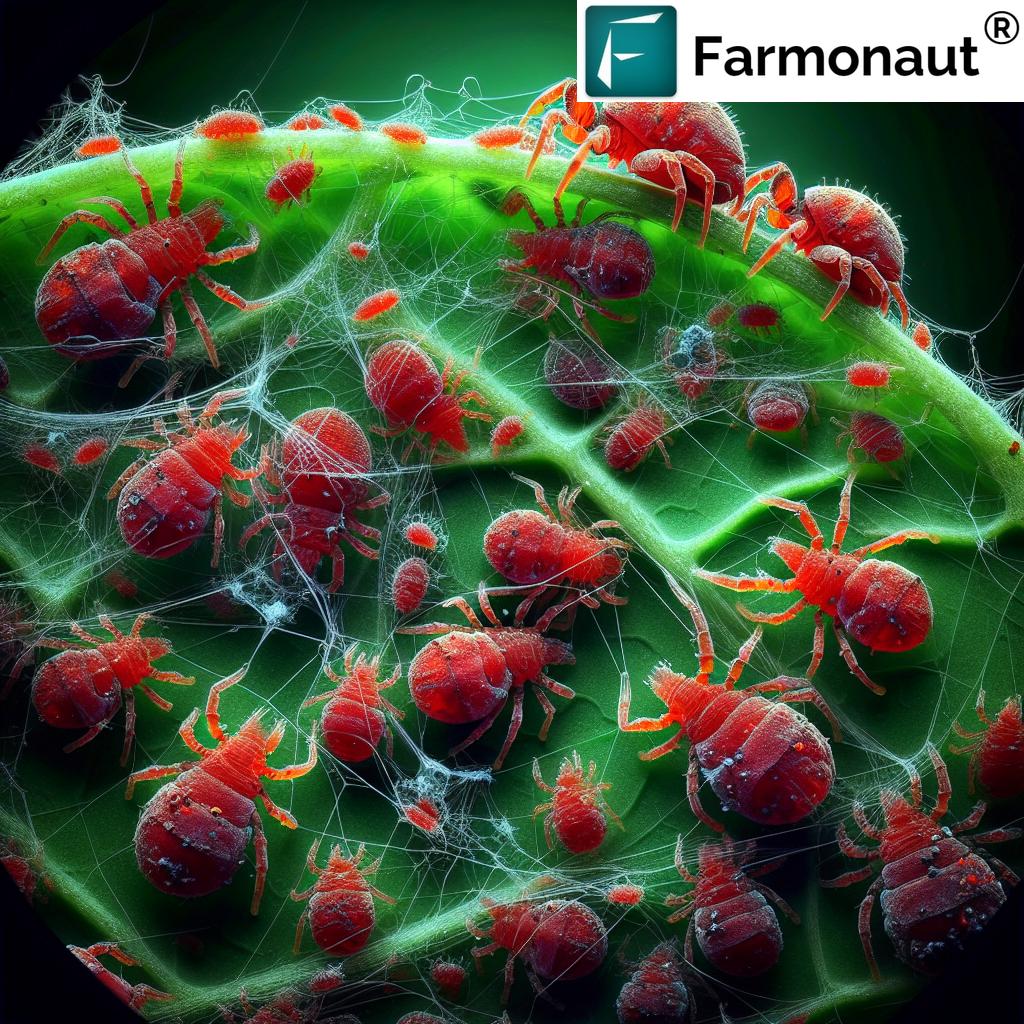
1. Biopesticides for Pest Control
These are natural substances or living organisms used to control pests and diseases. Types include:
- Microbial biopesticides: Utilize bacteria (e.g., Bacillus thuringiensis), fungi, and viruses that specifically target pest organisms without harming beneficial insects or the environment.
- Biochemical biopesticides: Include natural plant extracts, pheromones, or compounds disrupting insect mating or feeding.
- Plant-Incorporated Protectants (PIPs): Substances produced by genetically modified plants that offer innate protection.
Benefits: Biopesticides provide unique modes of action, helping manage resistance in pest populations and supporting organic crop protection efforts.
