Sustainability in Agriculture: 7 Game-Changing Secrets for Eco-Friendly Farming
“Sustainable farming can increase crop yields by up to 79% in developing countries while reducing chemical inputs by 30%.”
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on sustainable agriculture—the essential movement transforming how we grow our food and manage our natural resources. As we strive to feed a growing global population, the need to balance crop yields with environmental protection is more urgent than ever.
In this article, we’ll uncover 7 game-changing secrets in sustainable agriculture, exploring proven agricultural practices that safeguard soil health, reduce harmful inputs, increase farm profitability, and ensure resources are available for future generations. We’ll also highlight innovative technologies—like AI-based precision agriculture—empowering farmers worldwide. Whether you’re a producer, agri-professional, or an enthusiast, join us as we chart a path toward thriving, resilient, and eco-friendly farming systems.
Why Sustainability in Agriculture Matters
Our food systems face a stark reality: We must produce more food on less land, with less water and chemical inputs, all while ensuring the prosperity of farmers, workers, and communities.
Traditional agriculture, with its heavy dependence on synthetic inputs and intensive tillage, can degrade soil structure, pollute water sources, accelerate greenhouse gas emissions, and threaten biodiversity. In contrast, sustainable agriculture is an approach that integrates environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity, striving not only to feed the present but to ensure the well-being of future generations.
- Environmental health: Maintains eco-friendly balance and natural resource conservation through soil care, water efficiency, and integrated pest management.
- Economic profitability: Focusses on cost-effective, efficient farming practices ensuring long-term profitability.
- Social equity: Supports fair opportunities and community engagement.
By embracing sustainable farming practices, we work collectively to safeguard our planet and nourish our societies.
“Healthy soil from eco-friendly practices stores up to 20% more carbon, helping fight climate change and boost productivity.”
Key Principles of Sustainable Agriculture
At the heart of sustainable agriculture lies a commitment to three interconnected pillars that foster resilient food systems:
1. Environmental Health
- Preserving Soil and Water: Crop rotation, cover cropping, and minimal tillage maintain fertility, soil moisture, and ecosystem balance.
- Diversity: Biodiversity in plants, animals, and microorganisms enhances resilience against pests and disease outbreaks.
- Reducing Pollution: Efficient water use in farming and integrated pest management (IPM) lower the risk of harmful runoff and chemical exposure.
2. Economic Profitability
- Cost Control: Adopting precision agriculture technology (like GPS and AI-driven analytics) reduces input costs and increases yield.
- Viable Livelihoods: Sustainable systems ensure farmers and workers can support their families for the long term.
3. Social Equity
- Community Engagement: Farm systems that foster equitable access to resources and fair labor practices contribute to stronger, more resilient communities.
- Integration: Integrating livestock and crops can create closed-loop systems, increasing efficiency and profitability.
This sustainable approach paves the way for both efficient food production and the protection of our shared resources.
7 Game-Changing Secrets in Sustainable Agriculture
Let’s explore the most transformative sustainable farming practices uplifting modern agriculture while delivering soil health improvement, input reduction, and robust yields:
-
Crop Rotation and Diversity: Unlocking the Power of Crop Rotation Benefits
What it is: Systematically changing the crops grown in fields across seasons.
Benefits: Prevents the buildup of pests and diseases, improves (and sometimes restores) soil fertility, reduces reliance on chemical inputs, and enhances overall ecosystem diversity.
How it improves farm outcomes: By rotating nitrogen-fixing legumes with cereals, for example, we naturally replenish soil nutrients and break pest and disease cycles—leading to higher yields and resilience. -
Conservation Tillage: Protecting Soil Structure and Reducing Erosion
What it is: Minimizing or eliminating tillage to reduce soil disruption.
Benefits: Preserves soil structure, prevents erosion, increases water retention, and builds stable soil organic carbon stores.
How it improves farm outcomes: Practices like no-till farming help lock more carbon in the ground while maintaining yields and reducing labor and fuel costs. -
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Ecological Balance in Pest Control
What it is: IPM incorporates biological, cultural, and mechanical methods to manage pests with minimal chemicals.
Benefits: Reduces chemical inputs, lowers pest resistance risk, and is safer for the environment and public health.
