Lemon Tree Diseases and Pests: 7 Protection Tips for Healthy Citrus Cultivation
“Up to 40% of lemon tree yield can be lost annually due to unmanaged diseases and pests.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Lemon Tree Diseases and Pests
- Common Diseases Affecting Lemon Trees
- Common Lemon Tree Pests
- Comprehensive Disease and Pest Management Table
- 7 Protection Tips for Lemon Tree Pest and Disease Management
- Integrated Pest Management for Citrus: Steps & Strategies
- How Farmonaut Empowers Lemon Growers
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Introduction
Lemon trees (Citrus limon) are prized in agriculture for their economic benefits and culinary value, supplying fresh fruit and key ingredients to households and industries globally. Yet, successful lemon tree cultivation faces persistent challenges from a diverse variety of lemon tree diseases and common pests. These threats can significantly impact tree health, reduce yield, and affect the quality of fruit, potentially undermining the grower’s investment and effort.
In this guide, we comprehensively address the disease and pest management strategies essential for sustained productivity and robust lemon trees. We’ll explain citrus canker symptoms, reveal methods for how to treat citrus black spot, and detail integrated pest management for citrus to reduce losses, advance sustainability, and ensure successful cultivation. Our focus is on actionable, proven techniques—supplemented by cutting-edge technology provided by Farmonaut—to keep your lemon plantation flourishing.
Understanding Lemon Tree Diseases and Pests
Managing the threats to lemon trees begins with understanding how diseases and pests operate. Bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens invade plant tissues, causing symptoms like lesions, yellowing, brown spots, and premature leaf or fruit drop. Meanwhile, insects such as aphids, mites, and scale can sap nutrients from leaves, stems, or fruit, further weakening tree health and opening the gateway for secondary infections.
Awareness of common lemon tree pests and the conditions favoring disease outbreaks is essential for timely and effective management. The following sections will help you identify the most significant diseases and lemon pests, as well as equip you with best management practices to counter them.
Common Diseases Affecting Lemon Trees: Symptoms, Spread & Management
