Lemon Tree Leaf Problems: 7 Fixes for Yellow Leaves
“Up to 60% of lemon tree yellowing is caused by nutrient deficiencies, especially nitrogen and magnesium.”
“Overwatering accounts for nearly 40% of yellow leaf cases in homegrown lemon trees.”
- Introduction: Why Are Lemon Tree Leaves Turning Yellow?
- 1. Nutrient Deficiencies
- 2. Watering Issues
- 3. Lemon Tree Pests and Diseases
- 4. Environmental Stress
- 5. Soil Quality and Drainage
- 6. Sooty Mold
- 7. Problem-Solution Table for Lemon Tree Leaf Problems and Solutions
- Farmonaut’s Technology: Supporting Citrus Tree Health
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Lemon Tree Leaf Yellowing: Understanding the Issues
There’s nothing quite as rewarding as nurturing a vibrant, healthy lemon tree, with its glossy leaves and aromatic fruits. However, many citrus enthusiasts encounter a familiar and frustrating sight: the leaves turning yellow, diminishing both beauty and productivity. Lemon tree leaf yellowing can be a warning sign of deeper issues affecting tree health.
Yellow leaves, leaf drop, or discoloration are frequently reported as common “lemon tree leaf problems,” triggering growers to ask, “why are lemon tree leaves turning yellow?” The answer often lies in a combination of nutrient deficiencies, watering mistakes, pest infestations, soil quality problems, environmental stress, and diseases like sooty mold.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll tackle the seven most critical causes behind yellow leaves on lemon trees. We’ll break down the symptoms, dig into the science of each problem, and—most importantly—provide expert solutions to restore your citrus tree’s health. If you’re looking for a single resource covering all major lemon tree leaf problems and solutions, you’re in the right place.
1. Nutrient Deficiencies: The Main Culprit Behind Lemon Leaf Yellowing
Lemon trees require a balanced supply of essential nutrients for optimal growth. Nutrient deficiencies commonly manifest in yellowing leaves—sometimes as subtle discolorations, sometimes as stark, patchy areas. Understanding how deficiencies affect your citrus is step one to a thriving tree.
Key Nutrient Deficiencies and Their Symptoms
-
Nitrogen Deficiency – Characterized by: Light green to yellowing of older leaves, especially on the lower part of the tree, often beginning at the leaf base and progressing outward. A tree may exhibit stunted growth, reduced fruit production, and eventually, yellowing will also affect younger leaves if untreated.
Reference: edis.ifas.ufl.edu -
Phosphorus Deficiency – Symptoms include: Loss of deep green color in older leaves, new leaves appearing small, narrow, and sometimes with a purplish hue. Fruits may develop a rough rind and hollow core.
Reference: edis.ifas.ufl.edu -
Potassium Deficiency – Manifested by: Yellowing of leaf margins and tips on older leaves, progressing to broader areas of yellow, and in severe cases, leaf spotting and necrosis (death of tissue).
Reference: edis.ifas.ufl.edu -
Magnesium Deficiency – Appears as: Yellowish-green blotches near the base of older leaves, forming an inverted V-shape, with green areas at the tips and base. In advanced cases, leaves may turn completely yellow and drop prematurely.
Reference: edis.ifas.ufl.edu -
Micronutrient Deficiencies – Deficiencies in manganese, zinc, or iron cause yellowing of leaves with green veins (chlorosis), or mottled, patchy appearances.
Reference: thefruitgrove.com
Did you know? – Over 60% of lemon tree leaf yellowing cases result from nutrient deficiencies! Early detection and correction help prevent severe damage to your citrus foliage and fruit yield.
Lemon Tree Leaf Problems and Solutions: Tackling Nutrient Deficiency
- Conduct a Soil Test: Use a soil testing kit or consult your local extension office to diagnose which nutrients may be lacking. Comprehensive testing helps pinpoint specific issues.
- Apply the Best Fertilizer for Lemon Trees: Choose a balanced citrus fertilizer or custom formulas containing deficient nutrients (nitrogen, potassium, magnesium, etc.). Look for products labeled 6-6-6, 10-10-10, or use slow-release fertilizers designed for citrus.
