Corn Earworm in Hemp: 7 Powerful Pest Management Tips
“Corn earworm larvae can reduce hemp yields by up to 30% if left unmanaged during peak infestation periods.”
Understanding and Managing Corn Earworm in Hemp Cultivation
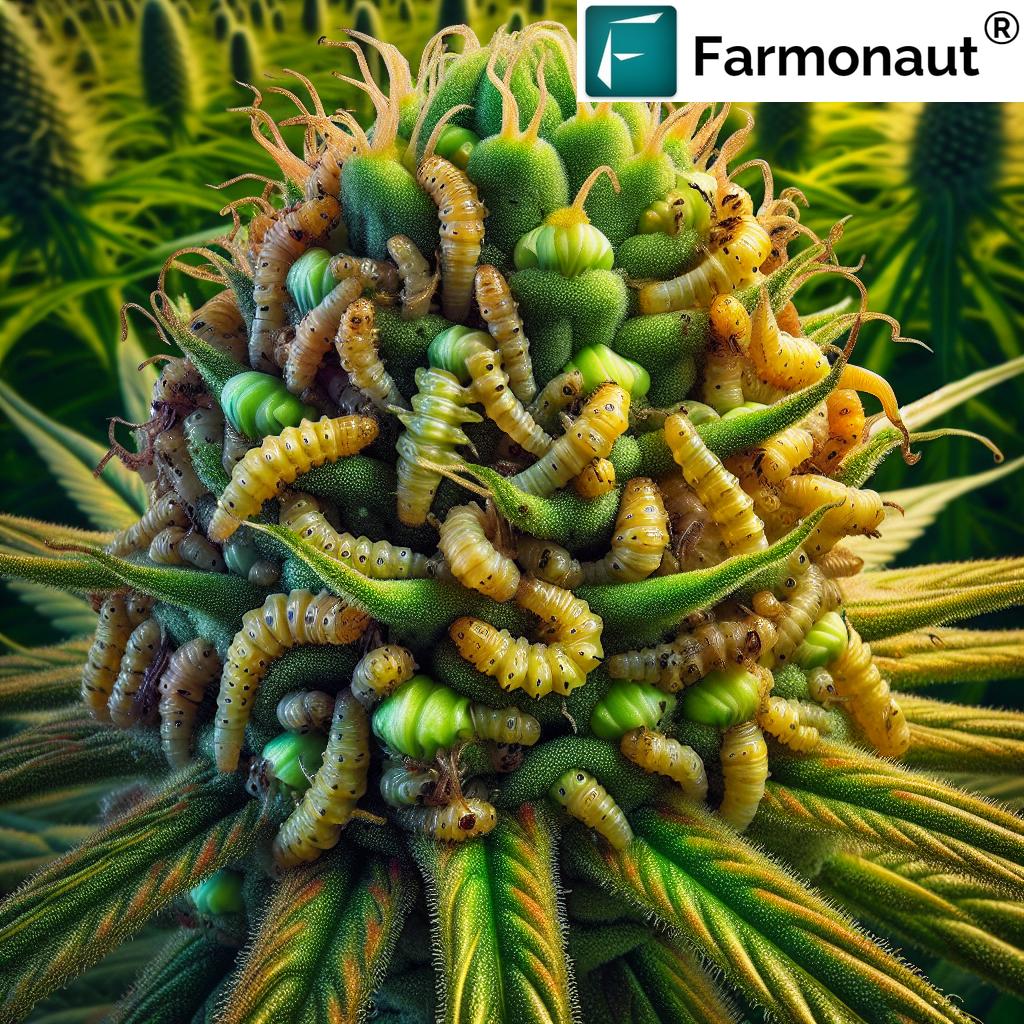
The corn earworm in hemp is an increasingly significant concern for hemp growers, particularly those cultivating flowering and cannabinoid-rich varieties. With larvae that aggressively feed on hemp flower buds, this notorious pest (scientifically known as Helicoverpa zea) can cause substantial crop damage, ranging from reduced yields and premature bud drop to quality degradation. For sustainable hemp cultivation, robust pest management is crucial to maintaining healthy crops, ensuring high yields, and supporting long-term economic viability.