Before we devise a lemon tree care and cultivation plan, let’s examine the major lemon tree diseases that threaten citrus orchards:
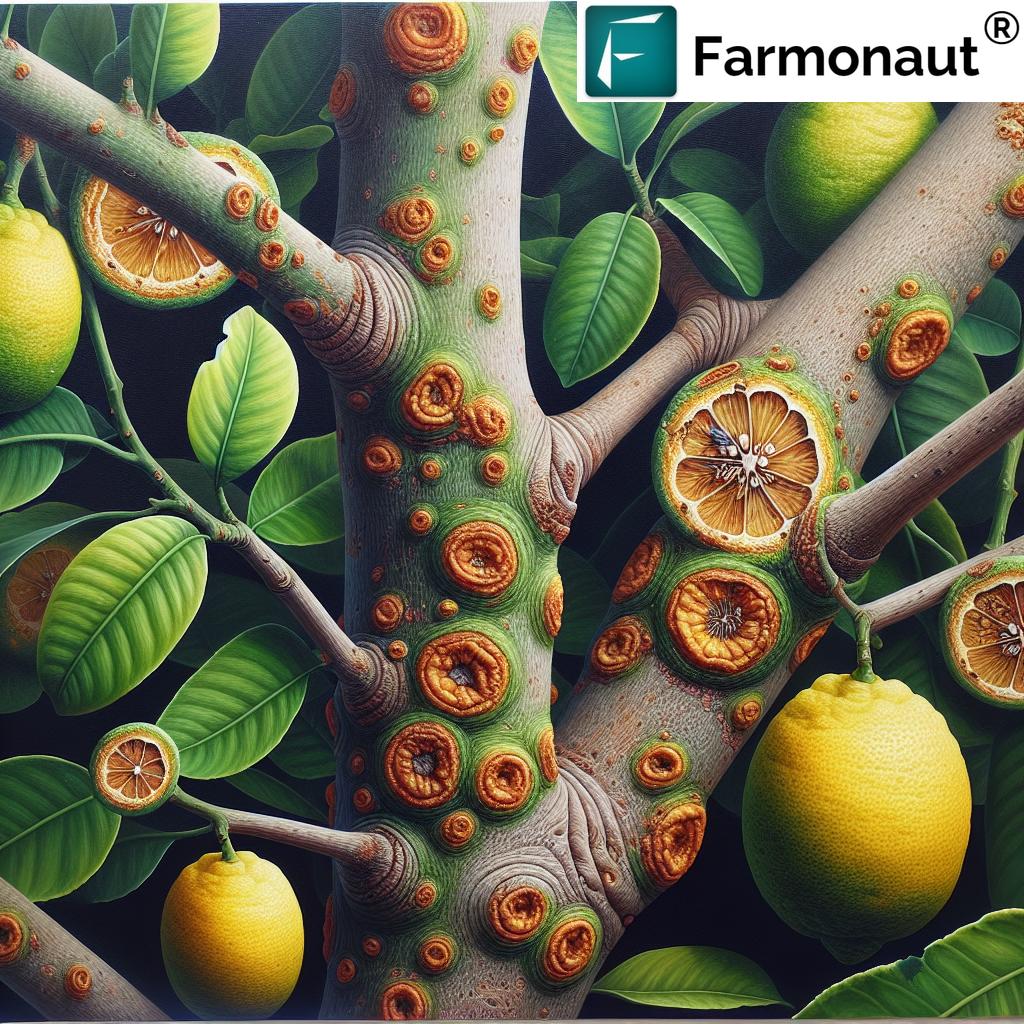
1. Citrus Canker (Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri)
Citrus canker is a notorious bacterial disease with distinctive canker symptoms: raised, water-soaked lesions on leaves, stems, and fruit, frequently surrounded by a yellow halo. The disease is particularly destructive as it:
- Spreads quickly via wind-driven rain and contaminated equipment
- Causes premature fruit drop and reduced tree vigor
- Leads to reduced yield and quality, occasionally making lemons unmarketable
Management:
Practicing good sanitation by removing and destroying infected material is fundamental. Apply copper-based bactericides during vulnerable growth stages, and maintain rigorous cleaning of farm tools to prevent further spread.
(Source)
2. Citrus Black Spot (Phyllosticta citricarpa)
Citrus black spot is a fungal disease characterized by dark, sunken lesions on both fruit and leaves, ultimately reducing yield and blemishing fruit quality. Black spot thrives in subtropical climates where wind and rain facilitate its spread. Symptoms start as small spots and evolve into larger sunken areas, often with a hard surface.
How to treat citrus black spot: Remove and destroy infected debris, prune affected twigs, and apply appropriate fungicides at recommended intervals to contain and reduce the disease.
(Source)
3. Melanose (Diaporthe citri)
This fungal disease mainly affects immature citrus tissue, leaving small, raised, brown or black lesions on leaves, fruit, and twigs. Severe cases lead to cosmetic damage that makes fruit unfit for sale.
Effective measures: Regularly prune and remove infected branches and dead material, and consider applying copper-based fungicides to reduce spread, especially after rainy periods.
(Source)
4. Botrytis (Botrytis cinerea)
More prevalent in cool, moist climates, Botrytis manifests as brown or gray velvety growths on twigs and blossoms. It frequently results in leaf loss, fruit drop, and dieback of young shoots. Botrytis often targets lemon trees in shaded or poorly ventilated areas.
Key management: Prune infected branches, avoid crowding by spacing trees adequately, ensure good sunlight exposure, and open the canopy for airflow. Prompt removal of infected material is crucial.