- Foliar Feeding: For rapid recovery, foliar sprays (liquid feeds sprayed on leaves) provide micronutrients like zinc or iron directly to the foliage.
- Maintain a Fertilization Calendar: Regular applications during active periods of growth, usually spring and summer, keep your lemon tree healthy.
Tip: For small or container-grown citrus, fertilize every 6–8 weeks during the growing season. Always follow product directions, as over-application can damage the roots.
For large plots or commercial orchards, leveraging satellite-based crop monitoring (like Farmonaut’s services described below) helps identify nutrient stress areas across your fields—targeting problem zones before widespread yellowing occurs.
2. Watering Issues: Overwatering & Underwatering in Lemon Trees
Correct watering is essential for healthy lemon tree leaves. Both inadequate and excessive watering are major lemon tree leaf drop causes and frequently responsible for yellowing or browning leaves.
- Underwatering: The leaves develop yellow or brown tips and edges, become crispy, curl, and eventually drop. Prolonged dryness can stunt fruit production and reduce flower set. ((https://www.thespruce.com/lemon-tree-leaves-turning-yellow-7505016?utm_source=openai))
- Overwatering: Causes root rot due to waterlogged soils, resulting in limp, wilting foliage, widespread yellowing, leaf drop, and ultimately, tree decline. ((https://www.thespruce.com/lemon-tree-leaves-turning-yellow-7505016?utm_source=openai))
Lemon Tree Watering Tips: Preventing Yellowing & Leaf Drop
- Assess Soil Moisture: Insert your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle. Water only if the upper 1 inch feels dry, ensuring the soil isn’t soggy.
- Ensure Proper Drainage: Lemon trees thrive in well-draining soils. For containers, use citrus-specific potting mix with perlite or coarse sand.
- Deep Watering: Water deeply but infrequently. Allow excess water to drain away from the root zone – avoid trays or saucers beneath pots.
- Monitor for Signs of Stress: Yellowing, abnormally soft leaves, or sudden leaf drop often point to overwatering problems.
Remember: Overwatering is the second leading cause of yellow leaves in homegrown lemon trees. Adjust your schedule for the season—watering less often in winter and more during hot, dry spells.
3. Lemon Tree Pests and Diseases: Aphids, Scales, Fungal Troubles
Pests and diseases are persistent threats to citrus tree foliage. Tiny insects, invisible eggs, or lurking fungal diseases can cause severe yellowing, distortion, and premature leaf drop.
Below are the most common lemon tree pests and diseases that cause yellow leaves:
Common Lemon Tree Leaf Pests and Fungal Diseases
-
Aphids: Small, green or black insects cluster on new leaves and stems, sucking sap and causing distorted, yellowing foliage.
They also leave sticky honeydew on leaves, fostering sooty mold. - Scale Insects: Hard or soft-bodied scales attach to the underside of leaves, sapping nutrients, causing pale yellow patches, and sometimes premature leaf drop ((https://ecofamilylife.com/garden/lemon-tree-leaf-drop-top-5-causes-and-solutions/?utm_source=openai)).
- Citrus Leaf Miners: Tiny moth larvae burrow between leaf layers. Look for winding silvery trails and puckered, twisted leaf distortion ((https://gardenine.com/meyer-lemon-problems//?utm_source=openai)).
- Fungal Diseases: Powdery mildew, greasy spot, anthracnose, and others create leaf spots, curling, browning, and ultimately, loss of leaves ((https://www.gardenguides.com/106019-leaf-diseases-lemon-trees.html?utm_source=openai)).
Solutions to Control Lemon Tree Pests and Fungal Diseases
- Inspect Leaves Regularly: Early detection of aphids, scales, or fungal diseases is critical to control.
- Use Insecticidal Soap or Horticultural Oil: Spray affected foliage and branches to control soft-bodied pests such as aphids and scales.
- Prune & Remove Infested Leaves: Dispose of severely infested or diseased foliage to limit spread.
- Apply Appropriate Fungicides: If fungal spots or powdery growth appears, treat with a citrus-safe fungicide per label instructions.
- Encourage Natural Predators: Ladybugs, lacewings, and other beneficial insects naturally reduce aphid and scale populations.