How it improves farm outcomes: By monitoring pest populations and deploying targeted interventions (like beneficial insects), we avoid broad-spectrum pesticide use, improving yields and environment. -
Agroforestry: Enhancing Resilience by Integrating Trees
What it is: Planting trees and shrubs alongside crops and livestock systems.
Benefits: Increases biodiversity, improves soil fertility via deep-root systems and leaf litter, supports habitat for beneficial species, and sequesters carbon.
How it improves farm outcomes: Agroforestry can buffer against climate volatility and generate additional income through timber, fruit, or nut harvests. -
Organic Farming: Rebalancing Inputs for a Healthier System
What it is: Avoids synthetic chemicals and GMOs, relying on natural fertilizers and crop protection.
Benefits: Boosts soil health, enhances biodiversity, and prevents pollution.
How it improves farm outcomes: Organically managed soils foster more abundant beneficial microbes and greater system stability. -
Efficient Water Use in Farming: Precision Irrigation and Resource Optimization
What it is: Practices including drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and irrigation scheduling using climate data.
Benefits: Minimizes water waste, protects soil structure, prevents runoff, and reduces energy expenditure.
How it improves farm outcomes: By aligning water delivery with crop demand, we conserve resources and cut input costs. -
Cover Cropping: The Shield for Off-Season Soil Health
What it is: Planting cover crops such as legumes or grasses during fallow periods.
Benefits: Protects against erosion, suppresses weeds, improves soil structure and nutrient cycling, and stores soil carbon.
How it improves farm outcomes: Cover crops reduce the need for herbicides and fertilizers while enhancing yields in main cropping seasons.
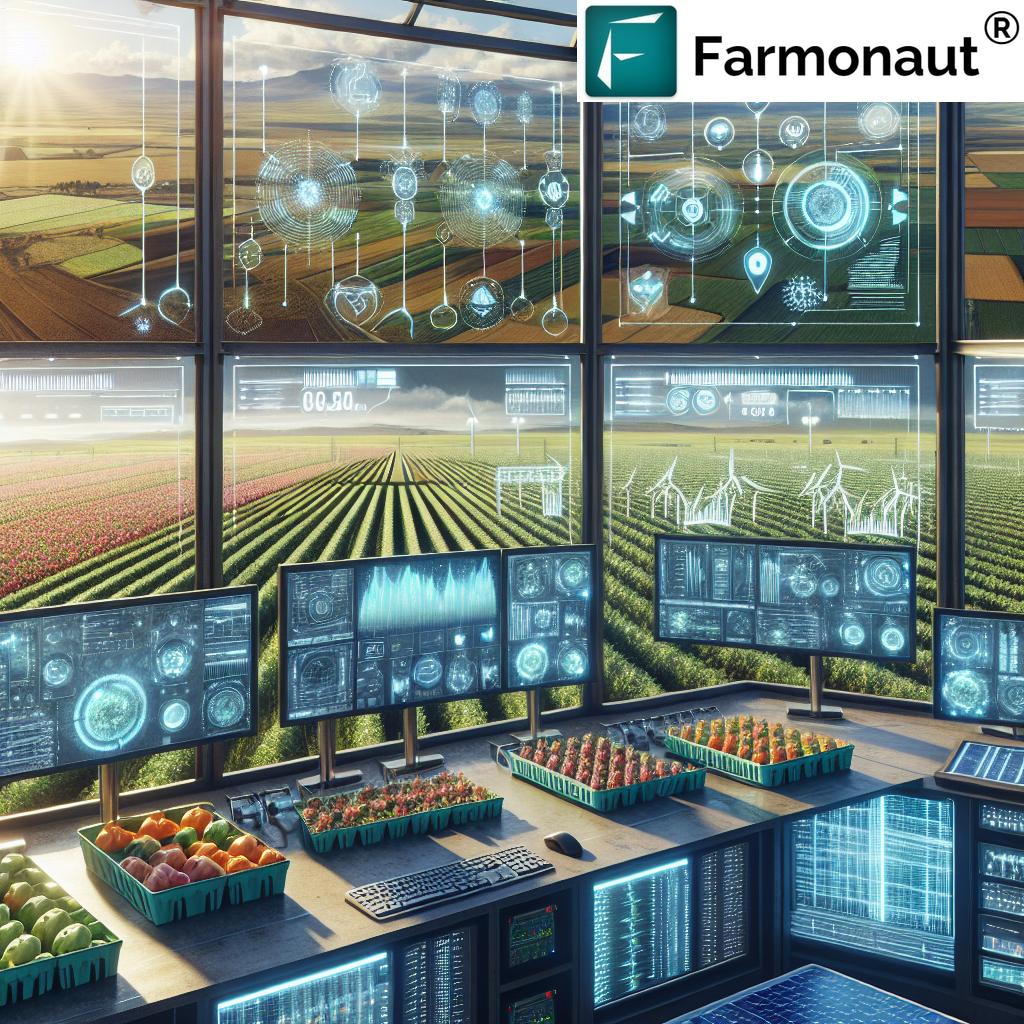
Technological Advances Powering Sustainable Farming
Today’s sustainable agriculture revolution is being supercharged by cutting-edge technology—with precision agriculture technology leading the way in optimizing every aspect of farm management.
