- Introduction: The Critical Importance of Plant Biosecurity
- Understanding Plant Biosecurity: Core Principles
- Plant Biosecurity: 7 Shocking Pest Control Secrets
- Secret 1: Real-Time Agricultural Pest Monitoring
- Secret 2: Integrated Pest Management Strategies (IPM)
- Secret 3: Quarantine Protocols for Plants
- Secret 4: Early Pest Detection and Rapid Response
- Secret 5: Sustainable Plant Pest Management Solutions
- Secret 6: Data-Driven Biosecurity Measures in Agriculture & Forestry
- Secret 7: Education, Training, and Public Awareness in Biosecurity
- Farmonaut: Empowering Modern Plant Biosecurity & Pest Monitoring
- Plant Biosecurity Strategies vs. Pest Threats (Table)
- Key Biosecurity Practices by Country
- Future Challenges and Directions in Plant Biosecurity
- FAQ: Plant Biosecurity and Pest Control
- Conclusion: Securing the Future with Plant Biosecurity
“Over 40% of global crop losses are caused by pests, making biosecurity strategies vital for sustainable agriculture.”
Plant Biosecurity: 7 Shocking Pest Control Secrets!
Plant biosecurity is a critical component in safeguarding the health of our crops and forests. Effective pest control isn’t just about using the latest spray—it’s about a comprehensive, sustainable approach that affects every corner of agriculture, forestry, and even our gardens. In a world increasingly threatened by invasive pests and plant diseases, we must explore revolutionary ways to protect crop health, sustain food security, conserve biodiversity, and maintain productive, resilient ecosystems.
We’re about to reveal 7 shocking secrets in plant biosecurity, showing how science, technology, and smart biosecurity measures can help us prevent, detect, and manage major pest threats.
Understanding Plant Biosecurity: Core Principles
Let’s start by clarifying what plant biosecurity means for us as farmers, foresters, agribusinesses, policymakers, and consumers.
What is Plant Biosecurity?
Plant biosecurity refers to a strategic, integrated approach—encompassing policies, regulations, practices, and technologies—to manage the risk of pests and diseases that could threaten plant health, agriculture, forestry, and the wider environment. Its core objectives are to:
- Protect plant health by preventing the introduction and spread of harmful pests and diseases
- Ensure food security for present and future generations
- Conserve biodiversity by safeguarding native plants and delicate ecosystems
- Facilitate international trade with trusted, healthy plant products
- Maintain productive and resilient agricultural and forestry systems
A comprehensive plant biosecurity system has four key components:
- Prevention – stopping harmful organisms from gaining entry or becoming established
- Early detection and rapid response – spotting and handling new threats fast
- Management and control – using smart, sustainable strategies to limit or eradicate pests
- Education, training, and awareness – empowering everyone to play their part
With the fundamentals covered, let’s uncover the 7 shocking pest control secrets reshaping crop, forest, and ecosystem protection!
Plant Biosecurity: 7 Shocking Pest Control Secrets
Secret 1: Real-Time Agricultural Pest Monitoring
Traditional pest inspections and manual scouting are important, but today’s best biosecurity measures use advanced technologies for real-time pest monitoring.
With evolving international trade pathways and climate change, pests can appear anywhere—often undetected—until they cause visible harm.
- High-performance satellite imagery and remote sensing tools (e.g., Farmonaut’s multispectral crop health monitoring platform) now allow us to identify subtle changes in crop health early.
- GIS mapping can pinpoint the distribution and movement of pest outbreaks across large regions, improving surveillance coverage and early warning systems.
- IoT-based traps and sensors (internet-connected devices) send automatic alerts of pest activity, helping to reduce manual labor and timing errors in pest control.
- Data-driven monitoring supports sustainable, targeted pesticide applications, minimizing chemical usage and environmental harm.
The upshot? Farmers and forestry managers are empowered to act quickly—often before major crop or ecosystem damage occurs.