2. Biostimulants for Plant Growth
Biostimulants are formulated substances or microbes that stimulate natural plant processes for enhanced growth, stress resilience, and nutrient uptake. Types include:
- Microbial biostimulants: Rhizobacteria and mycorrhizal fungi that help plants absorb nutrients and tolerate abiotic stress
- Non-microbial biostimulants: Seaweed extracts, protein hydrolysates, humic substances, amino acids, etc.
Benefits: Improve plant health, stimulate natural defense mechanisms, promote root development and increase tolerance to drought, salinity, and temperature stresses.
3. Biofertilizers for Soil Health
Biofertilizers contain beneficial living microorganisms that increase nutrient availability for plants. They are critical for promoting soil health, restoring fertility, and supporting organic production.
- Nitrogen-fixers: Convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants (e.g., Rhizobium, Azotobacter).
- Phosphate-solubilizers: Enable plants to absorb phosphorus from soil minerals.
- Potassium-mobilizing bacteria, mycorrhizal fungi, etc.: Improve the uptake of additional key nutrients.
Benefits: Reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers, improve soil structure and fertility, and foster healthy soil microbial ecosystems.
Note: All three categories are aligned with integrated pest and nutrient management strategies, and are key to carbon footprint reduction and responsible stewardship of agricultural ecosystems.
Applications: How Are Biologicals Utilized in Agriculture?
Across the globe, biologicals are being utilized in diverse ways to protect crops, improve soil, boost yields, and manage pests and diseases. The principal applications of agricultural biological products include:
- Horticultural Crops: In fruit and vegetable production, biologicals manage pests (biopesticides), enrich soils (biofertilizers), and enhance resilience and product quality (biostimulants).
- Broad Acre/Row Crops: Corn, wheat, soybean, and similar crops benefit from seed treatments, foliar sprays, or soil drenches that optimize plant health, improve nutrient efficiency, and offer organic crop protection.
- Greenhouse and Controlled Environment Agriculture: Biologicals are preferred for their safe, residue-free profile, helping manage disease and promote growth in enclosed or high-value production systems.
The adoption and integration of biologicals is growing, due to their synergy with precision agriculture (enabled by data-driven tools, like Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management platform), enabling smarter resource use, sustainability metrics tracking, and reduced environmental impact.
Discover Farmonaut’s agricultural data API and developer documentation to integrate advanced crop and weather insights into your agribusiness or research platform.
7 Shocking Benefits of Biologicals in Agriculture
-
Spectacular Boost in Soil Health
Biologicals—especially biofertilizers for soil health and microbial biostimulants—directly improve soil organic matter, support beneficial microbial activity, and restore the natural nutrient cycling processes. Our nutrient-depleted soils can recover dramatically with the addition of biofertilizers, leading to visible improvements in crop vigor and resilience. -
Reduced Reliance on Synthetic Chemicals
By offering a natural alternative to conventional chemical pesticides and fertilizers, biologicals in agriculture can cut chemical usage by as much as 30% to 50% in some programs. This leads to decreased pesticide residues on food, lower environmental toxicity, and better compliance with global export standards. -
Enhanced Crop Productivity – Naturally!
Through improved nutrient uptake and disease/pest suppression, farmers can expect crop yields to increase by up to 20%. Biostimulants in particular are known to enhance crop productivity naturally even under stress conditions (drought, salinity, and temperature fluctuations). -
Sustainable Pest and Disease Management
Biopesticides for pest control act with new modes of action, slowing the development of resistance seen in pests and pathogens against traditional chemicals. Integrated with precision application, they allow us to manage pests more effectively and keep our fields healthier for longer. -
Eco-Friendly & Biodiversity-Friendly Practices
Biologicals help reduce the detrimental side-effects of chemicals on ecosystems. Microbial inputs are safe for non-target organisms (bees, pollinators, beneficial insects), supporting biodiversity, and creating resilient agroecosystems. -
Improved Market Access and Food Safety
With consumers and trade partners demanding residue-free, sustainably produced food, biologicals offer a clear path. Their use supports certifications, premium pricing, and can open new export opportunities. -
Contributing to Climate-Resilient Agriculture
By restoring soil health and reducing emissions/inorganic fertilizer input, biologicals lower the carbon footprint of farming. With platforms like Farmonaut’s carbon footprint tracking, growers can now measure and set targets for improved sustainability outcomes.