In this guide, we will address the biology and identification of the corn earworm, examine its impact on hemp, and provide seven powerful, integrated pest management strategies supported by approved solutions, monitoring, and cultural practices. Whether you are an established farmer or new to hemp, these SEO-focused tips will help you mitigate the risk of infestation and secure the potential of your crop.
“Integrated pest management can decrease corn earworm populations in hemp fields by over 60% compared to conventional methods.”
Biology & Identification of Corn Earworm (Helicoverpa zea)
Getting to Know the Hemp Earworm Pest
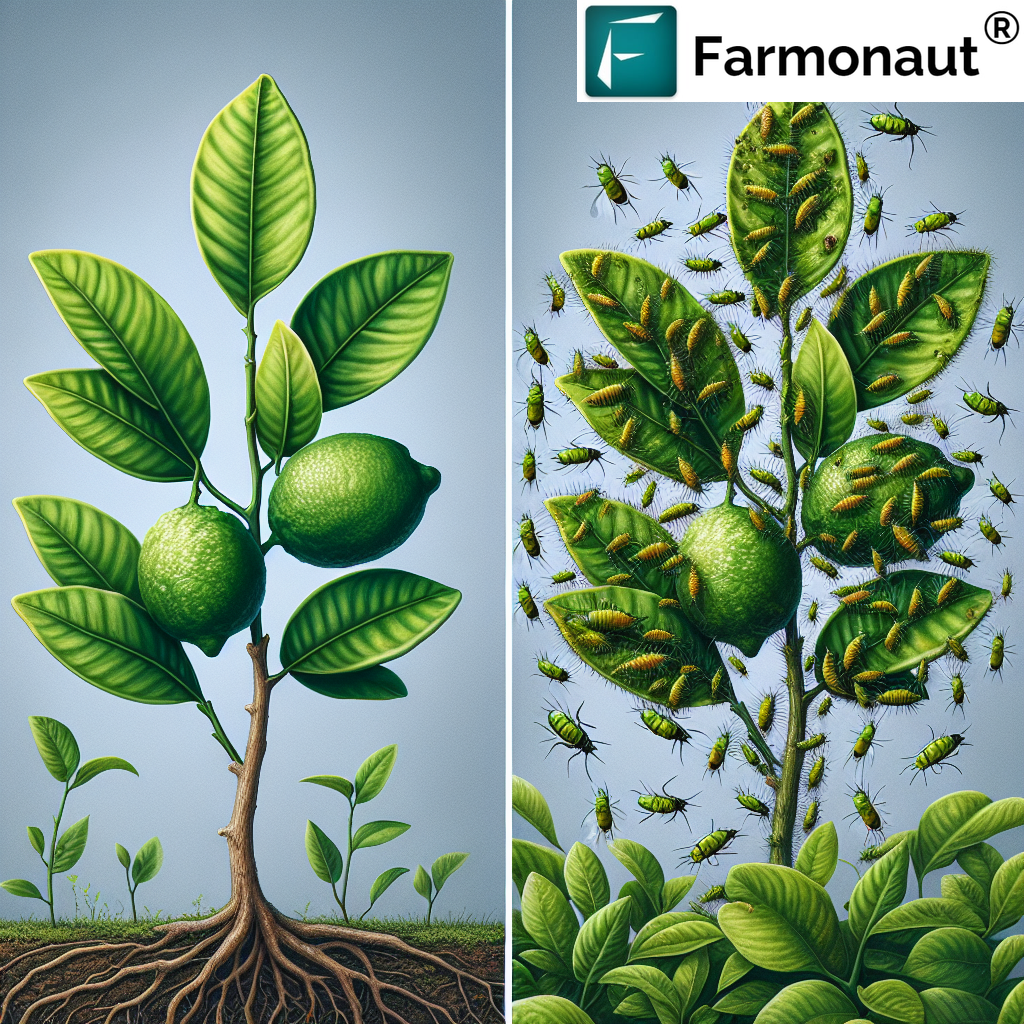
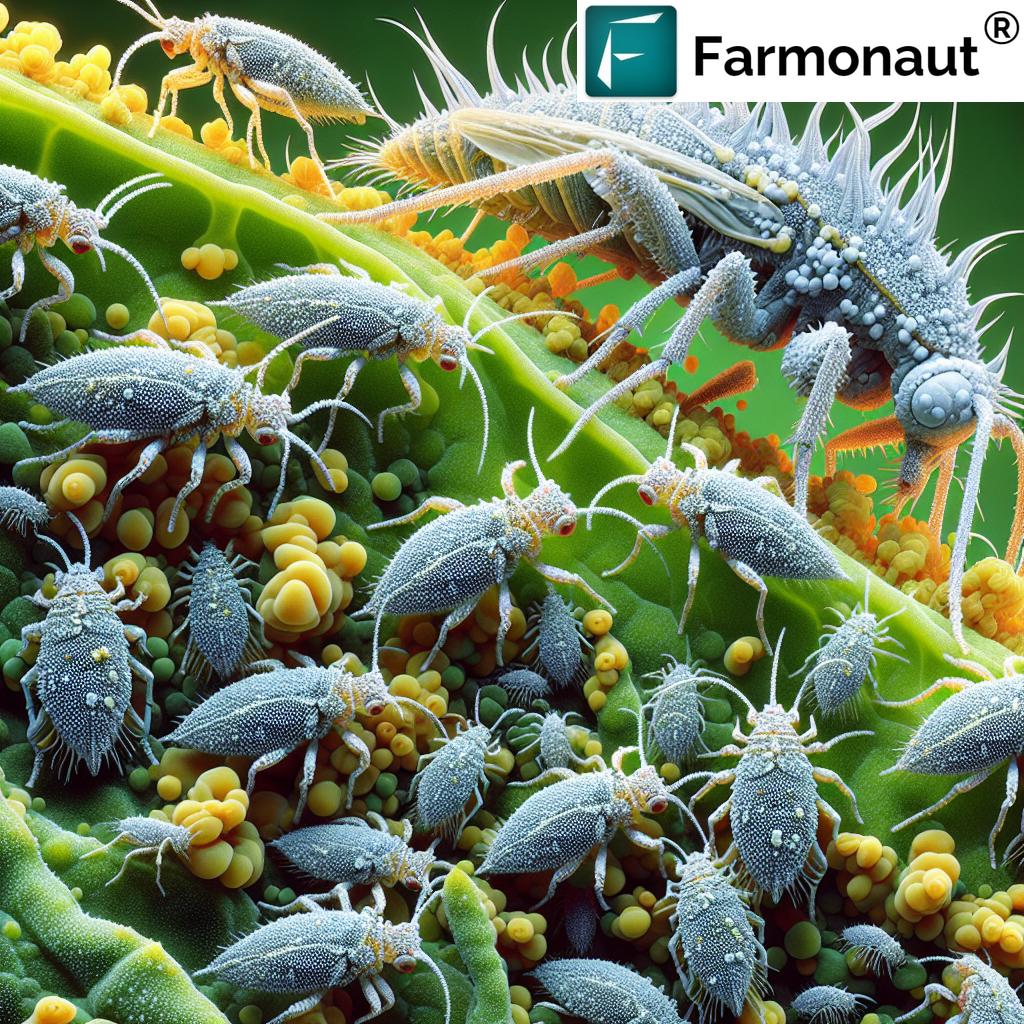
The corn earworm is a nocturnal moth with an extensive host range, attacking crops like corn, cotton, tomatoes, and increasingly, hemp. Recognizing the pest in its various developmental stages is essential for timely intervention and effective management.
Corn Earworm Life Cycle and Biology
- Eggs: The adult female moth lays between 20-25 eggs per day and up to 1,500 eggs over her short lifespan. Eggs are laid singly on the leaves and, most critically, on the flower buds of hemp. Eggs hatch within 2–4 days.
- Larvae: The newly emerging larvae immediately begin feeding on the hemp plant, with a preference for flower buds and tender foliage. Larvae exhibit color variations—including green, pink, and dark brown—but are typically green on hemp. Mature caterpillars reach 25 mm in length, passing through several molts over two to three weeks before dropping to the ground to pupate.
- Pupae: In summer, the pupal stage lasts two weeks before adults emerge. In the fall, pupae become dormant, overwintering in the soil and potentially causing recurring infestations.
Adult Identification
- Moth has a wingspan of 32–45 mm
- Forewings are light brown with a distinctive dark spot
- Adults are mainly active at night
Recognizing these stages early—eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults—supports rapid response and is central to effective hemp pest management.
Corn Earworm Damage in Hemp: Buds, Flowers, and Yields
How Hemp Yields and Quality Are Impacted
The primary threat from corn earworm larvae in hemp arises during flowering when the larvae feed extensively on flower buds. This feeding causes:
- Bud Tunneling and Wounds: The larvae bore into the flower buds, creating entry points for fungal and bacterial pathogens, often resulting in bud rot.
- Deformed Seeds and Flowers: Active feeding disrupts normal flower and seed development, leading to malformed flowers or seeds that can lower crop quality.
- Premature Bud Drop and Reduced Yields: With extensive feeding, buds may drop prematurely, leading to a direct reduction in yield and economic returns.
- Quality Degradation: Particularly in cannabinoid-rich hemp cultivars, feeding damage can lead to the loss of valuable flower material, reduced trichome density, and compromised product quality.
These impacts underscore why monitoring pests in hemp fields and early intervention are critical steps in any integrated pest management in hemp approach.
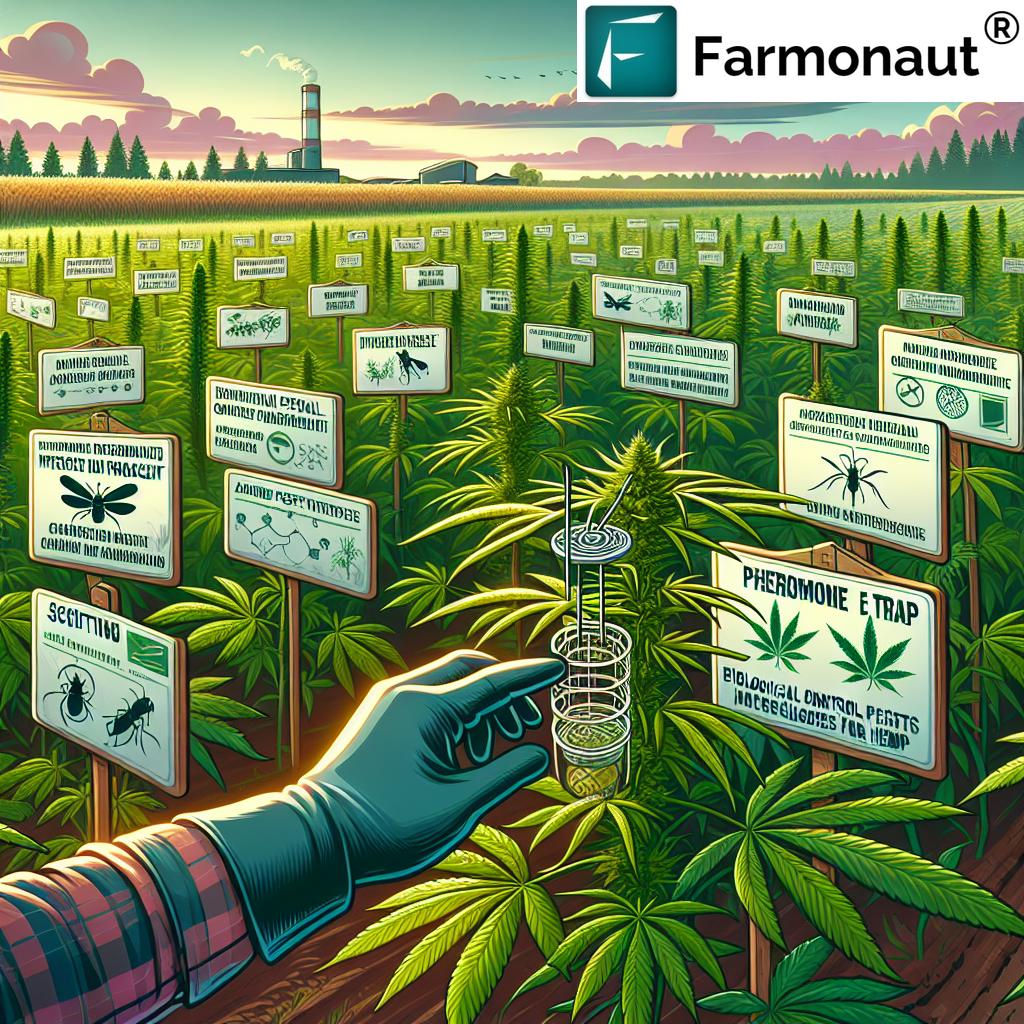
Monitoring & Trapping Corn Earworm in Hemp
How to Use Pheromone Traps & Regular Scouting
Successful corn earworm larvae control begins with rigorous monitoring and early detection. Here’s how growers can implement these crucial steps:
Deploying Pheromone Traps for Corn Earworm