Benefits:
- Prevents pest outbreaks from spreading unnoticed
- Enables precision agriculture: optimized input use, reduced losses
- Supports better decision-making with real-time data
Secret 2: Integrated Pest Management Strategies (IPM)
One of the most effective plant pest management approaches is Integrated Pest Management (IPM). This strategic system combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools for managing pests in an environmentally and economically sound manner.
- Biological controls: Introducing or encouraging natural enemies (like ladybugs, predatory beetles, fungi, or nematodes) to suppress pests.
- Cultural practices: Crop rotation, intercropping, maintaining healthy soils and using pest-resistant plant varieties.
- Physical methods: Traps, barriers, netting, or removing infested plant materials to control pest movement.
- Targeted chemical controls: Pesticides used only as needed, chosen for minimal impact and resistance management.
IPM is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, vital for reducing pesticide resistance, protecting beneficial organisms, and maintaining long-term productivity in our crops and forests.
Secret 3: Quarantine Protocols for Plants—Our Biosecurity Shield
What’s one of the biggest lines of defense in preventing plant diseases and pest introductions? The answer: robust quarantine protocols for plants—at borders, trade ports, and regional movement checkpoints.
-
Stringent inspection and quarantine measures ensure infected, infested, or high-risk plants and plant products don’t move into healthy zones.
This includes soil, seeds, equipment, and even field staff boots. - International phytosanitary standards (such as those by IPPC) are essential in regulating global trade and maintaining access to markets by preventing pest spread.
- Regular audits, records, and certification help trace plant material origins, making responses fast and effective if breaches occur.
It’s critical for stakeholders not only to obey regulations but to also implement local quarantine protocols diligently—from seed supply to replanting and equipment movement—to maintain our biosecurity shield.
Access Farmonaut’s suite of plant health, crop monitoring, and pest management services from web, Android, and iOS for an integrated biosecurity workflow—wherever you farm or manage plants!
Need to automate plant data collection in your own systems? Check out Farmonaut’s API and Developer Docs to connect satellite plant health, weather, and pest data directly to your business applications.
Secret 4: Early Pest Detection and Rapid Response Systems
When a new pest enters an area, time is everything. Delayed detection means costly eradication and major crop losses. The solution? Layered biosecurity programs for early detection and rapid response—across agriculture and forestry.
- Surveillance programs (visual surveys, satellite analysis, GIS mapping, remote sensors) monitor crops and forests for early pest and disease symptoms.
- Robust reporting mechanisms encourage farmers, field staff, and citizens to report unusual findings promptly—making local communities vital sentinels of biosecurity.
- Coordinated rapid response protocols allow quarantine, containment, or eradication measures within days of detection.
Countries like Australia and India have set up specialized biosecurity agencies and modern plant quarantine stations, strengthening early warning and response capabilities nationally.
With technology, we can now scale up surveillance and improve the speed, precision, and reach of early warning systems for plant health.
Practical Result:
Minimizing the lag between pest introduction and control action is the #1 factor in protecting crop health, preventing widespread ecological damage, and maintaining secure food production.
Secret 5: Sustainable Plant Pest Management Solutions
Protecting crops and forests shouldn’t cost us our environment. Sustainable plant pest management uses approaches that:
- Avoid overreliance on synthetic chemicals
- Favor eco-friendly options: targeted biologicals, bio-pesticides, physical exclusion, sterile insect release, cover cropping, healthy soil practices
- Encourage beneficial insects, predators, and diverse companion plants
- Promote habitat management supporting biodiversity within and around crop/forest landscapes (e.g., flower strips for pollinators, beetle banks)
- Monitor and record impact—using carbon footprinting tools to assess and reduce the ecological impact of farm and pest control operations
Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting solution (see it here) provides transparent, real-time data to help farms and agribusinesses track—and improve—their environmental practices, vital for sustainable biosecurity.
Secret 6: Data-Driven Biosecurity Measures in Agriculture & Forestry
The biggest leap in plant biosecurity comes from using big data and advanced analytics. Our pest monitoring, alerting, and intervention systems are only as good as the data they collect and analyze.
- Farmonaut’s Jeevn AI Advisory System provides real-time, personalized crop management advice to thousands of farmers by analyzing satellite, field, and weather data together.
- Blockchain-based traceability builds product history transparency, helping prove plant and crop health for market access and food safety.
- Remote, automated detection with machine learning algorithms helps identify pest and disease symptoms weeks before they become visible in the field.
- Fleet management tools (learn more) prevent accidental pest transfer by tracking equipment movement and enabling robust disinfection protocols.
The precision of these digital biosecurity solutions reduces manual labor, enhances surveillance intensity, and multiplies the speed and effectiveness of response.
Secret 7: Education, Training, and Public Awareness in Biosecurity
The success of any plant biosecurity plan relies on well-informed, proactive stakeholders. Technology can only do so much if farmers, transporters, vendors, and the public aren’t aware or prepared to spot, report, and help control pest and disease threats.
- Regular training programs for agronomists, foresters, and farm staff support skills in early identification, safe pesticide handling, and reporting protocols.
- Awareness campaigns (field days, seminars, in-app notifications, media) encourage the public—especially in high-risk areas—to get involved in biosecurity.
- Industry-wide adoption of best practices raises the baseline of plant protection across agriculture and forestry.
A culture of biosecurity isn’t built overnight. But as more people understand their role in preventing, detecting, or reporting pests, the effectiveness of all other biosecurity measures grows exponentially.
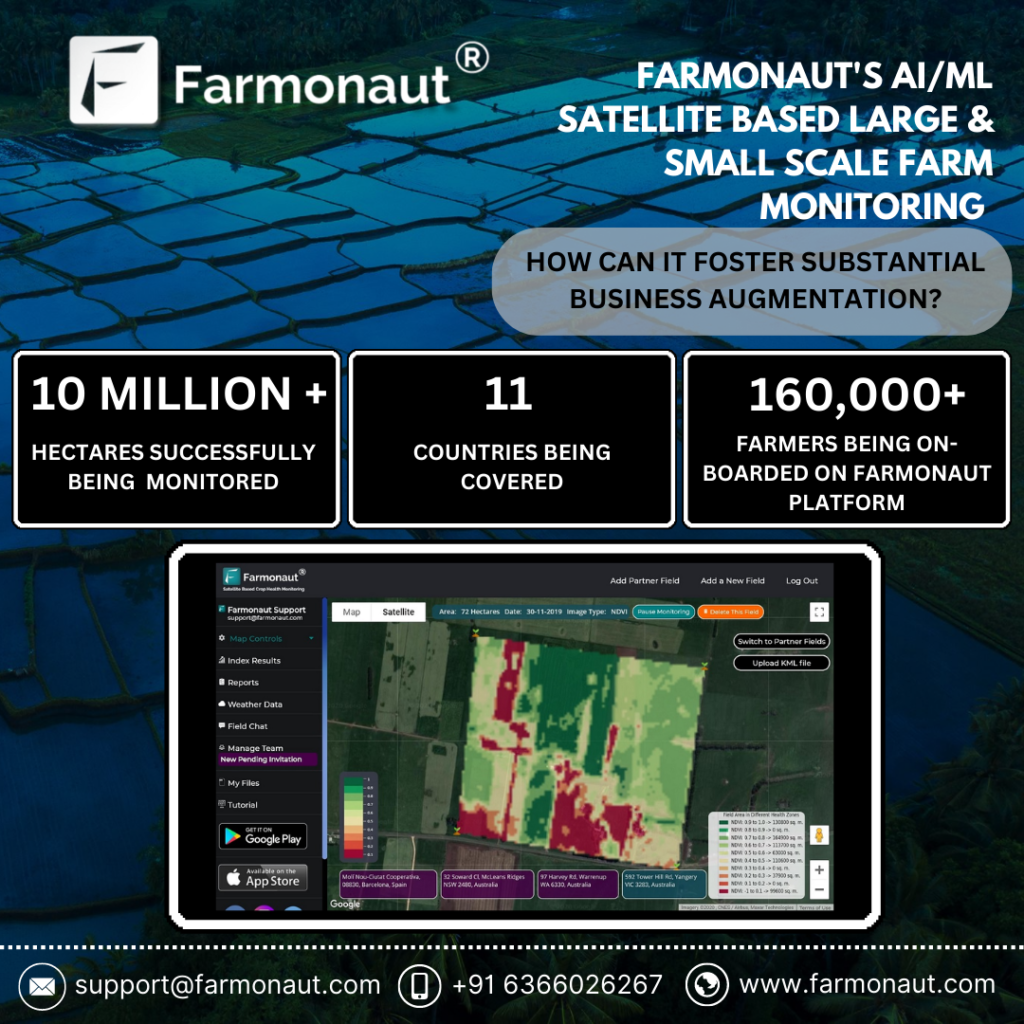
Farmonaut: Empowering Modern Plant Biosecurity & Pest Monitoring
With thousands of species and billions of plants at risk, digital innovation is transforming the biosecurity landscape.
