–>
What Is Regenerative Agriculture? 7 Secrets Unveiled!
“Regenerative agriculture can increase soil organic matter by up to 21% in just five years with no-till methods.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Regenerative Agriculture
- Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
- Regenerative Agriculture Practices Explained
- Conventional vs. Regenerative Agriculture Comparison
- 7 Secrets & Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
- Farmonaut’s Role in Modern Regenerative Agriculture
- Challenges and Considerations for Adoption
- Adoption and Future Outlook
- Recent Developments
- Farmonaut Subscription Plans
- FAQ: Regenerative Agriculture & Farmonaut
“Cover cropping in regenerative farms boosts biodiversity, supporting up to 50% more pollinator species than conventional fields.”
Introduction to Regenerative Agriculture
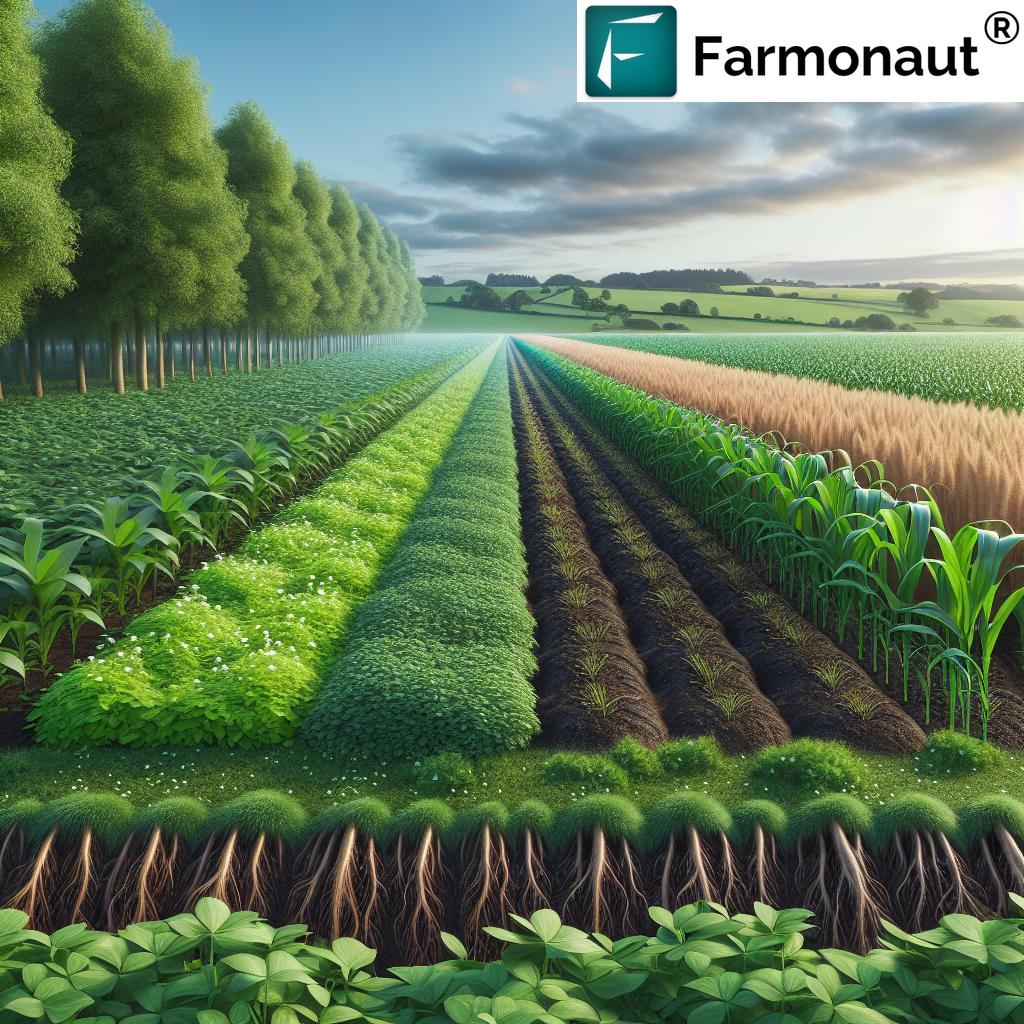
In the face of mounting agricultural and environmental challenges, a new, innovative approach to farming is emerging—one that not only supports crop production but also enhances vital ecosystem functions. Regenerative agriculture is rapidly gaining ground among farmers, agribusinesses, and policymakers as a future-ready solution for restoring soil health, increasing biodiversity, supporting farm resilience, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Unlike conventional agriculture—which typically depletes soil health through repeated tillage, monoculture crops, and heavy use of chemical inputs—regenerative farming seeks to work in harmony with natural processes. By prioritizing soil structure, organic matter, minimizing disturbance, and promoting a rich web of beneficial organisms, regenerative systems set a new standard for sustainable farming practices worldwide.