Comparison Table: Biologicals vs. Conventional Agrochemicals
| Criteria | Biologicals in Agriculture | Conventional Agrochemicals | Sustainability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Health Improvement | Improves soil organic matter; up to 60% higher microbial diversity | Can degrade soil biology; risk of compaction and nutrient runoff | Soil health score: 8.5/10 (biologicals) vs. 5.2/10 (chemicals) |
| Crop Yield Stability | Yield increases (10–20%) and resilience under stress | High short-term yield, but risk of yield drops with resistance development | Long-term stability better with biologicals |
| Pest/Disease Resistance | Unique modes of action; reduced risk of pest resistance | Uniform mechanism; high risk of resistance | Supports biodiversity and lasting effectiveness |
| Environmental Impact | 40–60% reduction in chemical use; safe for beneficial species | Potential pollution of water & non-target species harm | Up to 30% lower carbon footprint |
| Cost Over Time | Initial investment may be high; cost savings realized over 2–3 seasons | Typically lower upfront cost, but increases with resistance & remedial treatments | Biologicals lead to cost savings in the longer term |
| Adoption Challenges | Requires grower education, technical support & optimal field conditions | Well established but facing stricter regulation and resistance issues | Biologicals demand upskilling and support for farmers |
Challenges in the Adoption of Biologicals
While the benefits of biologicals in farming are substantial, certain challenges still impede their widespread adoption:
- Efficacy Variability: Results of biologicals can differ based on climate, soil, crop type, and application method. Unlike chemicals, their efficacy is more sensitive to environmental variability.
- Regulatory Approval: Gaining regulatory approval for biological products can be lengthy and complex—sometimes deterring rapid development and market entry.
- Grower Education and Training: Effective use depends on knowledge of timing, compatibility, and integration with other inputs. Strong education and extension support for farmers is crucial.
- Cost Considerations: Some biologicals are initially more costly than conventional inputs, though long-term economic and sustainability benefits are proven.
However, cutting-edge monitoring platforms—like Farmonaut’s crop and plantation advisory app—empower growers with data to time applications for maximum effect and optimize input investments.
Market Dynamics and Latest Trends in Agricultural Biologicals
The global market for agricultural biological products is expanding rapidly. In 2022, the market was estimated at $3 billion, with forecasts to double to $6 billion by 2030. Around 60% of the market is comprised of microbial products—from soil bacteria to beneficial fungi. Several established agricultural companies now have significant portfolios in biologicals, indicating strong, ongoing research and development efforts.
- Major Industry Players: Industry leaders like Syngenta, Bayer CropScience, BASF, Corteva Agriscience, and others are now investing deeply in biological development.
- Growth Drivers: Increasing demand for organic food, sustainable production methods, and climate-focused regulations support this trend.
- Regional Trends: North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are all experiencing increased adoption rates—for both large-acreage and smallholder systems.
Continued innovation is expected as companies seek to create more effective, affordable and easy-to-use biological products to promote sustainable agricultural practices worldwide.
Farmonaut’s Role: Technology Empowering Sustainable Farming
At Farmonaut, our mission is to make precision agriculture affordable and accessible to all farmers by integrating cutting-edge technology and data-driven insights into traditional farming practices. We do not manufacture biologicals ourselves; rather, we empower the adoption of biologicals through advanced monitoring and advisory solutions. Here’s how we align with the future of agricultural biologicals:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: We provide multispectral crop and soil health insights (NDVI, SAVI, Moisture Indexes) so farmers can diagnose nutrient deficiencies and detect pest/disease risks early, targeting biological input applications for greater effect.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our AI-driven platform analyzes satellite data plus weather to deliver custom advice, helping optimize fertilizer, biological, and water use in real time.
