Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Biology and Behavior of Peach Twig Borer
- Monitoring and Detection Strategies
- 7 Effective Tips for Peach Twig Borer Control
- 1. Strategic Monitoring and Use of Pheromone Traps
- 2. Pruning and Orchard Sanitation Measures
- 3. Consistent Irrigation and Promoting Tree Health
- 4. Encouraging Biological Control of Fruit Borers
- 5. Timely and Responsible Chemical Control
- 6. Integrated Pest Management for Peach Trees (IPM)
- 7. Action Thresholds and Regular Effectiveness Evaluation
- Comparison Table: Peach Twig Borer Control Methods
- How Farmonaut Empowers Peach Twig Borer Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Controlling Peach Twig Borer: 7 Effective Tips for Healthy Orchards
The peach twig borer (Anarsia lineatella) stands out as a major pest threatening peach and nectarine orchards across the globe. Effective peach twig borer control is paramount to prevent extensive damage to shoots, fruit, bark, and ultimately, to ensure quality fruit production. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the biology and behavior of this destructive pest, methods for monitoring its activity, and detail seven practical, integrated methods for successful peach twig borer management in your orchards.
Biology and Behavior of Peach Twig Borer
For effective management, understanding the biology of the peach twig borer is the first step. This small grayish moth, with a typical wingspan of 1.5 cm, has a complex life cycle that makes control challenging but not impossible. Here’s what sets their pest behavior apart:
- Adult moths emerge in late spring, when females begin laying eggs on tender new shoots and developing fruit.
- Larvae, pale green with a dark head and reaching a length of up to 1.5 cm, hatch and quickly burrow into shoots, causing shoot tips to wilt and die.
- As the season progresses, larvae may shift to the fruit, infesting it and causing scarring, premature fruit drop, and quality loss.
- Damaged fruit, shoots, and bark are often the earliest signs of peach twig borer infestation.
The pest undergoes several generations per year, increasing pressure with each cycle and making regular monitoring and adaptive control strategies crucial for orchard success.
Monitoring Peach Twig Borer in Orchards: Detection & Records
Monitoring peach twig borer in orchards is the cornerstone of any successful peach twig borer management program. The sooner the pest is detected, the more effective the control measures will be in reducing damage.
- Pheromone traps: These allow us to capture adult moths, providing a real-time indication of the pest’s presence and activity levels.
- Visual inspections: New shoots and fruit should be thoroughly examined for wilted or dead growth, holes, and signs of larval feeding.
- Maintaining orchard records: Tracking pest activity and environmental conditions each season helps us predict pest pressure and implement controls at the optimal time.
- Timing: Regular inspections during peak egg-laying and hatching periods—typically in late spring—yield the best results.
Early detection not only guides what action to take but also improves the cost-effectiveness of all subsequent control and management methods.
7 Effective Tips for Peach Twig Borer Control
Strong peach twig borer management stems from layered, practical methods that address prevention, detection, and intervention. Here, we detail 7 proven solutions—blending traditional orchard practices with modern integrated pest management.
1. Strategic Monitoring and Use of Pheromone Traps
- Pheromone traps should be installed before the adult moths begin to emerge in late spring.
- These traps are highly sensitive to fluctuations in pest activity, providing an indication of when egg laying and subsequent larval hatching is occurring.
- Weekly trap checks help us assess borer population density, thus informing when to initiate additional control actions.
- Combining trap data with weather information boosts the accuracy of timing for chemical or biological controls.