-
Precision Agriculture Technology
Precision farming refers to using satellite data, GPS mapping, sensors, and AI analytics to guide input application, monitor soil health improvement, and optimize harvest timing. Platforms like Farmonaut make these technologies accessible directly from desktop and mobile devices—so farmers can reduce waste, save on costs, and boost yields efficiently across any field size.
Discover Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting solution—to track, manage, and reduce agriculture’s carbon emissions for more climate-positive farming.
-
Genetic Modification and Breeding
Advances in plant breeding and genetic modification foster crop varieties that resist pests, diseases, and environmental stress. This reduces dependence on pesticides and supports higher, stable yields in challenging climates.
-
Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Modern CEA methods allow growing food year-round with minimal resources, controlling light, temperature, and humidity—including vertical farms in urban spaces. These systems reduce land and water use while ensuring high output and reliable quality.
-
Renewable Energy in Agriculture
Incorporating solar, wind, and bioenergy into farming operations significantly cuts greenhouse gas emissions and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. This transition is critical to sustainable, future-ready farming.
-
Blockchain in Food Supply Chain
Blockchain technology fosters traceability, transparency, and trust in the food supply chain. Platforms like Farmonaut enable product traceability—letting producers, retailers, and consumers verify if food is produced sustainably from farm to plate.
Together, these advances empower us to optimize resource management, maximize yields, and improve transparency across the global food system.
Comparison Table: Sustainable vs. Conventional Practices
To clearly understand the impact of sustainable approaches, here’s a comparative look between leading sustainable farming methods and conventional practices:
| Practice Name | Description | Input Reduction (% est.) | Soil Health Impact | Crop Yield Change (% est.) | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Rotation & Diversity | Alternating different crops/seasons for pest and fertility management. | 15–40% less fertilizer & pesticide use | Improves structure, increases organic matter | +10% to +25% | Reduces pests, boosts biodiversity |
| Conventional Monoculture | Same crop grown year after year. | — | Depletes nutrients, increases disease | Variable, risk of decline | Promotes pests, soil degradation |
| Conservation Tillage | No-till/reduced tillage to preserve soil. | 10–30% lower fuel/labor, less fertilizer need | Protects structure, builds carbon | Stable to +10% | Prevents erosion, stores carbon |
| Intensive Tillage | Regular plowing, breaking up soil. | — | Destroys structure, increases erosion | Short-term spike, long-term decline | High erosion, low carbon storage |
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) | Ecological pest control, minimal chemicals. | 30–60% pesticide reduction | No residue buildup, keeps beneficials | +5% to +15% | Reduces runoff, safer for pollinators |
| Conventional Pesticide Use | Synthetic pesticides as main defense. | — | Pesticide buildup, kills beneficials | Variable | Negative impacts on environment/health |
| Cover Cropping | Planting off-season covers for soil. | 15–30% less fertilizer & herbicides | Boosts organic matter, stops erosion | Up to +10% | Captures carbon, improves resilience |
| No Cover (Bare Fallow) | Fields left bare between crops. | — | Carbon loss, erosion risk | Yield may drop from degraded soil | High erosion, low resilience |
| Efficient Irrigation (Drip, Smart Scheduling) | Water delivered based on crop data/need. | 30–50% water savings | Prevents waterlogging/compaction | +8% to +20% | Conserves water and energy |
| Flood or Overhead Irrigation | High-volume, non-targeted. | — | Causes runoff, weakens soil | Lower with water stress | Wastes water, pollutes waterways |
Farmonaut: Enabling the Future of Sustainable Agriculture
As sustainable farming evolves, access to real-time data, robust management tools, and affordable technology becomes critical. Here’s how we at Farmonaut are advancing the mission:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Understand crop growth, detect stress, and optimize irrigation or fertilizer applications, thereby reducing inputs and maximizing yields.