(Source)
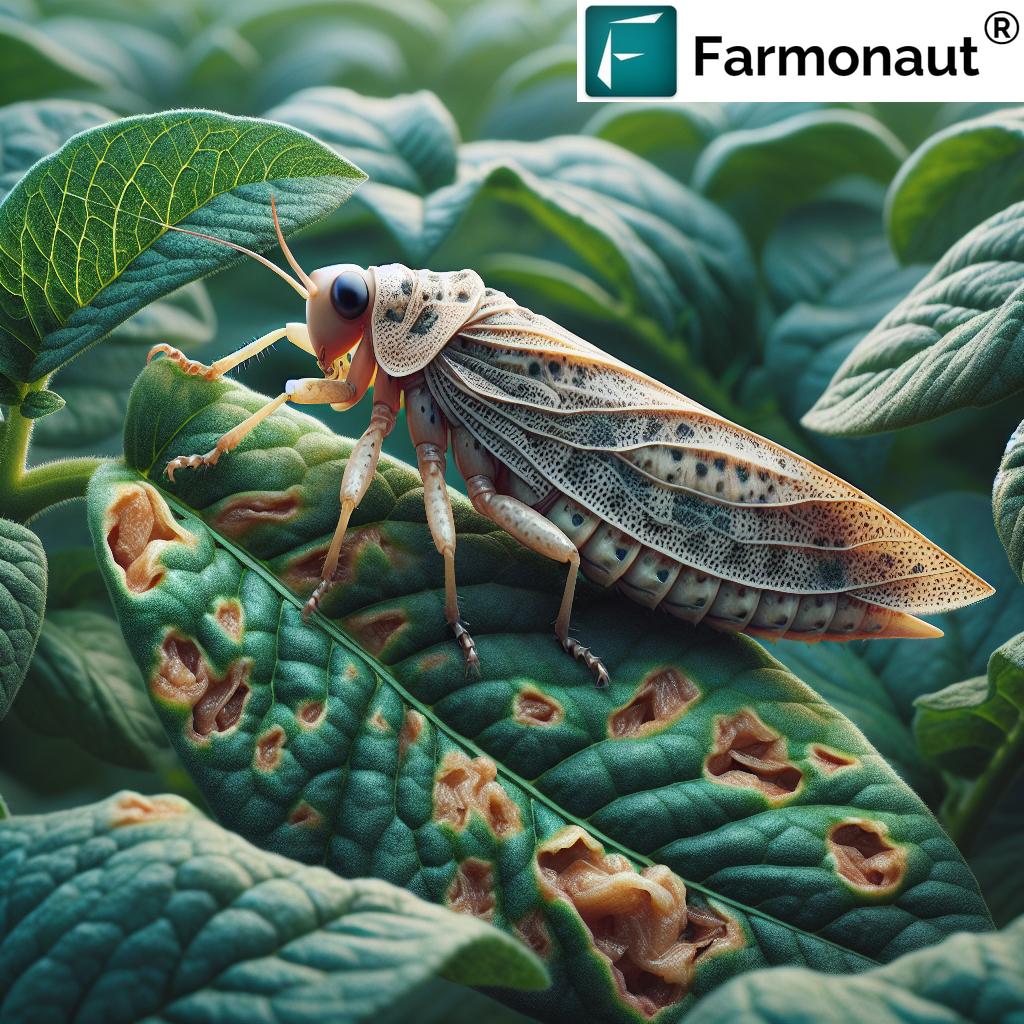
Common Lemon Tree Pests: Identification & Damage
“Lemon tree pest management begins with prompt identification and sound action.” Here’s what every citrus grower should know about common lemon tree pests:
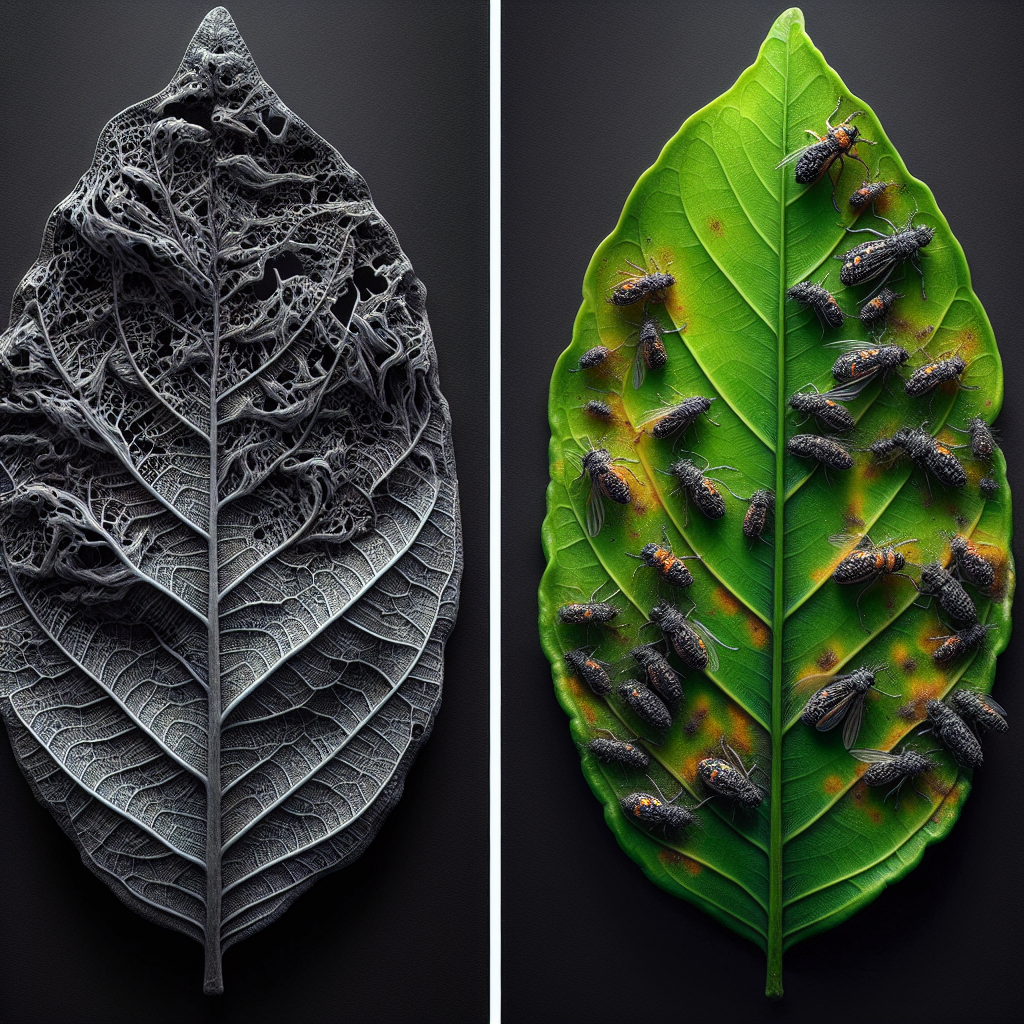
Aphids (Toxoptera citricida)
Tiny, soft-bodied insects that feed on sap from young leaves and tender stems, aphids cause:
- Deformed or curled leaves
- Premature leaf drop and shoot stunting
- Secretion of sticky honeydew, leading to sooty mold growth and decreased photosynthesis
Control: Use insecticidal soap/oil or encourage natural predators such as ladybugs. Promptly prune heavily infested shoots.
(Source)
Citrus Leaf Miner (Phyllocnistis citrella)
Leaf miner larvae tunnel inside lemon leaves, causing winding (serpentine) trails and blotches. The damaged leaves may appear distorted and lose vital photosynthetic area. While typically not fatal, chronic attacks stress young trees and expose wounds to secondary infections.
Managing citrus leaf miners: Prune out and destroy infested shoots. Use horticultural oils on young flushes and encourage beneficial insects.
(Source)
Scale Insects (Various species)
Scales are sap-sucking, often stationary insects (brown, black, or white depending on species) that attach to lemon stems, leaves, and fruit. Heavy infestations result in:
- Yellowing leaves and premature drop
- Reduced vigor and general tree weakening
- Honeydew secretion, sooty mold, and blocked photosynthesis
Mealybugs (Planococcus citri)
These waxy, white-powdered pests cluster in leaf axils and stems, extracting sap, causing yellowing, stunting growth, and leaving sticky honeydew that attracts ants and fuels mold growth.
Natural pest control for lemon trees: Encourage ladybugs and other beneficials, and wash off clusters with a strong stream of water.
(Source)
Citrus Bud Mite (Aceria sheldoni)
Almost invisible to the naked eye, the citrus bud mite feeds on developing leaf and flower buds, leading to deformation of leaves, flowers, and fruit, and can severely limit fruit yield and quality.
(Source)
Citrus Gall Wasp (Bruchophagus fellis)
This pest lays eggs in tender stems, producing characteristic galls. Emerging wasps from these swellings reduce future fruiting by distorting branch growth.
Control involves pruning and destroying galls before the wasps emerge and using sticky traps during the flight season.
(Source)
“Integrated pest management can reduce lemon tree disease incidence by over 50% compared to conventional methods.”