Maintaining strong, healthy trees with good air circulation and balanced nutrition boosts their defense against pests and disease.
4. Environmental Stress: Light, Temperature, and Weeds
Environmental stress can silently trigger yellowing and leaf drop—sometimes mimicking symptoms from nutrient deficiencies or disease. Let’s break down the primary environmental causes impacting lemon tree foliage:
-
Temperature Fluctuations:
- Rapid or extreme shifts—such as unexpected frosts or unseasonal heat waves—can shock the tree, prompting it to drop leaves and abort fruit.
(source)
- Rapid or extreme shifts—such as unexpected frosts or unseasonal heat waves—can shock the tree, prompting it to drop leaves and abort fruit.
- Insufficient Light: Lemon trees require at least 8 hours of direct sunlight daily for photosynthesis and strong, green leaves. Low light conditions (source) cause leaves to pale, yellow, or fall.
- Weeds Around the Root Zone: Competing weeds deplete essential nutrients and moisture, stressing lemon trees and resulting in leaf yellowing or loss.
Expert Solutions for Environmental Lemon Tree Leaf Problems
- Provide Shade Cloth for young trees during hot spells and frost protection blankets during cold snaps.
- Choose a Bright Location for potted trees, or prune overhanging branches to increase sun exposure for in-ground specimens.
- Mulch and Weed Control: Apply a thick organic mulch 3–4 inches deep, keeping it away from the trunk. Weed regularly to prevent competition in the root area.
Healthy trees withstand environmental stress with greater resilience.
“Up to 60% of lemon tree yellowing is caused by nutrient deficiencies, especially nitrogen and magnesium.”
5. Soil Quality and Drainage: Improving Soil Drainage for Citrus Trees
The quality and structure of your soil are vital for nutrient uptake, water retention, and preventing root diseases. Poor soil can directly affect tree health and promote yellowing, browning, or leaf drop.
- Compacted or Infertile Soils: Limit root expansion, reduce oxygen, and slow nutrient absorption—leaves grow smaller, paler, and overall growth is stunted. (source)
- Drainage Issues: Waterlogged soils drown roots, trigger root rot, and lead to yellow, wilting leaves. (source)
How to Improve Soil Quality and Drainage for Lemon Trees
- Amend with Organic Matter: Add compost, well-rotted manure, or leaf mold to enrich nutrient-poor soils and improve structure.
- Ensure Good Drainage: Grow in raised beds, or create planting mounds for in-ground trees. Use a free-draining potting mix for containers.