Focus keyword: regenerative agriculture.
In this blog, we unveil the seven key secrets behind regenerative agriculture—including its principles, practices, vital benefits like carbon sequestration in agriculture, barriers to adoption, and the role of technology platforms like Farmonaut in empowering modern, sustainable farms.
Read on to discover how regenerative principles can transform the future of food and environmental stewardship.
Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
At its core, regenerative agriculture is guided by foundational principles and practices designed to restore, preserve, and continuously enhance soil health, biodiversity in farming systems, and the resilience of agricultural ecosystems. Let’s break down these game-changing concepts:
1. Minimizing Soil Disturbance
Minimizing soil disturbance—primarily through no-till or reduced tillage methods—is the cornerstone of regenerative farming. Constant plowing in conventional systems destroys soil structure, disrupts microbial life, and accelerates erosion. Regenerative methods preserve the beneficial arrangement of soil particles, encourage water retention, and allow organisms to thrive—all of which are critical for nutrient cycling and continuous productivity.
2. Maintaining Soil Cover
Keeping soil covered at all times, whether with vegetation, mulches, or crop residues, protects fields from erosion, suppresses weeds, and adds organic matter back to the soil. This practice is central for both maintaining fertility and ensuring fields are resilient to harsh weather.
3. Enhancing Biodiversity in Farming Systems
A diverse ecosystem brims with beneficial organisms—from microbes and insects to plants and animals. Incorporating a variety of plant species (polyculture) and integrating livestock into cropping systems promote biodiversity, resulting in improved pest control and pollination, as well as a more resilient system overall.
4. Keeping Living Roots in the Soil Year-Round
Maintaining living roots through strategies like cover cropping ensures that soil is alive and actively engaged in nutrient cycling and stabilization. Living roots also support a huge population of soil organisms, further enhancing fertility and structure.
5. Integrating Livestock Into Crop Systems
Integrating livestock into crop systems creates synergistic benefits—animals add natural nutrients, improve soil structure through grazing and manuring, and support plant health. This practice mirrors natural grassland ecosystems, helping close nutrient cycles and enhance resilience.
6. Thoughtful Water Management
Regenerative farms prioritize practices that improve water retention, such as building organic matter, mulches, and strategic planting. These actions help mitigate drought, reduce runoff, and ensure long-term sustainability.
7. Strengthening the Whole System
Ultimately, regenerative agriculture sees the farm as an interconnected system. By aligning practices with these principles, we not only build soil health and improve biodiversity but also create a more resilient and productive agricultural future.
Regenerative Agriculture Practices Explained
To implement regenerative principles, a number of key practices are employed. These practices are designed to work together for enhancing ecosystem services, improving soil fertility, building resilience, and reducing dependence on chemical inputs. Below, we discuss the main methods that enable this sustainable transformation.
Cover Cropping Benefits
Cover cropping involves planting crops that do not compete with main cash crops but instead protect the soil between growing seasons. Benefits of cover cropping include:
- Reduces erosion by holding soil with live roots
- Improves soil structure and fertility
- Enhances nutrient cycling through nitrogen fixers
- Suppresses weeds naturally
- Promotes biodiversity—studies show up to 50% more pollinator species!
No-Till Farming Methods
No-till farming methods—or reduced tillage—are vital for preserving soil structure and minimizing disturbance. By not turning the soil, we maintain beneficial organisms, retain moisture, and safeguard organic matter for long-term fertility.
- Less energy-intensive compared to conventional plowing
- Supports continuous crop production and health
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
Diverse Crop Rotations
Rotating different crops through the same field across seasons helps:
- Break pest and disease cycles
- Prevent nutrient depletion by varying plant needs
- Enhance soil organic matter
- Support a diverse ecosystem both above and below ground
Agroforestry Advantages
Integrating trees with crops and/or livestock (agroforestry) delivers immense benefits:
- Provides habitat for wildlife and pollinators
- Mitigates erosion by stabilizing soil
- Contributes to carbon sequestration in agriculture
- Creates diversified income via timber, fruit, or nuts
Integrating Livestock: The Regenerative Way
Integrating livestock into crop systems is a proven way to enhance nutrient cycling, improve soil structure, and promote plant health. Managed grazing/mob grazing mimics wild herbivore patterns—distributing manure and stimulating plant regrowth without overgrazing.
Organic Mulching
Applying organic mulches adds a protective blanket over soil, reducing moisture loss, suppressing weeds, and returning essential organic matter back into the cycle.
Precision Nutrient Management & Reduced Chemical Inputs
Instead of relying on synthetic chemical fertilizers, regenerative farms optimize nutrient applications via soil testing, cover crops, and compost. This cuts input costs, reduces runoff, and further supports beneficial soil organisms.
Comparison Table: Conventional vs. Regenerative Agriculture Practices
| Practice Type | Description | Impact on Soil Health (Estimated) |
Biodiversity Change (Estimated) |
Water Usage (Estimated) |
Resilience to Climate Change (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Tillage | Plowing and turning soil before planting | Depletes organic matter; damages structure | Declines (-20%) | High (Water loss/grater runoff) | Low Resilience (more erosion) |
| Monoculture Planting | Same crop grown repeatedly | Declining fertility & organic matter | Low biodiversity (-25% est.) | High (less retention) | Low Resilience (pest/disease risk) |
| Synthetic Chemical Inputs | Artificial fertilizers/pesticides | Short-term yield, long-term depletion | Reduces beneficial organisms | Increased need (shallow roots) | Low (ecosystem disruption) |
| No-Till/Reduced Tillage | Minimal soil disruption; direct seeding | Increases organic matter (2-5%) | Boosts (+10% est.) | Reduces up to 30% | High (improved structure) |
| Cover Cropping | Living soil cover between cash crops | Increases OM up to 21% (5 years) | Boosts (+50% pollinators) | Improves retention | High (drought/flood buffering) |
| Diverse Crop Rotation | Varied crops by season/field | Builds structure/nutrients | Increases (+15-20%) | Improves | Moderate to High |
| Agroforestry | Trees in crop/livestock systems | Improves organic matter and physical structure | Increases habitat (+15-30% est.) | Better shading/retention | Very High (multilayer buffer) |
| Livestock Integration | Managed animal grazing/rotation | Enhances nutrients/cycling | Greater organism diversity | Manure boosts holding capacity | High |
Want to monitor your carbon footprint and track sustainability outcomes on your farm? Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting Solution provides detailed, real-time carbon emissions and sequestration analytics powered by satellite monitoring for responsible agriculture.
If you need robust crop tracking and transparent supply chains, explore Farmonaut’s Blockchain-Based Product Traceability platform—ensuring food authenticity and consumer trust from farm to table.
