Lemon Tree Disease and Treatment: 7 Best Solutions for Thriving Citrus Orchards
“Up to 40% of lemon tree yield loss is caused by untreated fungal diseases each season.”
Lemon trees are a valuable asset in agriculture, providing significant economic benefits and culinary delights for countless households and businesses worldwide. However, the journey to healthy, productive citrus orchards is challenged by a range of lemon tree diseases. These issues, if not properly managed, can compromise the health and productivity of your trees, leading to reduced fruit yields, declining tree vigor, and even eventual removal of affected plants.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common lemon tree diseases, their symptoms, and the treatments proven to be most effective in modern citrus farming. Along the way, we’ll outline prevention strategies, integrated pest management (IPM), and best practices for maintaining healthy citrus trees, drawing on both scientific expertise and the latest technology. Our goal: to help you protect your investment and enjoy bountiful lemon harvests, year after year.
Table of Contents
- Why Lemon Trees Are Vulnerable to Disease
- Overview: 7 Common Lemon Tree Diseases
- Lemon Tree Disease and Treatment: The 7 Best Solutions
- Disease-Symptom-Treatment Table
- Preventive Measures & Integrated Pest Management for Citrus
- Leveraging Technology: How Farmonaut Supports Disease Management
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Summary & Final Recommendations
Why Are Lemon Trees Susceptible to Disease? Understanding the Risks
Lemon trees, like other citrus species, are susceptible to a broad range of diseases and pests due to their biology and the climates they are usually grown in. Warm temperatures, high humidity, and periodic rains can create environments conducive to the growth and spread of fungal, bacterial, and insect-related problems. Additionally, the growing popularity of intensive lemon cultivation and global tree movement increases the risk of introducing new pathogens and pests.
Early detection and prompt, knowledgeable treatment are essential to maintaining healthy lemon trees and preserving the economic benefits of your orchard.
Let’s examine the most significant lemon tree diseases affecting growers worldwide, focusing on identifiable symptoms, treatments, and how to prevent or manage each one.
Overview of 7 Common Lemon Tree Diseases
- Citrus Canker (Xanthomonas citri pv. citri)
- Phytophthora Root Rot (Phytophthora citrophthora)
- Citrus Black Spot (Phyllosticta citricarpa)
- Mal Secco (Phoma tracheiphila)
- Sooty Mold
- Citrus Leafminer (Phyllocnistis citrella)
- Other Common Citrus Tree Problems (e.g., Greasy Spot, Tristeza Virus, nutrient deficiencies)
Each disease affects lemon trees in unique ways, with symptoms ranging from unsightly lesions to premature fruit drop and severe canopy necrosis. Identifying these early and applying the best treatment is critical for successful cultivation.
How Farmonaut’s Satellite Technology is Revolutionizing Land Use in Agriculture
Lemon Tree Disease and Treatment: The 7 Best Solutions
1. Citrus Canker (Xanthomonas citri pv. citri): Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
Overview: Citrus canker is a bacterial disease that targets all aerial parts of the citrus tree—leaves, stems, and fruit. The causal organism (Xanthomonas citri pv. citri) thrives in humid, windy, and warm environments, making areas with these conditions particularly vulnerable.
- Symptoms: Characterized by raised brown lesions with distinctive yellow halos on the leaves, stems, and fruit. In severe cases, it leads to premature fruit drop and extensive defoliation.
- Mode of Spread: Splashing rain, wind, insects (psyllids), tools, and equipment can contribute to the spread. The canker bacteria overwinter in infected tissue and are dispersed by physical contact and weather events.
Lemon Tree Disease Treatment for Citrus Canker
- No Cure Exists: There is no chemical or biological cure once infection occurs. Eradication and prevention must be the core strategy.
- Management Strategies Include:
- Strict Quarantining: Prevent the introduction of citrus psyllids and infected plant material to new areas.
- Prompt Removal: Infected trees must be removed and destroyed—preferably burned—immediately upon diagnosis to minimize further spread.
- Sanitation & Equipment Disinfection: Regularly clean pruning tools, machinery, and clothing used near infected trees.
How to prevent citrus canker: Grow resistant citrus varieties where possible, avoid overhead irrigation, and implement buffer zones between orchards. Always monitor for early symptoms and respond rapidly if lesions are found.
Explore Farmonaut’s Advanced Crop Monitoring & Yield Prediction
2. Phytophthora Root Rot in Lemons (Phytophthora citrophthora): Causes, Symptoms & Best Solutions
Overview: Among the most damaging lemon tree diseases, phytophthora root rot is caused by soil-borne pathogens that thrive in poorly-drained soils or after heavy rainfall. Early detection and soil management are vital!
- Symptoms:
- Dark, sunken longitudinal lesions near the soil line (tree base).
- Gummosis: Oozing, amber-colored sap from the trunk at or near the base.
- Sour, unpleasant odor present near infected areas.
- In advanced stages: Bark cracking, yellowing, necrosis of the canopy, leaf drop, and eventual death of sections of the tree.
- How it Spreads: Poor drainage and excessive irrigation create conditions for Phytophthora to thrive and infect lemon tree roots.
Lemon Tree Disease Treatment for Phytophthora Root Rot
- Implementing Resistant Varieties: When possible, choose Phytophthora-resistant lemon or rootstock varieties.
- Improved Planting Practices:
- Plant in light, sandy, well-drained soil.
- Ensure the top of the root ball is 1 inch above the soil surface during planting to avoid water collecting around the crown.
- Chemical Management: Apply copper-based fungicides before the rainy season as a protective measure—especially if your area is prone to waterlogging.
- Cultural Practices: Avoid overwatering, and improve air circulation by spacing trees for better sunlight and airflow.
Managing phytophthora root rot in lemons often requires combining the above practices. Adding organic matter and practicing crop rotation with non-host species can reduce inoculum in the soil.
“Integrated pest management can reduce lemon tree disease incidence by over 60% compared to conventional methods.”
Satellite & AI Based Automated Tree Detection For Precise Counting and Location Mapping
3. Citrus Black Spot (Phyllosticta citricarpa): Symptoms, Treatments & Management
Overview: Citrus black spot is a major fungal disease in many citrus-growing regions and can devastate lemon fruit quality and market value. The presence of this pathogen may prompt strict trade restrictions.
- Symptoms:
- Dark, sunken lesions—round to irregular, often with a “hard” edge—on both fruit and leaves.
- “False melanose” spots and premature drop of fruit in severe cases.
- Spread: Spores are spread by rain splash and wind, remaining viable in dead tissue on the ground. Poor orchard sanitation is a major contributor.
Citrus Black Spot Management & Lemon Tree Disease Treatment
- No Direct Cure: There is no single curative treatment, but integrated management can keep losses below economic thresholds.
- What Works:
- Immediately removing and destroying infected trees and fallen plant debris.
- Applying fungicides (copper, strobilurins) monthly from early May to mid-September.
- Prune to improve air circulation, reducing leaf wetness.
Citrus black spot management also requires close monitoring during periods of high humidity and rainfall—be vigilant for new lesions as early detection improves outcomes.
4. Mal Secco Disease (Phoma tracheiphila): Lethal Vascular Disease in Lemon Trees
Overview: Mal secco (“dry disease”) is a serious vascular fungal disease, highly damaging in Mediterranean and subtropical climates. Rapid spread can destroy entire trees if not managed promptly.
- Symptoms:
- Chlorosis (yellowing) of young leaves and pronounced downward leaf curling (epinasty).
- Progressive dieback of leaves, twigs, and branches.
- Infected wood develops distinct salmon, pink, or red coloration with gummy deposits inside.
- Spread: Primarily via rain splash, pruning tools, and windborne spores affecting wounds.
Mal Secco Lemon Tree Disease Treatment
- Sanitation: Promptly remove and destroy infected wood.
- Fungicide Application: Apply systemic fungicides as per local recommendations.
- Orchard Hygiene: Focus on regular sanitation, tool disinfection, and avoiding injuries during pruning.
Prevention is essential: Avoid planting susceptible varieties in endemic areas and maintain a rigorous, proactive IPM program in your orchard.
5. Sooty Mold: Unsightly Citrus Leaf and Fruit Disease
Overview: Sooty mold is a fungal growth appearing as black, powdery deposits on lemon leaves, stems, and fruit. Rather than infecting tissue directly, it grows on honeydew excreted by sap-sucking insects—especially aphids, mealybugs, and scale.
- Symptoms:
- Sticky honeydew accumulates, supporting the growth of a dark, soot-like mold on foliage and fruit.
- Blocks light, reducing photosynthetic efficiency.
- Impedes respiration and, if severe, reduces fruit quality and market appeal.
Lemon Tree Disease Treatment for Sooty Mold
- Control Insect Pests: The root of the problem is insect management:
- Use horticultural oils or insecticidal soaps to control the honeydew-producers.
- Once pests are eliminated, wash sooty mold off foliage if desired (gentle rinsing with water is usually sufficient).
- Fungicides: May be applied as needed—however, addressing pest issues will remove the mold’s food source and naturally resolve the problem.
Regular monitoring and integrated pest management for citrus are effective preventive measures. Promote beneficial insect activity and avoid excessive use of broad-spectrum pesticides that disrupt ecological balance.
Farmonaut Introduction – Large Scale Usage For Businesses and Governments
6. Citrus Leafminer (Phyllocnistis citrella): Pests Causing Lemon Tree Leaf Yellowing and Distortion
Overview: Citrus leafminers are tiny moths whose larvae tunnel inside young lemon leaves, resulting in wavy, “serpentine” mines. This reduces growth and may serve as an entry point for more severe diseases.
- Symptoms:
- Silvery, winding lines visible on new leaf surfaces.
- Leaf curling, distortion, stunting, and sometimes premature leaf yellowing and shedding.
Lemon Tree Disease Treatment for Leafminer Infestations
- For Young Trees: Apply horticultural oils (0.5–1% solution) to new shoot flushes. Completely coat the leaf surfaces while they are young and soft.
- For Older Trees: While unsightly, most mature lemon trees tolerate moderate leafminer activity without long-term effect.
- Promote Natural Enemies: Encourage predators and parasitoids (wasps, lacewings) that naturally regulate leafminer populations.
Keep an eye out for early symptoms, and combine specialist treatments with orchard-wide IPM for the best outcomes.
Disease, Symptom & Treatment Table: Quick Reference for Citrus Growers
| Disease Name | Common Symptoms (Severity/Incidence) |
Recommended Treatment | Prevention Tips | Est. Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus Canker (Xanthomonas citri pv. citri) | Raised brown lesions with yellow halos on leaves, stems, fruit; fruit drop, defoliation (High) | Remove/destroy infected trees; strict quarantine; sanitation | Grow resistant varieties; strict sanitization; prevent introduction of infected material | Immediate (tree removal); replant only after careful disinfection |
| Phytophthora Root Rot (Phytophthora citrophthora) | Gummosis at base, dark lesions, bark cracking, root decay, canopy yellowing (High) | Well-draining soil; resistant varieties; copper-based fungicides; plant higher | Improve drainage; avoid overwatering; mulch; sanitation | Weeks to months, depending on severity and intervention |
| Citrus Black Spot (Phyllosticta citricarpa) | Dark lesions on fruit/leaves; reduced quality; early drop (Moderate–High) | Remove infected fruit/leaves; monthly fungicide sprays | Sanitation; monitor weather; prune for air flow | Seasonal (varies depending on frequency of sprays and reduction of inoculum) |
| Mal Secco (Phoma tracheiphila) | Leaf yellowing, shoot dieback, pink discoloration, gum (High in Med. areas) | Remove infected branches; apply fungicides; sanitation | Regular pruning; tool disinfection; resistant cultivars | Depends on early intervention |
| Sooty Mold | Black, powdery mold on leaves/fruit; sticky honeydew (Mild–Moderate) | Control insect pests (aphids, mealybugs); wash foliage | Monitor for pests; encourage beneficial insects | 2–6 weeks after pest suppression |
| Citrus Leafminer (Phyllocnistis citrella) | Silvery, winding mines; leaf curling/distortion (Mild—mostly aesthetic) | Horticultural oils on new flush; encourage predators | IPM, avoid excess nitrogen, monitor flushes | 2–8 weeks, as new leaves mature |
| Other (Greasy Spot, Tristeza, Nutrient Def.) | Leaf spots, general yellowing, dieback (Variable) | Soil testing; balanced fert.; fungicides (if fungal) | Balanced irrigation/fertilization; routine scouting | Weeks–months, depending on correction |
7. Other Common Citrus Tree Problems and Solutions
-
Greasy Spot: Fungal leaf disease causing yellow-brown blisters and leaf drop.
Treatment: Copper fungicides; prune and remove diseased leaves. -
Citrus Tristeza Virus: Causes stunted trees, poor fruit set.
Treatment: Roguing (removing infected plants); certified virus-free stock; aphid control. -
Nutrient Deficiencies: Lemon tree leaf yellowing can result from insufficient nitrogen, zinc, magnesium, or iron.
Treatment: Conduct soil testing, apply balanced fertilizer, and monitor symptoms.
Best practices for lemon orchard sanitation include removing debris, sanitizing tools, monitoring for early signs of lemon tree fungus, and always practicing proper disposal of affected material.
Preventive Measures and Integrated Pest Management for Citrus Trees
Prevention is universally more effective than treatment for lemon tree diseases. Here are essential, proven preventive strategies:
1. Site Selection and Planting
- Choose locations with deep, well-draining soils; avoid depressions or low spots prone to standing water.
- Implement raised beds or berms to encourage rapid drainage and root health.
- Proper planting depth is crucial—never bury the root crown.
2. Orchard Sanitation
- Regularly remove and destroy fallen leaves and fruit to reduce sources of infection and pest breeding grounds.
- Practice best practices for lemon orchard sanitation by disinfecting tools between trees and after each use.
- Dispose of infected plant material well outside of the orchard zone.
3. Pruning and Air Circulation
- Prune to open canopies and improve air circulation, reducing humidity that promotes fungal growth.
- Remove water sprouts, crossing branches, and dense interior growth.
4. Irrigation Management
- Avoid over-irrigation and standing water—this limits root rot incidence.
- Use drip or micro-sprinkler systems to keep foliage dry and supply water only to the root zone.
5. Pest & Disease Monitoring
- Integrated pest management for citrus relies on regular orchard inspections for early detection of pests, diseases, and abnormal tree symptoms.
- Set pheromone traps, use yellow sticky cards, and keep detailed records.
6. Biological Controls
- Encourage beneficial insects—ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps—to control pest populations naturally.
- Plant flowering borders or cover crops that support predator populations.
7. Chemical Controls (As Needed)
- Only apply fungicides or insecticides when threshold levels are reached—this helps reduce impact on beneficial organisms and resistance buildup.
- Follow all local and product guidelines for application timing and safety.
Leveraging Farmonaut Technology for Disease Management & Citrus Orchard Success
Lemon growers today have access to powerful, cost-effective platforms to support disease management, pest monitoring, and sustainable practice adoption. At Farmonaut, we are committed to empowering citrus farmers by making precision agriculture affordable and accessible worldwide.
Our advanced platform synergizes satellite-based crop health monitoring, AI-driven farm advisory systems, and blockchain for traceability. Here’s how these solutions help control lemon tree diseases and optimize agricultural productivity for both small and large growers:
- Satellite Crop Health Monitoring: By using high-frequency multispectral imagery, we deliver real-time insights into vegetation health (NDVI), soil moisture, and other key metrics directly to your device. These tools help identify “hot spots” or early symptoms of stress, disease, or pest pressure well before visible signs appear.
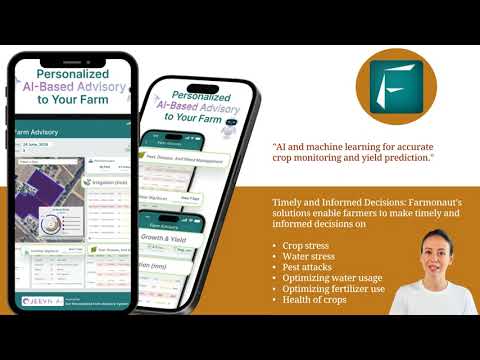
- Jeevn AI Advisory System: Our proprietary AI delivers personalized, real-time, and weather-aware management strategies—helping growers choose the most effective treatment or preventive measures for each specific disease risk.