- Test Soil Regularly: Soil tests reveal pH (ideal is 6–7 for citrus), and nutrient status, guiding precise adjustments.
- Monitor for Waterlogging: After heavy rains, check for ponding—consider installing drains or moving pots under shelter if required.
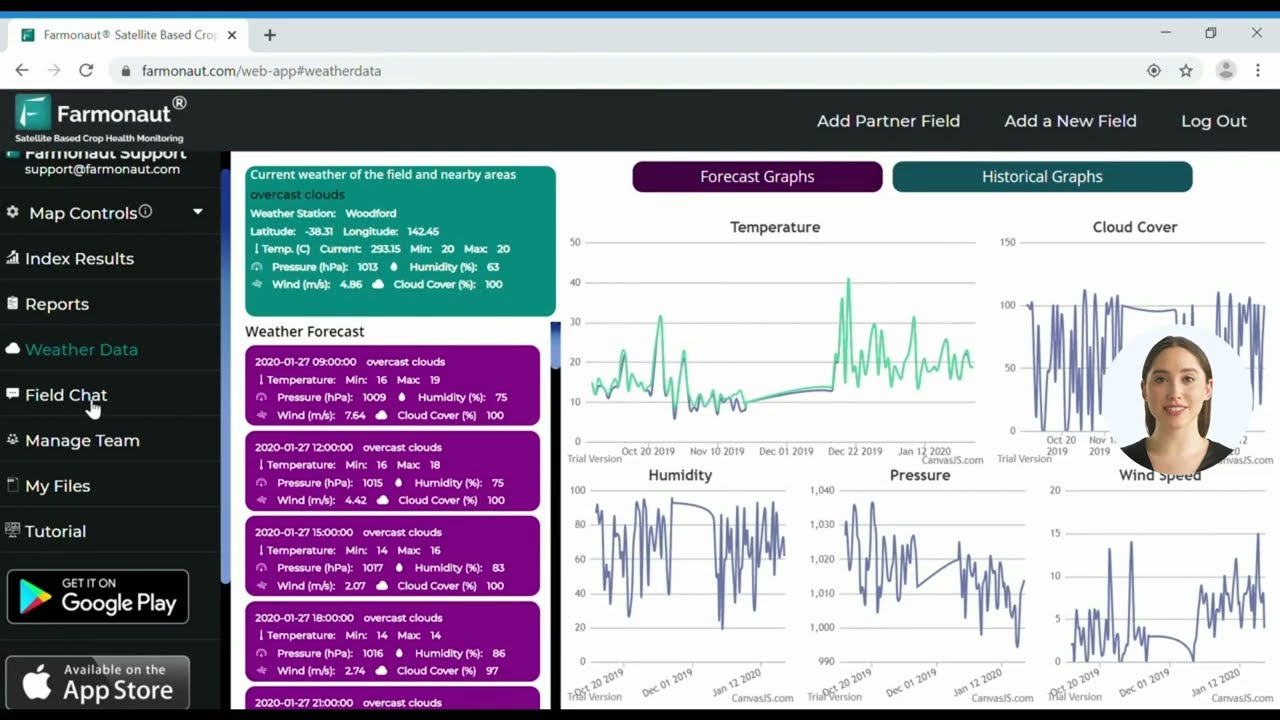
Learn more: Farmonaut’s crop plantation & forest advisory tools can provide precision weather, waterlogging risk alerts, and soil health monitoring in real time for large-scale citrus growers and home orchardists alike.
6. Sooty Mold: Removing Black Mold from Your Lemon Tree Foliage
Sooty mold forms on lemon leaves as a black, dusty layer. Although it does not parasitize the tree directly, it grows on the sticky honeydew deposited by aphids, scales, whiteflies, or mealybugs. This mold can block sunlight, disrupting photosynthesis and compounding yellowing and leaf problems.
Recognizing Sooty Mold:
- Leaves appear coated in dark, sooty powder or felt-like growth.
- You may notice sticky surfaces, which attract ants (feeding on the honeydew).
- Chlorosis or yellowing beneath the mold indicates the tree is stressed.
How to Treat Sooty Mold on Lemon Trees
- Identify and Remove Pests: The first step is eradicating the pests (aphids, scales, mealybugs, and whiteflies) creating honeydew. Spray with horticultural oil or insecticidal soap—repeat after 10-14 days if necessary.
- Wash the Foliage: Gently spray the leaves with water and a mild solution of dish soap to remove the sooty coating.
- Repeat and Monitor: Persistent infestations require regular follow-ups; clean affected areas and control pests to avoid recurrence.
- Promote Air Circulation: Prune crowded branches for better airflow, helping leaves dry faster and deterring mold.
Effective pest management is the long-term solution for sooty mold. Well-timed horticultural oil applications suffocate pest eggs and disrupt their life cycle, preventing new honeydew accumulation and thus limiting sooty mold resurgence.
For in-depth disease monitoring and targeted citrus protection strategies at scale, check out Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management Solutions.
7. Lemon Tree Leaf Problems and Solutions: Problem-Solution Table
For a quick reference, use the following problem-solution table to troubleshoot key lemon tree leaf yellowing symptoms. This structured approach links each problem’s appearance with its estimated occurrence, likely cause, recommended action, and expected recovery period.