Integrate satellite data into your own systems via the Farmonaut API or review the API Developer Documentation for actionable field information accessible in your workflow.
7 Secrets & Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
Why should we embrace regenerative agriculture? Here are the top secrets and benefits driving global adoption:
Secret 1: Improving Soil Health & Fertility
Regenerative practices increase soil organic matter content, stimulate diverse organisms (bacteria, fungi, worms), and result in improved physical structure. This leads to better water retention, enhanced nutrient cycling, and more resilient crops.
Secret 2: Building Farm Resilience with Diversity
Diverse cropping systems and integrated livestock mean farms can recover more rapidly from pest outbreaks, droughts, or disease pressure. Resilience is essential for food security in a changing climate.
Secret 3: Carbon Sequestration in Agriculture
Healthy soils act as powerful carbon sinks, removing CO2 from the air—making agriculture an active ally in climate change mitigation. No-till methods, cover cropping, and agroforestry are proven to capture significant atmospheric carbon.
For farm owners and agribusinesses aiming to quantify and reduce their environmental impact, Farmonaut’s Carbon Footprinting platform is the go-to solution for accurate, satellite-driven carbon accounting and regulatory compliance.
Secret 4: Biodiversity in Farming Systems
Introducing a variety of crops, integrating trees and livestock, and keeping soil covered all help attract a wider array of beneficial organisms—from pollinators to soil microflora. This makes the entire ecosystem stronger and more self-sustaining.
Secret 5: Reducing Reliance on Chemical Inputs
By improving natural nutrient cycling and leveraging organic processes, regenerative farms sharply cut the need for synthetic chemicals. This means fewer costs, reduced pollution, and safer food.
Secret 6: Enhancing Farm Profitability & Income Streams
Better soil health, less risk of crop failure, diversified products (like timber, fruit from agroforestry), and new “green” markets create sustainable income for farmers. Many regenerative products fetch premium prices due to transparency and environmental benefits, and advanced traceability solutions like Farmonaut’s Traceability platform further boost consumer trust and value.
Secret 7: Data-Driven Insights Power Adoption
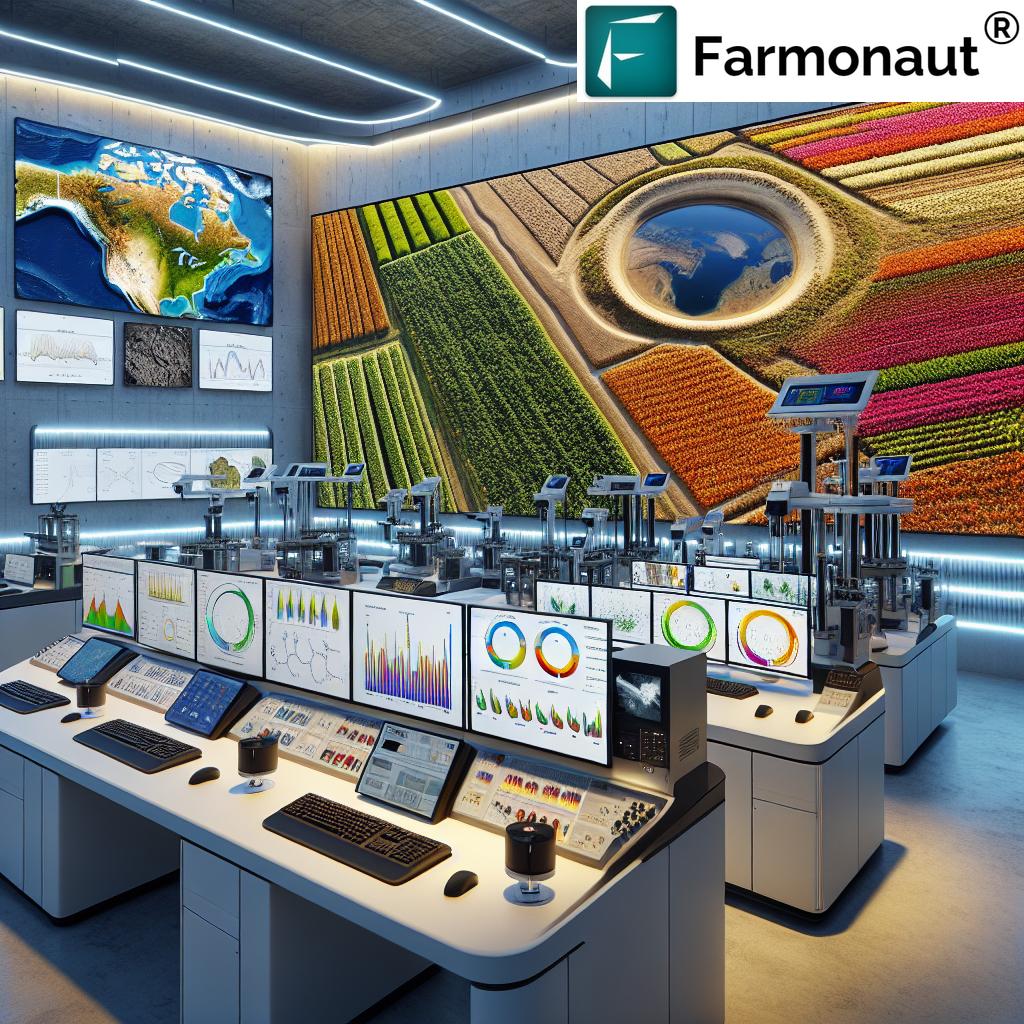
Modern precision platforms such as Farmonaut’s Large Scale Farm Management tools leverage satellite-based health monitoring, AI, and analytics. These enable farmers to monitor crop health, track resource usage, and get timely farm advisories, ensuring maximum success from regenerative transitions.