- Pheromone traps (e.g., Heliothis traps) lure male moths using species-specific lures—ideally set up at the field edge ahead of the flowering stage.
- Place a minimum of one trap per field, and maintain them for the duration of the growing season.
- Check traps and record captures twice weekly for accuracy. Replace lures every two weeks or according to manufacturer instructions.
Regular Scouting for Eggs and Larvae
- Manually inspect hemp plants—focusing on buds and leaves—for the presence of eggs and larvae.
- Early-stage larvae are easier to control, so early detection can significantly reduce damage.
Combining pheromone traps for corn earworm with robust field scouting ensures maximum readiness against infestations.
7 Powerful Hemp Pest Management Tips for Corn Earworm
1. Integrated Pest Management in Hemp (IPM)
A cornerstone for sustainable hemp production, IPM combines biological, cultural, and chemical tools in a coordinated way to minimize pest impact without harming the environment or developing resistance. Always adapt your plan based on ongoing monitoring and results.
2. Biological Control of Corn Earworm
- Encourage Natural Enemies: Promote populations of beneficial insects, such as lady beetles, minute pirate bugs, and lacewings, all of which prey on corn earworm eggs and early larvae.
- Utilize Parasitoids: Tachinid flies like Winthemia rufopicta and Lespesia aletiae actively parasitize earworm larvae. Their presence helps reduce pest numbers naturally.
These biological solutions have low environmental impact and can be augmented through habitat management (e.g., flowering borders for predator insects).
Traceability with Farmonaut ensures your hemp’s journey, including pest management records, remains transparent and easily auditable through our blockchain-based platform—boosting both consumer confidence and regulatory compliance.
3. Cultural Practices for Hemp Pests
- Trap Cropping: Planting a preferred host such as sweet corn near your hemp field can attract adult moths away from your cash crop.
- Field Sanitation: Remove weeds, spent hemp, and debris that serve as egg-laying sites or overwintering shelters for pupae, reducing pest carryover between seasons.
Rotating crops and maintaining field hygiene are critical cultural practices for hemp pests that can help disrupt the pest’s life cycle.
Measuring farm carbon footprint is easy and accurate with Farmonaut’s advanced satellite-based carbon footprinting solution, aiding growers in tracking and reducing environmental impact alongside pest management.
4. Approved Pesticides for Hemp: Biological Solutions
-
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt):
- Bt aizawai strains (such as XenTari) and virus-based products like Gemstar LC are effective biological control agents for corn earworm. Apply at the earliest sign of infestation, coating all parts of the plant, especially flower buds.
-
Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs):
- Products like Prevasyn Insect Repellant/Insecticide interfere with larval development, though efficacy in hemp requires further field trials.
Always verify product labels and regional approval before applying any pesticides.
Farmonaut’s Fleet Management tools can help schedule, execute, and record pesticide applications—maximizing application efficiency, reducing costs, and improving compliance.
5. Early-Stage Intervention via Monitoring and Scouting
- Regular, weekly monitoring using pheromone traps and ground scouting supports the earliest possible detection of eggs and newly emerging larvae.
- Early intervention is the most effective method for minimizing damage—as young larvae are more susceptible to biological and chemical treatments.
Leveraging remote, satellite-based pest and crop monitoring can also help prioritize scouting areas and optimize labor—available on the Farmonaut platform.
6. Physical Barriers and Resistant Varieties
- While true resistant hemp varieties are still under research, using row covers and nettings during moth flight peaks can minimize adult egg-laying on flowers.
- Exclusion devices work best in small, high-value plots or controlled-environment cultivation.
7. Maintain Field Hygiene Year-Round
- Post-harvest cleanup—including removal of plant debris and deep soil turning—can destroy overwintering pupae, reducing the next season’s infestation potential.
- Regular sanitation breaks the pest’s life cycle and encourages a healthier, more resilient crop.
For holistic, large-scale hemp and multi-crop management, Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management App offers robust field health monitoring, task management, and seamless integration of pest management best practices.
Pest Management Strategies Comparison Table
| Pest Management Strategy | Brief Description | Estimated Effectiveness (% Control) | Estimated Cost Level ($-$$$) | Application Timing/Stage | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring & Trapping | Frequent scouting, pheromone traps, recordkeeping | 30–50% | $ | Pre- & early-flowering, throughout season | Low |
| Biological Controls (e.g., Bt, parasitoids) | Use of beneficial insects, bacteria, and viruses | 60–80% | $$ | At first egg/larval detection | Low |
| Insecticide Use | App. of approved bio-insecticides or IGRs | 50–75% | $$ | Infestation or threshold breach | Medium |
| Crop Rotation | Rotating hemp with non-host crops | 30–40% | $ | Between seasons | Low |
| Resistant Varieties | Use plant types with natural pest resistance | Research-stage | $$-$$$ | Before planting | Low |
| Field Hygiene | Post-harvest cleanup, debris removal | 25–35% | $ | Post-harvest, pre-planting | Low |
| Physical Barriers | Using row covers, mesh nets | 50–65% | $$ | During adult flight, early flowering | Low |
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) in Hemp
Why Integrated Strategies Matter for Corn Earworm Control
Experience shows that managing corn earworm in hemp with a single solution is rarely effective. IPM fosters balanced strategies that reduce the threat of resistance development and ensure compliance with regional regulations, especially with limited chemical options. Key pillars include:
- Preseason Planning: Rotate crops, select clean seed, and choose planting dates to avoid peak moth activity.
- Proactive Monitoring: Consistent use of pheromone traps and visual scouting is essential.
- Biological and Cultural Controls: Favor environmentally friendly methods as a first line of defense.
- Targeted Use of Biological and Approved Chemical Pesticides: Apply only as needed and alternate modes of action to prevent resistance in pest populations.
Combining these strategies with continuous learning ensures healthy, resilient hemp crops and stronger yields.
Farmonaut API: Next-Gen Data for IPM
Refine your IPM approach further with API-driven integration of pest- and crop-health alerts into your farm management systems. Developers can access comprehensive documentation via our API developer docs.