- Blockchain-Based Product Traceability: We provide full digital traceability from field to fork using blockchain. This helps showcase or verify sustainable, biological, or organic production for value-chain partners and consumers (> read more here).
- Carbon Footprinting & Sustainability Tracking: Our tools help measure and reduce carbon footprints using actual field practices and input use, supporting compliance and certification.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Optimize equipment/vehicle operations and input application (fleet management), essential for efficient, sustainable integration of biologicals across large and small farms.
Farmonaut’s large-scale farm management solution enables agribusinesses and governments to digitally monitor the effectiveness of biological (and conventional) input regimes across thousands of fields.
To make these services accessible, we offer a range of subscription packages (see below), designed for individual farmers, agribusinesses, research institutions, and governments.
Future of Agricultural Biologicals: Trends, Research & Outlook
Looking forward, the future of agricultural biologicals is promising. Research in agricultural biotechnology, greater understanding of plant-microbe relationships, and technology-driven advisory and monitoring are catalyzing this progress.
- Product Development: Improvements in product formulation, efficacy, storage stability, and shelf-life are making biologicals more reliable and user-friendly.
- Integration with Precision Ag & Digital Tools: Platforms like Farmonaut help growers track the effectiveness of biologicals, fine-tune their use, and demonstrate sustainability—key for farm profitability and certification.
- Regulatory Evolution: As governments recognize the value of biologicals, regulatory pathways are being adjusted and streamlined (though more work is needed in many countries).
- Consumer Preference: With surging preference for organic and sustainably produced food, retailers and brands are investing in biological and low-chemical supply chains.
- Adoption Support: Ongoing grower training and digital extension services (including AI-driven recommendations) are helping expand reach even in remote areas.
Adopting these biological tools and technologies is no longer optional—it is quickly becoming essential for resilient, profitable, and environmentally sound agriculture globally.
FAQ: Biologicals in Agriculture
What are biologicals in agriculture?
Biologicals are natural products derived from living organisms (microbes, plants) or their byproducts, used in agriculture to enhance plant growth, promote soil health, and protect crops from pests and diseases.
How do biologicals differ from conventional agrochemicals?
Unlike synthetic chemicals, biologicals work by stimulating or reinforcing natural ecosystem processes. They are typically safer for the environment, reduce chemical residues on food, and support long-term soil fertility.
Are there limitations to using biologicals?
Biologicals may exhibit efficacy variability due to environmental conditions, and can require careful handling or knowledge for application. They also may be more expensive upfront but usually offer cost savings over multiple seasons.
What are the most well-known types of biologicals?
The key types include biopesticides for pest control, biostimulants for plant growth, and biofertilizers for soil health.
Can biologicals be integrated with digital farm management platforms?
Absolutely! Data-driven platforms (like Farmonaut) enable farmers to monitor field conditions, receive timing/location-specific input advice, and quantify the impact of biologicals on yield, soil health, and sustainability.
Learn more about Carbon Footprinting and its impact on sustainable agriculture
Discover Farmonaut’s Product Traceability—unlock trust and transparency in your supply chains
Explore Satellite Verification for Crop Loans & Insurance
Optimize resource use with Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tools
Digitally manage your farm, plantation, or advisory programs at scale
Conclusion & Next Steps
Biologicals represent a powerful paradigm shift in modern farming—offering eco-friendly solutions that enhance crop productivity naturally, protect against pests and diseases, and improve soil health. By embracing biologicals in agriculture and integrating them with advanced technologies (such as satellite, AI, and digital traceability from Farmonaut), we are paving the way for more resilient, sustainable, and profitable agriculture.
While challenges of adoption, regulatory approval, and education remain, the momentum is strong—and the rewards are too large to ignore. Let’s foster the future of agricultural biologicals together—one decision, one field, and one season at a time.
Ready to monitor & optimize your biological input strategies? Get started today with Farmonaut’s technology-powered solutions!




















I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav