Soil Carbon Sequestration: 7 Shocking Farm Secrets!
Introduction: The Power of Soil Carbon Sequestration
Welcome to the ultimate guide to soil carbon sequestration—a natural process that holds the key to climate resilience, healthy soils, and sustainable farms. As stewards of the land, we stand at the crossroads between traditional farming and innovative solutions that can transform our fields into powerful carbon sinks. In this blog, we’ll uncover the 7 shocking farm secrets that can maximize our soils’ ability to capture, store, and sequester carbon for the benefit of our crops, climate, and future generations.
We’ll discuss organic practices, agroforestry systems and carbon, and how integrated approaches—supported by the latest technologies like Farmonaut’s real-time carbon footprinting tools—create a synergy between productivity and sustainability. If you’re curious about “carbon farming practices”, “conservation tillage benefits”, or “cover cropping for soil health”, this is the resource for you.
The Role of Soil in Carbon Sequestration
Soil does more than support our plants—it is a living engine for managing carbon, underpinning the very systems that sustain life. The process of soil carbon sequestration refers to capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) and storing it in soil organic matter. This occurs through natural mechanisms as plants photosynthesize, die, and decompose into organic matter—locking away carbon beneath our feet.
Our soils are among the planet’s largest carbon sinks, holding an astounding 2,500 billion tons—about three times the atmospheric carbon store. This latent potential means that, with the right management, farming and forestry practices can dramatically shape soil carbon stocks and yield practical ways of mitigating greenhouse gases and reducing climate change.
Focusing on soil organic carbon unlocks improved soil structure, resilience to drought and flooding, and greater soil health—the foundations of increased productivity in any agricultural landscape.
Why Should We Sequester Carbon in Agriculture?
Let’s explore the core reasons why all of us—farmers, landowners, policymakers, and consumers—should advocate for soil carbon sequestration at scale:
- Mitigating Greenhouse Gases: By capturing CO₂ as soil organic matter, we directly counteract rising atmospheric carbon dioxide and slow climate change.
- Improving Soil Health: Building organic carbon brings myriad benefits: better structure, increased microbial activity, improved fertility, and higher water retention—all boosting agricultural productivity and climate resilience.
- Increasing Farm Profits: Healthier soils reduce need for synthetic inputs, cut costs, and raise yields. Participation in carbon markets can provide market incentives for farmers to adopt more sustainable practices.
- Offering Multi-Generational Benefits: A regenerative approach to farming ensures our fields remain productive and fertile—preserving food security and farm viability for future generations.
7 Shocking Farm Secrets for Soil Carbon Sequestration
Let’s reveal the practical management methods and innovations—the real farm secrets—that empower us to maximize soil carbon sequestration. Each approach addresses a unique aspect of the carbon capture process, driving the transition to climate-smart agricultural practices.
-
Conservation Tillage and No-Till Farming
- Secret: Traditional plowing and deep tillage disrupt soil structure and accelerate organic matter decomposition, causing rapid release of carbon back into the air.
- Farm Solution: No-till or conservation tillage preserves soil health by limiting disturbance. This not only reduces carbon loss but also improves soil aggregation, water infiltration, and root growth.
- Evidence: Studies show that consistent no-till systems can substantially raise soil organic carbon, with maximum benefits observed on fine-textured and cool-climate soils (source).
- Conservation tillage benefits: Less erosion, better moisture retention, and enhanced microbial activity.
-
Cover Cropping for Soil Health
- Secret: Leaving fields bare exposes soils to erosion, oxidation, and organic matter loss.
- Farm Solution: Planting cover crops in off-season periods protects soils, improves fertility, and adds new organic material—creating a year-round carbon cycle.
- Practice: Common cover crops include rye, clover, vetch, and radish. As these decompose, they enrich soil organic carbon and enhance microbial processes (source).
- Cover cropping for soil health also disrupts weed cycles and improves nutrient cycling.
-
Diverse Crop Rotation
- Secret: Growing the same crop year after year (monoculture) depletes soils, encourages pests, and encourages nutrient loss—reducing soil carbon over time.
- Farm Solution: Crop rotation—especially with legumes—facilitates nitrogen fixation, breaks pest and disease cycles, and builds soil organic matter (source).
- Implementation: Integrating 3 to 4 crop species within multi-year rotations intensifies the soil carbon sequestration effect.
- Promoting plant diversity not only directly sequesters carbon but also improves resilience to climate extremes.
-
Applying Organic Amendments: Compost, Manure & Biochar
- Secret: Most conventional fertilization ignores the power of organic residues, which are the backbone of healthy, carbon-rich soils.
- Farm Solution: Reintroducing organic amendments (such as compost, animal manure, or biochar) boosts soil organic carbon stocks and supports beneficial microbial activity.
- Benefits: Enhancing soil structure, nutrient cycling, and increasing the soil’s carbon holding capacity (source).
- This is the core of many regenerative, organic practices worldwide.
-
Agroforestry Systems and Carbon: Trees on Every Farm
- Secret: Many farms underestimate the value of integrating timber, fruit, or shade trees with crops or livestock.
- Farm Solution: Agroforestry embeds trees within farming landscapes, creating layered canopies, shading, and perennial carbon stores both above and below ground (source).
- Impact: Agroforestry can boost soil carbon by up to 21% in a single decade, while protecting soil from erosion and supporting biodiversity.
- This practice is a cornerstone of climate-smart agricultural practices for both smallholders and large-acreage farms.
-
Silvopasture: Livestock + Trees for Enhanced Carbon Storage
- Secret: Pasture-only or open-range livestock systems often lose out on the potential carbon captured by trees and woody vegetation.
- Farm Solution: Silvopasture integrates trees with grazing livestock and pasture. The trees’ deep root systems add organic matter, their leaves and branches trap carbon, and animals benefit from increased shade and forage (source).
- Benefits: This diverse system supports improved soil structure, enhanced soil moisture, and increased carbon sequestration.
- The presence of livestock helps distribute nutrients, making the cycle more efficient and sustainable.
-
Species Selection and Smart Forest Management
- Secret: Not all trees and plants have the same effect on soil carbon stocks—species matter.
- Farm Solution: Prioritize nitrogen-fixing species (such as acacia, alder, and certain legumes) or broadleaf trees proven to increase mineral soil carbon (source).
- Benefits: Mixed-species forests or hedgerows dramatically increase carbon sequestration in agriculture and provide ecosystem co-benefits like pollinator habitats.
- Mycorrhizal associations between trees and soil fungi further enhance carbon capture and soil stability.
Comparison Table: Soil Carbon Sequestration Practices and Benefits
| Practice | Estimated Carbon Sequestration Rate (tons/ha/year) | Impact on Soil Health | Climate Resilience Benefit (% Improvement) | Additional Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cover Cropping | 0.3 – 1.2 | High | 15 – 25% | Boosts biodiversity, water retention, pollinator support |
| No-Till / Conservation Tillage | 0.2 – 0.7 | Medium – High | 10 – 18% | Reduces erosion, improves moisture, supports soil life |
| Agroforestry | 1.0 – 3.5 | Very High | 22 – 40% | Enhances wildlife habitat, buffers climate extremes |
| Organic Amendments | 0.4 – 1.8 | High | 15 – 28% | Reduces synthetic fertilizer, increases nutrient retention |
| Diversified Crop Rotation | 0.3 – 0.8 | High | 14 – 20% | Reduces pest/disease, breaks cycles, encourages pollinators |
| Silvopasture | 1.2 – 3.0 | High | 20 – 37% | Supports biodiversity, improves forage, cooler microclimate |
| Species Selection/Forest Management | Varies (depends on species) | Medium – Very High | 20 – 35% | Improved diversity, resilience to disease/climate shocks |
The Farmonaut Edge: Technology for Sustainable Farming and Carbon Management
Monitoring real soil carbon sequestration is now possible with technology. Farmonaut empowers us to manage, measure, and optimize carbon-friendly practices with tools previously out of reach for most farmers and agribusinesses:
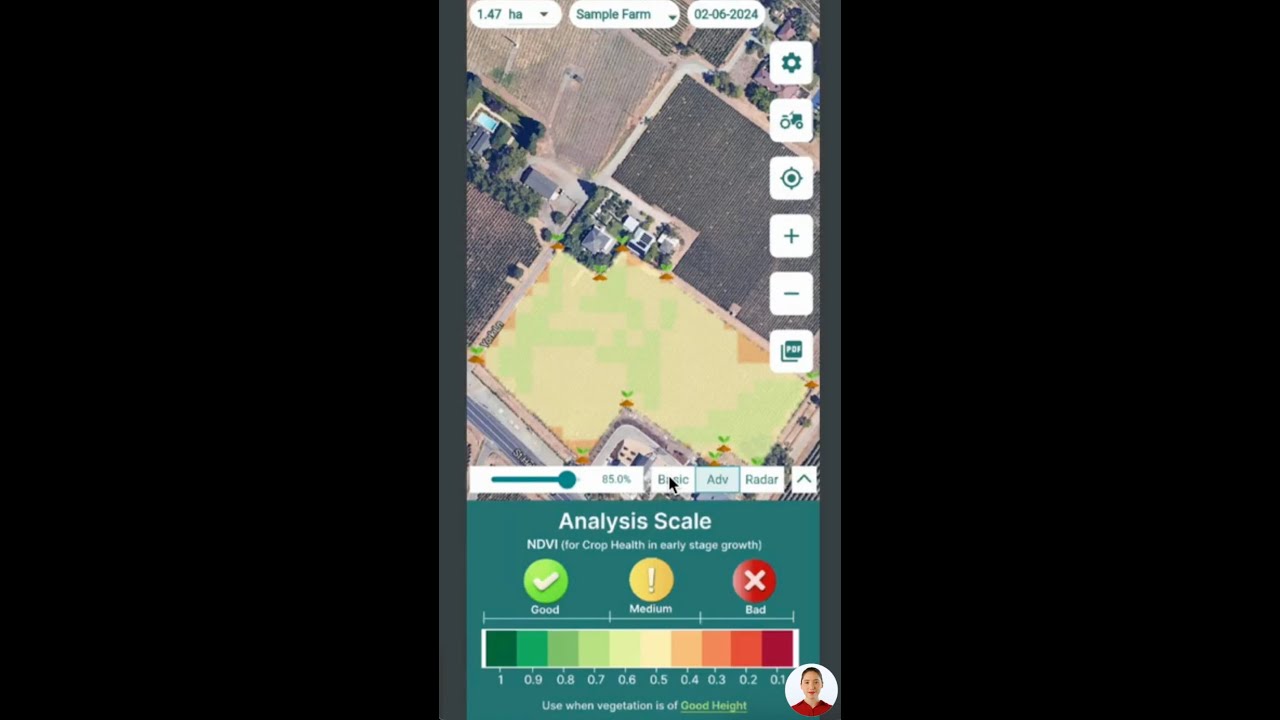
- Satellite-Based Crop & Soil Monitoring: Farmonaut’s farm management suite uses satellite imagery to track crop health, soil moisture, and vegetation indices—helping us assess field variability and spot issues rapidly.
- Jeevn AI: Smart Advisory for Carbon Practices: Personalized, real-time insights on crop management, irrigation, and input efficiency to ensure optimum conditions for carbon capture.
- Blockchain Traceability: Brings trust and transparency to supply chains, so sustainable, carbon-smart produce is traceable from field to market. See how Farmonaut can help with traceability solutions.
- Resource & Fleet Management: For large farms and agribusinesses, efficient machinery and fleet use mean less fuel, lower emissions, and better carbon outcomes.
- Carbon Footprinting & Environmental Tracking: Integrated toolkit for monitoring total farm carbon emissions and sequestration, supporting compliance, sustainability, and market claims.
- Loan & Insurance Verification: Satellite evidence increases access to climate-linked finance—learn more about crop loans and insurance support for your operation.
- API for Easy Integration: Businesses can plug into Farmonaut’s API for advanced satellite and weather data, while developers can explore API developer docs for seamless tech integration.
Challenges and Considerations in Soil Carbon Sequestration
Although the potential of soil carbon sequestration is extraordinary, results are site-specific, and success hinges on key factors:
- Soil Type: Sandy soils may store less carbon than heavy clay. Farm-level diagnosis, like that enabled by Farmonaut, helps optimize approach by field.
- Climate & Weather Patterns: Rainfall, temperature, and seasonal extremes dictate organic matter decomposition and carbon stability.
- Management Consistency: Reversion to conventional tillage or regular plowing may rapidly negate accumulated gains in soil carbon (source).