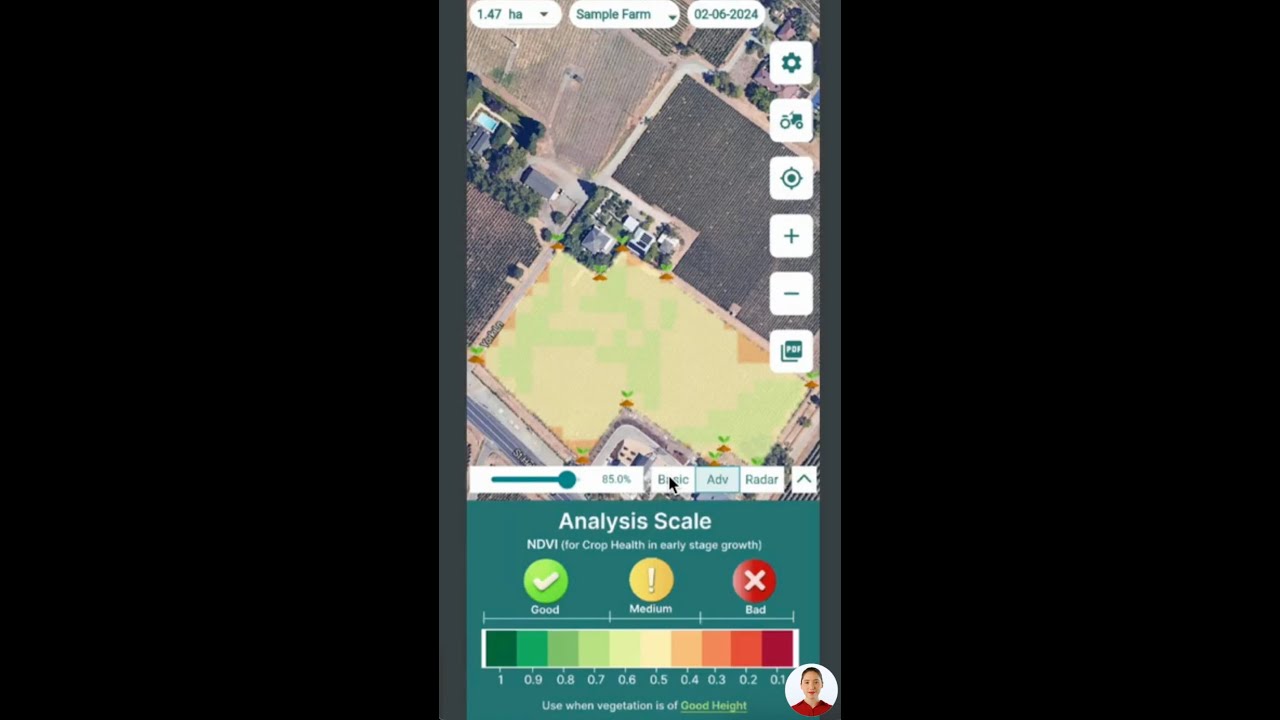
For enhanced pest presence monitoring, integrating Farmonaut’s real-time crop health platform can further optimize the timing and efficiency of detection and intervention. Learn more about Farmonaut’s API for integrating advanced monitoring tools.
2. Pruning and Orchard Sanitation Measures
- Regularly prune and remove infested shoots: Eliminating wilted or dead shoots (flagged shoots) directly removes larvae and eggs, cutting off breeding sites.
- Sanitation: All pruned and fallen material should be collected and destroyed—never left on the ground—since larvae can overwinter in this debris.
- Aim for winter and in-season clean-ups: Target both dormant and growing seasons for optimum prevention.
Cultural practices like pruning are a core pillar in preventing pest damage in peach orchards and form part of the most effective methods for peach tree pests.
For advice on scheduling tasks, try Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management platform for digital task management, planning, and resource coordination across orchards.
3. Consistent Irrigation and Promoting Tree Health
- Maintain consistent irrigation schedules to keep trees healthy, as drought-stressed or waterlogged trees become more susceptible to pest attacks.
- Proper irrigation management and timely fertilization—based on crop health monitoring—repel infestations by promoting vigorous, well-defended growth.
- Use digital tools: Solutions like Farmonaut’s real-time crop health monitoring enables growers to spot stress areas before pests like the peach twig borer can exploit them.
Tip: For orchards with access to advanced analytics, monitoring soil moisture and vegetation indices can pinpoint where pest pressure may increase.
4. Encouraging Biological Control of Fruit Borers
- Biological control of fruit borers relies on natural enemies of the peach twig borer.
- Parasitoid wasps (e.g., Trichogramma and Chelonus): These tiny wasps lay eggs inside borer larvae or eggs, eventually killing the pest.
- Predatory insects such as ladybugs, lacewing larvae, and ground beetles consume borer eggs and young larvae, reducing populations naturally.
- Encourage biodiversity: Planting nectar-rich flowers and maintaining ground covers attract beneficial insects, supporting ongoing biological suppression of pests.
Farmonaut’s platforms support biodiversity efforts and best management advice through crop health data. They can help assess the effectiveness of these biological control methods by monitoring orchard flushes and pest movement.
5. Timely and Responsible Chemical Control of Peach Twig Borer
- Chemical control of peach twig borer is warranted when pest densities cross economic thresholds or when previous measures are insufficient.
- Insecticides (select those labeled for use against the peach twig borer) should be applied during the peak egg hatch period—typically late spring.
- Timing is critical: Applying during larval hatching hits the pest at its most vulnerable stage, maximizing effectiveness.
- Resistance management: Rotate insecticides with different modes of action to prevent resistance.
- Avoid unnecessary sprays—target intervention only when trap counts, visual signs, and risk factors warrant action to protect beneficial insects and minimize environmental impact.
Pro Tip: To help ensure chemical treatments only when absolutely needed and minimize negative impacts, leverage satellite-based advisory platforms such as Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System for real-time, data-driven pesticide application recommendations.