Comprehensive Disease and Pest Management Table for Lemon Trees
| Disease/Pest | Symptoms/Indicators | Estimated Impact on Yield (%) | Integrated Control Strategies | Preventive Tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus Canker (Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri) | Raised, water-soaked lesions on leaves, stems, fruit; yellow halo, premature fruit drop, reduced vigor | 30-40% | Remove infected material; apply copper-based bactericides; sanitize equipment | Sanitation; regular monitoring; resistant varieties |
| Citrus Black Spot (Phyllosticta citricarpa) | Dark, sunken lesions; blemished fruit, rot spots, lower fruit quality and yield | 20-35% | Remove debris; fungicide sprays; prune affected twigs | Pruning; control humidity; dispose fallen fruit |
| Melanose (Diaporthe citri) | Small, raised brown/black lesions; surface blemish; affects young fruit/leaves | 10-20% | Prune infected limbs; copper fungicides; improve air flow | Canopy management; regular removal of debris |
| Botrytis (Botrytis cinerea) | Brown/gray mold on twigs/blossoms; fruit/leaf drop; twig dieback | 8-15% | Prune for sunlight; open canopy; remove infected parts | Space trees adequately; avoid overwatering |
| Aphids (Toxoptera citricida) | Curling, deformed leaves; sticky honeydew; sooty mold; stunted shoots | 10-18% | Insecticidal soaps; encourage ladybugs; prune infestation | Monitor new growth; natural predator conservation |
| Citrus Leaf Miner (Phyllocnistis citrella) | Serpentine leaflet tunnels; leaf curling/distortion; reduced photosynthesis | 6-10% | Remove infested leaves; horticultural oils; promote beneficial insects | Plant resistant varieties; prune regularly |
| Scale Insects (Various species) | Fixed, small, colored bumps; sticky leaves; leaf yellowing; black sooty mold | 10-15% | Manual removal; horticultural oil; support predator insects | Reduce dust; regular monitoring |
| Mealybugs (Planococcus citri) | White, waxy clusters; ant trails; yellowing leaves; stunting | 6-12% | Wash off with water; insecticidal soap; beneficial insects | Remove weeds; manage ants; prune infested twigs |
| Citrus Bud Mite (Aceria sheldoni) | Malformed leaves, flowers, fruit; reduced fruit set | 4-8% | Sulfur sprays; remove and destroy affected buds | Prune in dormant season; monitor buds |
| Citrus Gall Wasp (Bruchophagus fellis) | Stem galls; distorted branches; weakened growth | 5-14% | Prune/destroy galls; hang sticky traps during flying season | Winter pruning; regular orchard checks |
7 Protection Tips: Lemon Tree Pest and Disease Management
To establish sustainable citrus orchards and minimize crop loss, implement these **7 essential protection tips for effective lemon tree care and cultivation**:
-
1. Practice Rigorous Sanitation
- Remove infected plant material promptly and dispose of away from growing areas to reduce inoculum.
- Regularly clean equipment to prevent disease dissemination (especially canker and black spot).
-
2. Ensure Proper Pruning and Canopy Management
- Prune overcrowded branches and open the canopy to light and airflow to prevent melanose and botrytis.
- Target removal of dead/diseased twigs as soon as detected.
-
3. Implement Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
- Combine monitoring, cultural methods, biological control, and selective pesticide use for sustainable results (explained below).
-
4. Use Disease- and Pest-Resistant Varieties
- Opt for cultivars with built-in genetic tolerance, reducing reliance on chemicals and lowering disease incidence.
-
5. Optimize Nutrient and Water Management
- Maintain balanced nutrition for tree vigor—avoid excess nitrogen, which can make new growth more attractive to aphids/leaf miners.
- Ensure well-drained soil to prevent fungal build-ups and root diseases.
-
6. Encourage Natural Predators
- Promote **ladybugs**, lacewings, and parasitic wasps in your orchard to naturally suppress aphids, leaf miners, and scale.
- Avoid broad-spectrum insecticides that harm beneficials.
-
7. Timely and Targeted Chemical Intervention
- Apply **fungicides/bactericides** only as needed and rotate actives to minimize resistance.
- Spot-treat infestations early for best results and minimal residue.
Integrated Pest Management for Citrus: Steps & Strategies
Integrated Pest Management for citrus is the cornerstone of sustainable, effective lemon tree pest management, melding multiple strategies for long-term control with minimal environmental impact.
Key Steps in Citrus IPM:
-
Regular Monitoring:
- Inspect trees bi-weekly, focusing on young leaves, shoots, stems, and fruit for early disease or pest signs.
- Take action at the first sign of lesions, tunneling, honeydew, or abnormal growth.