| Problem/Symptom | Estimated Occurrence (%) | Possible Cause | Recommended Solution | Expected Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellowing of older leaves (all over) | 45% | Nitrogen Deficiency | Apply high-nitrogen fertilizers after conducting a soil test | 2–4 weeks |
| Yellow leaf margins/tips with brown spots | 25% | Potassium Deficiency, Salt Stress, Overwatering | Use potassium-rich fertilizer; adjust watering pattern | 2–6 weeks |
| Yellowing between green veins (mottled appearance) | 15% | Iron, Zinc, or Manganese Micronutrient Deficiency | Cheated iron or foliar micronutrient sprays | 2–3 weeks |
| Black, sooty film on leaves | 10% | Sooty Mold from Aphids/Scales | Wash leaves and control pests using horticultural oil | 1–4 weeks |
| Yellow, limp, dropping leaves | 40% | Overwatering, Poor Drainage, Root Rot | Improve soil drainage, reduce watering, check roots | 2–8 weeks |
| Winding, silvery trails on distorted leaves | 18% | Citrus Leaf Miner Insects | Remove infested leaves, use insecticidal sprays | 2–6 weeks |
| General yellowing after heat, cold, or rapid weather changes | 20% | Environmental Stress (temperature, sunlight) | Protect from extremes; relocate or provide shade/shelter | 1–8 weeks |
How Farmonaut’s Technology Supports Citrus Leaf Health
For those seeking cutting-edge solutions in lemon tree management, Farmonaut provides advanced, satellite-based monitoring and actionable insights for all growers—from hobbyists to professionals.
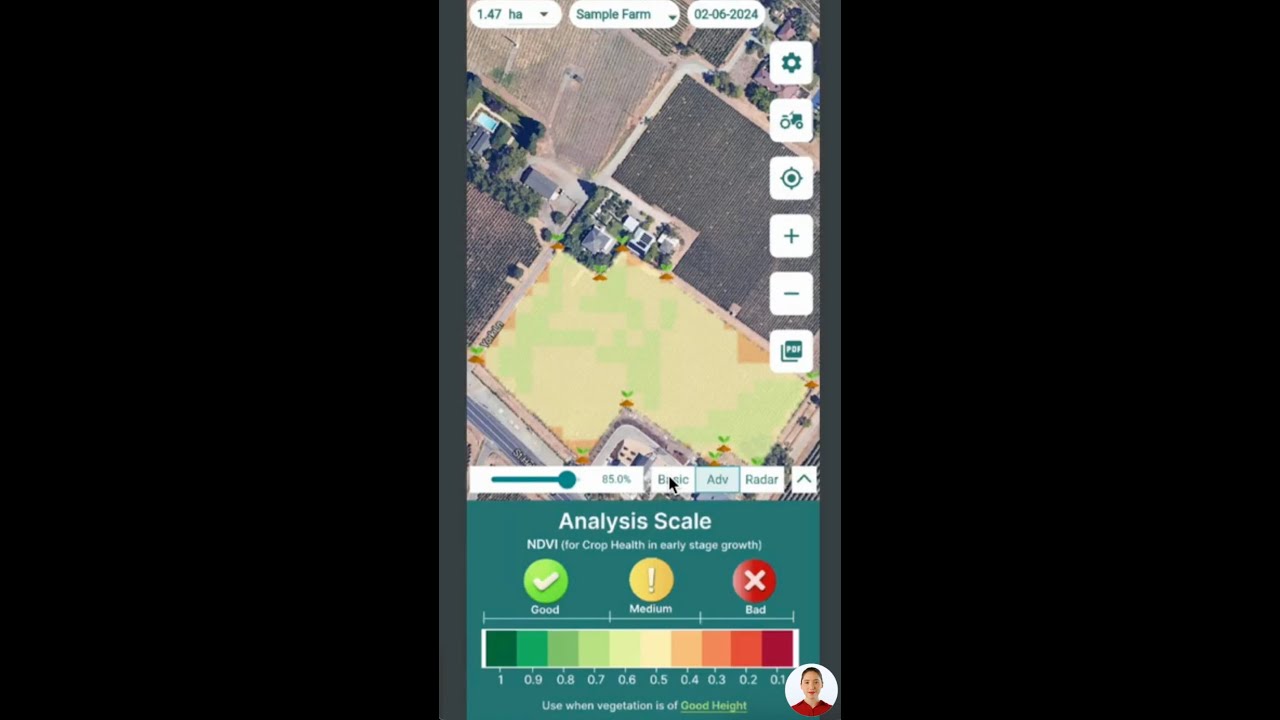
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: We at Farmonaut utilize multispectral satellite imagery to detect yellowing, nutrient stress, leaf diseases, and waterlogging on a massive scale. This technology highlights precise problem areas, enabling fast, targeted intervention (explore on web, Android, or iOS apps).