- Permanence: Keeping carbon locked in the ground for decades requires sustained implementation, monitoring, and, ideally, market support for land stewards choosing carbon-friendly practices.
- Economic Feasibility: Actions like organic amendment application require labor and investment, which should be offset by long-term gains or carbon market incentives for farmers.
Policies & Carbon Market Incentives for Farmers
Around the world, governments and private entities are creating market incentives to scale carbon farming practices:
- Carbon Markets: Verified increases in soil organic carbon stocks can be traded as carbon credits, providing supplemental income for farmers.
-
United States Programs:
- Growing Climate Solutions Act—Helps farmers access technical resources, eases carbon market entry, and connects them to buyers (source).
- Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP) & Conservation Reserve Program (CRP)—Financial incentives for adopting practices proven to sequester soil carbon.
- International Developments: Europe, Australia, and developing countries are piloting carbon market incentives for farmers through government and NGO initiatives supporting regenerative farming.
- Technology’s Role: Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting and environmental monitoring toolkit helps farms participate in markets by offering transparent, verifiable carbon reporting.
For practical advice in integrating these programs with your farming operation, consider using Farmonaut’s farm management dashboard—now available on desktop and mobile.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is soil carbon sequestration, and why is it important?
Soil carbon sequestration is the mechanism by which carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere is trapped within the soil as organic matter—primarily through plant growth, decomposition, and microbial activity. It’s important because it reduces greenhouse gases, improves soil health, boosts fertility, and increases farm productivity while fighting climate change.
How do “carbon farming practices” actually work?
Carbon farming practices are agricultural methods aimed at increasing the carbon content of soils and vegetation. Through actions such as cover cropping, reducing tillage, crop rotation, applying organic amendments, and establishing agroforestry or silvopasture systems, we can draw down atmospheric carbon and store it stably in the soil. These practices also bring added benefits for soil fertility and farm resilience.
What is the difference between soil organic carbon and total soil carbon?
Soil organic carbon (SOC) refers expressly to the carbon contained in plant and animal residues, humus, and microbial biomass within the soil. Total soil carbon includes both organic carbon and inorganic carbon (largely limestone and carbonates). SOC is the main target for sequestration strategies as it supports soil health directly.
Can Farmonaut help measure and optimize soil carbon sequestration?
Yes! Farmonaut’s carbon footprinting solution provides real-time monitoring of farm carbon emissions and gains, supporting both compliance and income from carbon markets. Farmonaut also offers satellite-powered analytics, AI-based advice, and historical data—empowering us to implement and refine climate-smart agricultural practices with precision and confidence.
What’s the long-term impact of reverting to conventional plowing and fertilizer use after sequestering carbon?
Reverting to intensive tillage or excessive chemical fertilizer use can rapidly undo years of carbon gains—releasing stored carbon to the atmosphere and degrading soil structure. Consistent implementation and monitoring are crucial to maintaining and enhancing soil carbon stocks for the long term.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Potential of Our Soils
Soil carbon sequestration is perhaps the greatest untapped lever for climate mitigation, regenerative agriculture, and sustainable food security. As we, the stewards of the land, embrace secrets such as conservation tillage, cover cropping, organic amendment, agroforestry, and integrated species management, we elevate our soils from passive dirt to dynamic engines of change.
To sustain this revolution, we must marry organic wisdom with modern technology—leveraging data-driven solutions like Farmonaut’s precision tools to monitor, report, and profit from our climate-positive impact. By adopting these climate smart agricultural practices and supporting policies, we not only reduce the carbon footprint of agriculture but build prosperity for ourselves and future generations.
Are we ready to activate the true potential of our soils and become climate heroes—one field, one tree, one practice at a time?
Get Started with Affordable Farmonaut Subscriptions
Ready to take your soil management, carbon tracking, and sustainable farm operations to the next level? Farmonaut offers flexible, scalable subscription packages for web, mobile, and API-based management. No matter your operation size—from a small family farm to a large corporate estate—precision insights and real-time monitoring have never been this accessible.
See our transparent, cost-effective plans below and join the new era of digital, climate-smart farming.
Soil carbon sequestration is not just an environmental buzzword—it’s the foundation of a profitable, sustainable, and climate-resilient future. Are you ready to unlock these farm secrets and lead the way to a greener world? Start with Farmonaut today!