- Blockchain Product Traceability: Enhance consumer trust and mitigate supply chain fraud by ensuring that every batch of lemon fruit is traceable, with a clear record of production practices, disease interventions, and geographic origin. Explore Farmonaut Product Traceability Solutions →
- Fleet Management: We offer specialized tools for larger agribusinesses needing to streamline logistics, reduce operating costs, and maintain oversight of machine usage. View Farmonaut Fleet Management Capabilities →
- Carbon Footprinting: Track the environmental impact of your orchard management practices, minimize emissions, and improve sustainability outcomes. Try Farmonaut Carbon Footprinting Now →
- Crop Loan and Insurance: Using satellite-based field verification, we help you secure affordable and quick crop loans or insurance without the risk of fraud. Learn About Crop Loan and Insurance Verification →
- Large-Scale Farm Management: Efficiently oversee plantation crops, citrus tree density, and orchard-level disease management anywhere. See Farmonaut’s Agro Admin App for Scale →
- API Access: Developers and agri-businesses can integrate satellite/weather data into their own systems via the Farmonaut Satellite API. See comprehensive API Developer Docs →
Our platform provides the digital backbone for integrated pest management for citrus at any scale—whether you’re a hobbyist orchardist or managing hundreds of hectares. Precision disease tracking, predictive weather insights, and data-driven advisories put control back in the hands of growers and help avoid crop loss.
Flexible Precision Agriculture Subscriptions
Frequently Asked Questions about Lemon Tree Diseases
Q1: What are the earliest signs of lemon tree fungus or root disease?
The earliest signs of lemon tree fungus include brown or black leaf spots, fuzzy or powdery growth on the underside of leaves, and wilting despite adequate soil moisture. Root diseases are often first noticed as canopy yellowing, slowed growth, and gummosis at the trunk base.
Q2: Can I use homemade remedies (e.g., vinegar, soap) to treat lemon tree disease?
Homemade remedies may provide short-term control of minor pest problems (like sooty mold via gentle leaf washing), but they are generally not effective against more serious lemon tree diseases such as phytophthora root rot or citrus canker. Use professionally recommended fungicides and follow best cultural practices for reliable results.
Q3: Is integrated pest management for citrus more effective than routine chemical spraying?
Yes, integrated pest management for citrus incorporates multiple strategies: monitoring, cultural control, biological enhancement, and targeted chemical use. Research shows IPM can reduce lemon tree disease incidence by up to 60% compared to conventional, routine chemical methods.
Q4: Why do my lemon tree leaves turn yellow?
Lemon tree leaf yellowing causes include overwatering, root rot, nutrient deficiencies (nitrogen, iron, magnesium), pest damage, or viral/fungal diseases. Testing soil, observing leaf patterns, and checking roots will clarify the cause.
Q5: When should I apply fungicides or horticultural oils?
Apply fungicides preventively before major rainy seasons or upon first symptoms. Horticultural oils for pests like scale or leafminers should be applied on new growth flushes and only during cool times of the day (morning/evening) to prevent leaf burn.
Q6: How can Farmonaut technology help me in monitoring lemon tree health?
We provide real-time satellite crop health monitoring including NDVI, soil moisture, and canopy density. Our tools make it easier to target at-risk zones, apply site-specific treatments, and minimize chemical applications for more sustainable citrus management.
Conclusion: Smart Strategies for Healthy, Productive Lemon Orchards
Lemon tree cultivation is both an art and a science, requiring vigilance and quick response to a wide range of diseases and pests. With proper understanding of disease cycles and symptoms—and by adopting integrated, technology-enabled management—you can protect your trees and maximize your harvests.
- Early detection and prompt intervention are the keys to successful lemon tree disease treatment.
- Cultural controls and orchard sanitation underpin every effective management strategy.
- Leveraging technology, like Farmonaut’s digital crop intelligence platform, empowers growers to scale up best practices and prevent problems before they compromise productivity.
Lemon trees are a valuable asset in both small gardens and commercial orchards. With reliable information and smart agricultural management, your lemons can remain healthy, vibrant, and abundantly fruitful for years to come.