-
Implementing Cultural Practices:
- Opt for proper tree spacing, routinely prune, and ensure proper irrigation and soil health.
- Debris management (removing fallen fruit and leaves) is critical to minimizing overwintering pests/pathogens.
-
Biological Control:
- Release or conserve beneficial insects (ladybugs, parasitoid wasps).
- Promote plant diversity to shelter these natural pest predators.
-
Chemical Control—As Needed:
- Apply targeted sprays (copper fungicides, horticultural oils) to outbreak areas.
- Rotate products and adhere to recommended intervals.
-
Preventive Measures:
- Sanitation (removing infected material).
- Choosing resistant varieties suited to your region.
By employing these strategies together, growers can reduce reliance on chemicals and safeguard both tree health and the environment.
How Farmonaut Empowers Lemon Growers: Precision Agriculture for Disease and Pest Management
At Farmonaut, we are committed to transforming lemon cultivation and citrus pest management globally through advanced, affordable precision agriculture tools. Our integrated platform offers a holistic view of the entire farm, enabling data-driven decisions and rapid response to emerging threats.
Our Key Technologies for Lemon Tree Care:
-
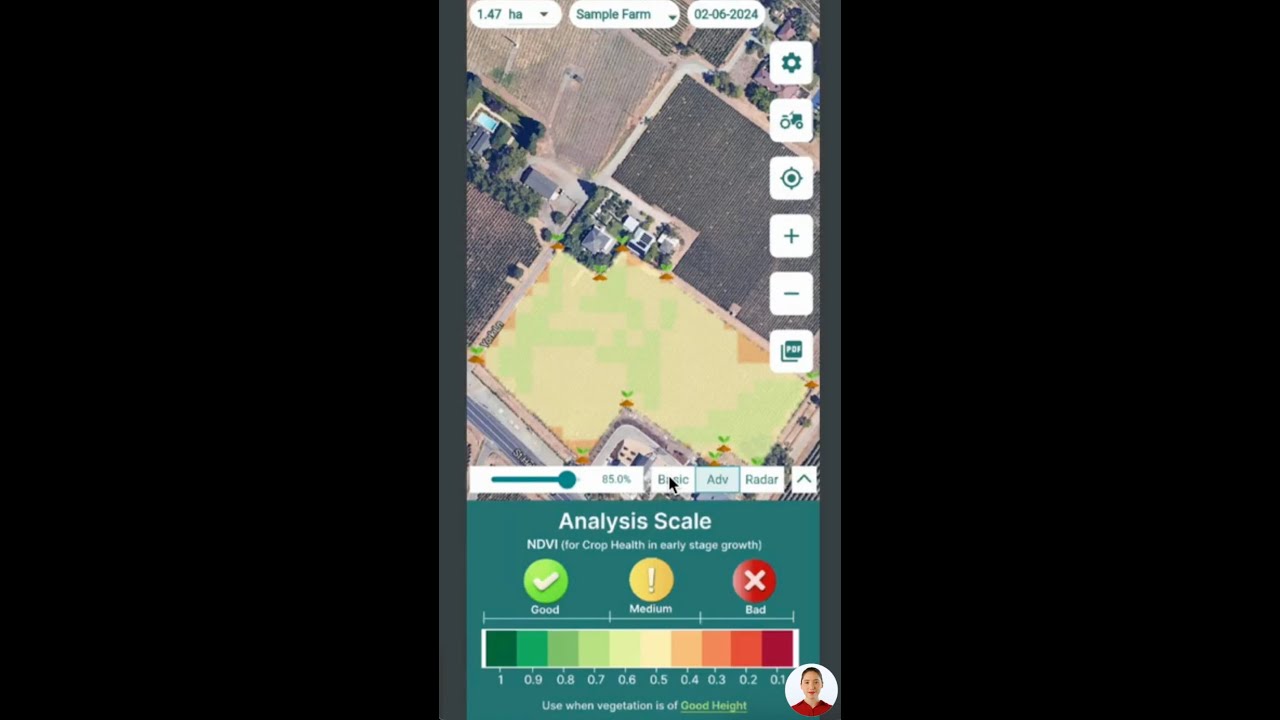
Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring:
We harness multispectral satellite imagery to detect vegetation health anomalies, stress due to disease or pest infestations, and early signs of nutrient deficiency. This enables proactive management of threats like citrus black spot and melanose, ultimately reducing losses. -
AI-Based Advisory System (Jeevn AI):
Our AI system analyzes farm and weather data to deliver tailored recommendations for fungicide spray schedules, optimal irrigation, and even biological control suggestions—direct to the farmer’s mobile device. -
Blockchain-Based Traceability:
With Farmonaut’s traceability solution, growers can assure buyers about the origin, disease-management protocols, and sustainability of their lemons—boosting market value and trust. -
Fleet & Resource Management:
Large growers benefit from fleet and resource management tools, improving labor efficiency and equipment use—crucial during peak pruning/spraying times. -
Carbon Footprinting:
With carbon tracking features, we support sustainable practices by helping citrus producers measure and reduce the environmental impact of chemical and resource use in their plantations.