- Farmonaut’s satellite-based crop health monitoring allows farmers and agribusinesses of all sizes to monitor crops, receive AI-powered advisory, assess soil moisture, and implement timely plant pest management—without the need for expensive on-farm sensors.
- Blockchain systems on the platform bolster traceability and compliance, supporting safe, transparent food and fiber supply chains.
- API access and cross-platform compatibility ensure that every stakeholder in the ecosystem—from independent farmers and large-scale managers to government agencies and researchers—has the data and cloud-connected tools to act fast.
Using Farmonaut’s precision agriculture platform, users gain access to:
- Real-time alerts for pest symptoms and outbreaks
- Data-driven resource management to minimize waste and environmental impact
- AI-based crop health advisory for proactive protection and higher yields
- Customizable satellite data APIs for large-scale, integrated surveillance and control systems
Need to manage loans and insurance for biosecurity-affected crops? Farmonaut offers satellite-based crop loan and insurance verification—reducing fraud, speeding up approvals, and supporting resilient agricultural financing.
To oversee multi-location operations or field teams, use the large-scale farm management platform to integrate and monitor plant health, pest, and movement data.
And if you advise or manage forests, Farmonaut’s crop plantation and forest advisory tool is designed for you!
Plant Biosecurity Strategies vs. Pest Threats
Effective plant biosecurity requires matching the right strategy to each pest threat. Here’s a comparative overview to guide sustainable, environmentally friendly choices for pest control and plant health protection:
| Pest Type | Estimated Annual Crop Loss (%) | Recommended Biosecurity Strategy | Sustainability Score (1-5) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphids | 10–20% | IPM (biological control, field monitoring, precision application) | 5 | Low |
| Nematodes | 8–12% | Soil testing, use of nematode-resistant varieties, sanitation measures | 4 | Low |
| Fungal Pathogens | 15–30% | Early detection, resistant cultivars, targeted fungicides (as needed) | 3 | Medium |
| Fruit Flies | 5–15% | Quarantine, trapping, rapid eradication programs | 4 | Medium |
| Bacterial Blight | 5–18% | Certified disease-free planting material, hygiene, resistant varieties | 5 | Low |
| Weeds (parasitic/invasive) | 5–10% | Physical removal, rotation, seed certification, early detection | 5 | Low |
| Moths/Borers | 10–25% | Monitoring, pheromone traps, targeted biopesticides | 4 | Low–Medium |
Key Takeaways:
- IPM, early detection, and certified materials dominate the most effective and sustainable biosecurity measures.
- Regular monitoring and swift, targeted responses reduce both crop loss and environmental impact.
- Data-driven systems (as provided by Farmonaut) multiply the efficiency and reliability of these strategies across large and small operations.