Our platform supports millions of hectares worldwide—helping not only smallholders but also large enterprise farms, agribusinesses, and governments tracking regenerative agriculture outcomes at scale.
Farmonaut’s Role in Modern Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative agriculture relies not only on traditional wisdom but also on modern, scalable technology. Here’s how Farmonaut’s platform empowers sustainable agricultural systems worldwide:
- Satellite-Based Crop Health Monitoring: Our platform offers real-time, AI-powered crop and soil health analytics: NDVI (vegetation), soil moisture, and more. This allows farmers to optimize irrigation, fertilizer, and input usage for resilient crop yields.
- AI-Driven Farm Advisory and Alerts (Jeevn): Our Jeevn AI system provides personalized insights and recommendations based on satellite data, weather forecasts, and advanced modeling—boosting farm productivity and decision-making.
- Blockchain Traceability: With Farmonaut, blockchain-powered traceability tracks every stage of product movement from field to consumer, ensuring transparency and supporting regenerative product value chains.
- Fleet & Resource Management: Our Fleet Management suite boosts efficiency for agribusinesses—optimizing machine and vehicle usage for lower costs and greater sustainability.
- Carbon Footprinting: Farmonaut enables precise carbon accounting, helping farmers and companies meet sustainability goals and regulatory compliance.
- Financing Verified by Satellite: Farmonaut assists financial institutions in verifying crop loans/insurance using unbiased satellite data, improving access to capital for regenerative farmers. Explore our Crop Loan & Insurance solutions.
Our mobile and web applications make all this actionable information available—from any device, anywhere in the world.
Challenges and Considerations for Regenerative Agriculture Adoption
While regenerative farming offers a promising, sustainable path forward, widescale implementation comes with several challenges we must carefully consider:
The Transition Period
It takes time for regenerative practices to restore soil health, increase yields, and develop resilience. Farms may experience temporary yield reductions and must patiently invest in soil improvement.
Financial Constraints
Some practices require upfront investments in cover crop seeds, equipment for no-till farming methods, or new livestock fencing. Access to financing and supportive policies is vital.