Our precision agriculture tools are accessible through robust Android, iOS, and web apps—making advanced crop and pest surveillance truly farm-ready, scalable, and affordable. For developers and agribusinesses, our satellite and weather data API and detailed developer documentation enable seamless integration and custom extensions.
Ready to experience next-generation lemon tree care and cultivation? Download our Farmonaut app today and transform your orchard management with real-time insights and actionable intelligence.
Flexible and Affordable Subscriptions for All Farmers
Our subscription model makes cutting-edge technology accessible to growers at every scale. Subscribe to Farmonaut below and unlock the power of smart, data-driven citrus farming:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the first signs of lemon tree diseases?
Early indicators include yellow halos on leaves (citrus canker), dark or sunken spots on fruit (black spot), twisted or curled new growth (aphid or leaf miner damage), and brown/black raised lesions (melanose). Periodic inspection is key for prompt intervention.
How can I prevent lemon tree pests without using chemicals?
Employ a combination of non-chemical measures: prune regularly, remove infected debris, promote beneficial insects like ladybugs, and avoid over-fertilizing. Releasing predator species and maintaining orchard hygiene can naturally suppress pest populations.
Should I always remove affected leaves or fruit?
Yes. Promptly removing infected material reduces inoculum and prevents further spread of diseases such as canker, black spot, and botrytis. Destroy removed materials well away from the orchard site.
What role does Farmonaut play in lemon tree care?
At Farmonaut, we empower growers with real-time crop monitoring, AI-based advisory for disease and pest management, traceability, and resource optimization. Our platform supports timely, site-specific action to reduce lemon tree disease and pest impact.
Is satellite-based crop monitoring suitable for smallholders?
Absolutely. We’ve made our services accessible and affordable, even for small and medium-sized farms, via user-friendly mobile and web apps. Satellite insights help all growers quickly spot pest and disease issues across their fields, reducing losses.
How do I know when to apply fungicides?
Fungicides should be used at the first sign of lesions, mold, or in prone seasons—especially after rain or damp periods. Follow an integrated pest management approach and rotate chemicals to minimize resistance.
What’s the best way to manage scale and mealybug infestations?
Promote natural predators, such as ladybugs, avoid dust buildup, eliminate ant trails, and use horticultural oils/insecticidal soap sprays where necessary.
Where do I start if I want to digitalize my lemon orchard’s management?
Start by signing up for the Farmonaut app. Our dashboard helps you visually assess your orchard’s health, receive crop-specific alerts, and access instant recommendations, making digital farm management simple.
Conclusion: Sustainable, Productive Lemon Farming Starts Here
Lemon trees are a cornerstone of global agriculture, but their productivity and quality are constantly threatened by a wide array of diseases and pests. Armed with detailed knowledge about prominent issues—such as citrus canker, black spot, melanose, aphids, leaf miners, and more—farmers can take decisive, early action to protect their orchards.
By adopting a proactive, integrated pest management approach that blends regular monitoring, cultural practices, biological interventions, and, where required, targeted chemical measures, you can prevent lemon tree diseases, control infestations, and ensure the ongoing health and vigor of your citrus plantation.
Leveraging smart farm management tools—like those offered by Farmonaut—can substantially streamline your lemon tree care, increase yields, and support long-term sustainability and traceability across all your citrus operations.
For growers determined to thrive in modern, competitive agriculture, prioritizing effective lemon tree pest and disease management is not an option—it’s a necessity. Start today, integrate technology, and reap the true potential of healthy, productive lemon trees.