Try it now: Farmonaut’s Large-Scale Farm & Plantation Management. - Jeevn AI Advisory: Instant weather, management, and crop-specific insight direct to your device, translating satellite data into results.
- Blockchain-Based Traceability: Ensure transparency and trust across supply chains—see Farmonaut Traceability Product for food brands seeking a competitive edge.
- Efficient Fleet and Resource Management: Reduce logistics costs and environmental impact—optimize your agri fleet at scale.
- Access to Finance: Secure and simplify crop insurance claims or loan verification with Farmonaut’s crop loan and insurance verification.
- API Integrations: Access Farmonaut’s satellite and weather data through public APIs and developer documentation to enhance your farm management platform.
With flexible subscriptions, a web/app platform, API access, and tools suited for individuals or entire cooperatives, Farmonaut empowers farmers and agri-businesses worldwide—helping all stakeholders increase profitability while preserving natural resources for the future.
Overcoming Barriers to Sustainable Agriculture
Despite remarkable advancements, the journey to a fully sustainable agriculture ecosystem presents challenges we must address together:
-
Economic Barriers:
Many smallholders may face significant upfront costs to adopt new technologies or methods, even if they yield cost savings and improved productivity over time.
-
Knowledge and Training:
Access to education on sustainable farming practices can be uneven. We must provide robust outreach and accessible materials—Farmonaut’s AI-driven advisory tools are a leap forward for community engagement.
-
Policy and Incentives:
Governments and organizations must sustain support for adoption with well-designed incentives and subsidies for eco-friendly technologies.
-
Market Access:
Farmers need reliable markets where sustainable produce is recognized and valued—here, transparency and traceability solutions (like Farmonaut’s blockchain) are vital.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): Sustainable Agriculture
What is sustainable agriculture, and why is it important?
Sustainable agriculture is an approach that aims to meet today’s food needs while protecting the environment, supporting healthy farm communities, and ensuring resources—such as soil and water—remain for future generations. It balances environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity, making it crucial for our long-term food security and the planet.
What are the key practices of sustainable agriculture?
The most effective practices include crop rotation, conservation tillage, integrated pest management (IPM), cover cropping, efficient water use (like drip irrigation), agroforestry, and organic farming. Embracing new technologies such as blockchain, satellite data, and AI-driven analytics helps optimize results and improve farm profitability.
How do sustainable farming methods improve soil health?
Sustainable practices increase soil organic matter, enhance soil structure, prevent erosion, and restore fertility by promoting biodiversity both above and below ground. Practices like cover cropping, minimizing tillage, and crop rotation naturally rebuild and maintain healthy, productive soils.
What is precision agriculture, and how does it support sustainability?
Precision agriculture uses GPS, satellite imagery, sensors, and AI analytics to optimize input use (like fertilizer, irrigation, and pest control) for every part of the field. This reduces waste, minimizes environmental impact, and improves both profitability and crop yield.
What is the role of renewable energy in agriculture?
Renewable energy (solar, wind, bioenergy) reduces greenhouse gas emissions, lowers operational costs, and boosts farm resilience. Using clean energy for irrigation, processing, and transport is a key pillar of sustainable agriculture.
How does Farmonaut support sustainable agriculture?
Farmonaut democratizes precision agriculture with affordable satellite-based crop monitoring, AI advisory, fleet/resource optimization tools, blockchain traceability, and carbon footprint tracking—all accessible to farmers, agribusinesses, governments, and NGOs to boost yields and minimize inputs efficiently.
Conclusion: Our Sustainable Legacy
Sustainable agriculture represents both a profound responsibility and an exciting opportunity. By adopting practices like crop rotation, conservation tillage, integrated pest management, efficient irrigation, and embracing new technology, we—farmers, agri-pros, and consumers—become stewards of the land and leaders in ecological innovation.
With data-driven tools and transparent systems like those offered by Farmonaut, we are on the path to improve soil health, safeguard our natural resources, and produce abundant, healthy food—preserving our planet for future generations.
Join us as we shape a thriving, equitable, and sustainable food system—for ourselves, our communities, and our shared future.