Farmonaut helps reduce costs by providing affordable, scalable precision agriculture solutions that don’t require hardware (learn more).
Knowledge Gaps and Training
Many farmers lack access to reliable information and on-the-ground training for these innovative practices. Extension services and digital tools bridge this gap with decision support and best practices.
Policy and Market Support
Widespread success requires policies that incentivize regenerative adoption, market demand for “regenerative certified” products, and fair access to supply chains.
Global Adoption & The Future Outlook
Regenerative agriculture is now being embraced across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia and Latin America. Increasing numbers of farmers, agribusinesses, and even global food corporations are turning to regenerative strategies to secure long-term supply chains, reduce risk, and unlock market premiums.
Initiatives such as the USDA Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities and major corporate pilot projects are supporting adoption of cover cropping, no-till, crop rotations, and digital farm management platforms (see Wikipedia: Regenerative Agriculture). Growing government and private sector investment bodes well for the future of sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
Reward structures are also emerging, enabling farmers to be paid for “ecosystem services” such as carbon sequestration and biodiversity enhancement.
Importantly, the next wave of adoption will rely on continued investment in education, supportive policies, and advanced technology platforms that make these practices both actionable and profitable at scale. Farmonaut remains committed to democratizing access and connecting farmers to transformative regenerative agriculture solutions.
Recent Developments in Regenerative Agriculture
-
Rewarding farmers for regenerative agriculture is ‘critical for decarbonising the food sector’
-
To tackle climate change we need to make regenerative agriculture the norm, not the exception
-
In the Face of a Climate Crisis, There’s a Better Way to Farm
Farmonaut Subscription Plans
Ready to boost your regenerative journey with data-powered insights?
FAQ: Regenerative Agriculture & Farmonaut
What is regenerative agriculture and how is it different from sustainable agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture goes beyond sustainability. While sustainable farming practices aim to maintain productivity without depleting resources, regenerative agriculture actively improves soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem functions—leaving farmland better than before.
Why is soil health so important in regenerative systems?
Healthy soils provide a foundation for plant growth, water retention, nutrient cycling, and support for beneficial organisms. Regenerative agriculture focuses on building and maintaining these qualities to ensure resilient, productive farms for generations.
What are examples of regenerative practices I can start today?
Begin with cover cropping, no-till or reduced tillage, crop rotation, and if possible, integrating livestock. Each step strengthens your soil and farming system.
How does Farmonaut support regenerative agriculture?
Farmonaut offers satellite-driven monitoring, AI farm advisories, carbon footprint tracking, and blockchain-based traceability—all of which empower farms to measure progress, optimize practices, and meet sustainability/compliance goals affordably.
How can I access Farmonaut’s services?
You can try our platforms via web or mobile apps. For integration into your business systems, check out our API and developer docs.
Is Farmonaut only for large farms?
No—our solutions are designed for farms of all sizes, from small family fields to large agribusinesses and government agencies. Flexible pricing and modular features mean you only pay for what you need.
How does regenerative agriculture impact climate change?
By boosting soil organic matter, increasing biodiversity, and reducing chemical inputs, regenerative agriculture enhances carbon sequestration and resilience—making it a pivotal ally in the fight against climate change.
Where do I start if I want to transition to regenerative systems?
Start small—try cover crops or reduced tillage on part of your land. Use digital tools like Farmonaut’s monitoring solutions to measure impact and adjust over time. Connect with local or online networks for support and best practice sharing.
Conclusion
Regenerative agriculture is more than a trend—it’s a necessary evolution to ensure the health of our land, our food, and our climate. By adopting proven regenerative principles and leveraging cutting-edge platforms—like Farmonaut—farmers and agri-entrepreneurs can secure a sustainable and prosperous future. Let us unlock nature’s secrets, work with the land, and become champions of regeneration.