- AI-Powered Advisory: Our Jeevn AI tool offers personalized advice, integrating crop and weather insights to maximize citrus tree health—from fertilization schedules to pest control tips.
- Resource & Fleet Management: Large growers benefit from Farmonaut’s fleet management tools, optimizing field operations and reducing resource wastage during citrus harvest and maintenance.
- Blockchain Traceability: For food safety and supply chain transparency, Farmonaut’s traceability solution brings trust to every lemon’s journey from the orchard to the end consumer.
- Carbon Footprinting for Citrus: We provide carbon tracking tools, helping large-scale growers and businesses comply with sustainability standards by monitoring emissions during lemon production.
- API Access for Developers & Businesses: Integrate our satellite and weather API into your own agriculture tech stack or explore detailed API documentation in our developer docs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Lemon Tree Leaf Yellowing
Why are my lemon tree leaves turning yellow?
Lemon tree leaves turn yellow mainly due to nutrient deficiencies (especially nitrogen and magnesium), poor watering practices (overwatering or underwatering), pests such as aphids and scales, fungal diseases like sooty mold, poor soil drainage, and environmental stress from lack of sunlight or extreme temperature changes.
What’s the best fertilizer for lemon trees to prevent yellow leaves?
The best fertilizer for lemon trees is a balanced, slow-release citrus fertilizer (6-6-6 or 10-10-10), with added micronutrients if specific deficiencies (iron, zinc, manganese) are identified. Always apply according to soil test recommendations and the manufacturer’s instructions.
How do you treat sooty mold on lemon trees?
How to treat sooty mold on lemon trees: First, control the insect pests (scales, aphids, whiteflies) producing honeydew by spraying horticultural oil or insecticidal soap. Then gently wash mold off leaves with water and mild soap.
How do I identify lemon tree nutrient deficiencies?
Each nutrient deficiency causes distinctive symptoms. Nitrogen shortage shows up as overall yellowing of older leaves, magnesium creates yellow V-shapes at the base, iron leads to yellow leaves with green veins. Soil testing is the most precise identification method.
Can overwatering cause lemon tree leaf yellowing?
Yes—overwatering is the second most common reason for yellow leaves in home-grown lemons. It leads to root rot, poor nutrient uptake, and severe leaf drop. Always ensure well-draining soil and water only when the top inch feels dry.
How can Farmonaut help commercial citrus growers?
Farmonaut’s platform provides real-time satellite imagery and AI-powered insights to monitor citrus leaf health, optimize resource usage, identify problem areas (nutrient, soil, water, pest issues), and reduce losses—scaling from small gardens to industrial groves. Learn more about large-scale farm management here.
Conclusion: Achieving Healthy, Green Lemon Tree Leaves
A thriving lemon tree is the sum of attentive care, proactive monitoring, and targeted problem-solving. The most common reasons for lemon tree leaf yellowing—from nutrient deficiencies and watering issues to pests, diseases, soil quality, drainage, and environmental stress—are all manageable with the right knowledge and consistent action.
- Test your soil regularly to spot early deficiencies and adjust fertilization.
- Adjust watering to suit seasons and environmental conditions—never allow roots to sit in waterlogged soils.
- Monitor leaves and growth habit for early signs of pests or diseases. Quick intervention prevents widespread damage.
- Promote healthy soils rich in organic matter and excellent drainage for vigorous root and foliage growth.
- Leverage technology—for those with large orchards or professional ambitions, platforms like Farmonaut deliver advanced, affordable precision agriculture solutions, helping you monitor, predict, and resolve citrus issues with minimal effort and maximum efficiency.
With this guide and the right lemon tree leaf problems and solutions, your citrus trees can bounce back from yellowing, produce abundant, high-quality fruit, and remain a vibrant, aromatic centerpiece of your home or orchard for years to come.
Want more insight or personalized advice? Try Farmonaut’s crop health tools via web, Android, or iOS below!