Challenges & Considerations in Managing Corn Earworm in Hemp
Overcoming Obstacles to Sustainable Hemp Pest Management
Effective corn earworm larvae control in hemp is complicated by several challenges:
- Limited Chemical Options: Only a select group of products are approved for hemp, making it imperative to lean on biological and cultural controls.
- Resistance Development: Repeated use of a single control method (e.g., only Bt applications) can result in pest populations becoming resistant.
- Regulatory Compliance: Growers must ensure all pest management interventions—especially with pesticides—meet regulatory standards for both human, animal, and environmental safety as well as market access.
- Monitoring Intensity: Hemp fields require routine, season-long monitoring during critical development windows, demanding both attention and resources.
These realities reinforce the need for robust, integrated pest management in hemp that leverages every available strategy in an adaptable pest management toolkit.
How Farmonaut Empowers Smart Hemp Pest Management
At Farmonaut, our mission is to democratize precision agriculture through advanced, yet affordable, farm management solutions. By leveraging AI, satellite imaging, and blockchain, we enable growers worldwide to:
- Monitor crop health and moisture with high-frequency satellite updates (NDVI, NDWI, VARI, and more)
- Receive AI-based pest management advisories via our Jeevn AI system, which interprets remote sensing data and field inputs for early warning about potential threats like corn earworm in hemp.
- Track pest population hotspots and prioritize in-field scouting and trap placement based on real-time satellite insights
- Adopt sustainable management practices, including resource optimization and carbon footprint tracking, as part of a complete IPM approach
- Maintain transparent, traceable records from planting to harvest via blockchain, simplifying regulatory compliance and supporting product quality assurance
- Manage resources and farm fleets for timely and precise pesticide and irrigation activities
Farmonaut’s subscription-based platform is accessible through our web app, Android and iOS apps, as well as via API—making smart pest and crop management possible for farms of every scale.
FAQ: Corn Earworm in Hemp Pest Management
- How do I identify corn earworm larvae in my hemp fields?
- Look for actively feeding, predominantly green caterpillars with sparse bristles on their bodies, especially burrowing into flower buds. Eggs are tiny, round, and whitish, often laid singly on new growth.
- What is the best time to scout for corn earworm?
- Regular, weekly scouting should begin prior to and throughout hemp flowering. Intensify inspection immediately following the first adult moth capture in pheromone traps.
- Are there any resistant hemp varieties?
- While some progress is being made, fully resistant hemp cultivars are not yet widely available. Growers should instead use IPM and integrate resistant traits when they become accessible.
- What pesticides are approved for use on hemp?
- Approved biologicals such as Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) and certain insect growth regulators (IGRs) are commonly used. Always verify product registration for your region and compliance with local regulations.
- How can satellite-based tools help in hemp pest management?
- Platforms like Farmonaut analyze crop health through multispectral imaging, helping to pinpoint stressed areas for targeted scouting, optimize pesticide use, and support proactive decision-making.
- My hemp crop had severe earworm damage last year. What should I change?
- Strengthen monitoring (traps and scouting), implement cultural and biological controls, and ensure robust post-harvest field hygiene to disrupt pest cycles.
- Where can I learn about Farmonaut’s features?
- Visit our web and mobile apps for detailed toolkits, or explore our traceability, carbon footprinting, and crop loan and insurance solutions on our website.
Conclusion: Sustainable Management of Corn Earworm in Hemp
The corn earworm in hemp is a formidable pest, especially for growers aiming for high-quality flower and cannabinoid yields. Through a strategy that combines monitoring, pheromone traps, cultural practices, biological control, and the judicious use of approved pesticides for hemp, you can reduce earworm populations and associated damage—all while maintaining ecological and economic sustainability.
Integrating these tips with the Farmonaut platform ensures you remain at the forefront of hemp pest management, leveraging the power of remote sensing, AI, and blockchain for a truly modern approach to staying ahead of pests and maximizing yield.
Remember: early detection, regular field hygiene, a strong focus on biological solutions, and adaptability to changing regulatory and environmental constraints are the keys to winning the fight against the corn earworm in hemp.