Key Biosecurity Practices by Country
Let’s see how leading nations structure their plant biosecurity systems:
- Australia—The Biosecurity Act 2015 drives comprehensive national protocols: strict border controls, emergency response plans, and industry-partnered pest monitoring across agricultural and forestry sectors.
- United Kingdom—The Plant Biosecurity Strategy for Great Britain (2023–2028) emphasizes surveillance, rapid response, risk-based pathway analysis, and cross-sectoral education for both agriculture and forestry.
- India—Expanding national quarantine stations and modernizing pest reporting systems, India’s biosecurity framework prioritizes early warning systems and digital pest data management—especially vital for large, climate-diverse regions.
Across the globe, agricultural pest monitoring and integrated biosecurity measures are key to safeguarding food supply chains and biodiversity.
Future Challenges and Directions in Plant Biosecurity
Despite strong progress, critical challenges remain:
- Globalization and movement: With more frequent movement of plants, products, and people, biosecurity risks are dynamic—increasing the chance of new pest introductions.
- Climate change: Changing conditions affect pest populations, distributions, and unpredictability.
- Resource constraints: In low-income or remote regions, implementing comprehensive plant biosecurity systems can be difficult.
What’s next?
- Enhanced collaboration among stakeholders and nations to share data, resources, and best biosecurity practices.
- Technological innovation: Wider, faster adoption of remote sensing, AI-powered analytics, carbon footprinting tools, and traceability systems.
- Adaptive policy frameworks: Laws and standards that evolve as threats do—covering everything from genetic resource protection to digital pest surveillance.
- Continuous education and stakeholder training: Ensuring everyone from smallholder farmers to government agents is equipped to monitor, report, and act.
Our path forward relies on stronger partnerships, innovation, and a shared commitment to sustainable, data-driven plant biosecurity.
Frequently Asked Questions: Plant Biosecurity and Pest Control
1. What is plant biosecurity?
Plant biosecurity is the strategic management of risks related to pests and diseases that threaten plant health, agriculture, forestry, and ecosystems. It involves policies, prevention, early detection, rapid response, and sustainable management measures.
2. Why is early pest detection important for agriculture and forestry?
Early detection of pests and diseases allows for quicker, targeted intervention—reducing crop losses, slowing the spread and establishment of harmful organisms, and saving costs on eradication.
3. How does satellite data improve pest monitoring?
Satellite data identifies changes in plant health (NDVI, soil moisture, etc.) across large fields or forests. These digital signals can reveal pest outbreaks days or weeks before they cause visible damage, allowing proactive pest management.
4. What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
IPM is a system combining biological, cultural, physical, and chemical practices to manage pests sustainably, protect beneficial species, and minimize environmental harm.
5. What is the role of data in plant biosecurity?
High-quality pest and plant data enable precise monitoring, early warning systems, AI-powered advice, and the ability to trace plant materials throughout the supply chain—vital for both biosecurity and market access.
6. Does biosecurity only concern large-scale farms or is it important for smallholders too?
All farms, from garden plots to vast commercial plantations, are at risk. Biosecurity measures protect everyone—especially smallholders who may lack resources for large-scale interventions if outbreaks occur.
7. How can Farmonaut help with plant biosecurity?
Farmonaut offers affordable, satellite-based tools and AI-powered advisory for crop health monitoring, pest detection, traceability, and sustainable farm management—supporting robust biosecurity for all scales.
Conclusion: Securing the Future with Plant Biosecurity
Plant biosecurity is the foundation of healthy agriculture, forestry, and resilient ecosystems. By using robust prevention, early detection, rapid response, and data-driven integrated pest management strategies, we can prevent plant diseases and control pests without sacrificing environmental sustainability.
With accessible solutions like Farmonaut, we all have tools at hand to safeguard crop health, enhance biodiversity, strengthen food security, and reduce the risks and impacts of invasive pest introductions.
Let’s make plant biosecurity a priority today—for a more secure, healthy, and sustainable agricultural and forestry future.
Protecting the world’s crops and forests is everyone’s responsibility.
Ready to revolutionize your approach? Try Farmonaut today!