For sustainable agriculture and minimized environmental harm, use Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting tools to track and reduce the overall impact of farm chemical use.
6. Integrated Pest Management for Peach Trees (IPM)
- IPM is about combining monitoring, cultural, biological, and chemical controls into a unified, stepwise approach.
- Thresholds and triggers: Set action thresholds, monitor pest populations, and deploy controls only when pest pressure demands it.
- Cultural controls (like pruning and sanitation) and biological controls are always first line, with chemical measures reserved for targeted intervention.
- Evaluate regularly to adapt and improve the strategy as orchard, weather, or pest pressures shift.
Integrated pest management for peach trees results in fewer interventions, lower costs, improved yields, and healthier, more robust crops ready for market or processing.
Farmonaut’s blockchain-based Traceability platform ensures every crop management action is recorded with full transparency—supporting regulatory and market requirements for quality and sustainably produced fruit.
7. Action Thresholds and Regular Effectiveness Evaluation
- Establish clear action thresholds (e.g., trap catches per week, percent wilted shoots, number of larvae observed).
- Only apply control interventions when thresholds are exceeded, avoiding unnecessary cost and negative ecosystem effects.
- After treatments, assess effectiveness by repeating monitoring surveys and comparing pre- and post-intervention levels.
- Use tools such as Farmonaut’s AI-based advisory to streamline decision-making and record evaluation outcomes for continuous improvement.
Evaluate which methods worked best in your context. Adjust strategies based on results and documented pest behavior each season.
Comparison Table of Peach Twig Borer Control Methods
| Control Method | How It Works | Estimated Effectiveness (%) | Application Frequency | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring with Pheromone Traps | Captures adult moths, signals pest activity and timing for control | Up to 60% pest reduction when combined with timely interventions | Weekly during active season | Low |
| Pruning & Sanitation | Removes infested shoots and potential breeding/overwintering sites | 40-55% pest reduction | 2-3 times per season | Low |
| Consistent Irrigation & Tree Health | Reduces stress and increases resistance to pest attacks | 30% reduction in pest susceptibility | Continuous | Low |
| Encouraging Biological Controls | Introduces or supports natural predators and parasitoids of larvae and eggs | 35-60% reduction in pest populations | Season-long | Low |
| Chemical Insecticide Application | Directly targets eggs and larvae during peak hatching periods | 50-85% reduction if properly timed | 1-2 times per generation | Medium to High (depending on product & method) |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Combines all available methods based on monitoring and thresholds | Up to 90% reduction in crop damage | Continuous/Adaptive | Low |
| Action Thresholds & Evaluation | Ensures response only when economically justified and tracks method success | 10-20% improvement (as part of larger program) | Ongoing | Low |
How Farmonaut Empowers Peach Twig Borer Management
At Farmonaut, our mission is to make precision agriculture and pest management both affordable and accessible. We offer a robust, data-driven suite of tools to help optimize monitoring and pest control for peach twig borer:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: See real-time maps of vegetation health and stress, so you spot problem areas before damage becomes severe.
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Receive personalized, AI-driven recommendations for irrigation, fertilization, and pest management based on satellite and field data.
- Record-Keeping and Threshold Tracking: Digitally log pest presence, trap data, and orchard actions for smarter, faster response times and continuous improvement.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Ensure every shipment of peaches and nectarines meets the highest standards for sustainability, transparency, and safety by recording every pest management action.
- Resource and Fleet Management: Tackle large orchard maintenance tasks more efficiently, coordinating crews and machinery using real-time digital maps and schedules. Explore: Farmonaut Fleet Management Solutions
- Crop Loan & Insurance Support: Satellite verification for crop loans and agri-insurance programs by assessing actual orchard losses due to pest infestations. More: Farmonaut Crop Loan and Insurance Tools
No matter your scale or tech experience, Farmonaut is dedicated to empowering growers to achieve healthier orchards, reject unnecessary losses, and maintain rigorous standards for pest control and fruit production.
Frequently Asked Questions About Peach Twig Borer Control
Conclusion: Protecting Your Orchards with Integrated Action
The pest threat posed by the peach twig borer is a serious one. However, with strategic monitoring, cultural control, harnessing natural biological agents, and, when necessary, a responsible use of chemical insecticides—all supported by data-driven technologies—orchards can minimize fruit and shoot damage while ensuring high-quality production.
By staying vigilant and combining these seven effective tips for peach twig borer control, growers everywhere can enhance their orchard’s resilience, productivity, and sustainability. Don’t forget to assess each season using digital records, regular monitoring, and thresholds—adapting your approach to changing conditions.
For more on peach twig borer management, integrated pest solutions, and advanced farm management services, explore Farmonaut’s platform today. Empower your orchard with technology, insight, and real-time control!